Abstract
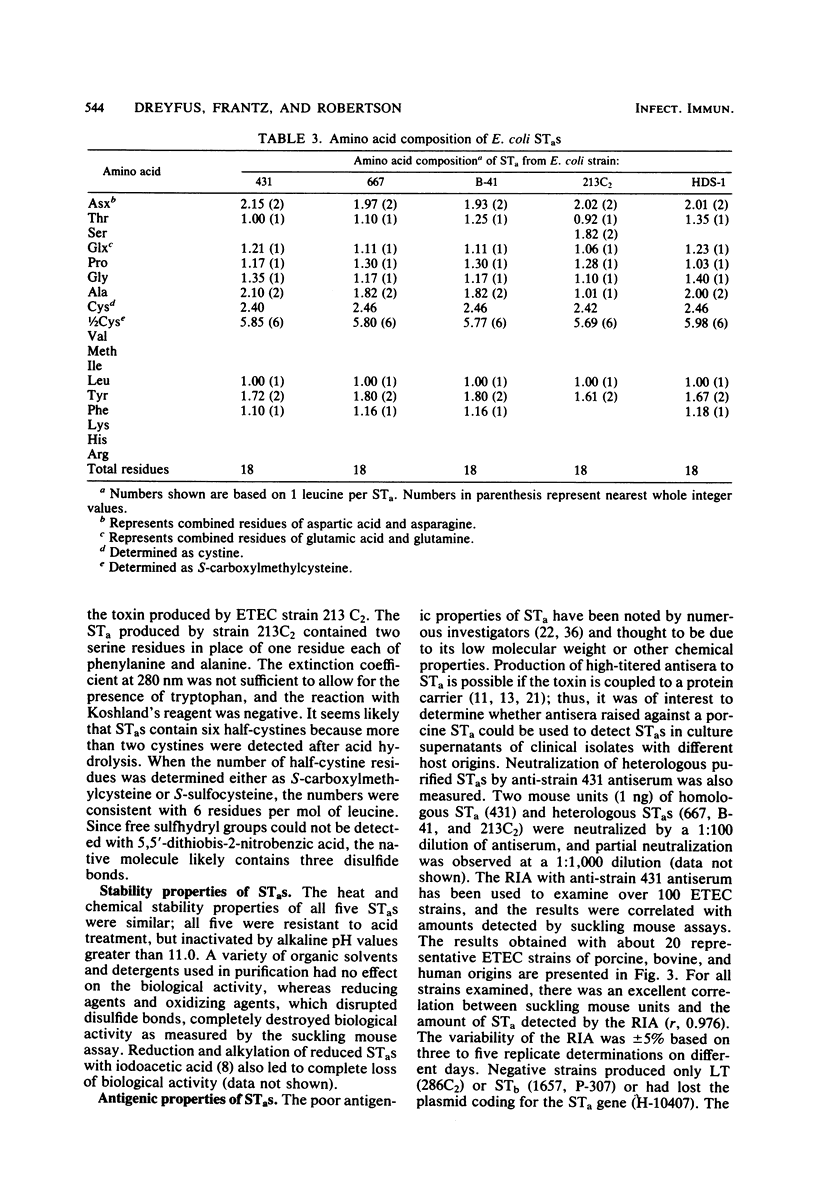
Five heat-stable enterotoxins (STs) produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains of porcine, bovine, and human host origins have been purified to apparent homogeneity. The STs with biological activity in suckling mice and piglets (STaS) contained 18 amino acid residues, 10 amino acids with a high proportion of acidic amino acids, and 6 half-cystines. The carboxy-terminal and amino-terminal residues of all STaS were tyrosine and asparagine, respectively. All five STa preparations were homogeneous by several criteria: (i) a single symmetrical peak on gel filtration, (ii) a single fluorescent band on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, (iii) single carboxyl-terminal and amino-terminal residues, and (iv) amino acid analysis data that indicated a stoichiometric relationship between the component amino acids. The isoelectric points of the five STaS ranged from 3.88 to 4.08. All five purified preparations were heat stable and not denatured by organic solvents, detergents, or treatment at pH 1, but were partially inactivated after incubation at pH 12.0. Biological activity was completely abolished by treatment with reducing and oxidizing agents, which suggested that one or more disulfide bonds play an important role in the mechanism of action of STaS. Antisera raised against strain 431 STa, produced by a porcine class II enterpathogen, neutralized homologous 431 STa as well as heterologous purified STa preparations. The antiserum was used as a reagent in a sensitive radioimmunoassay to detect suckling mouse-positive strains of enterotoxigenic E. coli.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aimoto S., Takao T., Shimonishi Y., Hara S., Takeda T., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Amino-acid sequence of a heat-stable enterotoxin produced by human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec 15;129(2):257–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Robertson D. C. Nutrition and enterotoxin synthesis by enterotoxigenic strains of Escherichia coli: defined medium for production of heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):781–788. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.781-788.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Robertson D. C. Purification and chemical characterization of the heat-stable enterotoxin produced by porcine strains of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1021–1030. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1021-1030.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black S. D., Coon M. J. Simple, rapid, and highly efficient separation of amino acid phenylthiohydantoins by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1982 Apr;121(2):281–285. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90480-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess M. N., Bywater R. J., Cowley C. M., Mullan N. A., Newsome P. M. Biological evaluation of a methanol-soluble, heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin in infant mice, pigs, rabbits, and calves. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):526–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.526-531.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess M. N., Mullan N. A., Newsome P. M. Heat-stable enterotoxins from Escherichia coli P16. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):1038–1040. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.1038-1040.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRESTFIELD A. M., MOORE S., STEIN W. H. The preparation and enzymatic hydrolysis of reduced and S-carboxymethylated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1963 Feb;238:622–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. K., Giannella R. A. Amino acid sequence of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by Escherichia coli pathogenic for man. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7744–7746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Graf L. H., Jr, Laird W. J., Smith P. L. Heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: in vitro effects on guanylate cyclase activity, cyclic GMP concentration, and ion transport in small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2800–2804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frantz J. C., Robertson D. C. Immunological properties of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxins: development of a radioimmunoassay specific for heat-stable enterotoxins with suckling mouse activity. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):193–198. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.193-198.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geary S. J., Marchlewicz B. A., Finkelstein R. A. Comparison of heat-labile enterotoxins from porcine and human strains of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):215–220. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.215-220.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Drake K. W., Luttrell M. Development of a radioimmunoassay for Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin: comparison with the suckling mouse bioassay. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):186–192. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.186-192.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray W. R., Luque A., Olivera B. M., Barrett J., Cruz L. J. Peptide toxins from Conus geographus venom. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4734–4740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Hughes J. M., Chang B., Robertson D. C., Murad F. Activation of intestinal guanylate cyclase by heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: studies of tissue specificity, potential receptors, and intermediates. J Infect Dis. 1980 Aug;142(2):220–228. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.2.220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Tsuji T., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Immunological nonidentity of heat-labile enterotoxins from human and porcine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):337–340. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.337-340.