Abstract
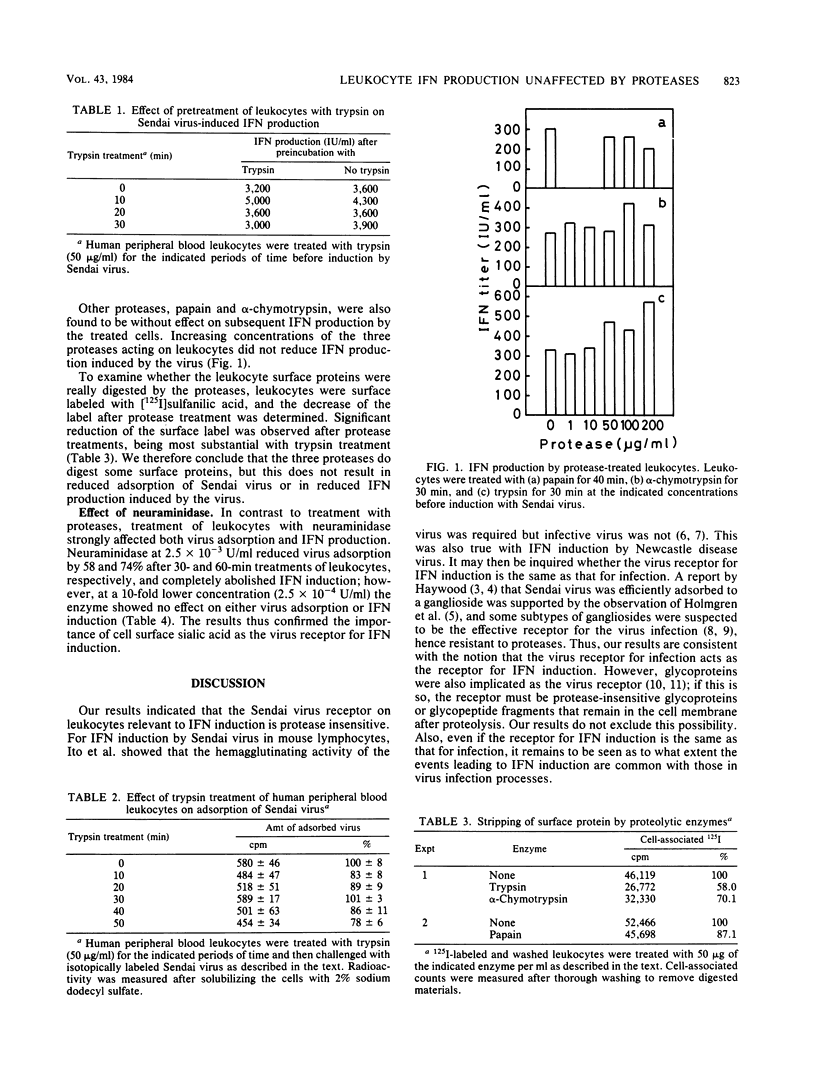
Trypsinization of human peripheral blood leukocytes was found to have no effect on Sendai virus adsorption or on interferon induction by the virus. alpha-Chymotrypsin and papain also did not affect interferon induction, although the three proteases did remove part of the leukocyte surface material. In contrast, treatment of leukocytes with neuraminidase reduced virus adsorption and thoroughly abolished interferon induction. We conclude that protease-resistant structures on leukocyte surfaces serve as the receptor of Sendai virus for the induction of interferon.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J. A. Cytopathic effect inhibition assay for interferon: microculture plate assay. Methods Enzymol. 1981;78(Pt A):381–387. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)78145-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Hirsh D. Synthesis of diazotized 35S sulfanilic acid of high specific activity: a label for the outer surface of cell membranes. Anal Biochem. 1975 Jun;66(2):629–631. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90630-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haywood A. M. Characteristics of Sendai virus receptors in a model membrane. J Mol Biol. 1974 Mar 15;83(4):427–436. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90504-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haywood A. M. Letter to the editor: Fusion of Sendai viruses with model membranes. J Mol Biol. 1974 Aug 15;87(3):625–628. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Svennerholm L., Elwing H., Fredman P., Strannegård O. Sendai virus receptor: proposed recognition structure based on binding to plastic-adsorbed gangliosides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1947–1950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Nishiyama Y., Shimokata K., Nagata I., Takeyama H., Kunii A. The mechanism of interferon induction in mouse spleen cells stimulated with HVJ. Virology. 1978 Jul 1;88(1):128–137. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Nishiyama Y., Shimokata K., Takeyama H., Kunii A. Active component of HVJ (sendai virus) for interferon on induction in mice. Nature. 1978 Aug 24;274(5673):801–802. doi: 10.1038/274801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Paulson J. C. Sendai virus utilizes specific sialyloligosaccharides as host cell receptor determinants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5693–5697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Svennerholm L., Paulson J. C. Specific gangliosides function as host cell receptors for Sendai virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5406–5410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oku N., Nojima S., Inoue K. Studies on the interaction of HVJ (Sendai Virus) with liposomal membranes. HVJ-induced permeability increase of liposomes containing glycophorin. Virology. 1982 Jan 30;116(2):419–427. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson J. C., Sadler J. E., Hill R. L. Restoration of specific myxovirus receptors to asialoerythrocytes by incorporation of sialic acid with pure sialyltransferases. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 25;254(6):2120–2124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu P. S., Ledeen R. W., Udem S., Isaacson Y. A. Nature of the Sendai virus receptor: glycoprotein versus ganglioside. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):304–310. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.304-310.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



