Abstract
A major challenge is to identify the physiological relevance of cancer-associated genetic polymorphisms. Several changes in the coding sequence of β integrin subunits have now been described in human tumours. One of these, T188Iβ1, was identified as a heterozygous mutation in a poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) and shown to activate extracellular matrix adhesion and inhibit keratinocyte differentiation in vitro. To study its contribution to tumour development, we overexpressed the mutant or wild-type (WT) human β1 subunit in the basal layer of mouse epidermis using the keratin 14 promoter. The transgenic integrins were expressed at the cell surface and were functional, T188Iβ1 promoting cell spreading to a greater extent than WTβ1. Epidermal proliferation and differentiation were unaffected and no expansion of the stem cell compartment was detected. During chemical carcinogenesis both transgenes increased papilloma formation, but only the T188Iβ1 transgene stimulated conversion of papillomas to SCCs. Papillomas bearing the mutation showed increased Erk activity and reduced differentiation. SCCs expressing T188Iβ1 were less well differentiated than those expressing WTβ1. These observations establish that expression of a genetic variant in the I-like domain of β1 integrins does not affect normal epidermal homeostasis, but increases tumour susceptibility and influences tumour type.
Introduction
Integrin extracellular matrix receptors regulate many aspects of epidermal cell behaviour (1). Within the basal layer of human epidermis stem cells express higher levels of integrins than cells that are committed to undergo terminal differentiation (2-4). Integrin signalling to Erk/MAPK plays a role in maintenance of the stem cell compartment (5, 6). Studies with cultured human epidermal cells show that integrin ligation suppresses the onset of terminal differentiation, with ligated integrins sending a ‘do not differentiate’ signal to the cells (7, 8). In mouse models, epidermal-specific deletion of specific integrins leads to a range of phenotypes, from epidermal blistering to a failure to maintain the hair follicles (1, 9, 10).
Integrins are implicated in a variety of epidermal diseases (1, 11-16). Integrin expression or signalling is often altered in squamous cell carcinomas. In studies of chemically induced skin carcinogenesis, overexpression of integrins in the suprabasal layers alters susceptibility to tumour development (17-19).
We previously identified a heterozygous mutation in the β1 integrin subunit in cells from a poorly differentiated human SCC of the tongue (20). The mutation, T188I, lies in the specificity loop of the I-like domain (21, 22) and results in constitutive activation of ligand binding, thereby stimulating cell spreading at low extracellular matrix concentrations (20). While expression of the mutation in cultured cells does not affect cell migration or invasion, it does lead to enhanced activation of Erk/MAPK signalling (20). In contrast to the wild-type β1 subunit, unligated T188Iβ1 does not trigger initiation of terminal differentiation in human keratinocytes (20).
Sequencing of the β1 I-like domain in 124 human head and neck squamous cell carcinomas has revealed several additional single nucleotide changes, one of which results in a change in amino acid sequence (A239V) (23). The same single nucleotide changes are present in normal tissue from the patients, indicating germline polymorphisms. In addition, sequencing by the Sanger Cancer Genome Project1 has identified two cancer-associated amino acid changes in the I-like domain of the β6 integrin subunit (P184S and N195Y). We conclude that changes in the amino acid sequence of β integrin I-like domains are found at low frequency in tumours and that they are probably polymorphisms rather than somatic mutations. In order to investigate the physiological role of the T188I mutation we expressed the human T188Iβ1 mutant or the wild-type human subunit in the epidermis of transgenic mice.
Materials and Methods
Generation of transgenic mice
Human wild-type and T188I mutant β1 integrin subunit cDNAs (24) were subcloned into the BamHI restriction site of the keratin 14 (K14) promoter cassette kindly provided by E. Fuchs and injected into the male pronucleus of day 1 fertilized FVB/N mouse eggs. Potential founder lines were screened by PCR using one primer specific for β-globin (TACTCTGAGTCCAAACCGGGC) and one specific for the human integrin β1 subunit (CAATTTGGCCCTGCTTGTATACATTCTCCA). K14T188Iβ1 founder lines were 4826B, 4828B (low) and 4828B (high). K14WTβ1 founders were 4898A and 4837A. Founder lines 4828B (low) and 4837A had lower transgene copy numbers than the other lines.
Experimental procedures on mice
Experiments were subject to CR-UK ethical review and performed under the terms of a UK Government Home Office licence. BrdU injections were performed as previously described (25).
Chemical carcinogenesis experiments were performed on seven week-old female K14WTβ1 (line 4898A), K14T188Iβ1 (4828B, high) mice and non-transgenic littermates (25 animals/group), essentially as described previously (17-19). Mice received one topical application of 100 nmol (25 μg) 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene (DMBA; Sigma-Aldrich; St Louis, MO) in 200 μl acetone followed by twice weekly applications of 6 nmol (3.7 μg) 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA; Sigma-Aldrich; St Louis, MO) in 200 μl acetone. As controls, transgenic and non-transgenic littermates (5-10 animals/group) were subjected to the same protocol but substituting DMBA or TPA with acetone.
Papillomas and SCC were recorded once per week for up to 54 weeks after the start of promotion. Tumour sections were graded as described previously (17).
Tissue processing
For sections, tissue was fixed in 10% neutral-buffered formalin and embedded in paraffin or frozen in liquid nitrogen-cooled isopentane and then embedded in OCT embedding matrix (Raymond A Lamb, UK). Epidermal whole mounts of tail skin were prepared as described previously (25), with minor modifications.
Antibodies
The following monoclonal antibodies were used: AIIB2, TS2/16, DH12 and P5D2 (anti-human β1 integrin subunit; Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank, Iowa City, IA) (26, 27); LHK15 (anti-keratin 15; 25); anti-BrdU (Clone 3D4, BD Pharmingen; San Jose, CA); MB1.2 (anti-mouse β1 integrins; 25); and GoH3 (anti-integrin α6 chain; BD Pharmingen). Rabbit antibodies were: anti-phospho p44/42 MAPK (Thr202/Tyr204) and anti-p44/42 MAPK (Cell Signaling Technology, Inc., Danvers, MA); anti-mouse keratin 14 (Covance Research Products, Inc; Denver, Pennsylvania); anti-laminin (Sigma-Aldrich; St Louis, MO); and anti-Ki67 (Neomarkers, Fremont, CA). AlexaFluor 488- or 594-conjugated secondary antibodies were obtained from Invitrogen Corp., Paisley, UK. Donkey anti-rabbit biotin antibody was from Jackson Laboratory; Bar Harbor, Maine.
Immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridisation
Ki67, laminin and phosphorylated Erk were detected with the Bond Intense R Detection kit (Leica Microsystems; Wetzlar, Germany) in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections following antigen-retrieval. Sections were photographed and analysed using the Ariol SL-50 system (Applied Imaging Corp., San Jose).
For immunofluorescence staining, frozen sections were fixed in 4% PFA/PBS for 10 minutes; paraffin sections were dewaxed and re-hydrated. Sections were permeabilized in 0.3% Triton X-100 for 5 minutes and blocked with 2% BSA, 0.02% fish skin gelatin and 10% fetal calf serum for 2 hours in PBS at room temperature. Sections were incubated in primary antibody overnight at 4°C, washed in PBS and incubated with secondary antibody for 45 minutes at room temperature.
Epidermal whole mounts were labelled as described previously (25). In situ hybridisation was performed as previously described (26).
Keratinocyte culture
Keratinocytes were isolated from 7-8 week-old mouse dorsal skin (28) and cultured on confluent J2-3T3 feeders in type I collagen coated flasks in calcium-free FAD medium supplemented with 10% FCS, hydrocortisone, insulin, cholera toxin and EGF. Spontaneously immortalised lines arose after approximately 10 passages.
The growth rates of immortalised lines were compared by plating 5 × 104 cells per well in 6 well plates in complete KSFM (Gibco) without feeders. Wells were pre-coated with 10 μg/ml human plasma fibronectin. Triplicate wells were harvested per time point. Cell number was determined using the CellTiter96Aqueous One Solution Cell Proliferation Assay kit from Promega, measuring absorbance at 490 nm.
To determine colony forming efficiency, 400 or 2000 primary keratinocytes were plated per well in 6-well type I collagen coated plates (BD Pharmingen). After 14 days, cultures were fixed and stained with 1% Rhodamine B and 1% Nile Blue (Acros Organic, Geel, Belgium) (2). Colony-forming efficiency was defined as percentage of plated cells that formed a colony of three or more cells.
Flow cytometry
Single cell suspensions were incubated for 20 min on ice with anti- β1 integrin antibodies diluted in pre-chilled PBS. After washing in chilled PBS cells were incubated with appropriate secondary antibodies as before. Flow cytometric analysis was performed using the FACS Calibur (BD FACSCalibur System, BD Biosystems) and Flow Jo software (Tree Star Inc.; Ashland, OR), excluding dead, 7AAD positive, cells and differentiated cells with high forward and side scatter.
Cell adhesion assays
96-well microtiter plates were coated with 50 μl human plasma fibronectin (Chemicon; Billerica, MA) or human placenta laminin (Sigma-Aldrich; St Louis, MO) overnight at 4°C and blocked with 1% heat-denatured BSA in PBS. 2 × 104 cells were added per well and incubated at 37°C for 30 min in serum-free medium containing 0.5% BSA. After washing, cells were fixed with 4% PFA in PBS and stained with Diff-Quik (International Reagents, Japan). Spread cells (defined as cells in which the long axis was more than twice the diameter of the nucleus) were counted in three independent fields/well. In some experiments cells were incubated with 10 μg/ml P5D2 antibody for 20 min at room temperature prior to plating.
To visualise F-actin, cells were fixed with 4% PFA in PBS for 10 min, permeabilised with 0.1% Triton X-100/PBS for 5 min and stained with phalloidin-conjugated Alexa-555 (Invitrogen Corp.; Paisley, UK).
Integrin turnover time
Adherent subconfluent keratinocytes were surface-labeled with 1 mg/ml EZ-Link Sulfo-NHS-LC-Biotin (PIERCE; Rockford, IL)/PBS (-) (pH 8.0) for 15 min at room temperature. Cells were washed twice with serum-free, calcium-free FAD medium and incubated in complete medium at 37°C for 0, 4, 8 or 20h. Cells were harvested with trypsin/EDTA, incubated with P5D2 antibody for 30 min on ice and washed twice with ice-cold PBS. Pellets containing 4 × 106 cells were lysed in RIPA buffer (0.1% SDS, 0.5% sodium deoxycholate, 1% Nonidet P-40, 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 150 mM NaCl) with proteinase inhibitors (Roche; Basel, Switzerland). Cell lysates were clarified by centrifugation, then 20 μl of a 50% slurry of UltraLink Immobilized Protein G Plus Gel (PIERCE; Rockford, IL) was added and incubated for 1h at 4°C with gentle agitation. Beads and immune complexes were washed 3 times with 0.5% Nonidet P-40, 0.6M NaCl, 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.3), resuspended in SDS-PAGE sample buffer without added reducing agent, boiled for 3 min, and resolved on 4-12% gradient polyacrylamide gels.
Following SDS-PAGE, separated proteins were transferred to PVDF membranes, blocked with 5% skim milk in TBS for 30 min and incubated with Extravidin-peroxidase (Sigma-Aldrich; St Louis, MO) in RIPA buffer for 1h at room temperature. After washing, Extravidin-peroxidase was visualized by ECL reagents (Amersham; Buckinghamshire, UK).
Erk signalling
Cells were starved overnight in serum-free, calcium-free FAD. 3.5 × 105 cells were plated per 60 mm dish on 10 μg/ml fibronectin in the same medium supplemented with 0.5% BSA. Protein lysates were prepared in RIPA buffer containing protease and phosphatase inhibitors. Lysates were examined by Western blotting, essentially as described above, except that nitrocellulose membrane was used and the blocking buffer consisted of 2.5% skim milk powder and 0.05% Tween 20.
Results
Wild-type and mutant human β1 integrin subunits are expressed at similar levels in transgenic epidermis
We used the keratin 14 (K14) promoter to target transgene expression to the known locations of epidermal stem cells (29). We initially compared three transgenic lines expressing the T188I mutant β1 subunit (T188Iβ1) and two expressing the human wild-type subunit (WTβ1). Mice from all founder lines were viable and fertile and none had any gross phenotypic abnormalities. We selected one founder line expressing each transgene for further analysis.
Transgene expression was confirmed by radioactive in situ hybridisation using a probe specific for the human β1 integrin. No signal was detected in sections of non-transgenic mice (NT; Figure 1A). In mice expressing either the wild-type human β1 subunit (K14WTβ1) or the mutant (K14T188Iβ1) the transgene was detected in the basal layer of the interfollicular epidermis, the sebaceous gland and hair follicle outer root sheath (Figure 1A). Using antibodies specific for the human (Figure 1B) or mouse (Figure 1C) β1 integrins we confirmed that the transgene-encoded integrins were co-expressed with the endogenous β1 integrins. However, in K14WTβ1 epidermis staining for endogenous β1 integrin was reduced (Figure 1C).