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T. M., Wu B. J. Biochemical properties of Escherichia coli low-molecular-weight, heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):342–347. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.342-347.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapitany R. A., Forsyth G. W., Scoot A., McKenzie S. F., Worthington R. W. Isolation and partial characterization of two different heat-stable enterotoxins produced by bovine and porcine strains of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):173–177. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.173-177.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauss S. W., Milman G. Characterization of cyanogen bromide peptides of hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase by a micromethod. Anal Biochem. 1977 Sep;82(1):38–45. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90131-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lallier R., Bernard F., Gendreau M., Lazure C., Seidah N. G., Chrétien M., St-Pierre S. A. Isolation and purification of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin of porcine origin. Anal Biochem. 1982 Dec;127(2):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90171-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lallier R., Lariviere S., St-Pierre S. Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin: rapid method of purification and some characteristics of the toxin. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):469–474. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.469-474.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen G. L., Knoop F. C. Physiochemical properties of a heat-stable enterotoxin produced by Escherichia coli of human origin. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):1051–1053. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.1051-1053.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Hardy J. W., Hug M. I., Echeverria P., Falkow S. Isolation and nucleotide sequence determination of a gene encoding a heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1167–1174. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1167-1174.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Huq I., Alim A. R., So M., Samadpour-Motalebi M., Falkow S. Detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by DNA colony hybridization. J Infect Dis. 1980 Dec;142(6):892–898. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.6.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson E., Söderlind O. Comparison of different assays for definition of heat-stable enterotoxigenicity of Escherichia coli porcine strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jan;11(1):6–15. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.1.6-15.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao M. C., Orellana S. A., Field M., Robertson D. C., Giannella R. A. Comparison of the biological actions of three purified heat-stable enterotoxins: effects on ion transport and guanylate cyclase activity in rabbit ileum in vitro. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):165–170. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.165-170.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D. C., Altekar W. W., Wood W. A. Structure of 2-keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconate aldolase. 3. Sequence of a hexadecapeptide containing the azomethine-forming lysine residue. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):2084–2090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rönnberg B., Wadström T., Jörnvall H. Structure of a heat-stable enterotoxin produced by a human strain of Escherichia coli. Differences from the toxin of another human strain suggest the presence of compensated amino acid exchanges. FEBS Lett. 1983 May 8;155(2):183–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80598-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Human diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:333–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saeed A. M., Sriranganathan N., Cosand W., Burger D. Purification and characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin from bovine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):701–707. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.701-707.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. J., Neuberger M. R., Liu T. Y. Complete amino acid analysis of proteins from a single hydrolysate. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):1936–1940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So M., McCarthy B. J. Nucleotide sequence of the bacterial transposon Tn1681 encoding a heat-stable (ST) toxin and its identification in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4011–4015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staples S. J., Asher S. E., Giannella R. A. Purification and characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by a strain of E. coli pathogenic for man. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4716–4721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swank R. T., Munkres K. D. Molecular weight analysis of oligopeptides by electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gel with sodium dodecyl sulfate. Anal Biochem. 1971 Feb;39(2):462–477. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90436-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Takeda T., Yano T., Yamamoto K., Miwatani T. Purification and partial characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):978–985. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.978-985.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarr G. E. Improved manual sequencing methods. Methods Enzymol. 1977;47:335–357. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(77)47036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whipp S. C., Moon H. W., Argenzio R. A. Comparison of enterotoxic activities of heat-stable enterotoxins from class 1 and class 2 Escherichia coli of swine origin. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):245–251. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.245-251.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


