Abstract
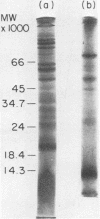
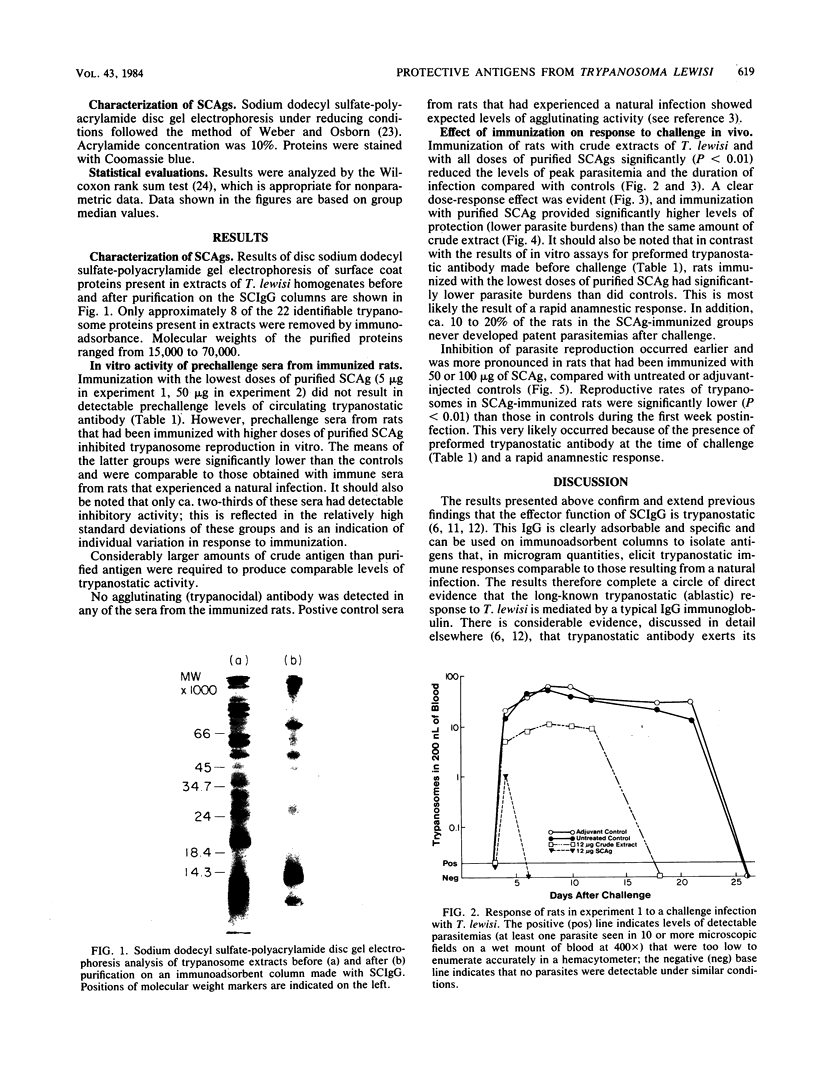
Antigens were purified from extracts of Trypanosoma lewisi on immunoadsorbent columns of trypanostatic immunoglobulin G eluted from parasite surface coats at 8 days postinfection. Eight absorbed proteins, with molecular weights between 15,000 and 70,000, were identified. These surface coat antigens (SCAgs) were then used to immunize rats. After immunization, sera were assayed in vitro for levels of circulating trypanostatic and trypanocidal antibodies. Approximately half of the immune sera had higher levels of trypanostatic antibody, compared with control sera; no trypanocidal antibodies (agglutinins) were detected in any of the sera. The rats were then challenged intraperitonally, and the parasitemias and division rates of the parasites were monitored. Parasitemias of all immunized rats were significantly (P less than 0.01) lower and of shorter duration than those of the controls. Division rates of trypanosomes were also significantly (P less than 0.01) lower in all immunized rats at all times before total cessation of division compared with control rats. A clear dose-response effect was observed, with greater amounts of SCAg eliciting higher levels of protection. Purified SCAgs were also more effective immunogens than were the crude trypanosome extracts from which they had been purified, and in which other proteins in addition to the SCAgs were present. These data provide conclusive evidence that the immunoglobulin G in the surface coats of T. lewisi, adsorbed during the course of infection, is specific antibody, in that it can be used to isolate parasite antigens that elicit a trypanostatic response in rats immunized with them.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clarkson A. B., Jr, Mellow G. H. Rheumatoid factor-like immunoglobulin M protects previously uninfected rat pups and dams from Trypanosoma lewisi. Science. 1981 Oct 9;214(4517):186–188. doi: 10.1126/science.7025211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Alesandro P. A. Ablastin: the phenomenon. Exp Parasitol. 1975 Dec;38(3):303–308. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(75)90115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Alesandro P. A., Clarkson A. B., Jr Trypanosoma lewisi: avidity and adsorbability of ablastin, the rat antibody inhibiting parasite reproduction. Exp Parasitol. 1980 Dec;50(3):384–396. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(80)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dusanic D. G. Immunosuppression and ablastin. Exp Parasitol. 1975 Dec;38(3):322–337. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(75)90118-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer D. M. Cell surface saccharides of Trypanosoma lewisi. I. Polycation-induced cell agglutination and fine-structure cytochemistry. J Cell Sci. 1975 Dec;19(3):621–644. doi: 10.1242/jcs.19.3.621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer D. M., D'Alesandro P. A. Isolation and characterization of pellicular membranes from Trypanosoma lewisi bloodstream forms. J Parasitol. 1980 Jun;66(3):377–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannini S. H., D'Alesandro P. A. Trypanosoma lewisi: accumulation of antigen-specific host IgG as a component of the surface coat during the course of infection in the rat. Exp Parasitol. 1979 Jun;47(3):342–355. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(79)90087-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannini S. H., D'Alesandro P. A. Trypanostatic activity of rat IgG purified from the surface coat of Trypanosoma lewisi. J Parasitol. 1982 Oct;68(5):765–773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanham S. M. Separation of trypanosomes from the blood of infected rats and mice by anion-exchangers. Nature. 1968 Jun 29;218(5148):1273–1274. doi: 10.1038/2181273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley H. A., Honigberg B. M., Cunningham I. Analysis of the antigenic composition of Trypanosoma brucei brucei bloodstream and culture forms by the quantitative direct fluorescent antibody methods. J Protozool. 1978 May;25(2):245–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1978.tb04406.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickler J. E., Mancini P. E., Patton C. L. Trypanosoma brucei brucei: isolation of the major surface coat glycoprotein by lectin affinity chromatography. Exp Parasitol. 1978 Dec;46(2):262–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(78)90140-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]