Figure 1. Transgene expression in adult dorsal epidermis and cultured keratinocytes.
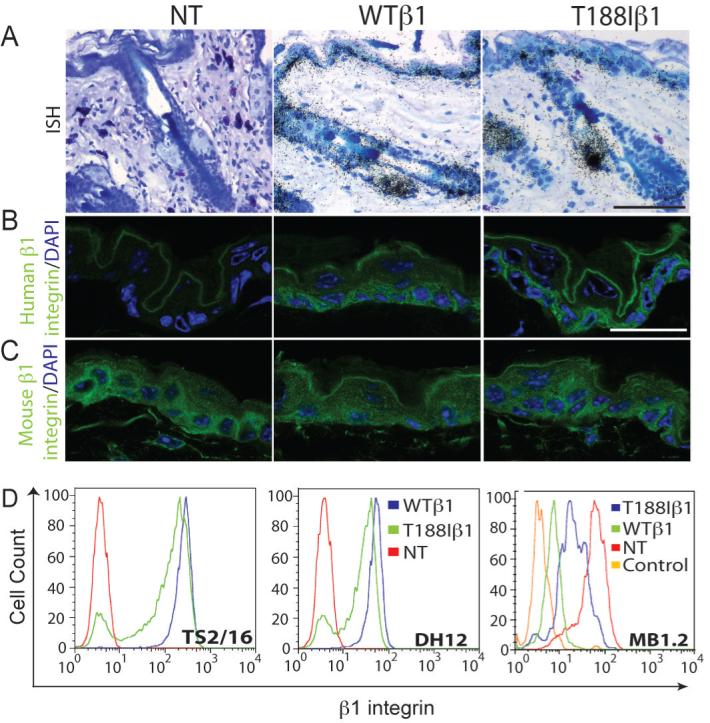
(A) In situ hybridisation with probe specific for human β1 integrin subunit. (B, C) Immunofluorescence staining for human (green; B) and mouse (green; C) β1 integrins with DAPI nuclear counterstain (blue). Scale bars: 60 μm (A), 25 μm (B, C). (D) Flow cytometry of viable basal keratinocytes labelled with the antibodies shown. NT: non-transgenic; WTβ1: K14WTβ1 transgenic; T188Iβ1: K14T188Iβ1 transgenic.
Cell surface β1 integrin levels were examined in primary keratinocyte cultures or immortalised keratinocyte lines. Cells were labelled with TS2/16 or DH12, two monoclonal antibodies to the human β1 integrin, or MB1.2, specific for mouse β1 integrins (Figure 1D). Flow cytometry established that cells from K14WTβ1 and K14T188Iβ1 transgenic mice expressed similar levels of human β1 integrins, with the caveat that the T188I mutation may affect the epitopes detected by the antibodies (Figure 1D). In cells expressing either transgene, the level of surface mouse β1 integrins was decreased relative to transgene-negative control cells, the effect being more marked in cells expressing the wild-type transgene (Figure 1C, D).
Downregulation of the endogenous mouse β1 integrin is expected, because surface levels of the β1 subunit are dependent on availability of endogenous α subunit partners (30). However, the fact that mouse β1 was not completely lost from the cell surface indicates that the T188Iβ1 mutant integrin was co-expressed on the cell surface with wild type (mouse) β1 (20).
To compare the turnover time of the transgene-encoded human β1 integrins (31), adherent keratinocytes were surface-labelled with biotin, chased for different periods of time and immunoprecipitated with P5D2 (Figure 2A). Consistent with the flow cytometry data, the levels of expression of WTβ1 and T188Iβ1 were similar. Two bands were detected by immunoprecipitation, corresponding to the mature β1 subunit and its α partners. Between 0 and 8 hours, the levels of the WT and mutant human β1 subunits were unchanged. By 20 hours, surface levels of both mutant and wild-type subunits had decreased to a similar extent. P5D2 displayed weak cross-reactivity with the endogenous mouse β1 integrin, and immunoprecipitation of surface labelled transgene-negative keratinocytes revealed that the kinetics of loss from the cell surface were similar to those of the transgene-encoded integrins (Figure 2A).
Figure 2. Effects of transgenic integrins on keratinocyte signalling, adhesion and proliferation.
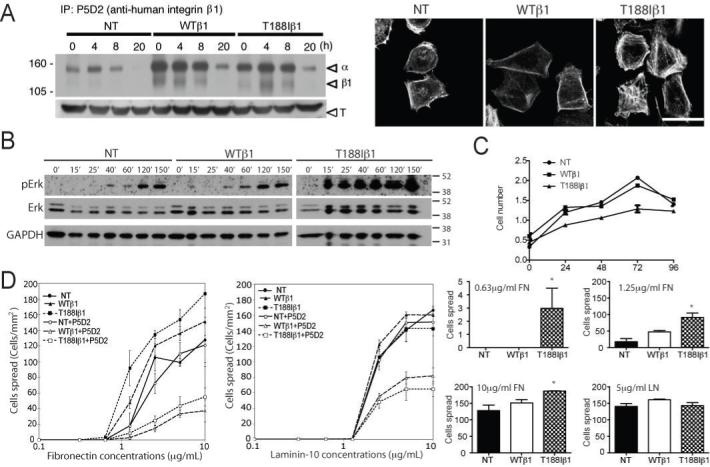
(A; left hand side) Immunoprecipitation of surface biotinylated β1 integrins in cells harvested immediately after labelling (0h) or after the chase periods shown. Arrows show α and β1 integrin subunits. Lower panel: β-tubulin immunoblot of total cell lysates (T). (A; right hand side) Cells plated for 30 min on 20 μg/ml fibronectin stained with phalloidin-conjugated Alexa-555. Scale bar: 50 μm. (B) Western blot of keratinocytes seeded on 10 μg/ml fibronectin for the number of minutes indicated. Time zero: single cell suspension prior to plating. Blots were probed with the antibodies indicated. (A, B) Molecular weights (kD) are indicated. (C) Proliferation of keratinocytes on fibronectin coated dishes. y axis: absorbance at 490 nm. Data are means ± SEM. (D) Immortalised keratinocytes were plated for 30 min on the concentrations of fibronectin or laminin-10 shown. Statistical significance of number of spread cells was evaluated (histograms). Asterisk indicates p < 0.05 (unpaired Student’s T test). NT: non-transgenic; WTβ1: K14WTβ1 transgenic; T188Iβ1: K14T188Iβ1 transgenic.
