Abstract
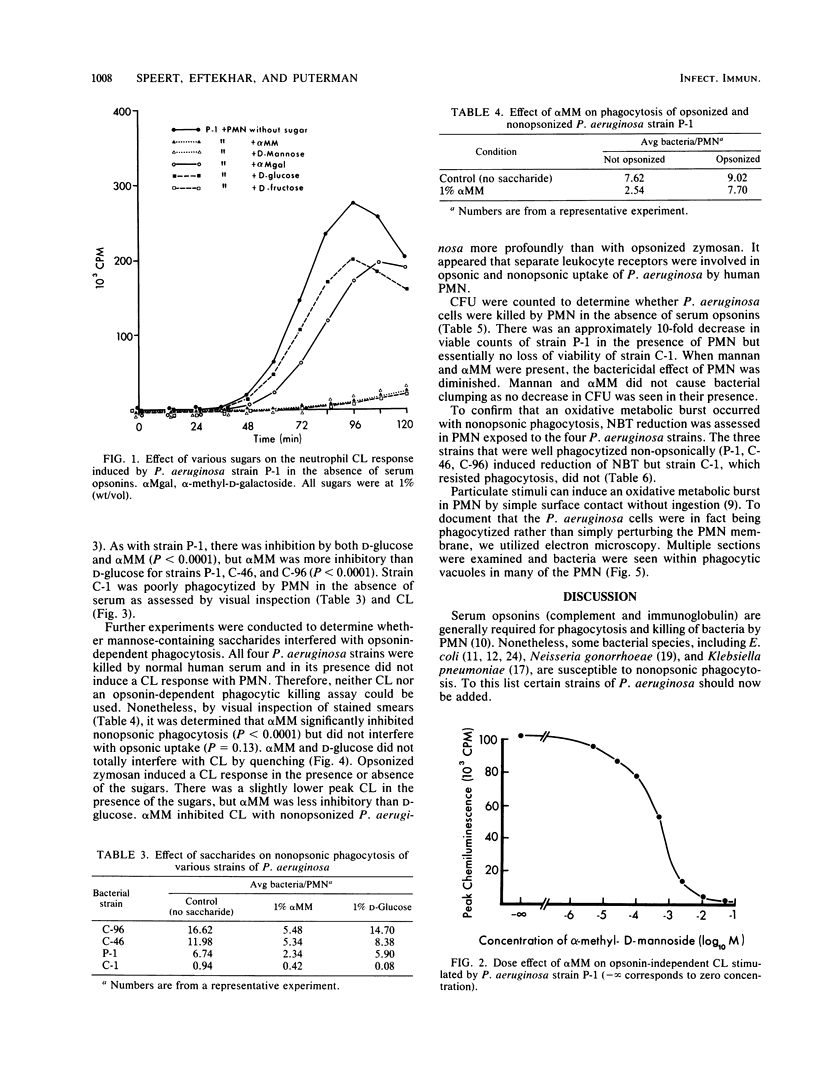
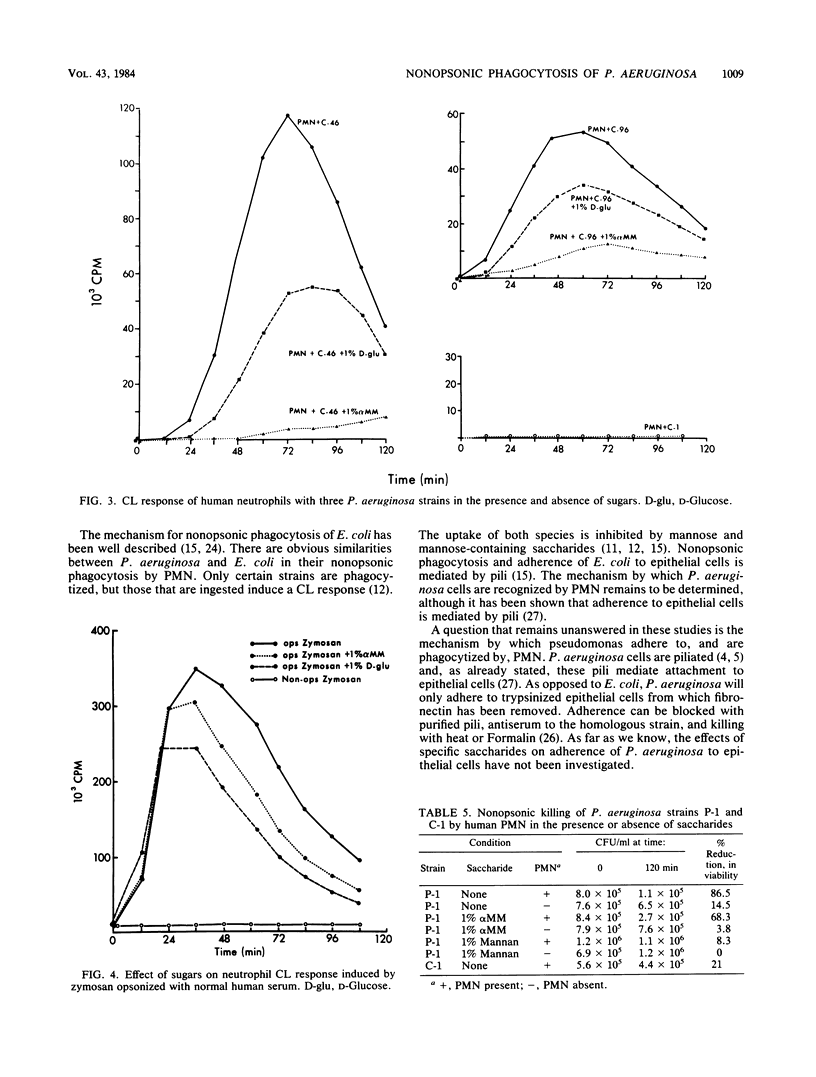
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is the predominant respiratory pathogen in patients with cystic fibrosis, but its mechanism of persisting in pulmonary secretions is poorly understood. We observed that three nonmucoid cystic fibrosis P. aeruginosa strains were phagocytized and one strain resisted phagocytosis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes in the absence of serum. Phagocytosis was assessed by luminol-enhanced chemiluminescence, inspection of stained smears, bactericidal assay, reduction of nitroblue tetrazolium dye, and electron microscopy. Phagocytosis, determined by visual inspection, occurred at 35 degrees C but not at 4 degrees C. Nonopsonic phagocytosis was inhibited most efficiently by D-mannose, mannose-containing saccharides, and D-fructose. Opsonin-dependent phagocytosis of P. aeruginosa and of zymosan was not markedly inhibited by mannose, suggesting different leukocyte receptors for nonopsonic and opsonic phagocytosis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore R. S., Mitchell M. Immunologic investigations of mucoid strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: comparison of susceptibility to opsonic antibody in mucoid and nonmucoid strains. J Infect Dis. 1980 Feb;141(2):238–247. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.2.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjornson A. B., Michael J. G. Factors in human serum promoting phagocytosis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. II. Interaction of opsonins with the phagocytic cell. J Infect Dis. 1974 Nov;130 (Suppl)(0):S127–S131. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.supplement.s127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkhard W., Marvin D. A., Watts T. H., Paranchych W. Structure of polar pili from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains K and O. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 15;149(1):79–93. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90261-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst J. A., Hayward A. C. Surface appendages similar to fimbriae (pili) on pseudomonas species. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Oct;58(2):227–237. doi: 10.1099/00221287-58-2-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilboa-Garber N., Mizrahi L., Garber N. Mannose-binding hemagglutinins in extracts of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Can J Biochem. 1977 Sep;55(9):975–981. doi: 10.1139/o77-145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilboa-Garber N., Mizrahi L., Garber N. Purification of the galactose-binding hemagglutinin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by affinity column chromatography using sepharose. FEBS Lett. 1972 Nov 15;28(1):93–95. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80685-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilboa-Garber N. Pseudomonas aeruginosa lectins. Methods Enzymol. 1982;83:378–385. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)83034-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Weissmann G. Nonphagocytic stimulation of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: role of the plasma membrane. Semin Hematol. 1979 Jul;16(3):175–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of microorganisms. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Jan-Feb;4(1):104–123. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.1.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangan D. F., Snyder I. S. Mannose-sensitive interaction of Escherichia coli with human peripheral leukocytes in vitro. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):520–527. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.520-527.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangan D. F., Snyder I. S. Mannose-sensitive stimulation of human leukocyte chemiluminescence by Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1014–1019. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1014-1019.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills E. L., Rholl K. S., Quie P. G. X-linked inheritance in females with chronic granulomatous disease. J Clin Invest. 