Abstract
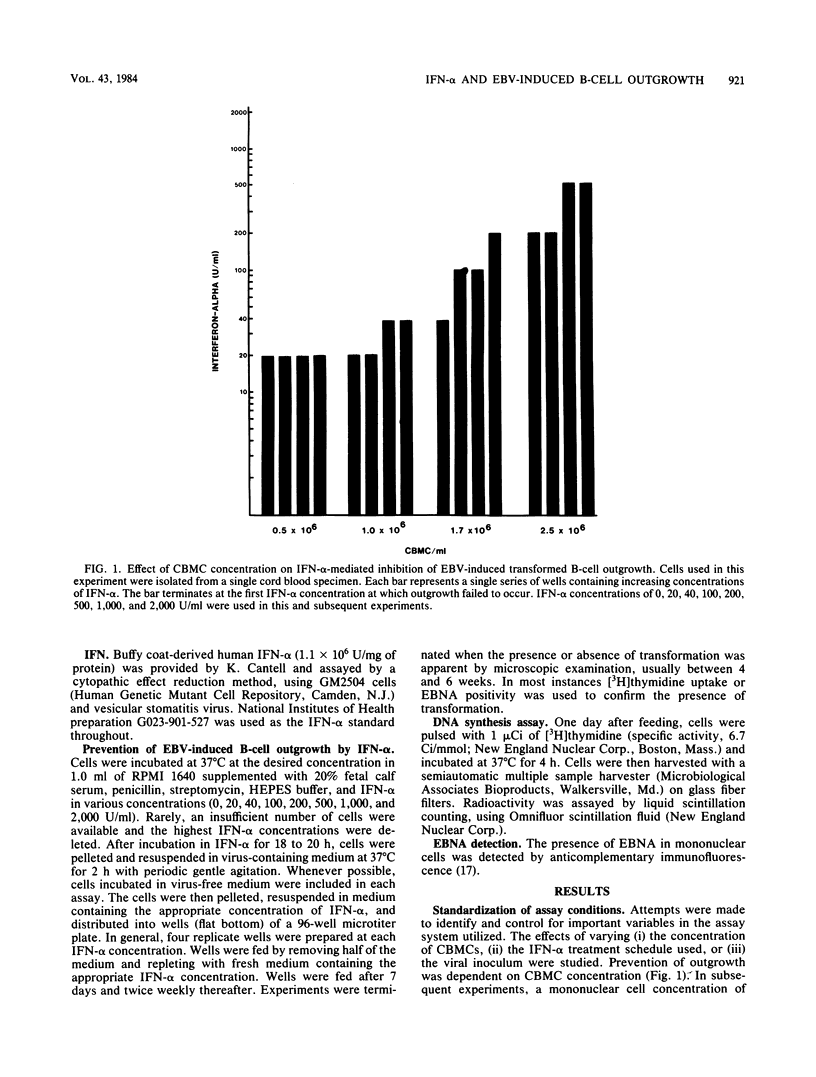
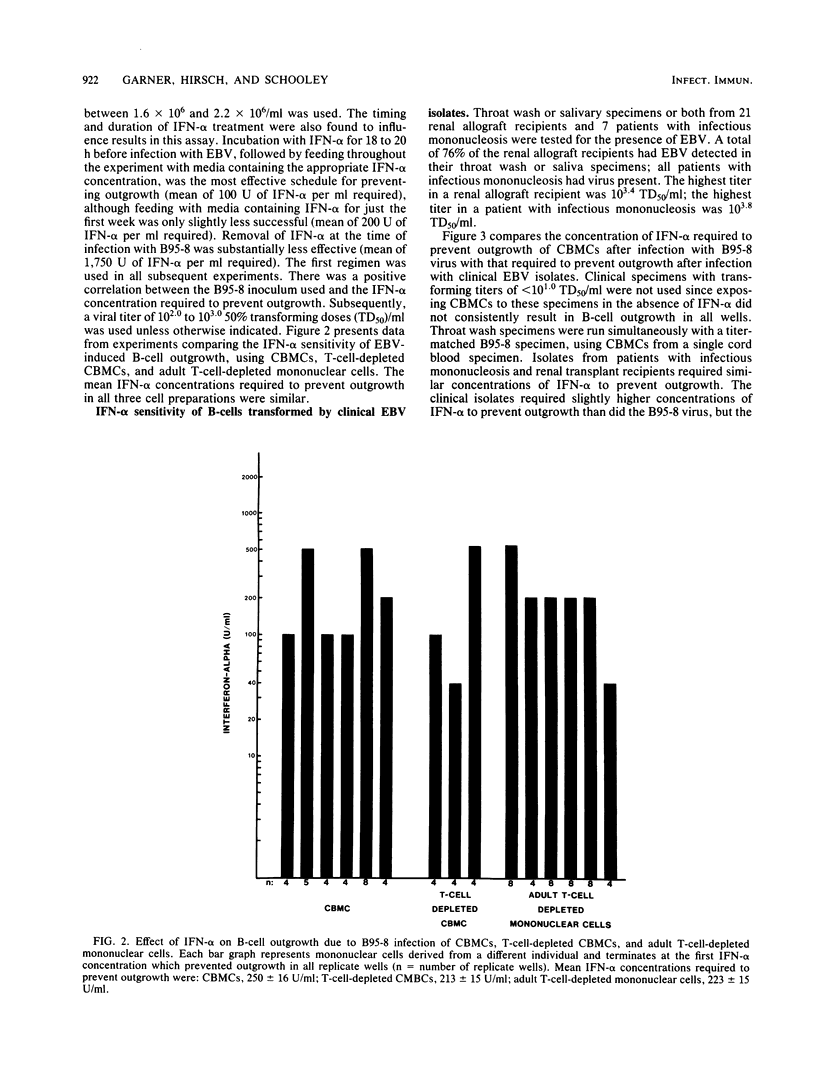
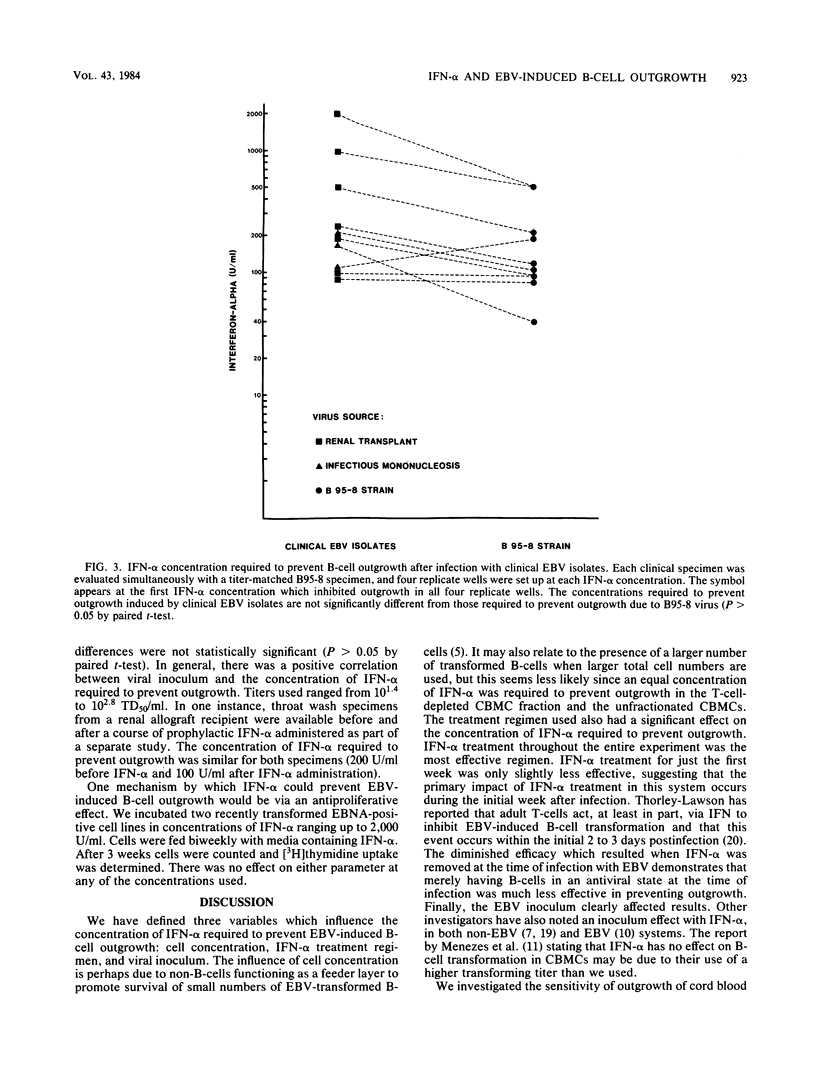
An in vitro system for determining the efficacy of interferon alpha (IFN-alpha) in preventing B-cell outgrowth due to Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) was developed. Unfractionated cord blood mononuclear cells, T-cell-depleted cord blood mononuclear cells, or adult T-cell-depleted mononuclear cells were exposed to IFN-alpha for 18 to 20 h followed by incubation with the B95-8 strain of EBV for 2 h. B-cell outgrowth was monitored by microscopic examination, [3H]thymidine incorporation, and Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen detection. Cell density and viral inoculum both affected the sensitivity of outgrowth to IFN-alpha. IFN-alpha was most effective when added at each feeding after infection as well as before infection with EBV. The mean of the lowest IFN-alpha concentration tested at which transformation failed to occur after infection with the B95-8 strain of EBV at a 50% transforming dose of 10(2.0) to 10(3.0)/ml was similar for unfractionated cord blood mononuclear cells, T-cell-depleted cord blood mononuclear cells, and adult T-cell-depleted mononuclear cells. The B95-8 strain and clinical EBV isolates required similar IFN-alpha concentrations to prevent outgrowth. In this system, IFN-alpha at pharmacologically achievable concentrations prevented EBV-induced B-cell outgrowth. These data indicate that IFN-alpha deserves further study as a potential therapeutic agent for EBV-induced syndromes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloom B. R. Interferons and the immune system. Nature. 1980 Apr 17;284(5757):593–595. doi: 10.1038/284593a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doetsch P. W., Suhadolnik R. J., Sawada Y., Mosca J. D., Flick M. B., Reichenbach N. L., Dang A. Q., Wu J. M., Charubala R., Pfleiderer W. Core (2'-5')oligoadenylate and the cordycepin analog: inhibitors of Epstein--Barr virus-induced transformation of human lymphocytes in the absence of interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6699–6703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutterman J. U., Fine S., Quesada J., Horning S. J., Levine J. F., Alexanian R., Bernhardt L., Kramer M., Spiegel H., Colburn W. Recombinant leukocyte A interferon: pharmacokinetics, single-dose tolerance, and biologic effects in cancer patients. Ann Intern Med. 1982 May;96(5):549–556. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-5-549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanto D. W., Frizzera G., Gajl-Peczalska J., Purtilo D. T., Klein G., Simmons R. L., Najarian J. S. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in the pathogenesis of posttransplant lymphoma. Transplant Proc. 1981 Mar;13(1 Pt 2):756–760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E., Miller G., Robinson J., Heston L. Efficiency of transformation of lymphocytes by Epstein-Barr virus. Virology. 1977 Jan;76(1):152–163. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90292-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W., Diehl V. Relation of Burkitt's tumor-associated herpes-ytpe virus to infectious mononucleosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):94–101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes A. R., Rasmussen L., Merigan T. C. Factors affecting the interferon sensitivity of human cytomegalovirus. Intervirology. 1978;9(1):48–55. doi: 10.1159/000148920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai P. K., Alpers M. P., MacKay-Scollay E. M. Epstein-Barr herpesvirus infection: inhibition by immunologically induced mediators with interferon-like properties. Int J Cancer. 1977 Jul 15;20(1):21–29. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman M., Andrews L., Niederman J., Miller G. Direct visualization of enveloped Epstein-Barr Herpesvirus in throat washing with leukocyte-transforming activity. J Infect Dis. 1975 Nov;132(5):520–523. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.5.520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lvovsky E., Levine P. H., Fuccillo D., Ablashi D. V., Bengali Z. H., Armstrong G. R., Levy H. B. Epstein-Barr virus and Herpesvirus saimiri: sensitivity to interferons and interferon inducers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1981 Jun;66(6):1013–1019. doi: 10.1093/jnci/66.6.1013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menezes J., Patel P., Dussault H., Joncas J., Leibold W. Effect of interferon on lymphocyte transformation and nuclear antigen production by Epstein-Barr virus. Nature. 1976 Apr 1;260(5550):430–432. doi: 10.1038/260430a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. The etiology of nasopharyngeal cancer and its management. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1980;13(3):467–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minato N., Reid L., Cantor H., Lengyel P., Bloom B. R. Mode of regulation of natural killer cell activity by interferon. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):124–137. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. G., Niederman J. C., Miller G., Smith H. W., Dowaliby J. M. Site of Epstein-Barr virus replication in the oropharynx. Lancet. 1979 Dec 1;2(8153):1154–1157. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92384-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postic B., Dowling J. N. Susceptibility of clinical isolates of cytomegalovirus to human interferon. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):656–660. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedman B. M., Klein G. Cellular localization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated complement-fixing antigen in producer and non-producer lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1973 May;11(3):499–520. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubach W. H., Hackman R., Neiman P. E., Miller G., Thomas E. D. A monoclonal immunoblastic sarcoma in donor cells bearing Epstein-Barr virus genomes following allogeneic marrow grafting for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 1982 Jul;60(1):180–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitz L., Schellekens H. Influence of input multiplicity of infection on the antiviral activity of interferon. J Gen Virol. 1980 Jan;46(1):205–210. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-46-1-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson D. A., Chess L., Strominger J. L. Suppression of in vitro Epstein-Barr virus infection. A new role for adult human T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1977 Aug 1;146(2):495–508. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.2.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson D. A. The suppression of Epstein-Barr virus infection in vitro occurs after infection but before transformation of the cell. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):745–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson D. A. The transformation of adult but not newborn human lymphocytes by Epstein Barr virus and phytohemagglutinin is inhibited by interferon: the early suppression by T cells of Epstein Barr infection is mediated by interferon. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):829–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler J. L. Burkitt's lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 1981 Sep 24;305(13):735–745. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198109243051305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