The T188Iβ1 mutation promotes Erk MAPK signalling, cell spreading and actin cytoskeletal assembly, but not proliferation
To examine Erk MAPK activation in transgenic keratinocytes, starved cells were plated on fibronectin for up to 150min (Figure 2B). The kinetics of Erk MAPK activation were similar in nontransgenic and K14WTβ1 transgenic cells. However, in K14T188Iβ1 transgenic cells Erk MAPK activation was greater at all time points examined (20). The ratio of phosphoErk to total Erk band intensity at 40 min was 0.34 for nontransgenic cells, 0.27 for K14WTβ1 cells and 1.63 for K14T188Iβ1 cells. In spite of the increased Erk activation, the T188I mutation did not increase the growth rate of immortalised keratinocytes on fibronectin-coated dishes under feeder-free, low calcium culture conditions (Figure 2C).
We next examined adhesion on fibronectin, which is mediated by α5β1, and laminin-10, which is mediated by α3β1 and α6β4 in combination (1). On fibronectin, transgene-positive keratinocytes adhered and spread to a greater extent than transgene-negative keratinocytes. The effect was greatest in cells expressing T188Iβ1 plated on low fibronectin concentrations (20) (Figure 2D). T188Iβ1 was also more effective than WTβ1 in promoting polymerisation of the actin cytoskeleton in cells plated on fibronectin, as evidenced by more intense labelling with phalloidin (Figure 2A). Adhesion of transgenic keratinocytes was markedly reduced by incubation with the anti-human β1 antibody P5D2. In contrast, P5D2 had no effect on transgene-negative keratinocytes (Figure 2D).
Keratinocyte adhesion and spreading on laminin-10 were similar in transgene-negative and positive keratinocytes, as predicted because of the role of α6β4 (1) (Figure 2D). Nevertheless, the transgene-encoded β1 integrins did contribute, since adhesion of transgenic keratinocytes to laminin-10 could be partially inhibited by P5D2 (Figure 2D).
The T188Iβ1 integrin mutation does not disturb epidermal organisation or homeostasis
Comparison of the histology of adult back skin from transgenic mice and transgene-negative littermate controls did not reveal any differences in the interfollicular epidermis (IFE), hair follicles (HF) or sebaceous glands (SG), and there was no evidence of a dermal inflammatory infiltrate (Figure 3A). Proliferation was evaluated by staining sections of adult back skin for Ki67 (data not shown) and by measuring BrdU incorporation into S phase cells in tail epidermal whole mounts (Figure 3B). K14WTβ1 and K14T188Iβ1 transgenic mice exhibited a similar number of proliferative cells in the back and tail interfollicular epidermis and hair follicles to transgene-negative littermates.
Figure 3. Transgene expression does not affect epidermal proliferation or result in expansion of the stem cell compartment.
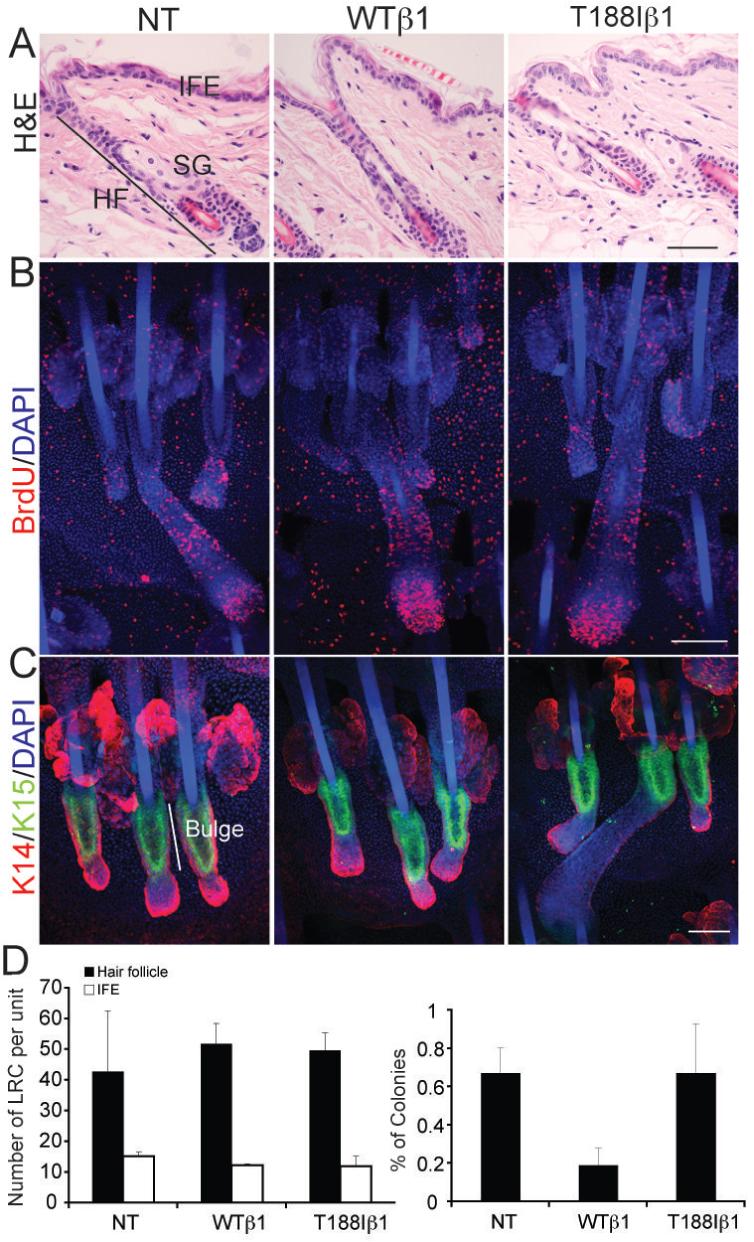
(A) H&E stained sections of adult mouse dorsal skin. IFE: interfollicular epidermis; SG: sebaceous gland; HF: hair follicle. (B, C) Adult tail epidermal whole mounts labelled with anti-BrdU to detect S-phase cells (red; B) or K15 (green; C) with DAPI nuclear counterstain (blue). Double labelling for keratin 14 (red; C) reveals epidermal morphology. Scale bars: 100 μm (A-C). (D) Quantitation of DNA label retaining cells (LRC) per epidermal unit (28) (left hand panel) and % colony forming cells (right hand panel). LRC in hair follicles and interfollicular epidermis (IFE) are shown separately. Data are average number of LRC in five epidermal units per mouse from three mice per genotype (+ standard deviation). Colony forming efficiency is average of 6 wells per mouse, four mice per genotype ± standard deviation. NT: non-transgenic; WTβ1: K14WTβ1 transgenic; T188Iβ1: K14T188Iβ1 transgenic.
