Abstract
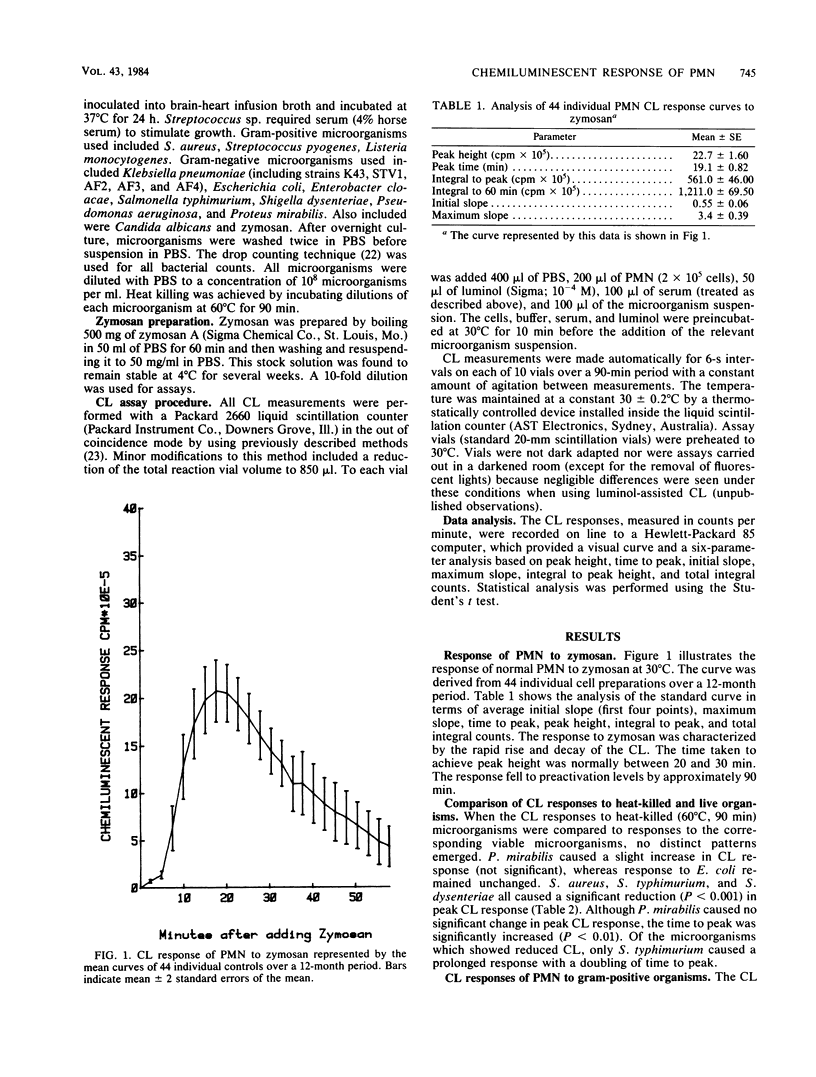
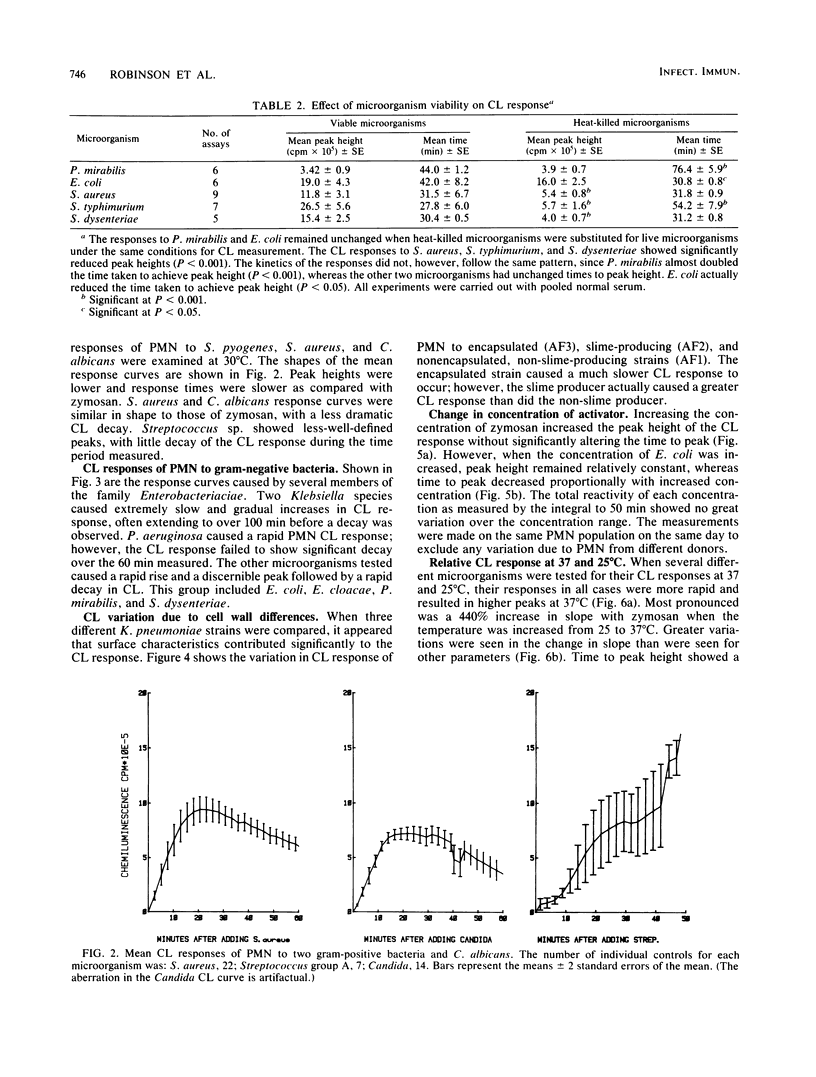
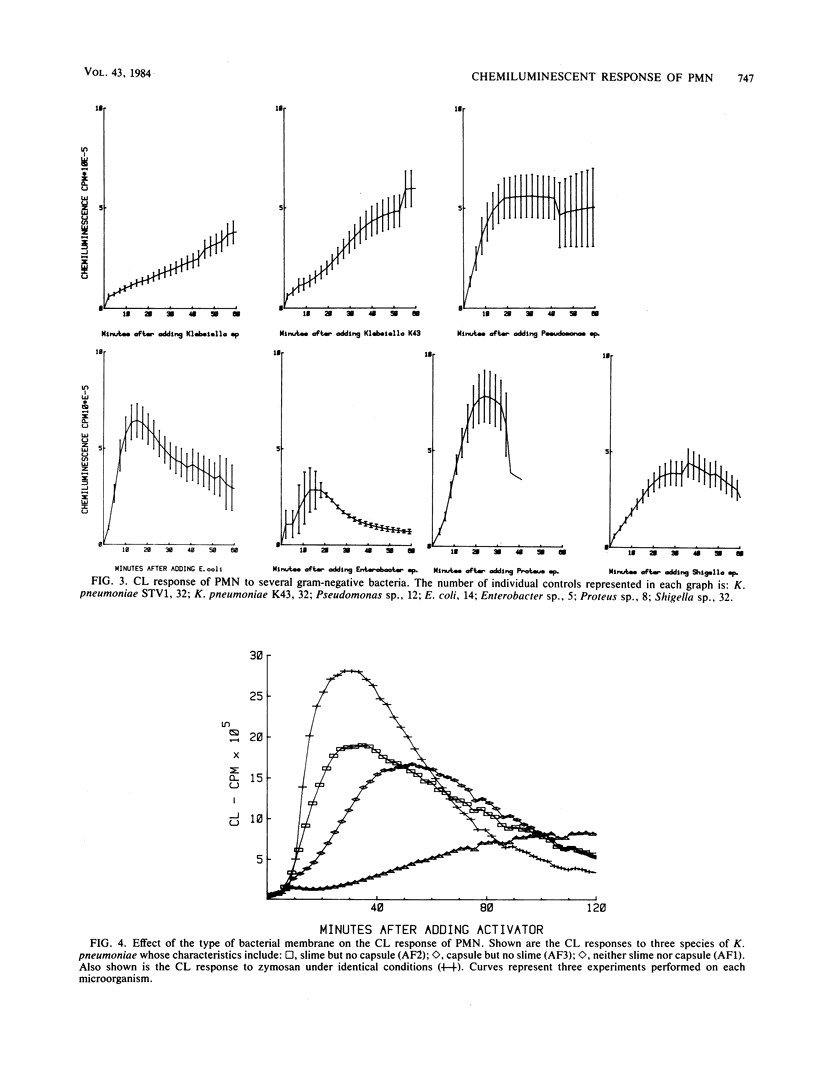
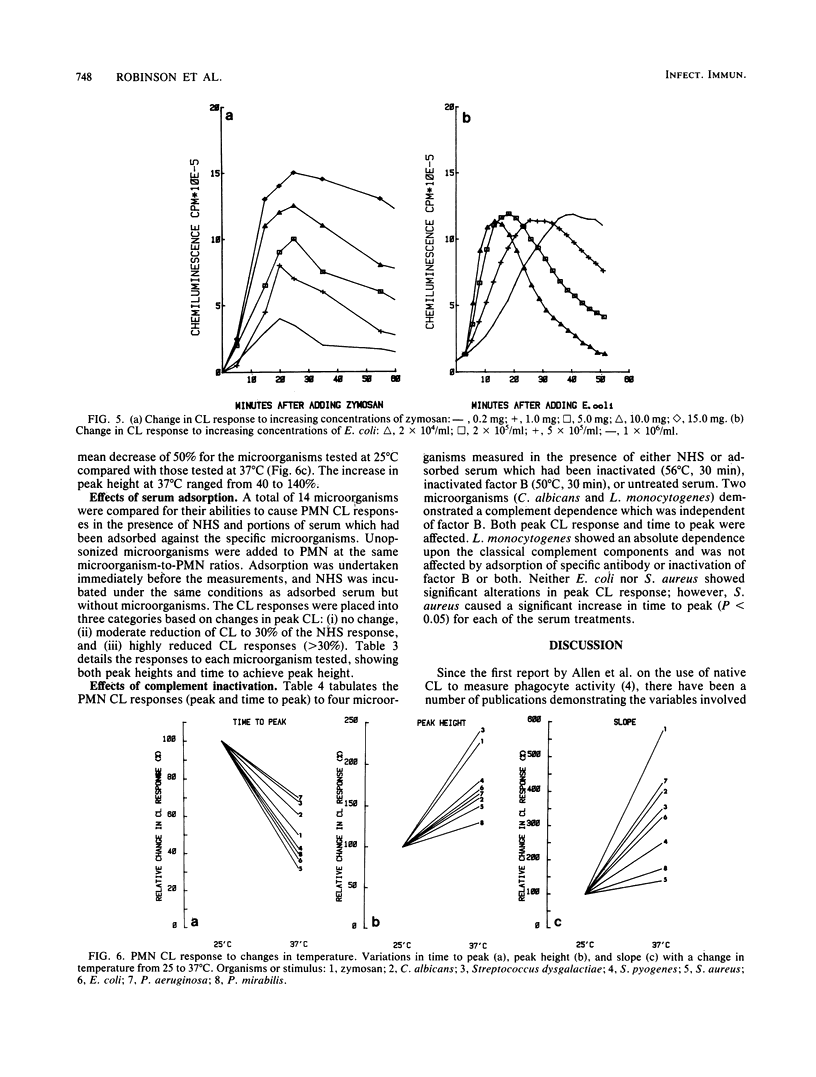
Chemiluminescence (CL) is a sensitive indicator of phagocytosis and intracellular killing; however, little is known of the normal CL response by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes to different pathogenic microorganisms. We investigated the luminol-enhanced CL response of normal polymorphonuclear leukocytes to a number of common bacterial pathogens and two yeasts. We analyzed the CL response to viable and heat-killed microorganisms at 25 and 37 degrees C. The CL response to all microorganisms was greater and more rapid at 37 degrees C. Variable responses were observed with viable and heat-killed microorganisms; some were unaffected, whereas other demonstrated reduced CL. Each microorganism caused a reproducible response pattern, which could be placed into two general categories. In the first category were those which caused a rapid exponential rise and decay in CL: Enterobacter cloacae, Salmonella typhimurium, Shigella flexneri, Staphylococcus aureus, Candida albicans, and zymosan. In the second category were those which rose slowly over a longer time course to a poorly defined peak: Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, and Streptococcus pyogenes. The CL response also reflected serum opsonic activity. The effect of inactivated complement, factor B, and removal of specific antibody were investigated. Increasing the concentration of zymosan gave a proportional rise in peak CL; however, a strain of E. coli caused a variation in peak time rather than peak height. Different CL kinetics were shown for three strains of K. pneumoniae, possibly a result of each having different membrane or cell wall characteristics. This study defines the nature and factors affecting the normal CL response to a variety of common pathogenic microorganisms.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. C. Evaluation of serum opsonic capacity by quantitating the initial chemiluminescent response from phagocytizing polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):828–833. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.828-833.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. C., Loose L. D. Phagocytic activation of a luminol-dependent chemiluminescence in rabbit alveolar and peritoneal macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Mar 8;69(1):245–252. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80299-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. C., Loose L. D. Phagocytic activation of a luminol-dependent chemiluminescence in rabbit alveolar and peritoneal macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Mar 8;69(1):245–252. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80299-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. C. Reduced, radical, and excited state oxygen in leukocyte microbicidal activity. Front Biol. 1979;48:197–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M., Kipnes R. S., Curnutte J. T. Biological defense mechanisms. The production by leukocytes of superoxide, a potential bactericidal agent. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):741–744. doi: 10.1172/JCI107236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M. Oxygen-dependent microbial killing by phagocytes (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 30;298(13):721–725. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803302981305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Allred C. D., Solberg C. O., Hill H. R. Chemiluminescence by polymorphonuclear leukocytes from patients with active bacterial infection. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jan;141(1):14–26. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.1.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeChatelet L. R., Long G. D., Shirley P. S., Bass D. A., Thomas M. J., Henderson F. W., Cohen M. S. Mechanism of the luminol-dependent chemiluminescence of human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1589–1593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeChatelet L. R., Shirley P. S. Chemiluminescence of human neutrophils induced by soluble stimuli: effect of divalent cations. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):206–212. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.206-212.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faden H., Maciejewski N. Whole blood luminol-dependent chemiluminescence. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1981 Sep;30(3):219–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Quie P. G. Influence of the alternate complement pathway in opsonization of several bacterial species. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):402–404. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.402-404.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glette J., Solberg C. O., Lehmann V. Factors influencing human polymorphonuclear leukocyte chemiluminescence. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1982 Apr;90(2):91–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1982.tb01423.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grebner J. V., Mills E. L., Gray G. H., Quie P. G. Comparison of phagocytic and chemiluminescence response of human polymorphonuclear neutrophils. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 Jan;89(1):153–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr, Keele B. B., Jr, Misra H. P., Lehmeyer J. E., Webb L. S., Baehner R. L., RaJagopalan K. V. The role of superoxide anion generation in phagocytic bactericidal activity. Studies with normal and chronic granulomatous disease leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun;55(6):1357–1372. doi: 10.1172/JCI108055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnovsky M. L. The metabolism of leukocytes. Semin Hematol. 1968 Apr;5(2):156–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Antimicrobial mechanisms in neutrophilic polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Semin Hematol. 1975 Apr;12(2):117–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kossack R. E., Guerrant R. L., Densen P., Schadelin J., Mandell G. L. Diminished neutrophil oxidative metabolism after phagocytosis of virulent Salmonella typhi. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):674–678. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.674-678.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangan D. F., Snyder I. S. Mannose-sensitive stimulation of human leukocyte chemiluminescence by Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1014–1019. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1014-1019.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthay K. K., Mentzer W. C., Wara D. W., Preisler H. K., Lameris N. B., Ammann A. J. Evaluation of the opsonic requirements for phagocytosis of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes VII, XIV, and XIX by chemiluminescence assay. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):228–235. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.228-235.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuwissen H. J., Rhee M. S., Rynes R. I., Pickering R. J. Phagocytosis, chemoluminescence, and intracellular killing of fungi by phagocytes from subjects with deficiency of the second component of complement. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1982;68(1):22–27. doi: 10.1159/000233062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E. The glomerular permeability determined by dextran clearance using Sephadex gel filtration. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1968;21(1):77–82. doi: 10.3109/00365516809076979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. P., Penny R. Chemiluminescence response in normal human phagocytes. I. Automated measurements using a standard liquid scintillation counter. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1982 Apr;7(3):215–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi F., Romeo D., Patriarca P. Mechanism of phagocytosis-associated oxidative metabolism in polymorphonuclear leucocytes and macrophages. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1972 Aug;12(2):127–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens P., Winston D. J., Van Dyke K. In vitro evaluation of opsonic and cellular granulocyte function by luminol-dependent chemiluminescence: utility in patients with severe neutropenia and cellular deficiency states. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):41–51. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.41-51.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita T., Blumenstock E., Kanegasaki S. Phagocytic and chemiluminescent responses of mouse peritoneal macrophages to living and killed Salmonella typhimurium and other bacteria. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1242–1248. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1242-1248.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugh H. A., Van Dijk W. C., Peters R., Van Der Tol M. E., Peterson P. K., Verhoef J. Staphylococcus aureus opsonization mediated via the classical and alternative complement pathways. A kinetic study using MgEGTA chelated serum and human sera deficient in IgG and complement factors C1s and C2. Immunology. 1979 Mar;36(3):391–397. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugh H. A., van Dijk W. C., Peters R., van Erne M. E., Daha M. R., Peterson P. K., Verhoef J. Opsonic recognition of staphylococci mediated by cell wall peptidoglycan: antibody-independent activation of human complement and opsonic activity of peptidoglycan antibodies. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1167–1173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch W. D. Correlation between measurements of the luminol-dependent chemiluminescence response and bacterial susceptibility to phagocytosis. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):370–374. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.370-374.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


