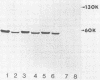
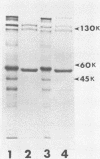
Abstract
Glycoprotein D is a virion envelope component of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. Sets of mice were immunized with purified gD-1 or gD-2 and were challenged with a lethal dose of herpes simple virus, either type 1 or type 2. All or virtually all of the immunized mice survived challenge with either agent, whereas challenge of sham-immunized mice was almost always fatal. Serum samples taken before challenge contained gD-specific antibodies which had 50% neutralization titers ranging from 1:16 to 1:512 against homologous and heterologous virus types. We conclude that either gD-1 or gD-2 is a potential candidate for a subunit vaccine against herpetic infections.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balachandran N., Bacchetti S., Rawls W. E. Protection against lethal challenge of BALB/c mice by passive transfer of monoclonal antibodies to five glycoproteins of herpes simplex virus type 2. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):1132–1137. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.1132-1137.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cappel R., Sprecher S., Rickaert F., de Cuyper F. Immune response to a DNA free herpes simplex vaccine in man. Arch Virol. 1982;73(1):61–67. doi: 10.1007/BF01341728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Katze M., Hydrean-Stern C., Eisenberg R. J. Type-common CP-1 antigen of herpes simplex virus is associated with a 59,000-molecular-weight envelope glycoprotein. J Virol. 1978 Jul;27(1):172–181. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.1.172-181.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Ponce de Leon M., Nichols C. Isolation of a herpes simplex virus-specific antigenic fraction which stimulates the production of neutralizing antibody. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):1021–1030. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.1021-1030.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dix R. D., Pereira L., Baringer J. R. Use of monoclonal antibody directed against herpes simplex virus glycoproteins to protect mice against acute virus-induced neurological disease. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):192–199. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.192-199.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberle R., Courtney R. J. gA and gB glycoproteins of herpes simplex virus type 1: two forms of a single polypeptide. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):665–675. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.665-675.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. J., Ponce de Leon M., Cohen G. H. Comparative structural analysis of glycoprotein gD of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1980 Aug;35(2):428–435. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.2.428-435.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. J., Ponce de Leon M., Pereira L., Long D., Cohen G. H. Purification of glycoprotein gD of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 by use of monoclonal antibody. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):1099–1104. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.1099-1104.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapoor A. K., Nash A. A., Wildy P., Phelan J., McLean C. S., Field H. J. Pathogenesis of herpes simplex virus in congenitally athymic mice: the relative roles of cell-mediated and humoral immunity. J Gen Virol. 1982 Jun;60(Pt 2):225–233. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-60-2-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitces E. N., Morahan P. S., Tew J. G., Murray B. K. Protection from oral herpes simplex virus infection by a nucleic acid-free virus vaccine. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):955–960. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.955-960.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. J., Buimovici-Klein E., Moser H., Moucha R., Hilfenhaus J. Efficacy of a virion envelope herpes simplex virus vaccine against experimental skin infections in hairless mice. Arch Virol. 1981;68(2):73–80. doi: 10.1007/BF01314437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawman M. J., Rouse B. T., Courtney R. J., Walker R. D. Cell-mediated immunity against herpes simplex induction of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):133–139. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.133-139.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrild B. Immunochemistry of herpes simplex virus glycoproteins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1980;90:67–106. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67717-5_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrild B., Shore S. L., Nahmias A. J. Herpes simplex virus glycoproteins: participation of individual herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein antigens in immunocytolysis and their correlation with previously identified glycopolypeptides. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):741–748. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.741-748.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notkins A. L. Immune mechanisms by which the spread of viral infections is stopped. Cell Immunol. 1974 Mar 30;11(1-3):478–483. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Dondero D. V., Gallo D., Devlin V., Woodie J. D. Serological analysis of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 with monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):363–367. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.363-367.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. L., Buchan A., Sim C., Watson D. H. Type-specific protein in herpes simplex virus envelope reacts with neutralising antibody. Nature. 1974 May 24;249(455):360–361. doi: 10.1038/249360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. W., Walz M. A., Wohlenberg C., Notkins A. L. Latent infection of sensory ganglia with herpes simplex virus: efficacy of immunization. Science. 1975 May 30;188(4191):938–940. doi: 10.1126/science.166432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rager-Zisman B., Allison A. C. Mechanism of immunologic resistance to herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) infection. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):35–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rector J. T., Lausch R. N., Oakes J. E. Use of monoclonal antibodies for analysis of antibody-dependent immunity to ocular herpes simplex virus type 1 infection. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):168–174. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.168-174.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier R. D., Pizer L. I., Moorhead J. W. Type-specific delayed hypersensitivity and protective immunity induced by isolated herpes simplex virus glycoprotein. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1413–1418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethi K. K., Omata Y., Schneweis K. E. Protection of mice from fatal herpes simplex virus type 1 infection by adoptive transfer of cloned virus-specific and H-2-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Gen Virol. 1983 Feb;64(Pt 2):443–447. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-2-443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner G. R., Buchan A., Hartley C. E., Turner S. P., Williams D. R. The preparation, efficacy and safety of 'antigenoid' vaccine NFU1 (S-L+) MRC toward prevention of herpes simplex virus infections in human subjects. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1980;169(1):39–51. doi: 10.1007/BF02123711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. I. Identification of four glycoprotein precursors and their products in type 1-infected cells. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):991–1008. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.991-1008.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturn B., Schneweis K. E. Protective effect of an oral infection with herpes simplex virus type 1 against subsequent genital infection with herpes simplex virus type 2. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1978 Jul 4;165(2):119–127. doi: 10.1007/BF02122747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worthington M., Conliffe M. A., Baron S. Mechanism of recovery from systemic herpes simplex virus infection. I. Comparative effectiveness of antibody and reconstitution of immune spleen cells on immunosuppressed mice. J Infect Dis. 1980 Aug;142(2):163–174. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.2.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]