Abstract
Roles of the ZnuACB and ZupT transporters were assessed in Escherichia coli K-12 and uropathogenic E. coli (UPEC) CFT073. K-12 and CFT073 Δznu ΔzupT mutants demonstrated decreased 65Zn2+ uptake and growth in minimal medium. CFT073Δznu demonstrated an intermediate decrease of 65Zn2+ uptake and growth in minimal medium, whereas the CFT073ΔzupT mutant grew as well as CFT073 and exhibited a less marked decrease in 65Zn2+ uptake. CFT073 mutants grew as well as the wild type in human urine. In competitive infections in CBA/J mice, the ΔzupT mutant demonstrated no disadvantage during urinary tract infection. In contrast, the UPEC Δznu and Δznu ΔzupT strains demonstrated significantly reduced numbers in the bladders (mean 4.4- and 30-fold reductions, respectively) and kidneys (mean 41- and 48-fold reductions, respectively). In addition, in single-strain infection experiments, the Δznu and Δznu ΔzupT mutants were reduced in the kidneys (P = 0.0012 and P < 0.0001, respectively). Complementation of the CFT073 Δznu ΔzupT mutant with the znuACB genes restored growth in Zn-deficient medium and bacterial numbers in the bladder and kidneys. The loss of the zinc transport systems decreased both motility and resistance to hydrogen peroxide, which could be restored by supplementation with zinc. Overall, the results indicate that Znu and ZupT are required for growth in zinc limited-conditions, that Znu is the predominant zinc transporter, and that the loss of Znu and ZupT has a cumulative effect on fitness during UTI, which may in part be due to reduced resistance to oxidative stress and motility.
Escherichia coli is a versatile bacterial species comprised of innocuous and pathogenic strains. Pathogenic E. coli cause intestinal or extraintestinal infections in humans and other animals (28). Extraintestinal pathogenic E. coli (ExPEC) cause an array of diseases, including urinary tract infections (UTIs), neonatal meningitis, and septicemia. ExPEC associated with UTI is termed uropathogenic E. coli (UPEC). Compared to E. coli K-12 and other commensal strains, ExPEC strains encode in their genomes a greater variety of characterized, as well as putative, metal transport systems (11, 54). The importance of pathogen-specific iron transport systems for ExPEC has been established (20, 21, 26). However, the importance of other metal transport systems in ExPEC is less well characterized, and in particular nothing has been reported on the potential implication of the zinc transporters for the virulence of ExPEC.
Zinc (Zn2+) is an essential micronutrient in all living cells, since this transition metal is a component of numerous metalloproteins and serves as an enzymatic cofactor or a structural element (5). In mammals, Zn2+ has an important immunomodulatory function and is critical for innate and acquired immunity (45). After exposure to lipopolysaccharide (LPS), zinc levels are decreased in the serum, and zinc is accumulated in the liver (38). In addition, during bacterial infection, the host protein calprotectin is released by neutrophils and may reduce bacterial numbers by restricting the availability of metals, including zinc and manganese (16, 39, 50). Also, although zinc concentrations are estimated to be in the millimolar range within host cells, available zinc may be mostly inaccessible to bacterial pathogens (3) and/or dramatically reduced after activation of innate immune defenses (45).
In bacteria, the uptake of zinc is mediated by two major types of transporters: ZnuACB, which belongs to the cluster C9 family of (TroA-like) ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters (15, 27), and ZupT, which is a member of the ZIP (for ZRT/IRT-like protein) family of transporters that are also present in eukaryotes (27). Thus far, the Znu transport system has been shown to be important for virulence in a number of bacterial pathogens, including Salmonella enterica, Brucella abortus, and Haemophilus ducreyi (3, 12, 35, 56). Currently, the roles of the Znu and ZupT transporters for ExPEC virulence have not been investigated.
The genomes of all E. coli strains that have been sequenced thus far contain genes encoding the two described zinc transporters: ZupT and ZnuACB. In addition to the transport of zinc, ZupT can also mediate the uptake of Co2+, Fe2+, and Mn2+ (24). The exact mechanism by which ZupT mediates metal uptake is currently unknown, although it may involve a chemiosmotic transmembrane gradient (24). Zinc uptake mediated by the Znu system requires hydrolysis of ATP by ZnuC to transport Zn2+ captured by the periplasmic binding protein ZnuA through the pore in the cytoplasmic membrane formed by a ZnuB dimer (36, 44). In ExPEC strains, the SitABCD transport system represents an additional ABC transporter belonging to the C9 (TroA-like) cluster (46). Sit transporters have thus far been characterized as manganese and iron transporters (8, 29, 47), although zinc has been shown to be an effective competitive inhibitor of manganese or iron uptake by SitABCD (8, 29). The SitA periplasmic binding protein also shares similarities to the TroA periplasmic binding protein of Treponema pallidum, which has been shown to bind both zinc and manganese with essentially equal affinities (19). It remains to be determined whether in addition to Znu and ZupT transporters, SitABCD or any other undefined transport systems may contribute to zinc transport or the virulence of ExPEC.
In the present study, the roles of the Znu, ZupT, and SitABCD transport systems for zinc uptake and growth in zinc-restricted medium were compared in an E. coli K-12 Δznu ΔzupT mutant. In addition, the roles of the Znu and ZupT transporters for growth of ExPEC strain CFT073 in zinc-restricted conditions and for colonization in the murine ascending UTI model were assessed.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains, plasmids, media, and growth conditions.
The bacterial strains and plasmids used in the present study are listed in Table 1. Strains were routinely cultured overnight in Luria-Bertani (LB) broth or on LB agar (15 g/liter agar) at 37°C and stored in 25% glycerol-LB broth at −80°C. Antibiotics were added as required at the following concentrations: kanamycin, 30 μg/ml; ampicillin, 100 to 200 μg/ml; chloramphenicol, 30 μg/ml; and tetracycline, 10 μg/ml.
TABLE 1.
