Abstract
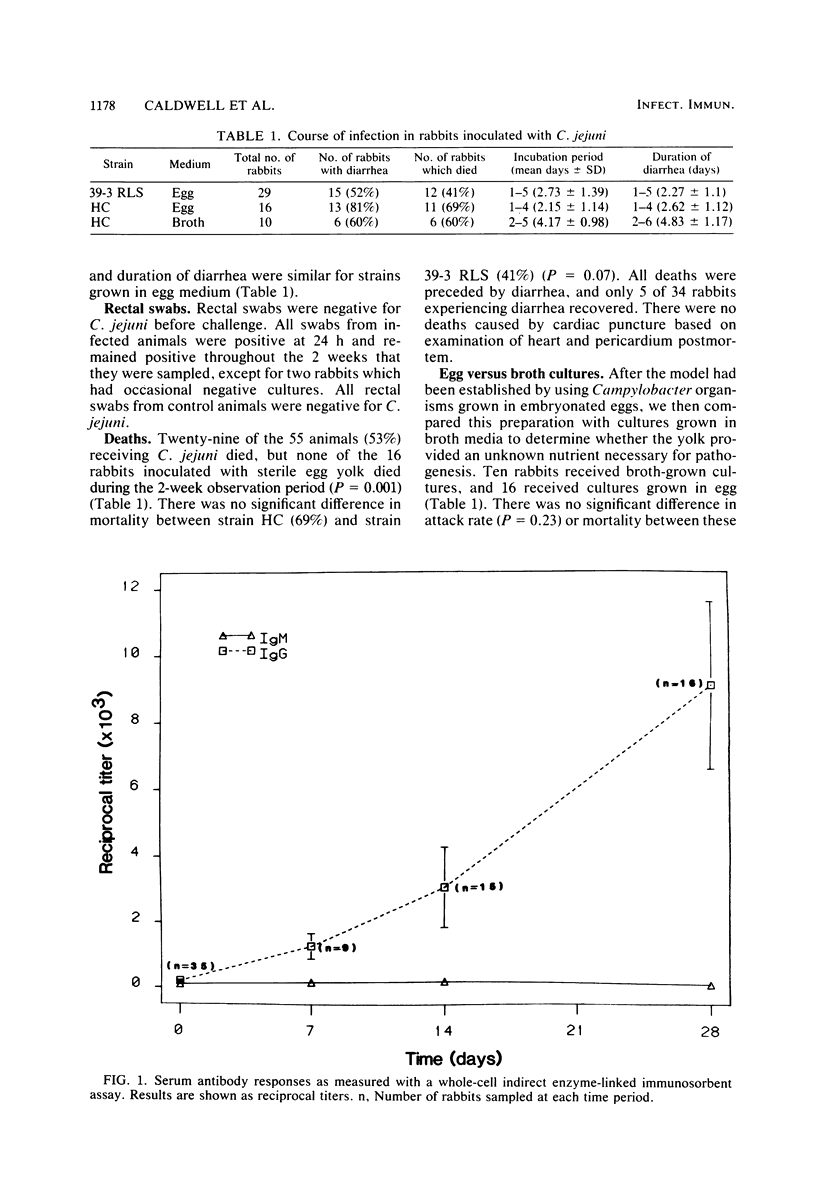
We tested the usefulness of the Removable Intestinal Tie Adult Rabbit Diarrhea model to establish Campylobacter jejuni infection in rabbits. The procedure involved ligation of the cecum, placement of a slip knot at the terminal ileum, and injection of the test inoculum into the mid-small bowel. The ends of the slip knot were externalized, and the tie was released 4 h later. Fifty-five rabbits received C. jejuni, and 16 received uninoculated medium as controls. Daily rectal swabs were positive for 2 weeks in infected rabbits. The diarrheal attack rate was 64% in infected rabbits and 0% in controls. Diarrhea was characterized by loose, mucus-containing stools after an incubation period ranging from 24 h to 6 days. When blood was obtained daily for culture from 30 rabbits for 4 days post-challenge, bacteremia was present in 96.3% 24 h after challenge but diminished to 5 of 19 (26.3%) at 96 h. Death occurred in 53% of rabbits and was always preceded by diarrhea. No control animal died. Only 5 of 35 animals experiencing diarrhea recovered. An indirect whole-cell enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to determine serum immunoglobulin G responses. Mean titers rose from 1:198 preoperatively to 1:9,087 on day 28. Necropsy on eight infected and two control animals showed inflammatory lesions with ulceration in 62.5% and goblet cell hyperplasia in 75% of infected rabbits. We conclude that the Removable Intestinal Tie Adult Rabbit Diarrhea procedure is a simple, effective method to establish C. jejuni infection which mimics human disease.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaser M. J., Berkowitz I. D., LaForce F. M., Cravens J., Reller L. B., Wang W. L. Campylobacter enteritis: clinical and epidemiologic features. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Aug;91(2):179–185. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Duncan D. J., Warren G. H., Wang W. L. Experimental Campylobacter jejuni infection of adult mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):908–916. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.908-916.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Wells J. G., Feldman R. A., Pollard R. A., Allen J. R. Campylobacter enteritis in the United States. A multicenter study. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Mar;98(3):360–365. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-3-360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butzler J. P., Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis. Clin Gastroenterol. 1979 Sep;8(3):737–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasch G. A., Halle S., Bourgeois A. L. Sensitive microplate enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibodies against the scrub typhus rickettsia, Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):38–48. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.38-48.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake A. A., Gilchrist M. J., Washington J. A., 2nd, Huizenga K. A., Van Scoy R. E. Diarrhea due to Campylobacter fetus subspecies jejuni. A clinical review of 63 cases. Mayo Clin Proc. 1981 Jul;56(7):414–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy M. C., Benson J. B., Rubin S. J. Mucosal invasion in campylobacter enteritis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1980 May;73(5):706–708. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/73.5.706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field L. H., Underwood J. L., Pope L. M., Berry L. J. Intestinal colonization of neonatal animals by Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):884–892. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.884-892.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firehammer B. D., Myers L. L. Campylobacter fetus subsp jejuni: its possible significance in enteric disease of calves and lambs. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Jun;42(6):918–922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgeorge R. B., Baskerville A., Lander K. P. Experimental infection of Rhesus monkeys with a human strain of Campylobacter jejuni. J Hyg (Lond) 1981 Jun;86(3):343–351. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400069096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Lahita R. G., Winn W. C., Jr, Roberts R. B. Campylobacteriosis in man: pathogenic mechanisms and review of 91 bloodstream infections. Am J Med. 1978 Oct;65(4):584–592. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90845-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert M. E., Schofield P. F., Ironside A. G., Mandal B. K. Campylobacter colitis. Br Med J. 1979 Mar 31;1(6167):857–859. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6167.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longfield R., O'Donnell J., Yudt W., Lissner C., Burns T. Acute colitis and bacteremia due to Campylobacter fetus. Dig Dis Sci. 1979 Dec;24(12):950–953. doi: 10.1007/BF01311952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manninen K. I., Prescott J. F., Dohoo I. R. Pathogenicity of Campylobacter jejuni isolates from animals and humans. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):46–52. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.46-52.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F., Barker I. K., Manninen K. I., Miniats O. P. Campylobacter jejuni colitis in gnotobiotic dogs. Can J Comp Med. 1981 Oct;45(4):377–383. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price A. B., Jewkes J., Sanderson P. J. Acute diarrhoea: Campylobacter colitis and the role of rectal biopsy. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Oct;32(10):990–997. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.10.990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Palacios G. M., Escamilla E., Torres N. Experimental Campylobacter diarrhea in chickens. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):250–255. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.250-255.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis: a "new" disease. Br Med J. 1977 Jul 2;2(6078):9–11. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6078.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spira W. M., Sack R. B., Froehlich J. L. Simple adult rabbit model for Vibrio cholerae and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhea. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):739–747. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.739-747.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walder M., Forsgren A. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for antibodies against Campylobacter jejuni, and its clinical application. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1982 Dec;90(6):423–433. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1982.tb00141.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







