Abstract
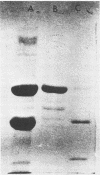
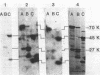
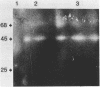
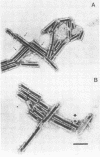
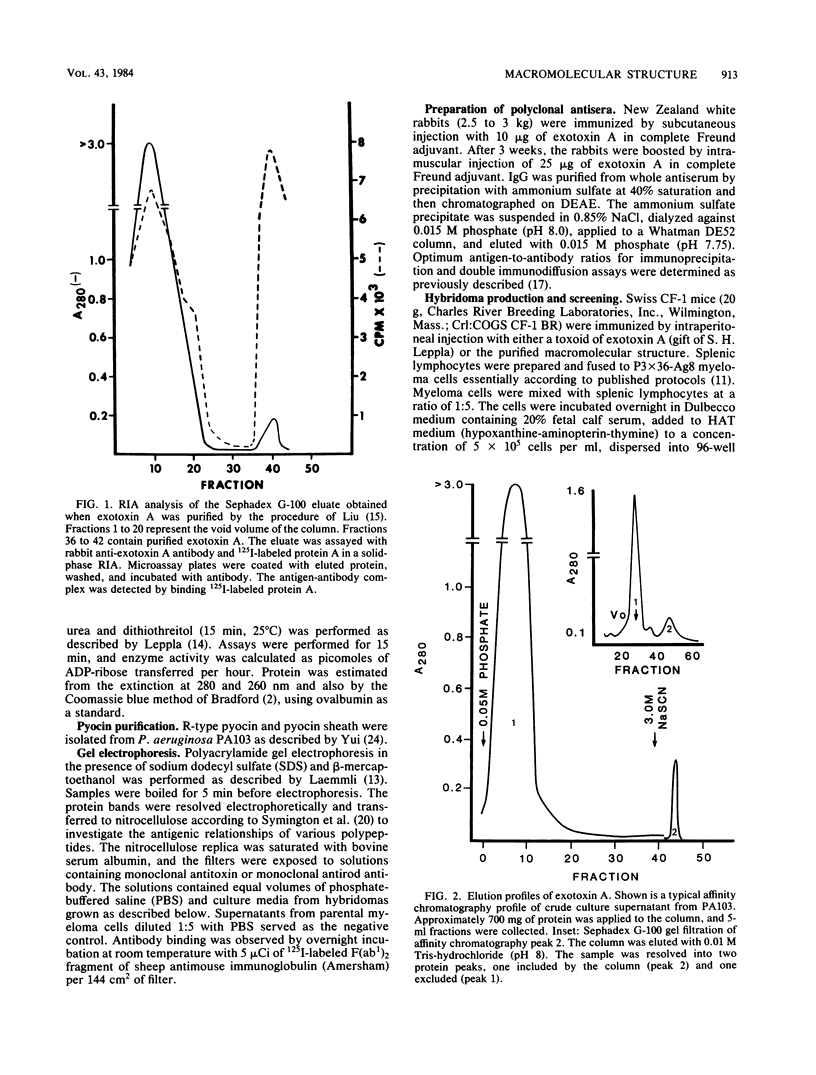
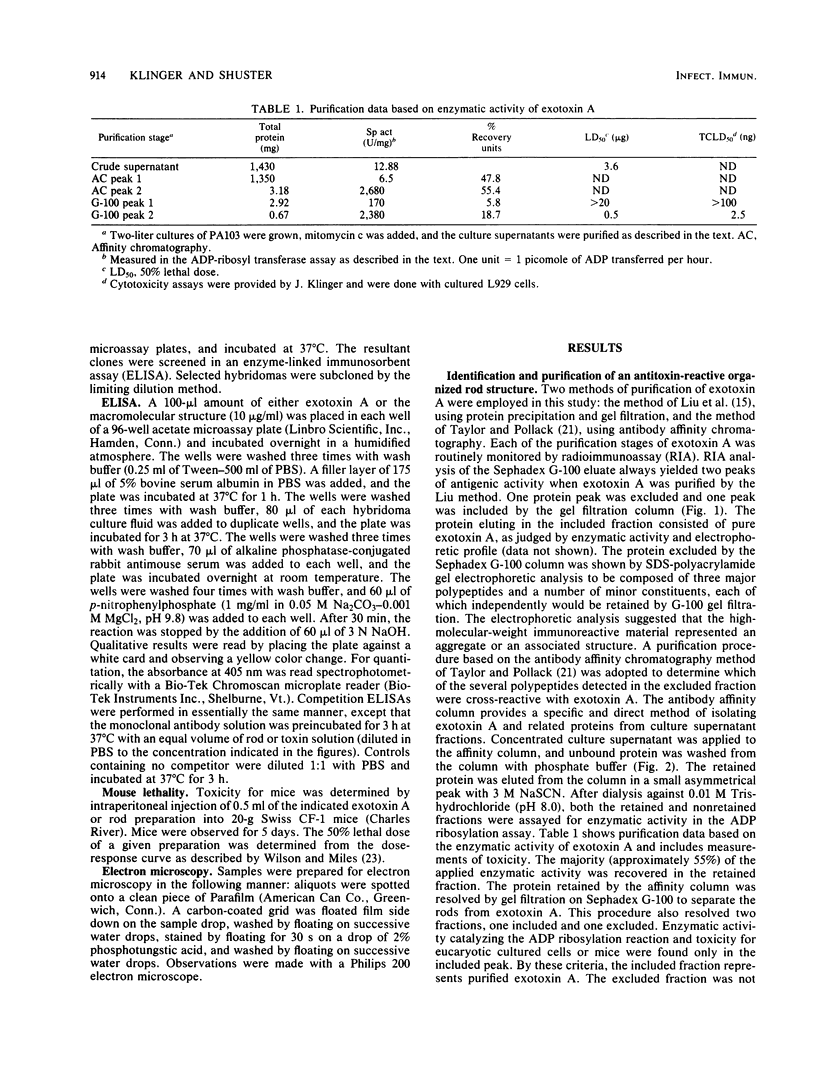
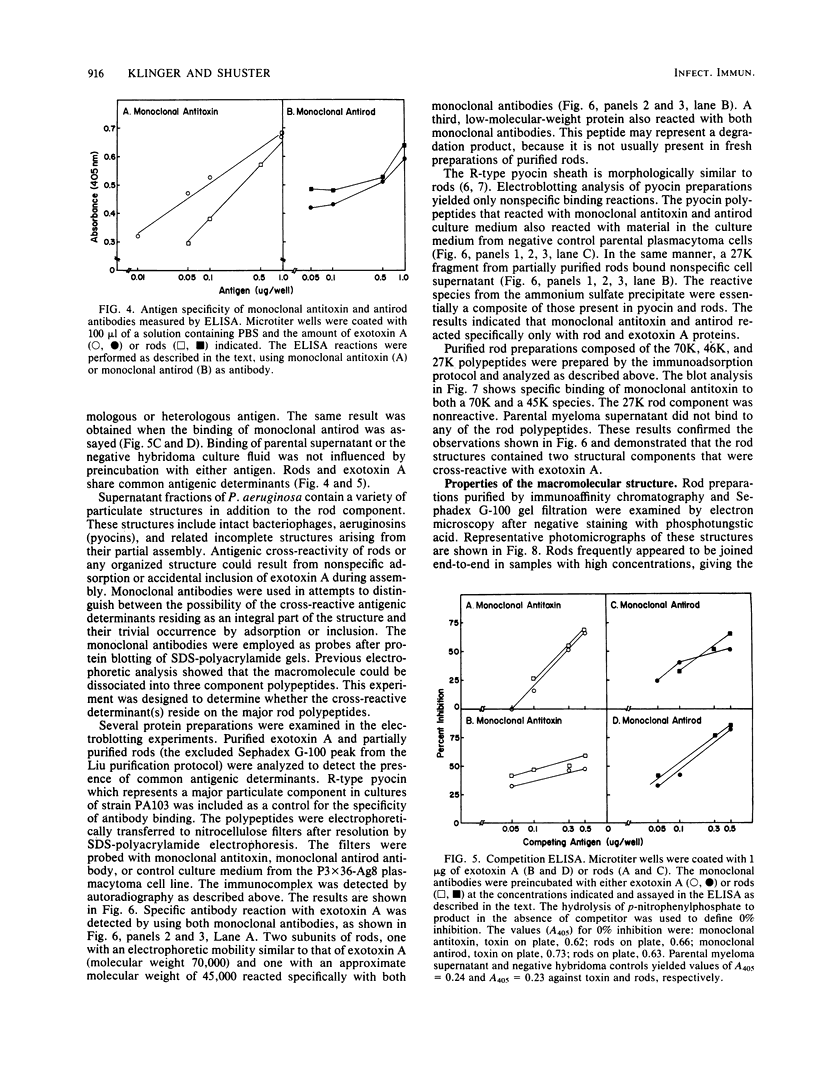
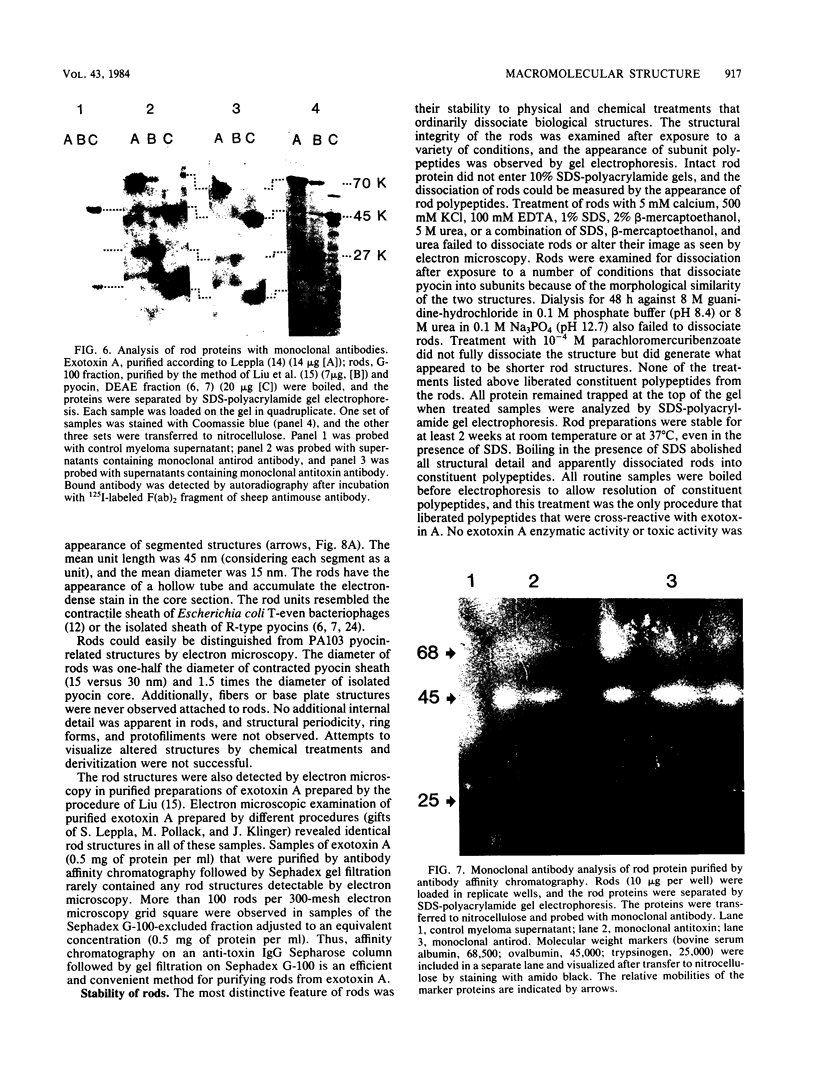
Organized particulate structures (rods) identified in purified preparations of exotoxin A from culture supernatants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA103 were found to be immunochemically cross-reactive with exotoxin A. The rods were visualized by electron microscopy after negative staining as hollow tubes or sheaths (45 by 15 nm). Purified rods were not toxic and not enzymatically active in the ADP-ribosylation assay. Antigenic cross-reactivity between exotoxin A and rods was demonstrated by using monoclonal antibodies directed against either rods or a toxoid of exotoxin A. Hybridoma clones derived from mice immunized with rods or toxoid reacted with both antigens in the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Rods could be dissociated by boiling and resolved by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis into three subunit polypeptides with molecular weights of 70,000, 45,000, and 27,000. Two of the three subunit polypeptides reacted both with antirod and antitoxin monoclonal antibodies after electrophoretic transfer of sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis-separated proteins to nitrocellulose filters. The results indicate that rods and exotoxin A share common antigenic determinants.