Bacterial strains and plasmids used in this study
| Strain or plasmid | Characteristic(s)a | Source or reference |
|---|---|---|
| Strains | ||
| E. coli K-12 | ||
| DH5α | F− λ− 80 (lacZYA-argF) endA1 recA1 hsdR17 deoR thi-1 supE44 gyrA96 relA1; Nalr | Bethesda Laboratories |
| BW25113 | F− λ− (lacIqrrnBT14 lacZWJ16 hsdR514 araBADAH33 rhaBADLD78) | 17 |
| JW5831-1 | BW25113 ΔznuA::kan; Kmr | 7 |
| MG1655 | F− λ−ilvG rfb-50 rph-1 | 9 |
| QT1369 | MG1655 Δznu::kan; Kmr | This study |
| QT1370 | MG1655 Δznu::FRT | This study |
| QT1435 | MG1655 Δznu::FRT ΔzupT::kan; Kmr | This study |
| QT1460 | QT1435(pACYC184); Kmr Cmr Tcr | This study |
| QT1461 | QT1435(pIJ28-pACYC184::sitABCD); Kmr Cmr | This study |
| QT1462 | QT1435(pIJ156-pACYC184::znuACB); Kmr Cmr | This study |
| QT1463 | QT1435(pIJ202-pACYC184::zupT); Kmr Cmr | This study |
| QT1553 | MG1655 ΔzupT::kan; Kmr | |
| ExPEC | ||
| CFT073 | UPEC wild-type pyelonephritis strain | 43, 54 |
| QT908 | CFT073 Δsit::tetAR; Tcr | This study |
| QT1081 | CFT073 ΔlacZYA | This study |
| QT1239 | APEC χ7122 Δsit::tetAR ΔmntH::kan; Kmr Tcr | 47 |
| QT1377 | CFT073 Δznu::kan; Kmr | This study |
| QT1378 | CFT073 Δsit::tetAR Δznu::kan; Kmr Tcr | This study |
| QT1434 | CFT073 Δznu::FRT | This study |
| QT1554 | CFT073 ΔzupT::kan; Kmr | This study |
| QT1555 | CFT073 Δznu::FRT ΔzupT::kan; Kmr | This study |
| QT1634 | CFT073 Δznu::FRT ΔzupT::kan Δsit::tetAR; Kmr Tcr | This study |
| QT1640 | CFT073 Δznu::FRT Δsit::tetAR; Tcr | This study |
| QT1932 | QT1555(pIJ254)(pGP704::znuACB); Kmr Apr | This study |
| Plasmids | ||
| pACYC184 | p15A replicon cloning vector; Cmr Tcr | 14 |
| pCP20 | FLP helper plasmid Ts replicon; Apr Cmr | 17 |
| pGP704 | oriR6K mobRP4; Apr | 42 |
| pIJ28 | sitABCD region of χ7122 cloned into HindIII site of pACYC184 plasmid vector; Cmr | 47 |
| pIJ156 | znuACB region of MG1655 cloned into HindIII site of pACYC184 plasmid vector; Cmr | This study |
| pIJ202 | zupT operon of MG1655 cloned into HindIII site of pACYC184 plasmid vector; Cmr | This study |
| pIJ254 | znuACB region cloned from pIJ156 into XbaI and EcoRV sites of pGP704 | This study |
| pKD13 | Template plasmid for the amplification of the kan cassette bordered by FRT sites | 17 |
| pKD46 | λ-Red recombinase plasmid Ts replicon; Apr | 17 |
Cmr, chloramphenicol resistance; Nalr, nalidixic acid; Tcr, tetracycline resistance; Apr, ampicillin resistance; Kmr, kanamycin resistance.
PCR and gene cloning.
The primers used for the PCRs are presented in Table 2. PCR was used to amplify znuACB and zupT genes from E. coli K-12 strain MG1655. PCR was also used to create and confirm all of the mutant genotypes throughout the present study. The templates used for PCR amplification were either crude lysates of bacterial strains or diluted plasmid DNA. New England Biolabs Taq DNA polymerase was used for routine PCR amplifications (confirmation of mutant alleles), and the high-fidelity Herculase DNA polymerase (Stratagene) was used for amplification of cloned fragments. A 5-μl portion of each bacterial cell lysate or a 1-μl aliquot of plasmid DNA was added to a PCR mixture to achieve a final volume of 25 μl containing 6.25 pmol of each primer, 5 nmol of each deoxynucleoside triphosphate, and 0.5 U of either Taq polymerase or Herculase in 1× buffer. The PCR conditions were as follows: 95°C for 1 min, followed by 30 cycles of 94°C for 30 s, 54°C for 30 s, and 72°C for 1 min, and with a final extension period of 72°C for 1 min. Restriction endonucleases and T4 DNA ligase were purchased from New England Biolabs. Plasmid DNA was purified by using Qiagen purification kits according to the supplier's protocol.
TABLE 2.
Primers used in this study
| Primer | Characteristic(s) | Sequence | Tm (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CMD23 | SitA-SitD region amplification (used with CMD42) | CGCAGGGGGCACAACTGAT | 54 |
| CMD42 | CTGTGCGCTGCTGTCGGTC | 54 | |
| CMD264 | Amplification of znu::kan from JWK5831_1 (used with CMD265) | AAAACGCCACAATCCAGTTC | 54 |
| CMD265 | CGGCAGTACGGTCATAGGTT | 56 | |
| CMD637 | Contains a HindIII restriction site; amplification of znuACB region of MG1655 for cloning (used with CMD638) | GACAAGCTTGGCCAGAGTAAGAACGG | 56 |
| CMD638 | Contains a HindIII restriction site | CGAAAGCTTCGTGGAATCACTTTGGC | 56 |
| CMD715 | Construction of zupT::kan using pKD13 template plasmid (used with CMD716) | TTCCCGCCGTTTGTAGCAGCACTAAACTGAATCCCATCACTGACATTCCAATTCCGGGGATCCGTCGACC | 68 |
| CMD716 | CTCTCATTCTGACCATACTGGCGGGGGCAGCCACGTTTATTGGCGCGTTTTGTAGGCTGGAGCTGCTTCG | 68 | |
| CMD717 | Contains a HindIII restriction site; amplification of zupT operon of MG1655 for cloning (used with CMD718) | GTTAAGCTTACGATCTGCCTGAAGGTGAA | 54 |
| CMD718 | Contains a HindIII restriction site | GAAGAAGCTTATGCGCTGGACAACTTCTG | 54 |
Plasmid pIJ156, containing the znuACB genes, was obtained by ligating a HindIII-digested fragment obtained by PCR using primers CMD637 and CMD638 (Table 2) into the HindIII site of pACYC184. Similarly, pIJ202 containing zupT, was obtained by ligating a HindIII-digested PCR product obtained using the primers CMD717 and CMD718 into HindIII site of pACYC184. The cloned inserts of plasmids pIJ156 and pIJ202 were sequenced and confirmed to be identical to MG1655 genomic sequences of the znuACB and zupT genes, respectively. The suicide plasmid used for single-copy complementation of znuACB genes, pIJ254, was constructed by digestion of plasmid pIJ156 with XbaI and EcoRV and ligation of the appropriate fragment into the same restriction sites of plasmid pGP704.
Construction of mutant strains.
All mutants were made by using one-step PCR fragment-mediated λ-Red recombination mutagenesis (17). The znuA::kan allele was amplified directly from strain JW5831-1 (ΔznuA::kan) (7) using the primers CM264 and CMD265 (Table 2) to generate ΔznuA::kan derivatives of K-12 strain MG1655 (QT1369) and UPEC strain CFT073 (QT1377) by recombination-mediated allelic exchange using plasmid pKD46 (17). The kanamycin cassettes, which are flanked by FRT sites, were lost in these strains through FLP recombinase-mediated excision using plasmid pCP20, generating the strains QT1370 (MG1655 ΔznuA::FRT) and QT1434 (CFT073 ΔznuA::FRT). The zupT::kan allele was obtained using primers CMD715 and CMD716 and specific amplification of the allele from the template plasmid pKD13. This allele was introduced into strains MG1655 and CFT073 as described above, generating strains QT1553 (MG1655 ΔzupT::kan) and QT1554 (CFT073 ΔzupT::kan). Similarly, the ΔzupT::kan allele was also introduced to the ΔznuA::FRT mutants to generate the ΔznuA::FRT ΔzupT::kan double mutant strains of MG1655 (QT1435) and CFT073 (QT1555). A Δsit::tetAR allele amplified from APEC QT205 (46) with the primers CMD23 and CMD42 was used to generate strains QT1640 (CFT073 ΔznuA::FRT Δsit::tet) and QT1634 (CFT073 ΔznuA::FRT ΔzupT::kan Δsit::tet). Strain QT1932, the UPEC znuACB complemented ΔznuA::FRT ΔzupT::kan derivative of CFT073, was obtained by conjugation of suicide plasmid pIJ254 into strain QT1555 by using previously described methods (46). UPEC strain QT1081 (CFT073 ΔlacZYA) was generated as previously described for strain χ7122 (40).