1980 Aug;66(2):332–340. doi: 10.1172/JCI109861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Mirelman D., Sharon N. Adherence of Escherichia coli to human mucosal cells mediated by mannose receptors. Nature. 1977 Feb 17;265(5595):623–625. doi: 10.1038/265623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Kim Y., Schmeling D., Lindemann M., Verhoef J., Quie P. G. Complement-mediated phagocytosis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Dec;92(6):883–894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruzzo C., Debbia E., Satta G. Mannose-inhibitable adhesins and T3-T7 receptors of Klebsiella pneumoniae inhibit phagocytosis and intracellular killing by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):949–957. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.949-957.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections: persisting problems and current research to find new therapies. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Jun;82(6):819–831. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-82-6-819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quie P. G., White J. G., Holmes B., Good R. A. In vitro bactericidal capacity of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: diminished activity in chronic granulomatous disease of childhood. J Clin Invest. 1967 Apr;46(4):668–679. doi: 10.1172/JCI105568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rest R. F., Fischer S. H., Ingham Z. Z., Jones J. F. Interactions of Neisseria gonorrhoeae with human neutrophils: effects of serum and gonococcal opacity on phagocyte killing and chemiluminescence. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):737–744. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.737-744.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y., Kazmierowski J. A., Newball H. H. Specificity of opsonic antibodies to enhance phagocytosis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by human alveolar macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1975 Aug;56(2):376–385. doi: 10.1172/JCI108102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root R. K., Isturiz R., Molavi A., Metcalf J. A., Malech H. L. Interactions between antibiotics and human neutrophils in the killing of staphylococci. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jan;67(1):247–259. doi: 10.1172/JCI110020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzmann S., Boring J. R. Antiphagocytic Effect of Slime from a Mucoid Strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1971 Jun;3(6):762–767. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.6.762-767.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverblatt F. J., Dreyer J. S., Schauer S. Effect of pili on susceptibility of Escherichia coli to phagocytosis. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):218–223. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.218-223.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. E., Boat T. F., Doershuk C. F. Cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Jun;113(6):833–878. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.113.6.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Straus D. C., Johanson W. G., Jr, Bass J. A. Role of fibronectin in the prevention of adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to buccal cells. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jun;143(6):784–790. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.6.784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Straus D. C., Johanson W. G., Jr, Berry V. K., Bass J. A. Role of pili in adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to mammalian buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1146–1151. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1146-1151.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Armstrong D. Human immunity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. I. In-vitro interaction of bacteria, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, and serum factors. J Infect Dis. 1972 Sep;126(3):257–276. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.3.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]