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN E. H., SCHWEET R. S. Synthesis of hemoglobin in a cell-free system. I. Properties of the complete system. J Biol Chem. 1962 Mar;237:760–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung D. W., Collier R. J. Enzymatically active peptide from the adenosine diphosphate-ribosylating toxin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):832–841. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.832-841.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. L., Vasil M. L. Isolation and genetic characterization of toxin-deficient mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. J Bacteriol. 1981 Aug;147(2):275–281. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.2.275-281.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanne L. F., Howe T. R., Iglewski B. H. Locus of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin A gene. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):383–386. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.383-386.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higerd T. B., Baechler C. A., Berk R. S. In vitro and in vivo characterization of pyocin. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jun;93(6):1976–1986. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.6.1976-1986.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higerd T. B., Baechler C. A., Berk R. S. Morphological studies on relaxed and contracted forms of purified pyocin particles. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1378–1389. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1378-1389.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Liu P. V., Kabat D. Mechanism of action of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin Aiadenosine diphosphate-ribosylation of mammalian elongation factor 2 in vitro and in vivo. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):138–144. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.138-144.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen S. E., Fecycz I. T., Stemke G. W., Campbell J. N. Demonstration of a cell-associated, inactive precursor of an exocellular protease produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Jan;26(1):87–93. doi: 10.1139/m80-013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krimm S., Anderson T. F. Structure of normal and contracted tail sheaths of T4 bacteriophage. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jul 28;27(2):197–202. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Derivation of specific antibody-producing tissue culture and tumor lines by cell fusion. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jul;6(7):511–519. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppla S. H. Large-scale purification and characterization of the exotoxin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):1077–1086. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.1077-1086.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V., Yoshii S., Hsieh H. Exotoxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. II. Concentration, purification, and characterization of exotoxin A. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(4):514–519. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.4.514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lory S., Collier R. J. Expression of enzymic activity by exotoxin A from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):494–501. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.494-501.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanai Y., Morihara K., Tsuzuki H., Homma J. Y., Kato I. Proteolytic cleavage of exotoxin A from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: formation of an ADP-ribosyltransferase active fragment by the action of Pseudomonas elastase. FEBS Lett. 1980 Oct 20;120(1):131–134. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symington J., Green M., Brackmann K. Immunoautoradiographic detection of proteins after electrophoretic transfer from gels to diazo-paper: analysis of adenovirus encoded proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):177–181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor N. S., Pollack M. Purification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin by affinity chromatography. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):66–70. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.66-70.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasil M. L., Kabat D., Iglewski B. H. Structure-activity relationships of an exotoxin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):353–361. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.353-361.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yui C. Structure of pyocin R. I. Isolation of sheath from pyocin R by alkali treatment and its properties. J Biochem. 1971 Jan;69(1):101–110. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]