Growth in minimal medium and ion rescue.
All media used for growth assays were made using the purest available water processed with the Milli-Q water purification system (Millipore) and were prepared in polypropylene labware rinsed three times with Milli-Q water. M9-glucose medium and M9-glucose agar (using 1.5% Noble agar from Sigma) were used as a defined minimal metal-limited medium to assess the growth of strains. For growth in a complex minimal medium, DT-glucose (diluent tryptone) was used as described previously, except that it was supplemented with a 200 μM concentration of the metal-chelator EGTA (47). The EGTA affinity constants for Mn2+, Fe3+, and Zn2+, taken from the NIST critically selected stability constants of metal complexes database are as follows: log K = 12.2 (Mn2+), log K = 20 (Fe3+), and log K = 12.6 (Zn2+). The growth of E. coli strains was assessed in DT-EGTA or M9-glucose broth. Briefly, after growth in rich LB medium, the strains were precultured in the appropriate minimal medium overnight. The following day, the strains were adjusted to an optical density at 600 nm (OD600) of 0.02. Growth as measured at OD600 was monitored every 2 h. All strains were tested in triplicate. Metal supplements (5 μM concentrations of ZnCl2, MnCl2, or FeCl2) were added to determine the effects of ion rescue on growth of strains. Human urine, pooled from three healthy women and sterile filtered, was also used in the present study to characterize growth of strain CFT073 and its mutant derivatives. LB broth was used as the metal-replete rich medium.
Isotope uptake.
Zinc isotope (65Zn2+) uptake was determined in the E. coli K-12 zinc transport-deficient (ΔznuA::FRT ΔzupT::kan) strain derivative of MG1655 (QT1435) transformed with the plasmids pIJ156 (znuACB), pIJ202 (zupT), pIJ28 (sitABCD), or pACYC184 (vector control) and the mutant derivatives of UPEC strain CFT073 lacking functional Znu, ZupT, and/or Sit transporters. All strains were grown in DT broth overnight. The following day, the strains were suspended in DT-EGTA (200 μM) for 2 h at 37°C with moderate shaking. The strains were washed three times with DT-EGTA (500 μM) and adjusted to an OD600 of 0.5 (corresponding to 108 cells/ml). Zinc isotope 65Zn2+ was added at a concentration of 20 nM. The strains were left in the presence of the isotope for 15 min at 37°C. Then, 1-ml samples of the strain and/or isotope suspension in DT-EGTA were distributed in 2-ml Eppendorf tubes. Triplicates of each strain were prepared, and samples were washed three times with cold DT-EGTA (1 mM) for 2 min and resuspended in Wallac Optiphase scintillation buffer. Scintillations counts were read on the channels 0 to 748 of an LS1701 scintillation counter (Beckman). Samples from the zinc-transport deficient strain without isotope were used as a blank to determine the value of the background that was subsequently subtracted. A triplicate of samples containing 100 μl of 20 nM 65Zn2+ DT-EGTA without bacterial cells was used as a standard to convert the value of the uptake from counts per minute to pmol/108 cells.
Oxidative stress resistance.
Oxidative stress resistance against hydrogen peroxide (30% [vol/vol]) using a disk diffusion assay was done using strain CFT073 and its mutant derivatives as previously described (46).
Motility assay.
Motility assays were done using strain CFT073 and its mutant derivatives as previously published (32), except that all of the strains screened for motility were washed three times with M9 medium prior to inoculation on motility agar plates. The motility area was measured after 18 h of growth at 37°C.
Experimental UTI in CBA/J mice.
A murine ascending UTI model was used in which a virulent ΔlacZYA derivative of UPEC CFT073 (strain QT1081) was coinfected with the different metal transporter mutants. Six-week-old CBA/J female mice were coinfected with 25 μl (109 CFU) of a mixed culture containing nearly equal amounts of two test strains through a catheter inserted in the urethra. The infected animals were euthanized 48 h postinfection, and the bacterial counts of the bladders and kidneys were determined on MacConkey agar plates, which allowed for direct comparison of the virulent Δlac CFT073 derivative (white colonies) and the metal transport mutants (red colonies). Competitive indexes (CI; calculated as the mutant CFU/Δlac CFT073) were determined for each sample and normalized for the input ratio of the inoculum. The log CI values were used for graphical representation, with negative log CI values indicating a decreased capacity of the transport mutant to compete with the virulent UPEC CFT073 derivative. In the single-strain experimental UTI model, individual groups of CBA/J mice were infected as described above but with pure cultures of each strain, and 48 h postinfection bacterial counts were determined from the bladders and kidneys.
Statistical analyses.
All data were analyzed by using GraphPad Prism 4 software. A Wilcoxon signed-rank test (two-tailed P ≤ 0.05) was used to determine statistical significance in the log CI values between groups in the competitive-infection experiments. A Mann-Whitney test was used to determine significant differences between groups in single-strain infection experiments.
RESULTS
Individual contribution of metal transport systems to the growth of E. coli zinc transport-deficient mutants.
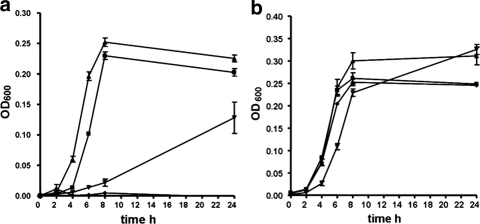
To investigate the individual roles of the Znu, ZupT, and SitABCD transport systems for growth in medium with limited zinc availability (DT-EGTA), genes encoding these systems on plasmid pACYC184 were introduced into E. coli K-12 MG1655 derivative strain QT1435, which lacks the known zinc transporters ZnuACB and ZupT. Strain QT1435 containing the pACYC184 vector alone failed to grow in DT-EGTA (Fig. 1a). In contrast, strain QT1435 complemented with znuACB (pIJ156) or zupT (pIJ202) regained growth. By comparison, introduction of the sitABCD genes (pIJ28), encoding a manganese/iron transport system, conferred a limited and late increase in growth (Fig. 1a). All mutant strains grew well in DT-EGTA medium supplemented with 5 μM ZnCl2, suggesting that the growth defect of the znu/zupT mutant was due to the lack of available Zn2+ (Fig. 1b).
FIG. 1.
Growth of the E. coli K-12 Δznu ΔzupT mutant QT1435 containing plasmid-encoded metal transporters in DT-EGTA medium (a) or DT-EGTA with 5 μM Zn2+ (b). Symbols: ⧫, QT1435(pACYC184) (vector control); ▴, QT1435(pIJ202) zupT; ▪, QT1435(pIJ156) znuACB; ▾, QT1435(pIJ28) sitABCD.