Keratin 15 (K15) and DNA label retention are markers of bulge stem cells (25, 32). No differences in K15 expression were observed between transgenic and non-transgenic epidermis examined in whole mount preparations of tail (Figure 3C). In addition, there were no differences in the number of label retaining cells, either within the hair follicles or interfollicular epidermis (Figure 3D).
As a further stem cell assay, we determined the colony forming efficiency of primary adult transgene-positive and -negative keratinocytes in culture (Figure 3D) (33). Whereas cells from non-transgenic and K14T188Iβ1 mice gave rise to a similar percentage of colonies, keratinocytes from K14WTβ1 mice had a lower ability to form colonies (Figure 3D).
WTβ1 and T188Iβ1 transgene expression stimulates papilloma development
To determine whether the T188Iβ1 integrin mutation influenced skin carcinogenesis, transgenic mice and their respective transgene-negative littermates were subjected to two-stage carcinogenesis with DMBA (to induce Ha-Ras mutations) and TPA (to promote tumour formation) (17) (Figure 4). Macroscopically, papillomas were identified as pedunculated or sessile mushroom-like lesions, while SCCs presented as ‘craters’ with signs of dermal ingrowth.
Figure 4. Papillomas and SCCs induced by chemical carcinogenesis.
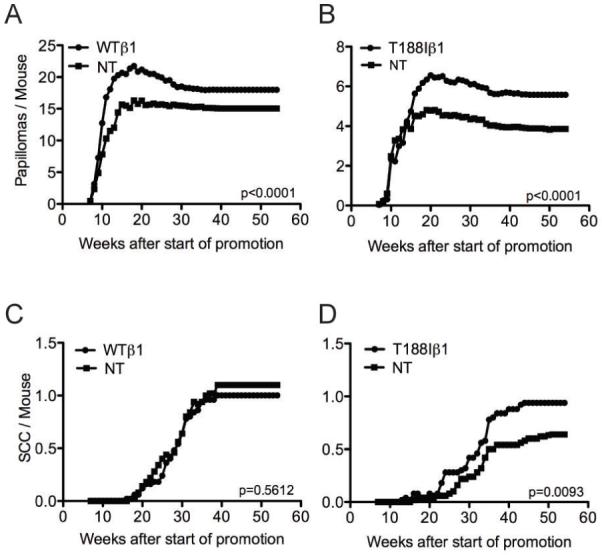
Number of papillomas (A, B) or malignant tumours (SCC) (C, D) per mouse is shown relative to start of promotion with TPA. (A, C) K14WTβ1 transgenic mice (WTβ1) and transgene-negative littermate controls (NT). (B, D) K14T188Iβ1 transgenic mice (T188Iβ1) and transgene-negative littermate controls (NT). Data pooled from two replicate experiments, each with starting cohort of 25 mice per group. P values (unpaired two-tailed student’s t-test) show difference between transgenic and non-transgenic mice.
Papillomas first emerged in all groups between 7 and 11 weeks after the start of TPA promotion, and the maximum number of papillomas was reached by 20 weeks (Figure 4A, B and data not shown). No papillomas developed in mice treated with DMBA or TPA only (data not shown).
The proportion of mice that developed papillomas was not increased by expression of either transgene (29/50 for T188I versus 32/50 for NT; 46/50 for WT versus 50/50 for NT). However, both K14WTβ1 and K14T188Iβ1 transgenic mice developed significantly more papillomas than non-transgenic mice (Student’s t-test, p<0.0001) (Figure 4A, B).
The T188Iβ1 integrin mutation stimulates malignant conversion
In K14WTβ1 mice and non-transgenic littermates SCC first emerged between 16 and 20 weeks, reaching a plateau by 40 weeks (Figure 4C). There was no significant difference in the number of SCCs in K14WTβ1 transgenic and transgene-negative mice (Student’s t-test, p=0.5612). In addition, the wild-type transgene did not increase SCC incidence (29/50 for WTβ1; 36/50 for NT).
K14T188Iβ1 transgenic mice started to develop SCC three weeks earlier than non-transgenic and K14WTβ1 transgenic mice, exhibiting malignancies by week 16 after the start of TPA promotion (Figure 4D). Whereas both transgenes stimulated papilloma formation (Figure 4A, B), only K14T188Iβ1 transgenic mice developed more SCC than littermate controls (Student’s t-test, p=0.0093). The incidence of SCC was also higher in K14T188Iβ1 mice than in the NT controls (32/50 for T188Iβ1; 26/50 for NT).
Metastasis is increased in transgenic mice
The reproductive tract, liver, lung, spleen and lymph nodes of mice from the chemical carcinogenesis experiments were screened histologically for the presence of tumour cells. Both transgenes stimulated lymph node metastasis. In the K14T188Iβ1 group 14/50 mice developed metastases, whereas 8/50 littermate controls developed metastases. 13/50 K14WTβ1 mice developed metastases, compared to 8/50 controls.
T188Iβ1 papillomas are less highly differentiated than WTβ1 papillomas
Papillomas were scored as well or poorly differentiated on the basis of whether or not they contained a high proportion of cornified cells (Figure 5A, B). In well differentiated papillomas the boundary between the basal layer and the adjacent stroma was clearly defined, whereas in poorly differentiated papillomas there were often regions in which the basal cell layer invaded the stroma (Figure 5A). The basement membrane was intact in both categories of papillomas, but laminin deposition was more diffuse in the regions of basal layer disturbance (Figure 5A). At 20-30 weeks after DMBA treatment, the time when conversion to SCC occurs (Figure 4C, D), the proportion of well differentiated papillomas was significantly lower in K14T188Iβ1 mice (total number of papillomas examined: n=42 total) than in K14WTβ1 mice (n=44) and transgene-negative littermates (n=110) (Figure 4B; Pearson’s chi-square test).
Figure 5. Papilloma differentiation.
