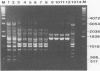
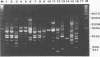
Abstract
Repetitive element PCR (rep-PCR) uses outward-facing primers to amplify multiple segments of DNA located between conserved repeated sequences interspersed along the bacterial chromosome. Polymorphisms of rep-PCR amplification products can serve as strain-specific molecular fingerprints. Primers directed at the repetitive extragenic palindromic element were used to characterize isolates of Legionella pneumophila and other Legionella species. Substantial variation was seen among the rep-PCR fingerprints of different Legionella species and serogroups. More limited, but distinct, polymorphisms of the rep-PCR fingerprint were evident among epidemiologically unrelated isolates of L. pneumophila serogroup 1. Previously characterized Legionella isolates from nosocomial outbreaks were correctly clustered by this method. These results suggest the presence of repetitive extragenic palindromic-like elements within the genomes of members of the family Legionellaceae that can be used to discriminate between strains within a serogroup of L. pneumophila and between different Legionella species. rep-PCR appears to be a useful technique for the molecular fingerprinting of Legionella species.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown A., Lema M., Ciesielski C. A., Blaser M. J. Combined plasmid and peptide analysis of clinical and environmental Legionella pneumophila strains associated with a small cluster of Legionnaires' disease cases. Infection. 1985 Jul-Aug;13(4):163–166. doi: 10.1007/BF01642803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimri G. P., Rudd K. E., Morgan M. K., Bayat H., Ames G. F. Physical mapping of repetitive extragenic palindromic sequences in Escherichia coli and phylogenetic distribution among Escherichia coli strains and other enteric bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(14):4583–4593. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.14.4583-4593.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H. Control of Legionella in hospitals. J Hosp Infect. 1986 Sep;8(2):109–115. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(86)90037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H., Nakahama C., Tobin J. O., Calarco K., Beer K. B., Joly J. R., Selander R. K. Paleoepidemiologic investigation of Legionnaires disease at Wadsworth Veterans Administration Hospital by using three typing methods for comparison of legionellae from clinical and environmental sources. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jun;23(6):1121–1126. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.6.1121-1126.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehret W., Ruckdeschel G. Membrane proteins of legionellaceae. I. Membrane proteins of different strains and serogroups of Legionella pneumophila. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1985 Jul;259(4):433–445. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(85)80075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellsworth D. L., Rittenhouse K. D., Honeycutt R. L. Artifactual variation in randomly amplified polymorphic DNA banding patterns. Biotechniques. 1993 Feb;14(2):214–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezzeddine H., Van Ossel C., Delmée M., Wauters G. Legionella spp. in a hospital hot water system: effect of control measures. J Hosp Infect. 1989 Feb;13(2):121–131. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(89)90018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson E., Clément J. M., Brutlag D., Hofnung M. A family of dispersed repetitive extragenic palindromic DNA sequences in E. coli. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1417–1421. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01986.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Lus P., Fields B. S., Benson R. F., Martin W. T., O'Connor S. P., Black C. M. Comparison of arbitrarily primed polymerase chain reaction, ribotyping, and monoclonal antibody analysis for subtyping Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Jul;31(7):1940–1942. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.7.1940-1942.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart C. A., Makin T. Legionella in hospitals: a review. J Hosp Infect. 1991 Jun;18 (Suppl A):481–489. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(91)90060-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly J. R., McKinney R. M., Tobin J. O., Bibb W. F., Watkins I. D., Ramsay D. Development of a standardized subgrouping scheme for Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 using monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Apr;23(4):768–771. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.4.768-771.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogan S. C., Doherty M., Gitschier J. An improved method for prenatal diagnosis of genetic diseases by analysis of amplified DNA sequences. Application to hemophilia A. N Engl J Med. 1987 Oct 15;317(16):985–990. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198710153171603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lema M., Brown A. Electrophoretic characterization of soluble protein extracts of Legionella pneumophila and other members of the family Legionellaceae. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jun;17(6):1132–1140. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.6.1132-1140.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher W. E., Plouffe J. F., Para M. F. Plasmid profiles of clinical and environmental isolates of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Dec;18(6):1422–1423. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.6.1422-1423.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney R. M., Thacker L., Wells D. E., Wong M. C., Jones W. J., Bibb W. F. Monoclonal antibodies to Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1: possible applications in diagnostic tests and epidemiologic studies. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1983 Jul;255(1):91–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muder R. R., Yu V. L., Woo A. H. Mode of transmission of Legionella pneumophila. A critical review. Arch Intern Med. 1986 Aug;146(8):1607–1612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott M., Bender L., Marre R., Hacker J. Pulsed field electrophoresis of genomic restriction fragments for the detection of nosocomial Legionella pneumophila in hospital water supplies. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Apr;29(4):813–815. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.4.813-815.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders N. A., Harrison T. G., Haththotuwa A., Kachwalla N., Taylor A. G. A method for typing strains of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 by analysis of restriction fragment length polymorphisms. J Med Microbiol. 