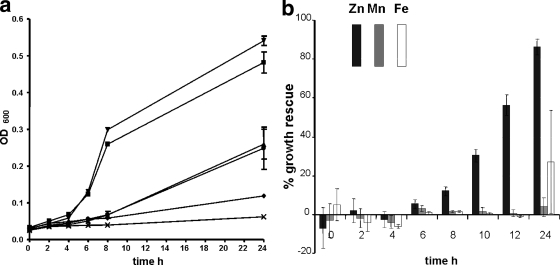
The CFT073 Δznu mutant also exhibited a marked lag and decreased growth in minimal medium (Fig. 2a). Loss of the sit genes from the Δznu strain had no discernible effect on growth (Fig. 2a). The ΔzupT mutant (QT1554) demonstrated no growth defect compared to the wild-type parent strain, whereas the Δznu ΔzupT mutant (QT1555) grew very poorly, and additional loss of sitABCD completely impeded growth of strain QT1634 (Fig. 2a). Supplementation with 5 μM Zn2+ restored growth of the CFT073 Δznu ΔzupT mutant (86% growth of the wild type at 24 h), whereas addition of Fe2+ only slightly increased growth (27% compared to the wild type at 24 h of incubation), and the addition of Mn2+ had no appreciable effect (Fig. 2b). These results confirmed that the lack of Zn2+ in minimal medium was likely responsible for the growth-deficient phenotypes observed for the Δznu and Δznu ΔzupT mutant derivatives of CFT073.
FIG. 2.
(a) Growth of UPEC strain CFT073 and metal transport-defective mutant derivatives in M9-glucose medium. Symbols: ▪, CFT073 wild type; ▴, Δznu mutant (QT1434); ▾, ΔzupT mutant (QT1554); ⧫, Δznu ΔzupT mutant (QT1555); •, Δznu ΔsitABCD mutant (QT1640); ×, Δznu ΔzupT ΔsitABCD mutant (QT1634). (b) Growth rescue of the UPEC Δznu ΔzupT strain QT1555 in M9-glucose medium supplemented with 5 μM Zn2+ (▪), Mn2+ (░⃞), or Fe3+ (□). Growth of the strain is presented as the percent growth compared to the wild-type strain CFT073 based on the formula: [(OD600 of the mutant in metal-enriched medium) − (OD600 of the mutant)]/(OD600 of the wild-type strain) × 100.
Roles of Znu, ZupT, and Sit metal transport systems for zinc transport.
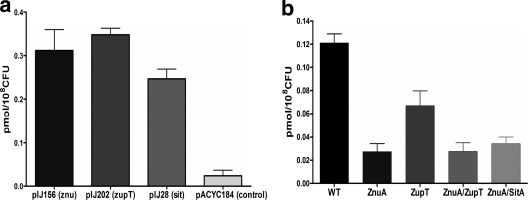
We investigated the capacity of the Znu, ZupT, and Sit systems to transport zinc by comparing 65Zn2+ uptake in the E. coli K-12 Δznu ΔzupT strain QT1435, complemented with plasmids encoding the Znu or ZupT transporters and in mutants of UPEC strain CFT073 (Fig. 3). Strain QT1435 complemented with the vector control demonstrated only a background level of 65Zn2+ uptake. In contrast, complementation with plasmids encoding either Znu (pIJ156), or ZupT (pIJ202) systems conferred increased uptake of 65Zn2+. Further, introduction of sit genes (pIJ28 plasmid) increased 65Zn2+ accumulation, albeit at lower levels than the Znu- or ZupT-encoding plasmids (Fig. 3a). In uptake studies with UPEC strain CFT073 and mutant derivatives, loss of the Znu system resulted in the greatest decrease in 65Zn2+ accumulation. The decrease in 65Zn2+ uptake observed was similar for the Δznu (QT1434), Δznu ΔzupT (QT1555) and Δznu ΔsitABCD (QT1640) strains, whereas loss of the ZupT system had a less marked effect on 65Zn2+ uptake (Fig. 3b). These results indicate that, despite its ability to acquire 65Zn2+ when expressed from a medium-copy-number plasmid (pIJ202), ZupT is a less efficient zinc transporter than the ZnuACB transporter when expressed at wild-type levels in UPEC strain CFT073. Finally, the loss of sit in the znu mutant strain did not result in a cumulative reduction in 65Zn2+ acquisition, suggesting that despite its ability to accumulate 65Zn2+ when expressed from a medium-copy-number plasmid (pIJ28), SitABCD does not contribute significantly to zinc acquisition by UPEC strain CFT073.
FIG. 3.
Uptake of 65Zn2+ by E. coli K-12 Δznu ΔzupT mutant QT1435 containing plasmid-encoded metal transporters or the control vector (a) or UPEC strain CFT073 and mutant derivatives (b). WT, wild-type CFT073; ZnuA, Δznu strain QT1434; ZupT, ΔzupT strain QT1554; ZnuA/ZupT, Δznu ΔzupT strain QT1555; ZnuA/SitA, Δznu ΔsitABCD strain QT1640.
Contribution of the Znu and ZupT transporters in the murine UTI model.
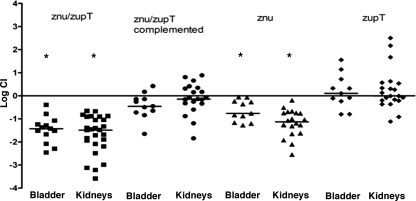
UPEC strain CFT073 zinc transporter mutants were tested in a murine coinfection model using virulent ΔlacZYA CFT073 strain QT1081 as the competitor strain (Fig. 4). In this infection model, bacterial numbers of the ΔzupT mutant in the bladders and kidneys were similar to the virulent competitor strain, indicating that zupT alone does not contribute significantly to colonization and survival during UTI. The Δznu mutant strain QT1434 was significantly attenuated and, compared to the virulent competitor strain, demonstrated a mean 4.4-fold reduction in bladders (P = 0.0005) and a mean 44-fold reduction in kidneys (P < 0.0001). Further, the Δznu ΔzupT strain (QT1555) was even more attenuated and demonstrated a mean 30-fold decrease in bladders (P = 0.0001) and a mean 48-fold decrease in kidneys (P < 0.0001). Reintroduction of the znuACB genes into the Δznu ΔzupT strain, QT1932, resulted in complementation as demonstrated by a significant increase of the CI in the bladder (P = 0.001) and a complete regain in the kidneys (P < 0.0001) compared to the attenuated Δznu ΔzupT mutant QT1555.
FIG. 4.
Comparative colonization of bladders and kidneys of CBA/J mice coinfected with UPEC CFT073 derivatives defective in zinc transporter systems and virulent CFT073 Δlac derivative strain QT1081. A competitive coinfection model was used in which a mixture of QT1081 and different metal transporter mutants were inoculated simultaneously. At 48 h postinfection, tissues were sampled, and results are presented as the log10 CI. The CI represents the ratio of numbers of the two test strains (mutant/Δlac virulent strain QT1081) from the tissues sampled (the output ratio) normalized for the initial numbers of each strain in the inoculum (input). Negative CI values indicate a decreased capacity for the mutant to compete with the virulent test strain QT1081. Horizontal bars indicate the median log10 CI values. Each data point represents a sample from an individual mouse. Both kidneys were sampled separately. Strains tested: strain QT1434 (Δznu), strain QT1554 (ΔzupT), strain QT1555 (Δznu ΔzupT), and strain QT1932, the Δznu ΔzupT mutant complemented with znaACB. Statistically significant decreases in CI values are indicated by asterisks (*, P < 0.001) as determined by the Wilcoxon matched-pair test.
In the single-strain infection model, the Δznu and Δznu ΔzupT mutant strains showed a significant decrease in bacterial numbers in the kidneys (P = 0.0012 and P < 0.0001, respectively) but were present in the bladder at levels similar to the virulent CFT073 Δlac strain (Fig. 5). Thus, taken together, these results indicate that zinc transport systems impart a competitive advantage to ExPEC strain CFT073 during UTI in the murine model and that the ZnuACB system plays a predominant role, whereas ZupT appears to be a zinc transporter of secondary importance.
