Abstract
A number of strains of Streptococcus sanguis were found to aggregate in nonimmune serum and in crevicular fluid. All strains which aggregated in serum also aggregated in saliva, but some strains which aggregated in saliva did not aggregate in serum. Aggregation was destroyed by treatment of serum or crevicular fluid with neuraminidase and was inhibited by gangliosides. Treatment of serum with proteases reduced aggregating activity. Adsorption of serum to hydroxyapatite did not reduce the aggregating activity. The aggregating factor was partially purified by gel filtration and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and was found to be an acidic glycoprotein with a molecular weight of greater than 200,000, comprised of subunits with molecular weights of approximately 100,000. It did not appear to be an immunoglobulin and could not be identified with any other serum component tested. The possible role of the aggregating factor in providing nonimmune protection against colonization of S. sanguis in the gingival crevice and blood is discussed.
Full text
PDF


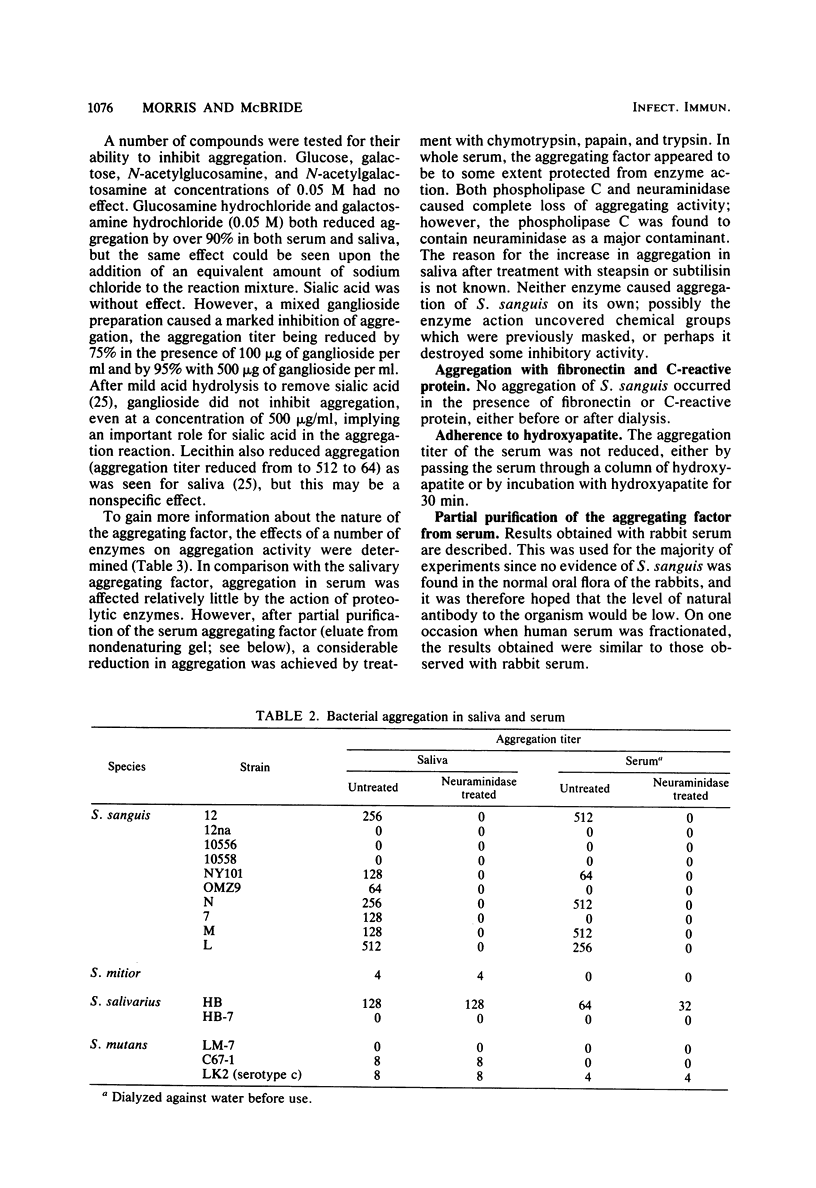

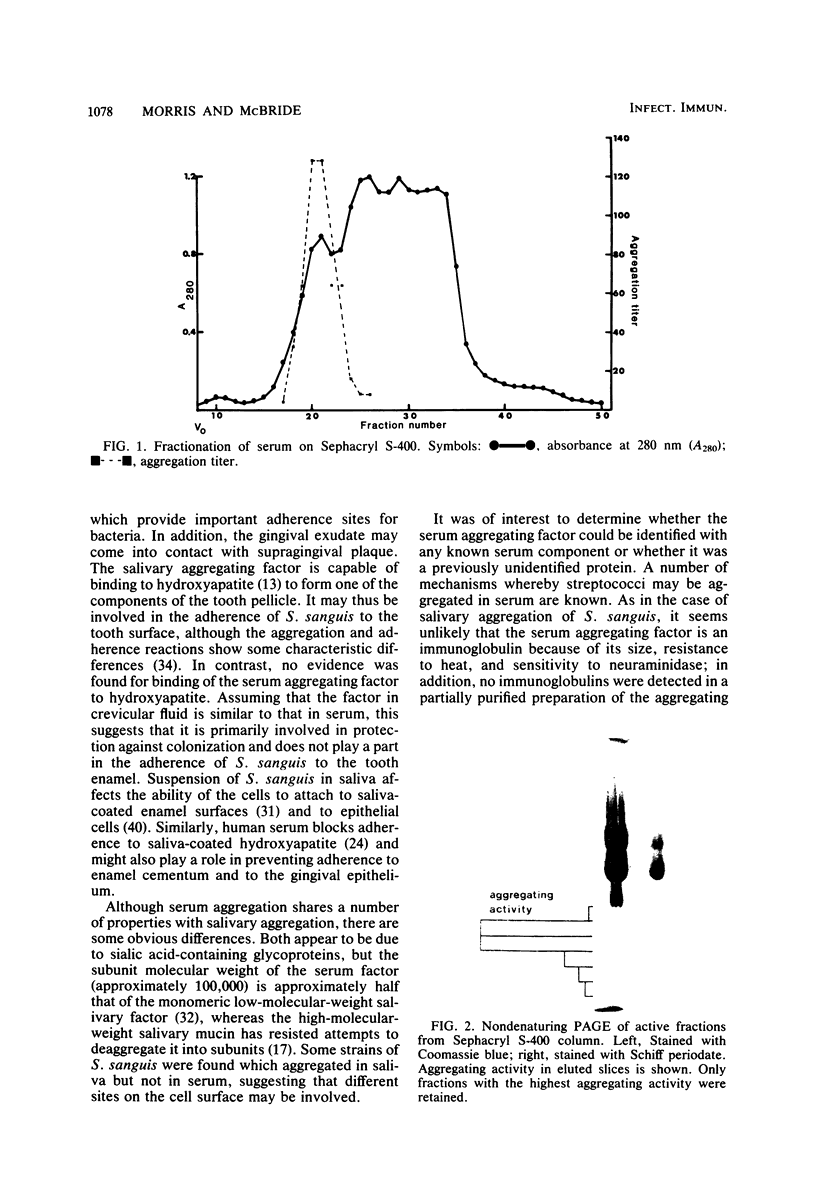


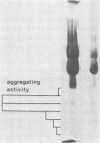
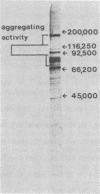
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CONNELL G. E., SMITHIES O. Human haptoglobins: estimation and purification. Biochem J. 1959 May;72(1):115–121. doi: 10.1042/bj0720115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clamp J. R. The relationship between secretory immunoglobulin A and mucus [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1977;5(5):1579–1581. doi: 10.1042/bst0051579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark W. B., Gibbons R. J. Influence of salivary components and extracellular polysaccharide synthesis from sucrose on the attachment of Streptococcus mutans 6715 to hydroxyapatite surfaces. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):514–523. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.514-523.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUTHIE E. S. The action of fibrinogen on certain pathogenic cocci. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Oct;13(2):383–393. doi: 10.1099/00221287-13-2-383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggert F. M. Salivary and amniotic-fluid agglutinin and aggregating factors: evidence for complexing between high-molecular-weight non-mucin glycoproteins and immunoglobulins [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1979 Feb;7(1):194–196. doi: 10.1042/bst0070194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggert F. M. The nature of secretory agglutinins and aggregating factors. I. Secretory conglutinin-like factor, secretory bacterial aggregating factors and secretory IgA antibody in human saliva and amniotic fluid. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1980;61(2):192–202. doi: 10.1159/000232433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggert F. M. The nature of secretory agglutinins and aggregating factors. II. Biochemical and immunochemical properties of factors in human saliva and amniotic fluid. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1980;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1159/000232434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggert F. M. The nature of secretory agglutinins and aggregating factors. IV. Complexing between non-mucin glycoproteins, immunoglobulins and mucins in human saliva and amniotic fluid. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1980;62(1):46–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson D., Bratthall D., Björck L., Myhre E., Kronvall G. Interactions between human serum proteins and oral streptococci reveal occurrence of receptors for aggregated beta 2-microglobulin. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):279–283. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.279-283.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson T., Magnusson I. Affinity for hydroxyapatite of salivary substances inducing aggregation of oral streptococci. Caries Res. 1976;10(1):8–18. doi: 10.1159/000260185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Houte J. V. Bacterial adherence in oral microbial ecology. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:19–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Qureshi J. V. Selective binding of blood group-reactive salivary mucins by Streptococcus mutans and other oral organisms. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):665–671. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.665-671.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay D. I., Gibbons R. J., Spinell D. M. Characteristics of some high molecular weight constituents with bacterial aggregating activity from whole saliva and dental plaque. Caries Res. 1971;5(2):111–123. doi: 10.1159/000259739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg S. D., Embery G. The isolation and partial characterization of a sulphated glycoprotein from human whole saliva which aggregates strains of Streptococcus sanguis but not Streptococcus mutans. Arch Oral Biol. 1979;24(10-11):791–797. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(79)90040-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler W., Prokop O., Uhlenbruck G. Zur agglutinin-Natur der menschlichen Haptoglobine gegenüber Streptokokken mit dem T4-Antigen. Naturwissenschaften. 1977 Oct;64(10):538–538. doi: 10.1007/BF00483564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laible N. J., Germaine G. R. Adsorption of lysozyme from human whole saliva by Streptococcus sanguis 903 and other oral microorganisms. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):148–159. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.148-159.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. J., Herzberg M. C., Levine M. S., Ellison S. A., Stinson M. W., Li H. C., van Dyke T. Specificity of salivary-bacterial interactions: role of terminal sialic acid residues in the interaction of salivary glycoproteins with Streptococcus sanguis and Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):107–115. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.107-115.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Bloomquist C. G., Ofstehage J. C. Aggregation and adherence of Streptococcus sanguis: role of human salivary immunoglobulin A. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1104–1110. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1104-1110.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Schauer S. V., Bloomquist C. G. Compounds which affect the adherence of Streptococcus sanguis and Streptococcus mutans to hydroxyapatite. J Dent Res. 1978 Feb;57(2):373–379. doi: 10.1177/00220345780570023901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride B. C., Gisslow M. T. Role of sialic acid in saliva-induced aggregation of Streptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):35–40. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.35-40.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mold C., Rodgers C. P., Kaplan R. L., Gewurz H. Binding of human C-reactive protein to bacteria. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):392–395. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.392-395.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. A., Levine M. J., Tabak L. A., Reddy M. S. Specificity of salivary-bacterial interactions: II. Evidence for a lectin on Streptococcus sanguis with specificity for a NeuAc alpha 2, 3Ga1 beta 1, 3Ga1NAc sequence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 31;106(2):390–396. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91122-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson J., Bratthall D., Carlén A. Association between bacterial agglutinins and immunoglobulin A in human saliva. Acta Odontol Scand. 1981;39(2):61–66. doi: 10.3109/00016358109162260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orstavik D., Kraus F. W., Henshaw L. C. In vitro attachment of streptococci to the tooth surface. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):794–800. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.794-800.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakobphol A., Levine M. J., Tabak L. A., Reddy M. S. Purification of a low-molecular-weight, mucin-type glycoprotein from human submandibular-sublingual saliva. Carbohydr Res. 1982 Oct 1;108(1):111–122. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)81896-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosan B., Malamud D., Appelbaum B., Golub E. Characteristic differences between saliva-dependent aggregation and adhesion of streptococci. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):86–90. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.86-90.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runehagen A., Schönbeck C., Hedner U., Hessel B., Kronvall G. Binding of fibrinogen degradation products to S. aureus and to beta-hemolytic streptococci group A, C and G. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1981 Apr;89(2):49–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1981.tb00151_89b.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. A., Beachey E. H. Adherence of group A streptococci to fibronectin on oral epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):275–279. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.275-279.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terleckyj B., Willett N. P., Shockman G. D. Growth of several cariogenic strains of oral streptococci in a chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):649–655. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.649-655.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A. H., McBride B. C. Adherence of Streptococcus salivarius HB and HB-7 to oral surfaces and saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):150–158. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.150-158.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A. H., McBride B. C. Characterization of the adherence properties of Streptococcus salivarius. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):459–468. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.459-468.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Gibbons R. J. Inhibition of streptococcal attachment to receptors on human buccal epithelial cells by antigenically similar salivary glycoproteins. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):711–718. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.711-718.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Olden K. Fibronectins--adhesive glycoproteins of cell surface and blood. Nature. 1978 Sep 21;275(5677):179–184. doi: 10.1038/275179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]