Abstract
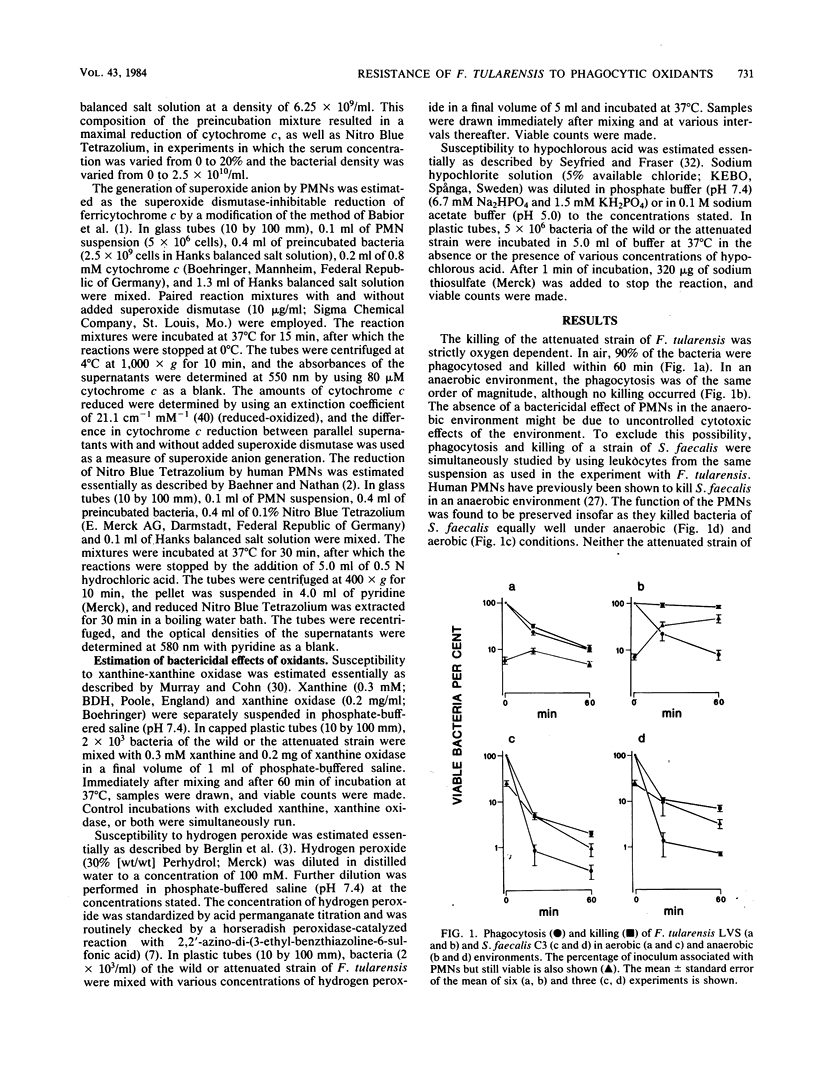
We have previously reported that a wild strain of Francisella tularensis is much less efficiently killed by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes than is an attenuated strain. In the present study, the killing of the attenuated strain was found to be strictly oxygen dependent. The wild and the attenuated strains both induced a respiratory burst in the leukocytes. The difference between the strains in susceptibility to agents produced at the burst could be explained by a difference in susceptibility to hypochlorous acid.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babior B. M., Kipnes R. S., Curnutte J. T. Biological defense mechanisms. The production by leukocytes of superoxide, a potential bactericidal agent. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):741–744. doi: 10.1172/JCI107236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baehner R. L., Nathan D. G. Quantitative nitroblue tetrazolium test in chronic granulomatous disease. N Engl J Med. 1968 May 2;278(18):971–976. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196805022781801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berglin E. H., Edlund M. B., Nyberg G. K., Carlsson J. Potentiation by L-cysteine of the bactericidal effect of hydrogen peroxide in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):81–88. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.81-88.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARLISLE H. N., HINCHLIFFE V., SASLAW S. Immunodiffusion studies with Pasteurella tularensis antigen-rabbit antibody systems. J Immunol. 1962 Nov;89:638–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canonico P. G., McManus A. T., Mangiafico J. A., Sammons L. S., McGann V. G., Dangerfield H. G. Temporal appearance of opsonizing antibody to Francisella tularensis: detection by a radiometabolic assay. Infect Immun. 1975 Mar;11(3):466–469. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.3.466-469.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J., Carpenter V. S. The recA+ gene product is more important than catalase and superoxide dismutase in protecting Escherichia coli against hydrogen peroxide toxicity. J Bacteriol. 1980 Apr;142(1):319–321. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.1.319-321.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs R. E., Bardsley W. G. The steady-state kinetics of peroxidase with 2,2'-azino-di-(3-ethyl-benzthiazoline-6-sulphonic acid) as chromogen. Biochem J. 1975 Jan;145(1):93–103. doi: 10.1042/bj1450093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIOGUARDI N., AGOSTONI A., FIORELLI G., LOMANTO B. Characterization of lactic dehydrogenase of normal human granulocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 May;61:713–723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper P., Rees R. J. Electron-transparent zone of mycobacteria may be a defence mechanism. Nature. 1970 Nov 28;228(5274):860–861. doi: 10.1038/228860a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EIGELSBACH H. T., DOWNS C. M. Prophylactic effectiveness of live and killed tularemia vaccines. I. Production of vaccine and evaluation in the white mouse and guinea pig. J Immunol. 1961 Oct;87:415–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foote C. S., Goyne T. E., Lehrer R. I. Assessment of chlorination by human neutrophils. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):715–716. doi: 10.1038/301715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Lochner J. E., Bigley R. H., Iglewski B. H. The effects of Legionella pneumophila toxin on oxidative processes and bacterial killing of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Infect Dis. 1982 Sep;146(3):328–334. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.3.328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabig T. G., Babior B. M. The killing of pathogens by phagocytes. Annu Rev Med. 1981;32:313–326. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.32.020181.001525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goren M. B., D'Arcy Hart P., Young M. R., Armstrong J. A. Prevention of phagosome-lysosome fusion in cultured macrophages by sulfatides of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2510–2514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goren M. B., Grange J. M., Aber V. R., Allen B. W., Mitchison D. A. Role of lipid content and hydrogen peroxide susceptibility in determining the guinea-pig virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1982 Dec;63(6):693–700. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood A. M. Virulence factors of Francisella tularensis. J Hyg (Lond) 1977 Aug;79(1):47–60. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400052840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacques Y. V., Bainton D. F. Changes in pH within the phagocytic vacuoles of human neutrophils and monocytes. Lab Invest. 1978 Sep;39(3):179–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen M. S., Bainton D. F. Temporal changes in pH within the phagocytic vacuole of the polymorphonuclear neutrophilic leukocyte. J Cell Biol. 1973 Feb;56(2):379–388. doi: 10.1083/jcb.56.2.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Antimicrobial mechanisms in neutrophilic polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Semin Hematol. 1975 Apr;12(2):117–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Myeloperoxidase-halide-hydrogen peroxide antibacterial system. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2131–2138. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2131-2138.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreutzer D. L., Dreyfus L. A., Robertson D. C. Interaction of polymorphonuclear leukocytes with smooth and rough strains of Brucella abortus. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):737–742. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.737-742.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lochner J. E., Friedman R. L., Bigley R. H., Iglewski B. H. Effect of oxygen-dependent antimicrobial systems on Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):487–489. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.487-489.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löfgren S., Tärnvik A., Bloom G. D., Sjöberg W. Phagocytosis and killing of Francisella tularensis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):715–720. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.715-720.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löfgren S., Tärnvik A., Carlsson J. Demonstration of opsonizing antibodies to Francisella tularensis by leukocyte chemiluminescence. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):329–334. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.329-334.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell G. L. Bactericidal activity of aerobic and anaerobic polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):337–341. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.337-341.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRipley R. J., Sbarra A. J. Role of the phagocyte in host-parasite interactions. XII. Hydrogen peroxide-myeloperoxidase bactericidal system in the phagocyte. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1425–1430. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1425-1430.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. M., Garbus J., Hornick R. B. Lack of enhanced oxygen consumption by polymorphonuclear leukocytes on phagocytosis of virulent Salmonella typhi. Science. 1972 Mar 3;175(4025):1010–1011. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4025.1010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Cohn Z. A. Macrophage oxygen-dependent antimicrobial activity. I. Susceptibility of Toxoplasma gondii to oxygen intermediates. J Exp Med. 1979 Oct 1;150(4):938–949. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.4.938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen H., Klebanoff S. J. Bactericidal activity of a superoxide anion-generating system. A model for the polymorphonuclear leukocyte. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):27–39. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKOOG W. A., BECK W. S. Studies on the fibrinogen, dextran and phytohemagglutinin methods of isolating leukocytes. Blood. 1956 May;11(5):436–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal A. W., Geisow M., Garcia R., Harper A., Miller R. The respiratory burst of phagocytic cells is associated with a rise in vacuolar pH. Nature. 1981 Apr 2;290(5805):406–409. doi: 10.1038/290406a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyfried P. L., Fraser D. J. Persistence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in chlorinated swimming pools. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Mar;26(3):350–355. doi: 10.1139/m80-057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sips H. J., Hamers M. N. Mechanism of the bactericidal action of myeloperoxidase: increased permeability of the Escherichia coli cell envelope. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):11–16. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.11-16.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. L. Myeloperoxidase, hydrogen peroxide, chloride antimicrobial system: nitrogen-chlorine derivatives of bacterial components in bactericidal action against Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):522–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.522-531.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. L. Myeloperoxidase-hydrogen peroxide-chloride antimicrobial system: effect of exogenous amines on antibacterial action against Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):110–116. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.110-116.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thore M., Löfgren S., Tärnvik A. Oxygen and serum complement in phagocytosis and killing of Propionibacterium acnes. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1983 Apr;91(2):95–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch D. F., Sword C. P., Brehm S., Dusanic D. Relationship between superoxide dismutase and pathogenic mechanisms of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):863–872. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.863-872.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Tsai V., Remington J. S. Failure to trigger the oxidative metabolic burst by normal macrophages: possible mechanism for survival of intracellular pathogens. J Exp Med. 1980 Feb 1;151(2):328–346. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.2.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van GELDER B., SLATER E. C. The extinction coefficient of cytochrome c. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Apr 23;58:593–595. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90073-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