FIG. 5.
Colonization of bladders and kidneys of CBA/J mice infected with virulent UPEC CFT073 derivative strain QT1081 (Δlac) and transport mutant CFT073 derivatives in the single-strain infection model. The data are presented as the log CFU/gram of tissue. Each data point represents a tissue sample from an individual infected mouse 48 h postinfection. Both kidneys were sampled separately. Strains tested were the CFT073 ΔlacZYA strain QT1081 (Δlac), the QT1434 Δznu strain (Δznu), and the QT1555 Δznu ΔzupT strain (Δznu ΔzupT). Horizontal bars represent the median values of each group. Samples that were significantly decreased compared to the virulent Δlac strain are indicated with asterisks (*, P < 0.005). P values of comparative differences were determined by the Mann-Whitney test.
Since the zinc transporter mutants demonstrated a growth defect in zinc-limited medium (Fig. 1 and 2), we investigated whether the UPEC zinc transport mutants were less able to grow in human urine. Loss of either or both of the Znu and ZupT systems in strain CFT073 did not effect growth of the strains in human urine (data not shown). Moreover, we performed competition assays between the zinc transport-deficient mutants and the CFT073 Δlac derivative in human urine in vitro. During competitive growth in human urine, the zinc transport mutants remained at levels similar to the CFT073 Δlac derivative, and after 24 h the CI values were 0. 92 for the Δznu (QT1434) strain and 0.78 for the Δznu ΔzupT (QT1555) strain. These results suggest that the levels of zinc present in urine from healthy individuals were adequate for growth of the strains in vitro.
Zinc transporters contribute to resistance to H2O2.
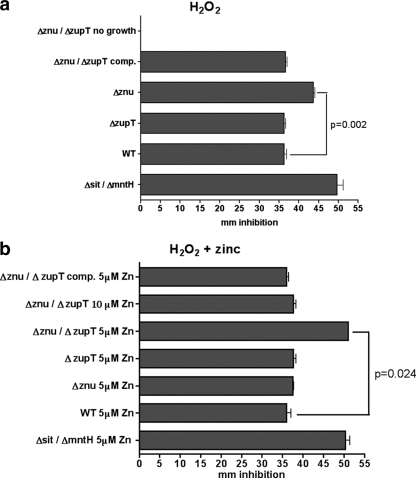
Since other metal transporters contribute to bacterial resistance to oxidative stress mediated by exogenous H2O2 (10, 47), we assessed whether the loss of zinc transporters increased susceptibility of strain CFT073 to H2O2 (Fig. 6). The Δznu mutant strain (QT1434) was more sensitive to H2O2, whereas the ΔzupT strain QT1554 was as resistant as the wild-type strain (Fig. 6a). Without zinc supplementation, the Δznu ΔzupT strain (QT1555) was unable to grow on M9-glucose plates. However, when QT1555 was complemented with the znuACB genes (strain QT1932), both growth and resistance to H2O2 were restored (Fig. 6a). Supplementation with 5 μM zinc restored the growth of all strains and was sufficient to restore resistance of the Δznu strain QT1434 (Fig. 6b). In contrast, although the Δznu ΔzupT strain (QT1555) regained the capacity to grow when supplemented with 5 μM zinc, it was even more sensitive to H2O2 than the Δznu strain QT1434 without zinc supplementation. However, supplementation with 10 μM Zn2+ resulted in a regain in resistance of strain QT1555 to H2O2 (Fig. 6b). Supplementation with zinc had no effect on the resistance of the wild-type strain or the H2O2-sensitive Δsit ΔmntH control strain, which is defective for the transport of manganese. Therefore, supplementation with zinc alone did not have a nonspecific effect of increased resistance to H2O2.
FIG. 6.
Sensitivity to H2O2. UPEC strain CFT073 and derivatives were seeded onto M9-glucose agar plates without zinc supplementation (a) or with zinc supplementation (b) and subjected to H2O2 placed on sterile filter disks. Differences in resistance were assessed from the diameter of the inhibition zone of a culture after overnight growth. Samples were done in triplicate, and bars represent the means ± the standard deviation. Strains used were wild-type CFT073 (WT), strain QT1434 (Δznu), strain QT1554 (ΔzupT), strain QT1555 (Δznu ΔzupT), and the QT1555 znuACB-complemented strain, QT1932. Avian pathogenic E. coli strain QT1239 (ΔsitABCD ΔmntH), which is sensitive to H2O2, was used as an internal control. Significant differences between the WT parent and isogenic zinc transporter mutants are indicated by P values to the right of the figures.
Zinc transport mutants demonstrate decreased motility.
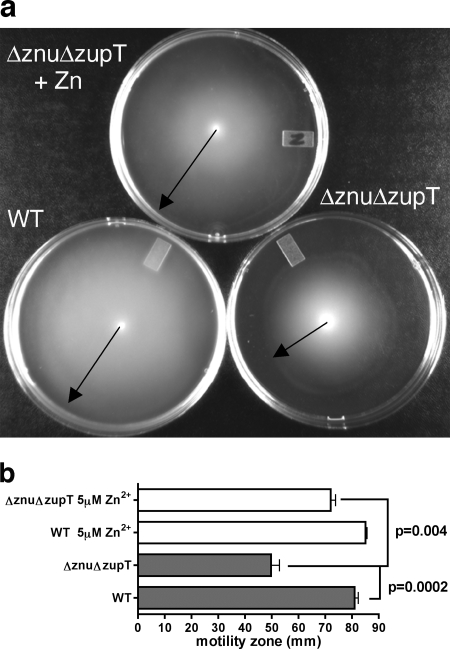
Because genes required for the production of flagella and motility are affected by zinc availability (34, 49) and since motility contributes to colonization and persistence in the urinary tract (32), we investigated whether the loss of zinc transporters affected motility. No difference in motility was observed for the Δznu or ΔzupT mutants. However, the Δznu ΔzupT strain QT1555 was less motile than the UPEC strain CFT073. The motility of this mutant was partially restored by supplementation with zinc (Fig. 7), and the znu complemented mutant strain QT1932 regained motility to wild-type levels.
FIG. 7.
Loss of zinc transporters affects the swimming motility. Uropathogenic strain CFT073 and derivatives were tested after 18 h growth at 37°C on tryptone motility agar plates (44). (a) Image showing motility distances of the Δznu ΔzupT strain QT1555 (znu/zupT) with or without 5 μM Zn2+ supplementation compared to the CFT073 wild-type strain (WT). (b) Bar graph indicating distances of motility zones. Statistically different motility between the WT parent and isogenic QT1555 (Δznu ΔzupT) strain or QΤ1555 with or without Zn2+ are indicated by P values to the right of the figure. Other mutants—strain QT1434 (Δznu), strain QT1554 (ΔzupT), and the QT1555 znuACB-complemented strain, QT1932—were as motile as the WT parent with or without zinc supplementation (data not shown).
DISCUSSION
In the present study, we determined the roles of the Znu and ZupT zinc transporters for growth and 65Zn2+ uptake by E. coli K-12 and UPEC strain CFT073, and the contribution of these transporters to UTI by strain CFT073 in mice. Our results indicate that the Znu and ZupT transporters are required for growth in medium where zinc is limited. Zn2+ rescued the growth of the zinc transporter-deficient E. coli strains in minimal medium, while Mn2+ and Fe2+ failed to do so, indicating that zinc deficiency in the absence of these transporters was a limiting factor for growth (Fig. 1 and 2).
