Abstract
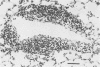
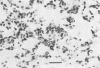
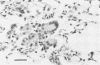
The A2 strain of human respiratory syncytial virus replicated in the nose and lung of BALB/c mice, with virus growing to higher titers in older animals than in younger animals. Virus was recovered from the nose between days 2 and 7 with peak titers on days 3 and 4, and from the lungs between days 2 and 9, with peak titers on days 4 through 6. Serum antibody developed 2 weeks after infection. Viral antigen was demonstrated in the alveolar cells of the lung by immunofluorescence. Histopathological changes included infiltration by mononuclear cells of the peribronchiolar and perivascular tissue, some interstitial thickening, and formation of multinucleated giant cells. Virus could not be recovered from the respiratory tract of mice inoculated with bovine strains of respiratory syncytial virus. Growth of the A2 strain of human respiratory syncytial virus in different cell lines affected its infectivity for mice. Infection of BALB/c mice with respiratory syncytial virus provides a highly reproducible model for the study of the pathogenesis of and mechanisms of immunity to this virus.
Full text
PDF

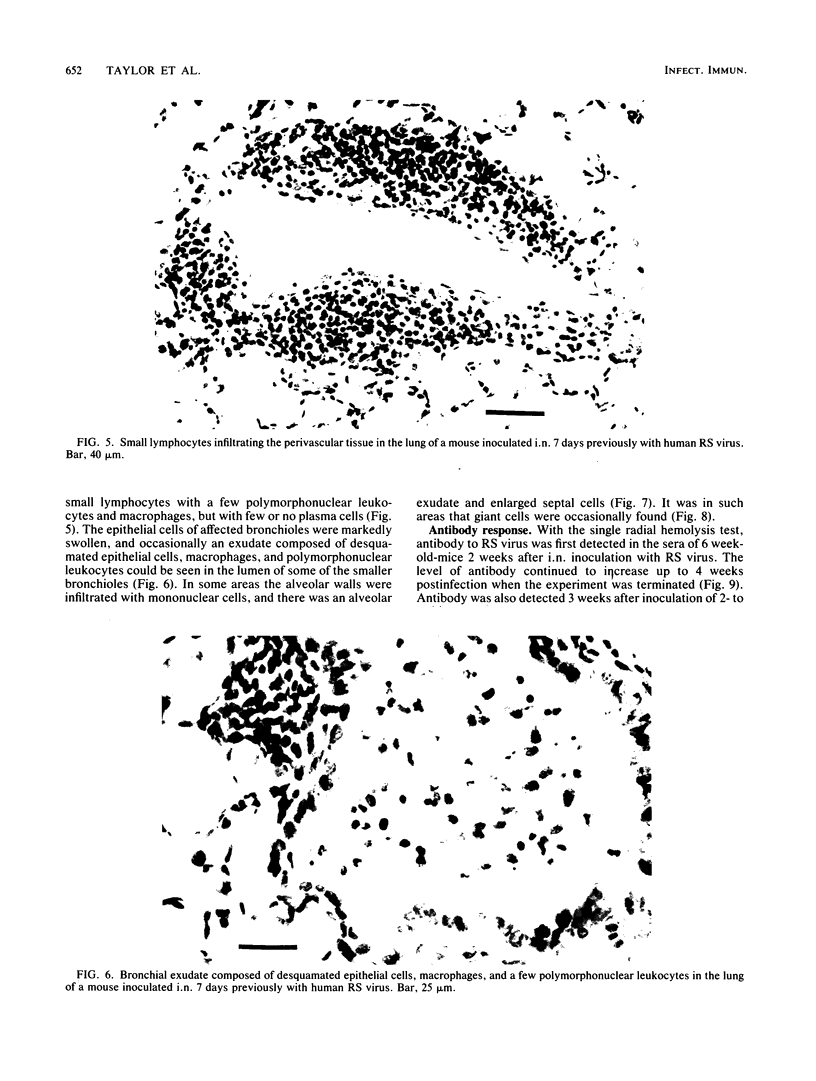

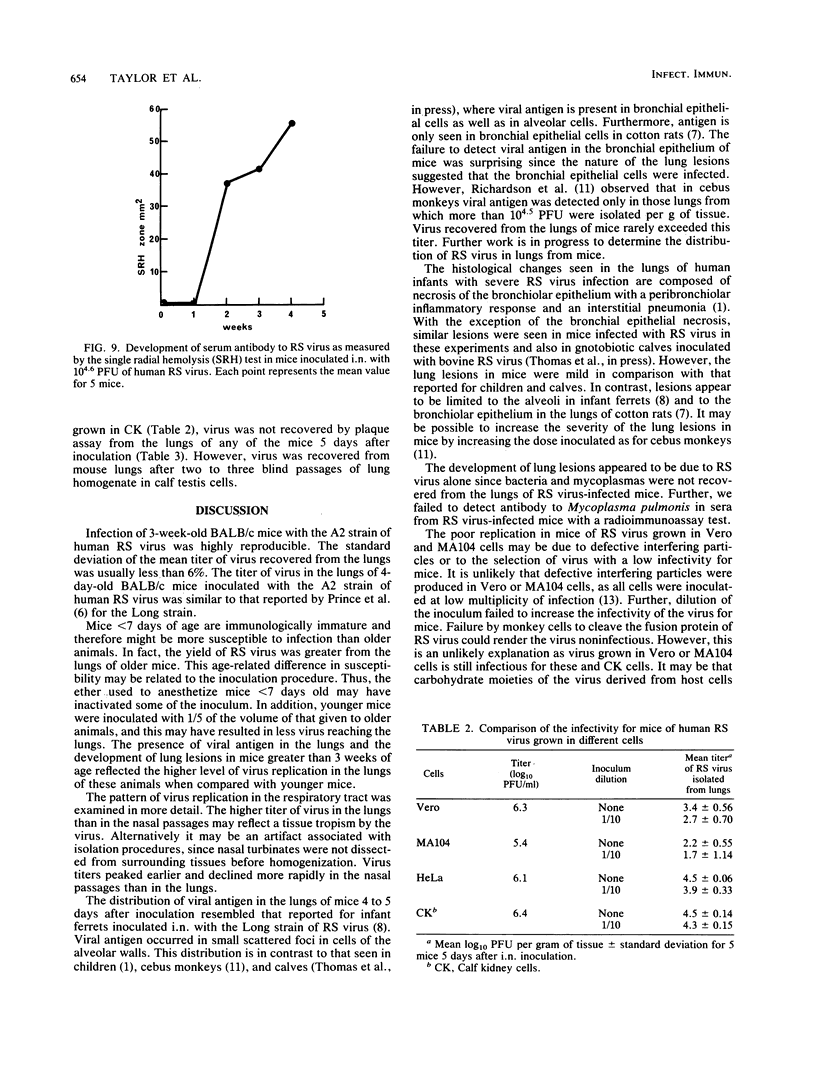

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aherne W., Bird T., Court S. D., Gardner P. S., McQuillin J. Pathological changes in virus infections of the lower respiratory tract in children. J Clin Pathol. 1970 Feb;23(1):7–18. doi: 10.1136/jcp.23.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belshe R. B., Richardson L. S., London W. T., Sly D. L., Lorfeld J. H., Camargo E., Prevar D. A., Chanock R. M. Experimental respiratory syncytial virus infection of four species of primates. J Med Virol. 1977;1(3):157–162. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890010302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourlay R. N., Leach R. H. A new mycoplasma species isolated from pneumonic lungs of calves (Mycoplasma dispar sp. nov.). J Med Microbiol. 1970 Feb;3(1):111–123. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-1-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince G. A., Horswood R. L., Berndt J., Suffin S. C., Chanock R. M. Respiratory syncytial virus infection in inbred mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):764–766. