Abstract
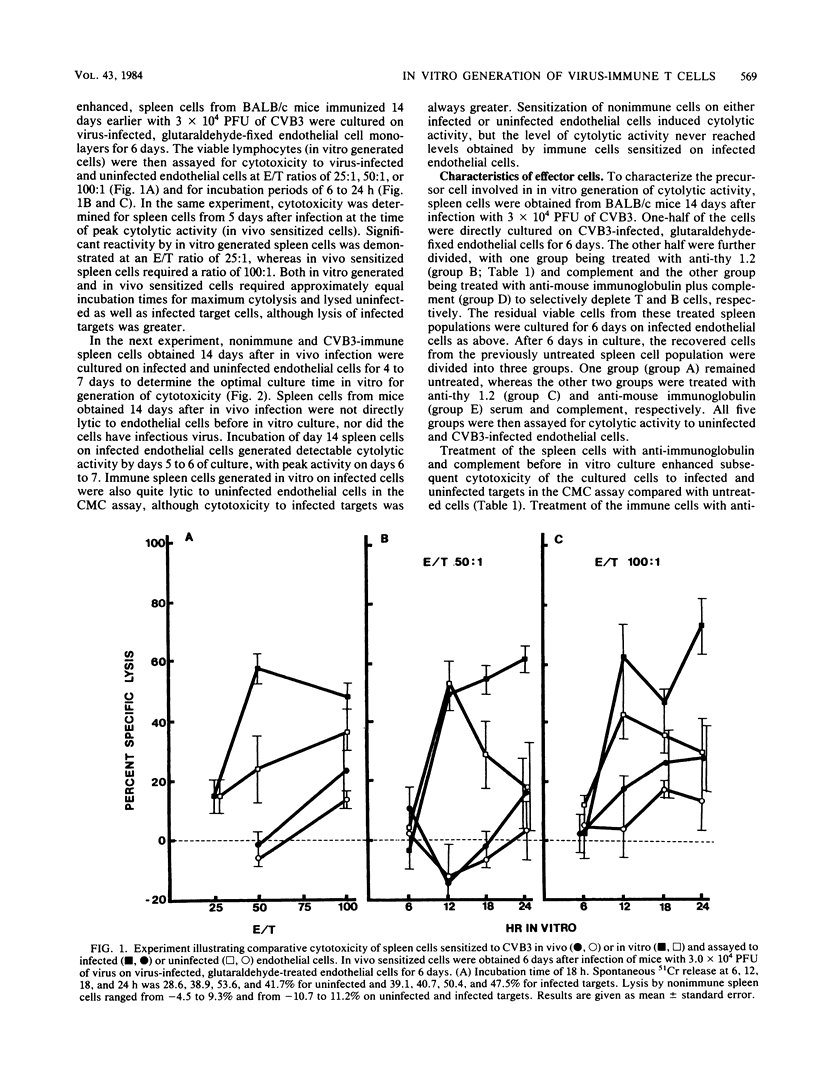
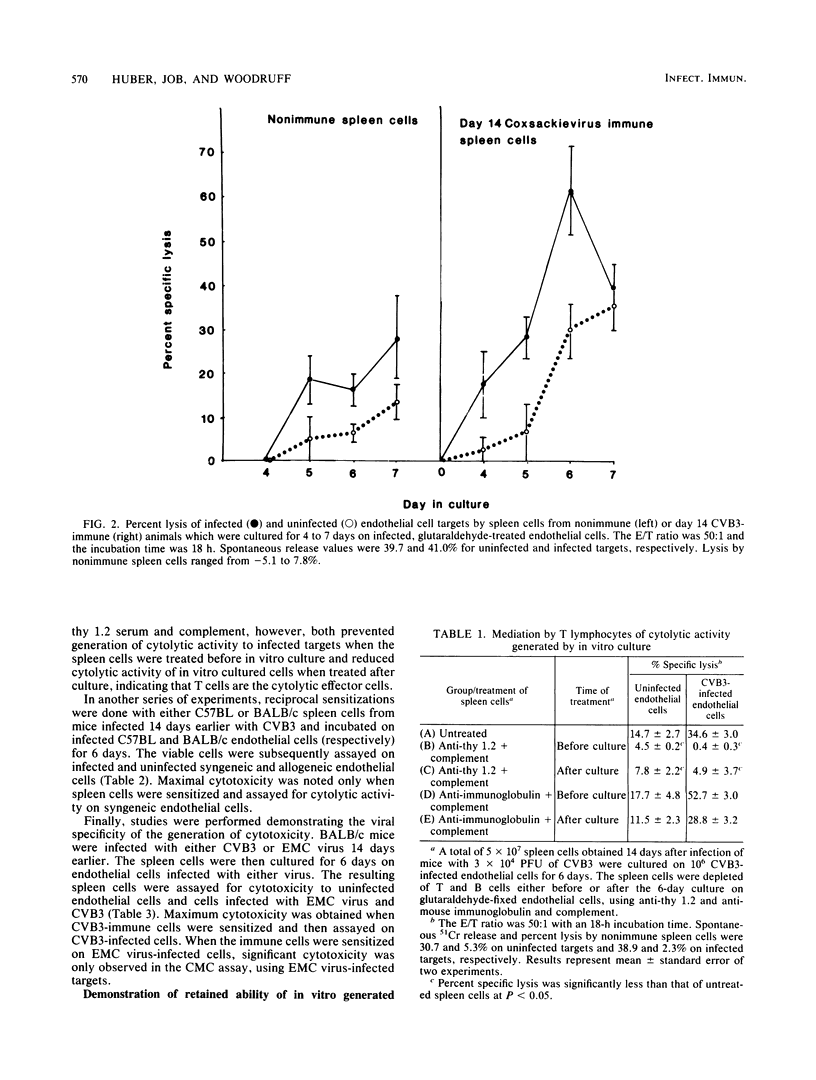
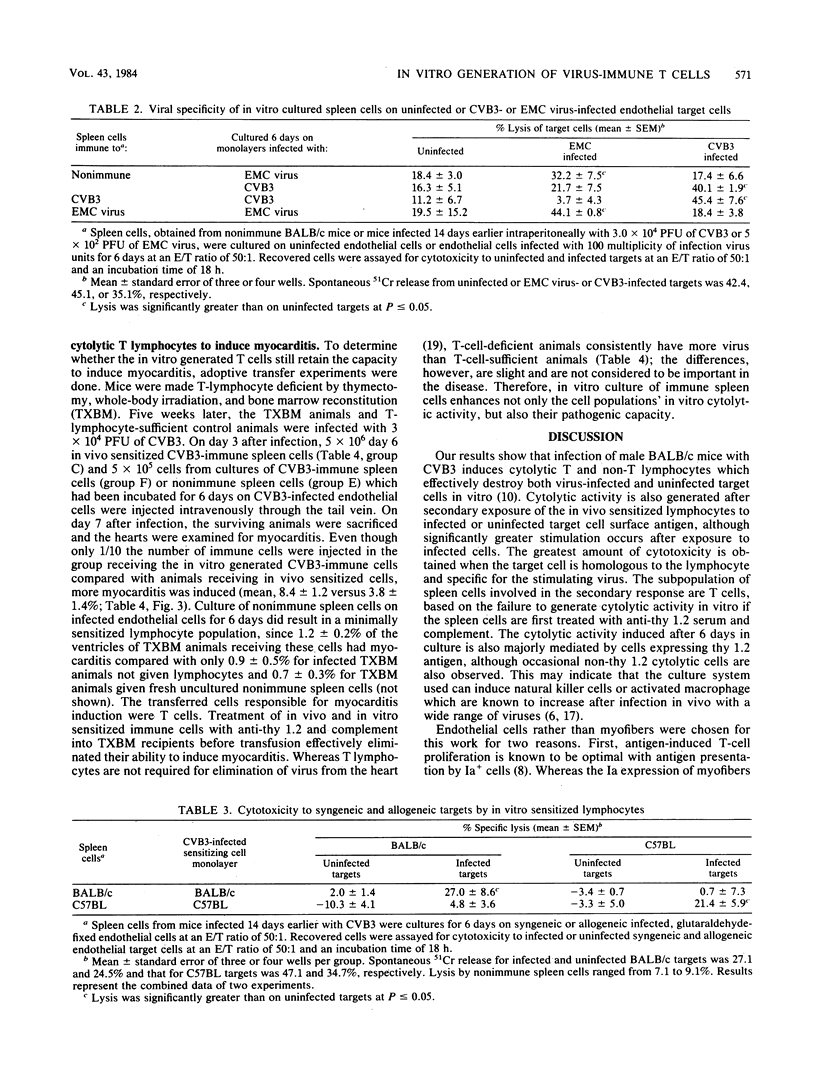
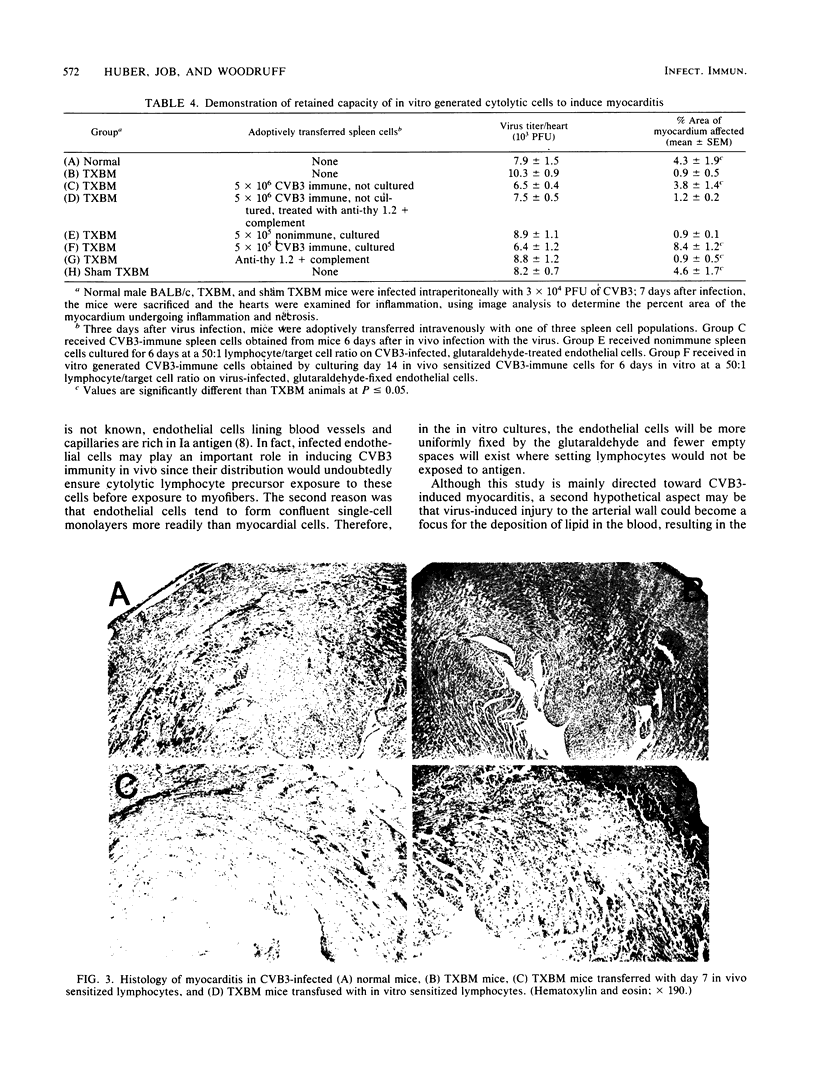
Spleen cells from male BALB/c mice infected 7 days earlier by an intraperitoneal injection of 3 X 10(4) PFU of a myocarditic strain of coxsackievirus B-3 lysed virus-infected endothelial cells in a 51Cr release assay. Cytotoxic activity in the in vivo sensitized spleen cell population could be further increased by culturing the immune spleen cells from infected mice on virus-infected or uninfected endothelial cells for 6 to 7 days in vitro. Cytotoxicity of in vitro cultured spleen cells to infected targets was mediated by T lymphocytes since reactivity was abolished by treatment of the spleen cells with anti-thy 1.2 serum and complement. Reciprocal assays with BALB/c and C57BL cells indicated that maximum cytotoxicity occurred when spleen cells were sensitized on syngeneic endothelial cells. Other experiments showed that spleen cells sensitized to coxsackievirus B-3 or encephalomyocarditis virus were selectively cytolytic to targets infected with the homologous virus. Adoptive transfer of T cells cultured in vitro on infected endothelial cells retained their ability to induce myocarditis in T-lymphocyte-deficient mice.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler K. B., Brody A. R., Craighead J. E. Studies on the mechanism of mucin secretion by cells of the porcine tracheal epithelium. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1981 Jan;166(1):96–106. doi: 10.3181/00379727-166-41030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch G. E., Harb J. M., Hiramoto Y., Shewey L. Viral infection of the aorta of man associated with early atherosclerotic changes. Am Heart J. 1973 Oct;86(4):523–534. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(73)90150-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROWELL R. L., SYVERTON J. T. The mammalian cell-virus relationship. VI. Sustained infection of HeLa cells by Coxsackie B3 virus and effect on superinfection. J Exp Med. 1961 Feb 1;113:419–435. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.2.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop M. B., Blanden R. V. Secondary cytotoxic cell response to lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. I. Kinetics of induction in vitro and yields of effector cells. Immunology. 1976 Aug;31(2):171–180. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R., Alexander P. Mechanism of immunologically specific killing of tumour cells by macrophages. Nature. 1972 Mar 24;236(5343):168–170. doi: 10.1038/236168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HINZE H. C., WALKER D. L. Occurrence of focal three-dimensional proliferation in cultured human cells after prolonged infection with herpes simplex virus. J Exp Med. 1961 May 1;113:885–898. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.5.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschberg H., Braathen L. R., Thorsby E. Antigen presentation by vascular endothelial cells and epidermal Langerhans cells: the role of HLA-DR. Immunol Rev. 1982;66:57–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00434.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber S. A., Job L. P., Auld K. R., Woodruff J. F. Sex-related differences in the rapid production of cytotoxic spleen cells active against uninfected myofibers during Coxsackievirus B-3 infection. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1336–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber S. A., Job L. P., Woodruff J. F. Lysis of infected myofibers by coxsackievirus B-3-immune T lymphocytes. Am J Pathol. 1980 Mar;98(3):681–694. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNETTE E. H., MAGOFFIN R. L., KNOUF E. G. Viral central nervous system disease. An etiologic study conducted at the Los Angeles County General Hospital. JAMA. 1962 Mar 3;179:687–695. doi: 10.1001/jama.1962.03050090015003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minick C. R., Fabricant C. G., Fabricant J., Litrenta M. M. Atheroarteriosclerosis induced by infection with a herpesvirus. Am J Pathol. 1979 Sep;96(3):673–706. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minkowitz S., Berkovich S. Hepatitis produced by coxsackievirus B1 in adult mice. Arch Pathol. 1970 May;89(5):427–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sainani G. S., Krompotic E., Slodki S. J. Adult heart disease due to the Coxsackie virus B infection. Medicine (Baltimore) 1968 Mar;47(2):133–147. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196803000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M., Jr Mouse natural killer cells: induction specificity, and function. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):1631–1635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C. Y., Woodruff J. J., Woodruff J. F. Generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes during coxsackievirus tb-3 infection. II. Characterization of effector cells and demonstration cytotoxicity against viral-infected myofibers1. J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1165–1169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff J. F. Viral myocarditis. A review. Am J Pathol. 1980 Nov;101(2):425–484. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff J. F., Woodruff J. J. Involvement of T lymphocytes in the pathogenesis of coxsackie virus B3 heart disease. J Immunol. 1974 Dec;113(6):1726–1734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon J. W., Austin M., Onodera T., Notkins A. L. Isolation of a virus from the pancreas of a child with diabetic ketoacidosis. N Engl J Med. 1979 May 24;300(21):1173–1179. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197905243002102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