When expressed from a medium-copy plasmid, znuACB or zupT genes complemented the growth defect of a Δznu ΔzupT E. coli K-12 mutant strain, whereas the SitABCD transporter only provided a slight gain in growth (Fig. 1). The ZnuACB transporter was shown to be the predominant Zn transporter in UPEC strain CFT073 in growth and uptake assays, and in a Δznu background a cumulative loss of zupT or sitABCD did not reduce 65Zn2+ uptake any further (Fig. 3). ZnuACB belongs to the same family of transporters as SitABCD, the C9 cluster of ABC manganese and zinc permeases (15), whereas ZupT belongs to the ZRT IRT-like proteins (ZIP) family of transporters (25). While ZnuACB uses ATP hydrolysis for transport, ZupT is thought to require a chemo-osmotic gradient. ZnuACB functions as a Zn2+-specific transporter, whereas ZupT has also been shown to mediate the uptake of Mn2+ and Fe2+ (24, 57). The transport specificity and higher affinity of ZnuACB could explain why the loss of ZnuACB had greater impact on the growth of CFT073 than loss of the ZupT transporter. The higher Zn2+ affinity of ZnuACB is probably due to the ZnuA periplasmic ligand binding protein, which contains a metal-binding histidine-rich loop protruding from the vicinity of the protein in addition to the high-affinity Zn2+-binding pocket located inside the protein (13, 57).
The ExPEC-associated SitABCD transporter was suspected to be a possible zinc transporter, since SitA is a member of the cluster 9 transition metal transporters, such as TroA, which has been shown to efficiently bind zinc and other metals such as manganese and iron (19). As well, uptake of Fe2+ and Mn2+ by the Salmonella Sit and of Fe2+ by the orthologous Yersinia Yfe transporter was inhibited by Zn2+ at micromolar concentrations (8, 29). Indeed, when expressed from a medium-copy plasmid, SitABCD partially restored growth and also increased accumulation of 65Zn2+ in a Δznu ΔzupT K-12 strain. However, SitABCD-mediated 65Zn2+ accumulation did not correlate with an increase in growth in minimal media. It is therefore likely that SitA can bind Zn2+ in the periplasm resulting in zinc accumulation, although this binding results in little or no Zn2+ uptake into the cytoplasm. Since sitABCD only provided a marginal growth increase to the CFT073 Δznu ΔzupT strain in growth assays (Fig. 2), and since the CFT073 Δznu ΔzupT mutant was no more able to grow on minimal plates than the E. coli K-12 Δznu ΔzupT mutant, these results suggest that Sit is unable to compensate for the transport of Zn2+ in the absence of the Znu and ZupT systems. Hence, Znu and ZupT appear to be the only transporters that can provide sufficient Zn2+ uptake for the growth of either E. coli K-12 strain MG1655 or UPEC strain CFT073.
Our results demonstrate the importance of zinc transporters for UPEC strain CFT073 during UTI (Fig. 4 and 5). Loss of the Znu transporter attenuated UPEC strain CFT073. Loss of both the Znu and the ZupT systems further decreased bacterial numbers in the urinary tract in the murine coinfection challenge and in the kidneys in the single-strain infection model. It is interesting that in the single-strain infection model, Zn transport mutants were only significantly reduced in kidneys and not in bladders. These results suggest that colonization of, access to, and/or survival in the kidneys is affected in the Zn transport mutants. Known factors that contribute to enhanced colonization of the kidneys include P fimbriae, which mediate mannose-resistant hemagglutination, and increased tissue tropism for the kidneys (28, 33, 41). However, since mannose-resistant hemagglutination titers of the wild-type CFT073 and Zn transport mutants were similar after growth in different conditions, including urine, as well as liquid and solid culture media, it is unlikely that decreased bacterial numbers in the kidney in the Zn transport mutants are due to decreased production of P fimbriae. Decreased bacterial numbers in the kidneys compared to the bladder may be due to increased sensitivity of these strains to oxidative stress. Compared to the bladder, the kidneys may represent a tissue with a higher level of oxidative stress due to increased infiltration of inflammatory mediators and immune cells, as well as oxygen from the circulatory system. In addition, decreased swimming motility in Zn transport mutants could also reduce access to the distal renal tissues of the urinary tract.
The UPEC zinc transport mutants grew well in human urine, which is considered to be a relatively zinc-replete environment, since urinary zinc losses amount to an average of 9 μM/day in healthy subjects and vary little when a diet is zinc balanced (31). However, despite the apparently adequate availability of zinc in urine in healthy individuals, zinc availability after infection may be dramatically altered following infection in both extracellular and intracellular host environments (3, 38, 45). A recent study on zinc transport-related virulence phenotypes of S. enterica demonstrated that ZnuACB is expressed in intracellular environments, which strongly suggests that Zn2+ availability is limited within such cells (3). UPEC strains have been shown to form intracellular bacterial communities in bladder epithelial cells (4), whereas intracellular zinc has been shown to be bound to metallothioneins and transported to specific cellular vacuoles for storage (37, 48). Thus, zinc could be limited during intracellular-bacterial-community formation. ExPEC also cause septicemia, and in plasma zinc is mainly bound to albumin and to a lesser extent to α2-macroglobulin (22). Zinc also could be bound by other immune-induced proteins such as calprotectin released by neutrophils during response to bacterial infection (16, 38). Thus, overall, during UTI as with other extraintestinal infections, zinc availability may be reduced, and bacterial zinc transporters may therefore contribute to increased fitness for colonization of host tissues or cells.
Zinc is second only to iron in abundance inside E. coli cells and is the only metal that is a cofactor for enzymes belonging to six different major functional groups (6). Although decreased zinc availability could potentially result in decreased activity of many bacterial enzymes implicated in cellular metabolism, physiology, and growth, we have specifically identified two phenotypes that could contribute to urinary tract virulence that were impaired in the zinc transport mutants: sensitivity to oxidative stress and decreased motility.
The implication of zinc transporters in oxidative stress resistance is a new finding which will require further investigation. Zinc protects against iron-triggered membrane lipid oxidation (30, 58), which may partially explain why Znu- and ZupT-mediated zinc transport may provide resistance to oxidative stress. One explanation for increased sensitivity to hydrogen peroxide may be due to lowered activity or decreased expression of the E. coli SodC, Zn/Cu superoxide dismutase. In E. coli SodC has been shown to contribute to increased resistance to H2O2 (23, 30), and zinc ions have been shown to be required for stable binding of copper to the SodC catalytic site (2). In S. enterica serovar Typhimurium, Ammendola et al. (2) recently reported that zinc limitation and the loss of ZnuA resulted in a decreased level of expression of SodCII, which is the Salmonella ortholog of E. coli SodC. Hence, increased zinc availability through zinc transporters, particularly the Znu transporter, may provide an important signal for increased SodC expression that may protect against oxidative stress.