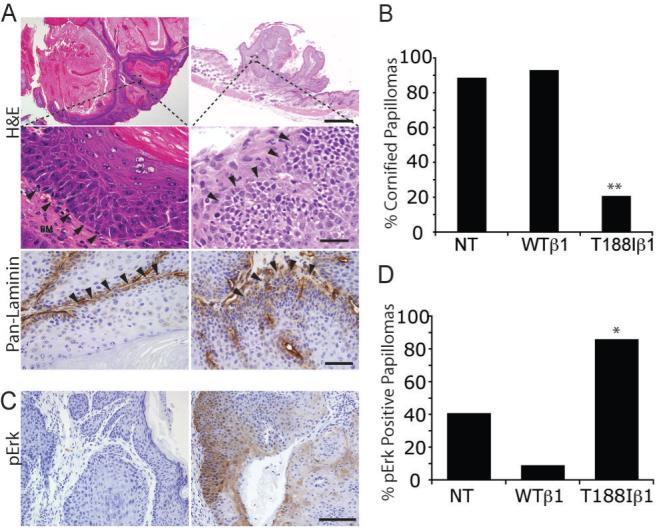
(A, C) Sections of papillomas stained with H&E (A, upper and middle panels), anti-laminin (brown; A, lower panels) or anti-phospho Erk (brown; C) with haematoxylin counterstain. Middle panels in (A) are higher magnification views of regions in upper panels. Left hand panels in (A): well differentiated papillomas. Right hand panels: poorly differentiated papillomas. Boundary between epithelium and stroma indicated by arrowheads. Scale bars: 200 μm (A), 100 μm (C). (B) Quantitation of % well differentiated papillomas 20-30 weeks after start of promotion (number of papillomas examined: 110 (NT), 44 (WTβ1), 42 (T188Iβ1) and (D) phospho Erk positive papillomas (total examined: 152 (NT); 68 (WTβ1); 43 (T188Iβ1). NT: non-transgenic WTβ1: K14WTβ1 transgenic; T188Iβ1: K14T188Iβ1 transgenic. Statistical analysis was performed using the Pearson’s chi-square test. * indicates p < 0.01; ** indicates p<0.001.
In cultured keratinocytes integrin signalling through Erk/MAPK suppresses terminal differentiation (5, 34). To investigate whether Erk/MAPK signalling was influenced by the T188I mutant in vivo, we immunostained sections with an antibody to phosphoErk (pErk) (Figure 5C, D). Between 60% and 90% of the papillomas that developed in non-transgenic (total number of papillomas examined: n=152) and K14WTβ1 transgenic mice (n=68) were negative for pErk, while approximately 90% (n=43) of the T188Iβ1 papillomas were positive (Figure 5D; Pearson’s chi-square test).
K14T188Iβ1 transgenics are more likely to develop poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinomas than K14WTβ1 and non-transgenic mice
All the SCCs from every tumour-bearing mouse in the chemical carcinogenesis experiments were assigned to one of four categories (Figure 6A), based on Broders’ classification (17). Undifferentiated tumours (spindle cell carcinomas) contained cells of fibroblastic morphology (Broders’ grade 4). Well (grade 1), moderately (grade 2) and poorly (grade 3) differentiated tumours had a decreasing proportion of differentiated cells (Figure 6A). In undifferentiated tumours there were proliferating, Ki67 positive, cells throughout the tumour mass (Figure 6B). There was also widespread proliferation in the poorly differentiated tumours (Figure 6B), whereas in the moderately and well differentiated tumours proliferation was confined to the cell layers closest to the tumour stroma (Figure 6B).
Figure 6. Different types of malignant tumour.
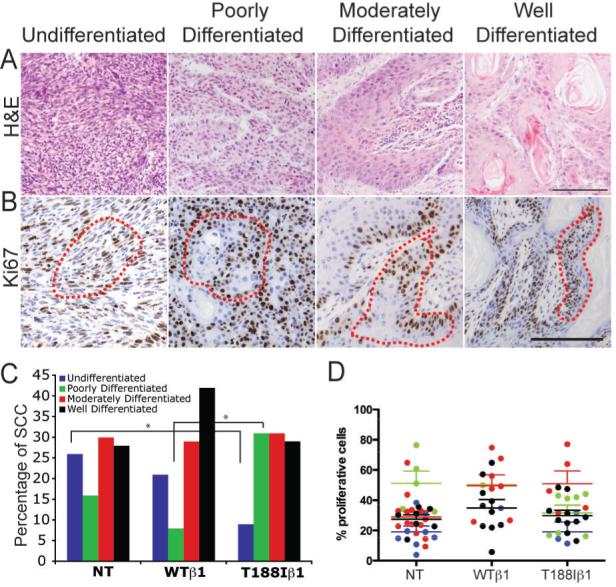
Sections of malignant tumours labelled with H&E (A) or anti-Ki67 (brown) with haematoxylin counterstain (B). Red dotted lines in (B) demarcate proliferative regions quantitated in (D). Scale bars: 100 μm. (C, D) Quantitation of proportion of each tumour type (C) and % Ki67 positive cells within the proliferative regions of each tumour type (D). NT: non-transgenic WTβ1: K14WTβ1 transgenic; T188Iβ1: K14T188Iβ1 transgenic. * indicates p < 0.05 (Pearson’s chi-square test).
The frequency of undifferentiated (spindle) tumours was higher in K14WTβ1 transgenic (number of SCC analysed: n=24) and non-transgenic mice (n=50) than in K14T188Iβ1 transgenics (n=35) (Pearson’s chi-square test) (Figure 6C). In contrast, the frequency of poorly differentiated tumours was significantly higher in K14T188Iβ1 transgenics (Figure 6C).
Although the distribution of proliferating cells differed between the different tumour types (Figure 6B), the proportion of proliferating cells within the Ki67 positive regions (demarcated in Figure 6B) did not differ significantly between tumour types nor between transgenic and transgene-negative mice (Figure 6D). This suggests that the effect of the T188I mutation is primarily on tumour differentiation rather than on proliferation.
Discussion
We have developed an in vivo model to examine the effect of a tumour-associated integrin. Expression of the T188I mutation did not affect normal skin architecture or homeostasis, but did increase the susceptibility of the epidermis to developing malignant tumours and also reduced tumour differentiation.
The transgenic human β1 integrins, were co-expressed with endogenous mouse β1 at the cell surface, were functional in mediating extracellular matrix adhesion, and had the same turnover time as the endogenous mouse β1 integrins. The T188I mutation enhanced Erk MAPK signalling and actin cytoskeletal assembly, and promoted cell spreading on low fibronectin concentrations to a greater extent than the wild-type subunit (20).
