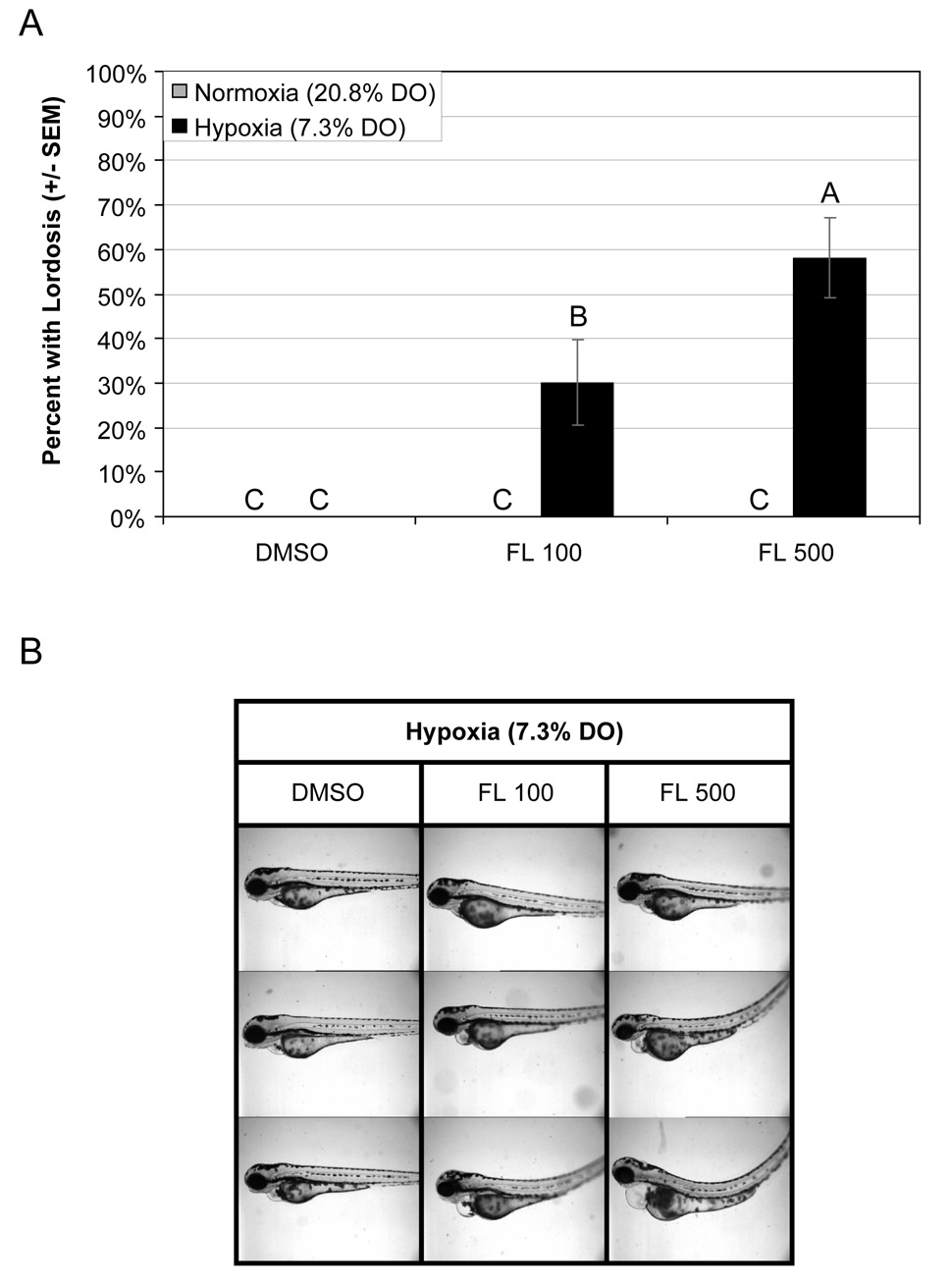
Fig. 4.
(A) Occurrence of lordosis in developing zebrafish larvae exposed to hypoxia (7.3% DO) and 0, 100, or 500 µg L−1 fluoranthene (FL). Groups not sharing a common letter are significantly different (p ≤ 0.05), based on Bonferroni-corrected post hoc multiple comparisons following ANOVA. (B) Images of 96 hpf zebrafish larvae showing the range of trunk abnormalities observed for coexposed embryos. While embryos exposed only to hypoxia and carrier control (DMSO) showed no evidence of trunk abnormalities, a significant proportion of embryos coexposed to hypoxia and FL developed lordosis.