Another possible explanation of a role for Zn transport in resistance to oxidative stress is suggested by the fact that the global iron uptake repressor Fur is a zinc metalloprotein (1, 18). Fur expression is under the control of the global oxidative stress resistance regulators OxyR and SoxS; Fur is directly implicated in oxidative stress, and its inactivation results in increased oxidative damage to the cell through the iron-dependent Fenton chemistry reactions (51, 52). In addition, in E. coli K-12 znu genes have been shown to be induced under iron repletion and repressed under iron depletion (44). Under iron repletion, bacterial cells require the Fur regulator to control iron homeostasis and reduce iron overload and oxidative stress. Therefore, reduced Zn2+ uptake may possibly compromise Fur function and lead to increased susceptibility to oxidative stress.
Loss of both the Znu and ZupT transporters was required to reduce the motility of UPEC strain CFT073, and this decrease in motility was Zn dependent. FlhC, a subunit of the FlhCD transcriptional regulator of flagellar genes, is a zinc metalloprotein (53), and expression of flagellar genes has been shown to decrease under conditions of zinc restriction (49). The importance of motility for the competitive fitness and establishment of UTI by UPEC strain CFT073 and particularly colonization of the kidneys has been established previously (32, 55). In the present study, using both coinfection and single-strain infection models, colonization of the kidneys was shown to be reduced in the zinc transport deficient strains, which could at least in part be due to a decrease in motility.
Taken together, our overall findings establish that in E. coli Znu plays a predominant role in zinc transport and UTI and that ZupT plays a secondary role. Future investigations will be important to establish the specific mechanisms by which loss of these transporters compromise ExPEC fitness and physiology during extraintestinal infections.
Acknowledgments
Funding for this project was provided to C.M.D. by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the Canada Research Chairs program. M.S. was the recipient of a scholarship from the Fondation Armand-Frappier.
Editor: B. A. McCormick
Footnotes
Published ahead of print on 22 December 2008.
REFERENCES
- 1.Althaus, E. W., C. E. Outten, K. E. Olson, H. Cao, and T. V. O'Halloran. 1999. The ferric uptake regulation (Fur) repressor is a zinc metalloprotein. Biochemistry 386559-6569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ammendola, S., P. Pasquali, F. Pacello, G. Rotilio, M. Castor, S. J. Libby, N. Figueroa-Bossi, L. Bossi, F. C. Fang, and A. Battistoni. 2008. Regulatory and structural differences in the Cu,Zn-superoxide dismutases of Salmonella enterica and their significance for virulence. J. Biol. Chem. 28313688-13699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ammendola, S., P. Pasquali, C. Pistoia, P. Petrucci, P. Petrarca, G. Rotilio, and A. Battistoni. 2007. High-affinity Zn2+ uptake system ZnuABC is required for bacterial zinc homeostasis in intracellular environments and contributes to the virulence of Salmonella enterica. Infect. Immun. 755867-5876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Anderson, G. G., S. M. Martin, and S. J. Hultgren. 2004. Host subversion by formation of intracellular bacterial communities in the urinary tract. Microbes Infect. 61094-1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Andreini, C., L. Banci, I. Bertini, and A. Rosato. 2006. Zinc through the three domains of life. J. Proteome Res. 53173-3178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Auld, D. S. 2001. Zinc coordination sphere in biochemical zinc sites. Biometals 14271-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Baba, T., T. Ara, M. Hasegawa, Y. Takai, Y. Okumura, M. Baba, K. A. Datsenko, M. Tomita, B. L. Wanner, and H. Mori. 2006. Construction of Escherichia coli K-12 in-frame, single-gene knockout mutants: the Keio collection. Mol. Syst. Biol. 22006 0008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bearden, S. W., and R. D. Perry. 1999. The Yfe system of Yersinia pestis transports iron and manganese and is required for full virulence of plague. Mol. Microbiol. 32403-414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Blattner, F. R., G. Plunkett III, C. A. Bloch, N. T. Perna, V. Burland, M. Riley, J. Collado-Vides, J. D. Glasner, C. K. Rode, G. F. Mayhew, J. Gregor, N. W. Davis, H. A. Kirkpatrick, M. A. Goeden, D. J. Rose, B. Mau, and Y. Shao. 1997. The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science 2771453-1474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Boyer, E., I. Bergevin, D. Malo, P. Gros, and M. F. Cellier. 2002. Acquisition of Mn(II) in addition to Fe(II) is required for full virulence of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Infect. Immun. 706032-6042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Brzuszkiewicz, E., H. Bruggemann, H. Liesegang, M. Emmerth, T. Olschlager, G. Nagy, K. Albermann, C. Wagner, C. Buchrieser, L. Emody, G. Gottschalk, J. Hacker, and U. Dobrindt. 2006. How to become a uropathogen: comparative genomic analysis of extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli strains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 10312879-12884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Campoy, S., M. Jara, N. Busquets, A. M. Perez De Rozas, I. Badiola, and J. Barbe. 2002. Role of the high-affinity zinc uptake znuABC system in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium virulence. Infect. Immun. 704721-4725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chandra, B. R., M. Yogavel, and A. Sharma. 2007. Structural analysis of ABC-family periplasmic zinc binding protein provides new insights into mechanism of ligand uptake and release. J. Mol. Biol. 367970-982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chang, A. C., and S. N. Cohen. 1978. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J. Bacteriol. 1341141-1156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Claverys, J. P. 2001. A new family of high-affinity ABC manganese and zinc permeases. Res. Microbiol. 152231-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Corbin, B. D., E. H. Seeley, A. Raab, J. Feldmann, M. R. Miller, V. J. Torres, K. L. Anderson, B. M. Dattilo, P. M. Dunman, R. Gerads, R. M. Caprioli, W. Nacken, W. J. Chazin, and E. P. Skaar. 2008. Metal chelation and inhibition of bacterial growth in tissue abscesses. Science 319962-965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Datsenko, K. A., and B. L. Wanner. 2000. One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 976640-6645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.D'Autreaux, B., L. Pecqueur, A. Gonzalez de Peredo, R. E. Diederix, C. Caux-Thang, L. Tabet, B. Bersch, E. Forest, and I. Michaud-Soret. 2007. Reversible redox- and zinc-dependent dimerization of the Escherichia coli fur protein. Biochemistry 461329-1342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Desrosiers, D. C., Y. C. Sun, A. A. Zaidi, C. H. Eggers, D. L. Cox, and J. D. Radolf. 2007. The general transition metal (Tro) and Zn2+ (Znu) transporters in Treponema pallidum: analysis of metal specificities and expression profiles. Mol. Microbiol. 65137-152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Dozois, C. M., F. Daigle, and R. Curtiss III. 2003. Identification of pathogen-specific and conserved genes expressed in vivo by an avian pathogenic Escherichia coli strain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100247-252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Fischbach, M. A., H. Lin, L. Zhou, Y. Yu, R. J. Abergel, D. R. Liu, K. N. Raymond, B. L. Wanner, R. K. Strong, C. T. Walsh, A. Aderem, and K. D. Smith. 2006. The pathogen-associated iroA gene cluster mediates bacterial evasion of lipocalin 2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 10316502-16507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Folin, M., E. Contiero, and G. M. Vaselli. 1994. Zinc content of normal human serum and its correlation with some hematic parameters. Biometals 775-79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Gort, A. S., D. M. Ferber, and J. A. Imlay. 1999. The regulation and role of the periplasmic copper, zinc superoxide dismutase of Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 32179-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Grass, G., S. Franke, N. Taudte, D. H. Nies, L. M. Kucharski, M. E. Maguire, and C. Rensing. 2005. The metal permease ZupT from Escherichia coli is a transporter with a broad substrate spectrum. J. Bacteriol. 