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.764-766.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince G. A., Jenson A. B., Horswood R. L., Camargo E., Chanock R. M. The pathogenesis of respiratory syncytial virus infection in cotton rats. Am J Pathol. 1978 Dec;93(3):771–791. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince G. A., Porter D. D. The pathogenesis of respiratory syncytial virus infection in infant ferrets. Am J Pathol. 1976 Feb;82(2):339–352. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probert M., Russell S. M. Measurement of parainfluenza-3 virus antibody by the single radial hemolysis technique. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Sep;2(3):157–161. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.3.157-161.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson L. S., Belshe R. B., London W. T., Sly D. L., Prevar D. A., Camargo E., Chanock R. M. Evaluation of five temperature-sensitive mutants of respiratory syncytial virus in primates: I. Viral shedding, immunologic response, and associated illness. J Med Virol. 1978;3(2):91–100. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890030202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson L. S., Belshe R. B., Sly D. L., London W. T., Prevar D. A., Camargo E., Chanock R. M. Experimental respiratory syncytial virus pneumonia in cebus monkeys. J Med Virol. 1978;2(1):45–59. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890020108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stott E. J., Thomas L. H., Collins A. P., Crouch S., Jebbett J., Smith G. S., Luther P. D., Caswell R. A survey of virus infections of the respiratory tract of cattle and their association with disease. J Hyg (Lond) 1980 Oct;85(2):257–270. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400063294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treuhaft M. W., Beem M. O. Defective interfering particles of respiratory syncytial virus. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):439–444. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.439-444.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]