1990 Jan;31(1):45–55. doi: 10.1099/00222615-31-1-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoonmaker D., Heimberger T., Birkhead G. Comparison of ribotyping and restriction enzyme analysis using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for distinguishing Legionella pneumophila isolates obtained during a nosocomial outbreak. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jun;30(6):1491–1498. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.6.1491-1498.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., McKinney R. M., Whittam T. S., Bibb W. F., Brenner D. J., Nolte F. S., Pattison P. E. Genetic structure of populations of Legionella pneumophila. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1021–1037. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1021-1037.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M. J., Ames G. F., Smith N. H., Robinson E. C., Higgins C. F. Repetitive extragenic palindromic sequences: a major component of the bacterial genome. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1015–1026. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90436-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout J. E., Joly J., Para M., Plouffe J., Ciesielski C., Blaser M. J., Yu V. L. Comparison of molecular methods for subtyping patients and epidemiologically linked environmental isolates of Legionella pneumophila. J Infect Dis. 1988 Mar;157(3):486–495. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.3.486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout J. E., Yu V. L., Muraca P., Joly J., Troup N., Tompkins L. S. Potable water as a cause of sporadic cases of community-acquired legionnaires' disease. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jan 16;326(3):151–155. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199201163260302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struelens M. J., Maes N., Rost F., Deplano A., Jacobs F., Liesnard C., Bornstein N., Grimont F., Lauwers S., McIntyre M. P. Genotypic and phenotypic methods for the investigation of a nosocomial Legionella pneumophila outbreak and efficacy of control measures. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jul;166(1):22–30. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.1.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin J. O., Beare J., Dunnill M. S., Fisher-Hoch S., French M., Mitchell R. G., Morris P. J., Muers M. F. Legionnaires' disease in a transplant unit: isolation of the causative agent from shower baths. Lancet. 1980 Jul 19;2(8186):118–121. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins L. S., Troup N. J., Woods T., Bibb W., McKinney R. M. Molecular epidemiology of Legionella species by restriction endonuclease and alloenzyme analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;25(10):1875–1880. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.1875-1880.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tram C., Simonet M., Nicolas M. H., Offredo C., Grimont F., Lefevre M., Ageron E., Debure A., Grimont P. A. Molecular typing of nosocomial isolates of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 3. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):242–245. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.242-245.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Versalovic J., Kapur V., Mason E. O., Jr, Shah U., Koeuth T., Lupski J. R., Musser J. M. Penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae strains recovered in Houston: identification and molecular characterization of multiple clones. J Infect Dis. 1993 Apr;167(4):850–856. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.4.850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Versalovic J., Koeuth T., Lupski J. R. Distribution of repetitive DNA sequences in eubacteria and application to fingerprinting of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 25;19(24):6823–6831. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.24.6823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickers R. M., Stout J. E., Tompkins L. S., Troup N. J., Yu V. L. Cefamandole-susceptible strains of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1: implications for diagnosis and utility as an epidemiological marker. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Mar;30(3):537–539. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.3.537-539.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods C. R., Jr, Versalovic J., Koeuth T., Lupski J. R. Analysis of relationships among isolates of Citrobacter diversus by using DNA fingerprints generated by repetitive sequence-based primers in the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Nov;30(11):2921–2929. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.11.2921-2929.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods C. R., Versalovic J., Koeuth T., Lupski J. R. Whole-cell repetitive element sequence-based polymerase chain reaction allows rapid assessment of clonal relationships of bacterial isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Jul;31(7):1927–1931. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.7.1927-1931.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruijn F. J. Use of repetitive (repetitive extragenic palindromic and enterobacterial repetitive intergeneric consensus) sequences and the polymerase chain reaction to fingerprint the genomes of Rhizobium meliloti isolates and other soil bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jul;58(7):2180–2187. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.7.2180-2187.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Belkum A., Struelens M., Quint W. Typing of Legionella pneumophila strains by polymerase chain reaction-mediated DNA fingerprinting. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Aug;31(8):2198–2200. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.8.2198-2200.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ketel R. J. Similar DNA restriction endonuclease profiles in strains of Legionella pneumophila from different serogroups. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Sep;26(9):1838–1841. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.9.1838-1841.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ketel R. J., de Wever B. Genetic typing in a cluster of Legionella pneumophila infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 May;27(5):1105–1107. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.5.1105-1107.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ketel R. J., ter Schegget J., Zanen H. C. Molecular epidemiology of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):362–364. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.362-364.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]