1871604-1611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Grass, G., M. D. Wong, B. P. Rosen, R. L. Smith, and C. Rensing. 2002. ZupT is a Zn(II) uptake system in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 184864-866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hancock, V., L. Ferrieres, and P. Klemm. 2008. The ferric yersiniabactin uptake receptor FyuA is required for efficient biofilm formation by urinary tract infectious Escherichia coli in human urine. Microbiology 154167-175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hantke, K. 2005. Bacterial zinc uptake and regulators. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 8196-202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kaper, J. B., J. P. Nataro, and H. L. Mobley. 2004. Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2123-140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kehres, D. G., A. Janakiraman, J. M. Slauch, and M. E. Maguire. 2002. SitABCD is the alkaline Mn2+ transporter of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 1843159-3166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kim, Y. H., Y. Lee, S. Kim, J. Yeom, S. Yeom, B. Seok Kim, S. Oh, S. Park, C. O. Jeon, and W. Park. 2006. The role of periplasmic antioxidant enzymes (superoxide dismutase and thiol peroxidase) of the Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O157:H7 in the formation of biofilms. Proteomics 66181-6193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.King, J. C., D. M. Shames, and L. R. Woodhouse. 2000. Zinc homeostasis in humans. J. Nutr. 1301360S-1366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lane, M. C., V. Lockatell, G. Monterosso, D. Lamphier, J. Weinert, J. R. Hebel, D. E. Johnson, and H. L. Mobley. 2005. Role of motility in the colonization of uropathogenic Escherichia coli in the urinary tract. Infect. Immun. 737644-7656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Le Bouguenec, C. 2005. Adhesins and invasins of pathogenic Escherichia coli. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 295471-478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lee, L. J., J. A. Barrett, and R. K. Poole. 2005. Genome-wide transcriptional response of chemostat-cultured Escherichia coli to zinc. J. Bacteriol. 1871124-1134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lewis, D. A., J. Klesney-Tait, S. R. Lumbley, C. K. Ward, J. L. Latimer, C. A. Ison, and E. J. Hansen. 1999. Identification of the znuA-encoded periplasmic zinc transport protein of Haemophilus ducreyi. Infect. Immun. 675060-5068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Linton, K. J. 2007. Structure and function of ABC transporters. Physiology 22122-130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Liuzzi, J. P., and R. J. Cousins. 2004. Mammalian zinc transporters. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 24151-172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Liuzzi, J. P., L. A. Lichten, S. Rivera, R. K. Blanchard, T. B. Aydemir, M. D. Knutson, T. Ganz, and R. J. Cousins. 2005. Interleukin-6 regulates the zinc transporter Zip14 in liver and contributes to the hypozincemia of the acute-phase response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1026843-6848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lusitani, D., S. E. Malawista, and R. R. Montgomery. 2003. Calprotectin, an abundant cytosolic protein from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes, inhibits the growth of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect. Immun. 714711-4716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lymberopoulos, M. H., S. Houle, F. Daigle, S. Leveille, A. Bree, M. Moulin-Schouleur, J. R. Johnson, and C. M. Dozois. 2006. Characterization of Stg fimbriae from an avian pathogenic Escherichia coli O78:K80 strain and assessment of their contribution to colonization of the chicken respiratory tract. J. Bacteriol. 1886449-6459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Marrs, C. F., L. Zhang, and B. Foxman. 2005. Escherichia coli mediated urinary tract infections: are there distinct uropathogenic E. coli (UPEC) pathotypes? FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 252183-190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Miller, V. L., and J. J. Mekalanos. 1988. A novel suicide vector and its use in construction of insertion mutations: osmoregulation of outer membrane proteins and virulence determinants in Vibrio cholerae requires toxR. J. Bacteriol. 1702575-2583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Mobley, H. L., D. M. Green, A. L. Trifillis, D. E. Johnson, G. R. Chippendale, C. V. Lockatell, B. D. Jones, and J. W. Warren. 1990. Pyelonephritogenic Escherichia coli and killing of cultured human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells: role of hemolysin in some strains. Infect. Immun. 581281-1289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Patzer, S. I., and K. Hantke. 1998. The ZnuABC high-affinity zinc uptake system and its regulator Zur in Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 281199-1210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Rink, L., and H. Haase. 2007. Zinc homeostasis and immunity. Trends Immunol. 281-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Sabri, M., M. Caza, J. Proulx, M. H. Lymberopoulos, A. Bree, M. Moulin-Schouleur, R. Curtiss III, and C. M. Dozois. 2008. Contribution of the SitABCD, MntH, and FeoB metal transporters to the virulence of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli O78 strain χ7122. Infect. Immun. 76601-611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Sabri, M., S. Leveille, and C. M. Dozois. 2006. A SitABCD homologue from an avian pathogenic Escherichia coli strain mediates transport of iron and manganese and resistance to hydrogen peroxide. Microbiology 152745-758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Sekler, I., S. L. Sensi, M. Hershfinkel, and W. F. Silverman. 2007. Mechanism and regulation of cellular zinc transport. Mol. Med. 13337-343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Sigdel, T. K., J. A. Easton, and M. W. Crowder. 2006. Transcriptional response of Escherichia coli to TPEN. J. Bacteriol. 1886709-6713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sohnle, P. G., M. J. Hunter, B. Hahn, and W. J. Chazin. 2000. Zinc-reversible antimicrobial activity of recombinant calprotectin (migration inhibitory factor-related proteins 8 and 14). J. Infect. Dis. 1821272-1275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Storz, G., and J. A. Imlay. 1999. Oxidative stress. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2188-194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Touati, D., M. Jacques, B. Tardat, L. Bouchard, and S. Despied. 1995. Lethal oxidative damage and mutagenesis are generated by iron in delta fur mutants of Escherichia coli: protective role of superoxide dismutase. J. Bacteriol. 1772305-2314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Wang, S., R. T. Fleming, E. M. Westbrook, P. Matsumura, and D. B. McKay. 2006. Structure of the Escherichia coli FlhDC complex, a prokaryotic heteromeric regulator of transcription. J. Mol. Biol. 355798-808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Welch, R. A., V. Burland, G. Plunkett III, P. Redford, P. Roesch, D. Rasko, E. L. Buckles, S. R. Liou, A. Boutin, J. Hackett, D. Stroud, G. F. Mayhew, D. J. Rose, S. Zhou, D. C. Schwartz, N. T. Perna, H. L. Mobley, M. S. Donnenberg, and F. R. Blattner. 2002. Extensive mosaic structure revealed by the complete genome sequence of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 9917020-17024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Wright, K. J., P. C. Seed, and S. J. Hultgren. 2005. Uropathogenic Escherichia coli flagella aid in efficient urinary tract colonization. Infect. Immun. 737657-7668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Yang, X., T. Becker, N. Walters, and D. W. Pascual. 2006. Deletion of znuA virulence factor attenuates Brucella abortus and confers protection against wild-type challenge. Infect. Immun. 743874-3879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Yatsunyk, L. A., J. A. Easton, L. R. Kim, S. A. Sugarbaker, B. Bennett, R. M. Breece, I. I. Vorontsov, D. L. Tierney, M. W. Crowder, and A. C. Rosenzweig. 2008. Structure and metal binding properties of ZnuA, a periplasmic zinc transporter from Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 13271-288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Zago, M. P., and P. I. Oteiza. 2001. The antioxidant properties of zinc: interactions with iron and antioxidants. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 31266-274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]