In comparison to transgene-negative mice, there was no change in proliferation and no evidence for any disruption of normal skin architecture or homeostasis in the K14WTβ1 and K14T188Iβ1 transgenics. This was unexpected because high integrin expression is an epidermal stem cell marker (2-4) and integrins regulate keratinocyte growth and differentiation (5, 20, 35-38). Thus whereas integrin-mediated adhesion is required for maintenance of the epidermal stem cell niche, β1 integrin activation is not sufficient to expand the stem cell compartment.
Expression of either the wild-type or mutant β1 transgene resulted in increased development of papillomas and increased lymph node metastases. This is consistent with reports that β1 integrin deletion impairs tumour initiation and maintenance (39). The positive effect of the transgenic integrins on papilloma development does not reflect simple overexpression of β1 integrins at the cell surface (Figure 2) (30). Instead it is likely to reflect the fact that the K14 promoter is not subject to the same negative regulation as the endogenous mouse β1 promoter (10, 24).
Three effects were selectively attributable to the T188I mutant integrin: more rapid conversion of papillomas to SCCs; a higher conversion frequency; and a higher proportion of poorly differentiated tumours. Expression of T188Iβ1 reduced differentiation in both the papillomas and SCCs, without affecting proliferation in the SCCs. This is consistent with the observation that the T188I mutation was found in a poorly differentiated SCC and that it has an impaired ability to trigger initiation of terminal differentiation of keratinocytes in culture (20).
One surprising effect of the T188I mutation was that it reduced the number of spindle cell tumours. These tumours are believed to arise from SCCs by a process of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (40). It is possible that this requires downregulation of extracellular matrix adhesion, which would be inhibited by the T188Iβ1 integrin transgene. The T188I mutation may prevent the changes in actin cytoskeletal assembly associated with spindle cell tumour formation (41). Alternatively, expression of the mutant integrin may decrease responsiveness to TGFβ (18, 19, 42, 43) or negatively regulate metalloproteinase expression (44), both of which are implicated in formation of spindle cell tumours.
K14T188Iβ1 papillomas had high levels of phosphoErk (Figure 5), which is likely to contribute to their reduced differentiation, and expression of T188Iβ1 enhanced Erk/MAPK signalling in vitro (Figure 2B; 5, 20). β1 integrin signalling through Erk/MAPK is associated with maintenance of the stem cell compartment in cultured human epidermis (5, 16, 34) and is linked to papilloma development in transgenic mice (16, 45). It is possible that activation of other signals, such as focal adhesion kinase (46), also contribute to the effect of T188I, although in cultured keratinocytes we have not observed a correlation between β1 integrin mediated adhesion and focal adhesion kinase activity (5).
Our data demonstrate that tumour-associated integrin mutations and polymorphisms have the potential to influence cancer susceptibility and disease outcome. While the tumour-associated integrin mutations are relatively rare, common integrin polymorphisms are associated with a range of other diseases, such as SLE (47, 48). Our studies indicate that it will be worthwhile to develop mouse models of additional integrin polymorphisms.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by CR-UK; the Fundacão para a Ciência e Tecnologia (MF); and the Uehara Memorial Foundation (HF). We are deeply grateful to Ian Rosewell, Rob Rudling, Richard Poulsom, Will Howatt and other staff at the CR-UK London and Cambridge Research Institutes for advice and expert technical assistance. We acknowledge the support of the University of Cambridge and Hutchison Whampoa Ltd.
Abbreviations
- DMBA
7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene
- HF
hair follicle
- IFE
Interfollicular epidermis
- K14
keratin 14
- NT
non-transgenic
- SCC
squamous cell carcinoma
- SG
sebaceous gland
- SLE
systemic lupus erythematosus
- TPA
12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate
Footnotes
References
- 1.Watt FM. Role of integrins in regulating epidermal adhesion, growth and differentiation. Embo J. 2002;21:3919–26. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdf399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Jones PH, Watt FM. Separation of human epidermal stem cells from transit amplifying cells on the basis of differences in integrin function and expression. Cell. 1993;73:713–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90251-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jones PH, Harper S, Watt FM. Stem cell patterning and fate in human epidermis. Cell. 1995;80:83–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90453-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Jensen UB, Lowell S, Watt FM. The spatial relationship between stem cells and their progeny in the basal layer of human epidermis: a new view based on whole-mount labelling and lineage analysis. Development. 1999;126:2409–18. doi: 10.1242/dev.126.11.2409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zhu AJ, Haase I, Watt FM. Signaling via β1 integrins and mitogen-activated protein kinase determines human epidermal stem cell fate in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96:6728–33. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.12.6728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Janes SM, Watt FM. Switch from αvβ5 to αvβ6 integrin expression protects squamous cell carcinomas from anoikis. J Cell Biol. 2004;166:419–31. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200312074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Adams JC, Watt FM. Fibronectin inhibits the terminal differentiation of human keratinocytes. Nature. 1989;340:307–9. doi: 10.1038/340307a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Levy L, Broad S, Diekmann D, Evans RD, Watt FM. β1 integrins regulate keratinocyte adhesion and differentiation by distinct mechanisms. Mol Biol Cell. 2000;11:453–66. doi: 10.1091/mbc.11.2.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Benitah SA, Frye M, Glogauer M, Watt FM. Stem cell depletion through epidermal deletion of Rac1. Science. 2005;309:933–5. doi: 10.1126/science.1113579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Watt FM, Frye M, Benitah SA. MYC in mammalian epidermis: how can an oncogene stimulate differentiation? Nature Reviews Cancer. 2007;8:234–42. doi: 10.1038/nrc2328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Guo W, Giancotti FG. Integrin signalling during tumour progression. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:816–26. doi: 10.1038/nrm1490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Brakebusch C, Fassler R. β1 integrin function in vivo: adhesion, migration and more. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2005;24:403–11. doi: 10.1007/s10555-005-5132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Janes SM, Watt FM. New roles for integrins in squamous-cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:175–83. doi: 10.1038/nrc1817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wilhelmsen K, Litjens SH, Sonnenberg A. Multiple functions of the integrin α6β4 in epidermal homeostasis and tumorigenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26:2877–86. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.8.2877-2886.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hobbs RM, Watt FM. Regulation of interleukin-1α expression by integrins and epidermal growth factor receptor in keratinocytes from a mouse model of inflammatory skin disease. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:19798–807. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M300513200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hobbs RM, Silva-Vargas V, Groves R, Watt FM. Expression of activated MEK1 in differentiating epidermal cells is sufficient to generate hyperproliferative and inflammatory skin lesions. J Invest Dermatol. 