Abstract
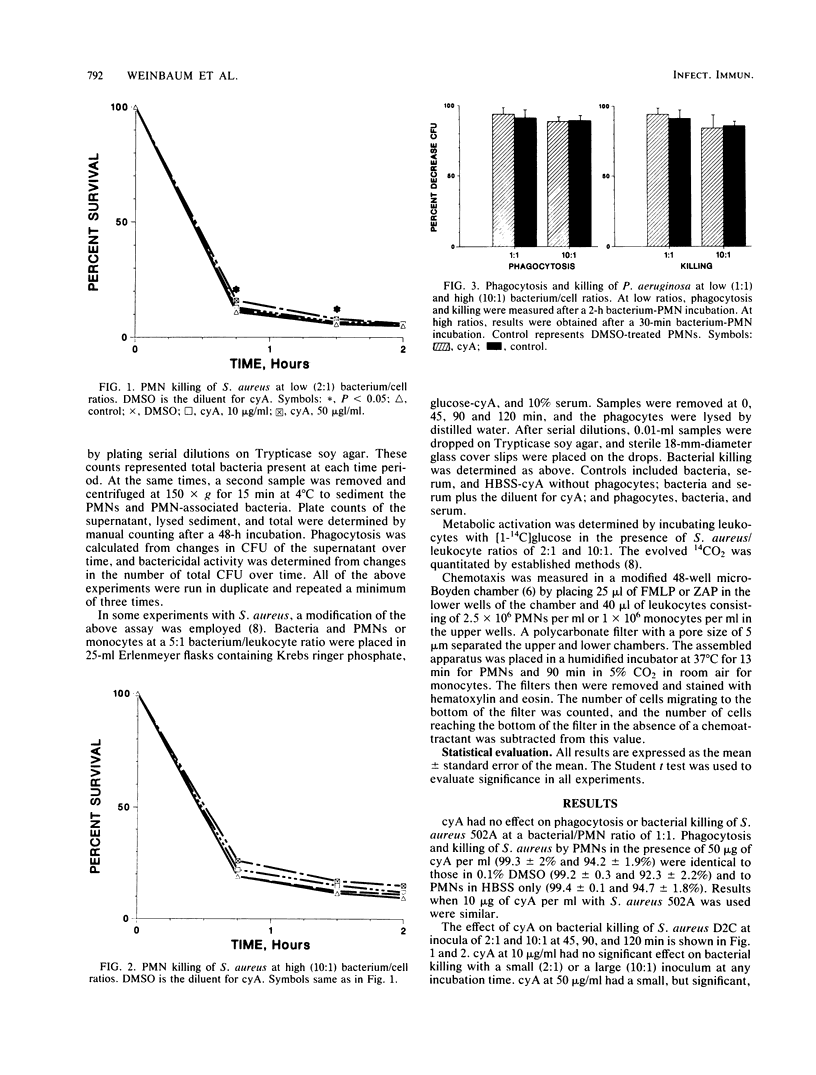
The effects of cyclosporin A (cyA) on human polymorphonuclear leukocyte function, including phagocytosis, its associated metabolic burst, bacterial killing, and chemotaxis, were evaluated. Both Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus were used as test particles. Polymorphonuclear leukocytes incubated in 10 and 50 micrograms of cyA per ml behaved normally with respect to phagocytosis and hexose monophosphate shunt activity at both high (10:1) and low (2:1) S. aureus/leukocyte ratios. With a small bacterial inoculum, killing of S. aureus was slightly impaired at early times only in the presence of 50 micrograms of cyA per ml. Phagocytosis and killing of P. aeruginosa with both large and small bacterial inocula were unaffected by cyA. Chemotaxis was within normal limits under all conditions. In addition, polymorphonuclear leukocytes from four renal transplant recipients receiving both cyA and prednisone demonstrated normal metabolic bursts and bacterial killing with both small and large inocula of S. aureus.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borel J. F., Feurer C., Gubler H. U., Stähelin H. Biological effects of cyclosporin A: a new antilymphocytic agent. Agents Actions. 1976 Jul;6(4):468–475. doi: 10.1007/BF01973261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. S., Isturiz R. E., Malech H. L., Root R. K., Wilfert C. M., Gutman L., Buckley R. H. Fungal infection in chronic granulomatous disease. The importance of the phagocyte in defense against fungi. Am J Med. 1981 Jul;71(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90259-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Densen P., Mandell G. L. Gonococcal interactions with polymorphonuclear neutrophils: importance of the phagosome for bactericidal activity. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1161–1171. doi: 10.1172/JCI109235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dummer J. S., Hardy A., Poorsattar A., Ho M. Early infections in kidney, heart, and liver transplant recipients on cyclosporine. Transplantation. 1983 Sep;36(3):259–267. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198309000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk W., Goodwin R. H., Jr, Leonard E. J. A 48-well micro chemotaxis assembly for rapid and accurate measurement of leukocyte migration. J Immunol Methods. 1980;33(3):239–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Newman S. L. Chronic granulomatous disease. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1977 May;24(2):365–376. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)33424-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan S. S., Basford R. E. Effect of vitamin B12 and folic acid deficiencies on neutrophil function. Blood. 1976 May;47(5):801–805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masur H., Cheigh J. S., Stubenbord W. T. Infection following renal transplantation: a changing pattern. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Nov-Dec;4(6):1208–1219. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.6.1208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitz B. A., Wallwork J. L., Hunt S. A., Pennock J. L., Billingham M. E., Oyer P. E., Stinson E. B., Shumway N. E. Heart-lung transplantation: successful therapy for patients with pulmonary vascular disease. N Engl J Med. 1982 Mar 11;306(10):557–564. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198203113061001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root R. K., Cohen M. S. The microbicidal mechanisms of human neutrophils and eosinophils. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 May-Jun;3(3):565–598. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.3.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawchuk R. J., Cartier L. L. Liquid-chromatographic determination of cyclosporin A in blood and plasma. Clin Chem. 1981 Aug;27(8):1368–1371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzl T. E., Klintmalm G. B., Porter K. A., Iwatsuki S., Schröter G. P. Liver transplantation with use of cyclosporin a and prednisone. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jul 30;305(5):266–269. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198107303050507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapia H. R., Holley K. E., Woods J. E., Johnson W. J. Causes of death after renal transplantation. Arch Intern Med. 1973 Feb;131(2):204–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade B. H., Mandell G. L. Polymorphonuclear leukocytes: dedicated professional phagocytes. Am J Med. 1983 Apr;74(4):686–693. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)91028-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinbaum D. L., Sullivan J. A., Mandell G. L. Human neutrophil membrane topography: examination of distribution, movement, and regeneration of recognition sites using lectins as probes. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1983 Apr;33(4):249–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