2004;123:503–15. doi: 10.1111/j.0022-202X.2004.23225.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Owens DM, Watt FM. Influence of β1 integrins on epidermal squamous cell carcinoma formation in a transgenic mouse model: α3β1, but not α2β1, suppresses malignant conversion. Cancer Res. 2001;61:5248–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Owens DM, Broad S, Yan X, Benitah SA, Watt FM. Suprabasal α5β1 integrin expression stimulates formation of epidermal squamous cell carcinomas without disrupting TGFβ signaling or inducing spindle cell tumors. Mol Carcinog. 2005;44:60–6. doi: 10.1002/mc.20118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Owens DM, Romero MR, Gardner C, Watt FM. Suprabasal α6β4 integrin expression in epidermis results in enhanced tumourigenesis and disruption of TGFβ signalling. J Cell Sci. 2003;116:3783–91. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Evans RD, Perkins VC, Henry A, Stephens PE, Robinson MK, Watt FM. A tumor-associated β1 integrin mutation that abrogates epithelial differentiation control. J Cell Biol. 2003;160:589–96. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200209016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Takagi J, Kamata T, Meredith J, Puzon-McLaughlin W, Takada Y. Changing ligand specificities of αvβ1 and αvβ3 integrins by swapping a short diverse sequence of the beta subunit. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:19794–800. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.32.19794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Luo BH, Carman CV, Springer TA. Structural basis of integrin regulation and signaling. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:619–47. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.25.022106.141618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Evans RD, Jones J, Taylor C, Watt FM. Sequence variation in the I-like domain of the β1 integrin subunit in human oral squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer Lett. 2004;213:189–94. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2004.05.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gebhardt A, Frye M, Herold S, et al. Myc regulates keratinocyte adhesion and differentiation via complex formation with Miz1. J Cell Biol. 2006;172:139–49. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200506057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Braun KM, Niemann C, Jensen UB, Sundberg JP, Silva-Vargas V, Watt FM. Manipulation of stem cell proliferation and lineage commitment: visualisation of label-retaining cells in wholemounts of mouse epidermis. Development. 2003;130:5241–55. doi: 10.1242/dev.00703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Carroll JM, Romero MR, Watt FM. Suprabasal integrin expression in the epidermis of transgenic mice results in developmental defects and a phenotype resembling psoriasis. Cell. 1995;83:957–68. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Adams JC, Watt FM. Changes in keratinocyte adhesion during terminal differentiation: reduction in fibronectin binding precedes α5β1 integrin loss from the cell surface. Cell. 1990;63:425–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90175-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Silva-Vargas V, Lo Celso C, Giangreco A, et al. Beta-catenin and Hedgehog signal strength can specify number and location of hair follicles in adult epidermis without recruitment of bulge stem cells. Dev Cell. 2005;9:121–31. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2005.04.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Owens DM, Watt FM. Contribution of stem cells and differentiated cells to epidermal tumours. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:444–51. doi: 10.1038/nrc1096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Levy L, Broad S, Zhu AJ, et al. Optimised retroviral infection of human epidermal keratinocytes: long-term expression of transduced integrin gene following grafting on to SCID mice. Gene Ther. 1998;5:913–22. doi: 10.1038/sj.gt.3300689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hotchin NA, Watt FM. Transcriptional and post-translational regulation of β1 integrin expression during keratinocyte terminal differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:14852–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Cotsarelis G. Epithelial stem cells: a folliculocentric view. J Invest Dermatol. 2006;126:1459–68. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5700376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Popova NV, Tryson KA, Wu KQ, Morris RJ. Evidence that the keratinocyte colony number is genetically controlled. Exp Dermatol. 2002;11:503–8. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0625.2002.110602.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Haase I, Hobbs RM, Romero MR, Broad S, Watt FM. A role for mitogen-activated protein kinase activation by integrins in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. J Clin Invest. 2001;108:527–36. doi: 10.1172/JCI12153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Brakebusch C, Grose R, Quondamatteo F, et al. Skin and hair follicle integrity is crucially dependent on β 1 integrin expression on keratinocytes. Embo J. 2000;19:3990–4003. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.15.3990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Raghavan S, Bauer C, Mundschau G, Li Q, Fuchs E. Conditional ablation of β1 integrin in skin. Severe defects in epidermal proliferation, basement membrane formation, and hair follicle invagination. J Cell Biol. 2000;150:1149–60. doi: 10.1083/jcb.150.5.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lopez-Róvira T, Silva-Vargas V, Watt FM. Different consequences of β1 integrin deletion in neonatal and adult mouse epidermis reveal a context-dependent role of integrins in regulating proliferation, differentiation, and intercellular communication. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;125:1215–27. doi: 10.1111/j.0022-202X.2005.23956.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Taddei I, Deugnier MA, Faraldo MM, et al. β1 integrin deletion from the basal compartment of the mammary epithelium affects stem cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10:716–22. doi: 10.1038/ncb1734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.White DE, Kurpios NA, Zuo D, et al. Targeted disruption of β1-integrin in a transgenic mouse model of human breast cancer reveals an essential role in mammary tumor induction. Cancer Cell. 2004;6:159–70. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2004.06.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Stoler AB, Stenback F, Balmain A. The conversion of mouse skin squamous cell carcinomas to spindle cell carcinomas is a recessive event. J Cell Biol. 1993;122:1103–17. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.5.1103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Psichari E, Balmain A, Plows D, Zoumpourlis V, Pintzas A. High activity of serum response factor in the mesenchymal transition of epithelial tumor cells is regulated by RhoA signaling. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:29490–5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112368200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Reynolds LE, Conti FJ, Silva R, et al. α3β1 integrin-controlled Smad7 regulates reepithelialization during wound healing in mice. J Clin Invest. 2008;118:965–74. doi: 10.1172/JCI33538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Cui W, Fowlis DJ, Bryson S, et al. TGFβ1 inhibits the formation of benign skin tumors, but enhances progression to invasive spindle carcinomas in transgenic mice. Cell. 1996;86:531–42. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80127-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Papathoma AS, Zoumpourlis V, Balmain A, Pintzas A. Role of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in progression of mouse skin carcinogenesis. Mol Carcinog. 2001;31:74–82. doi: 10.1002/mc.1042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Scholl FA, Dumesic PA, Khavari PA. Mek1 alters epidermal growth and differentiation. Cancer Res. 2004;64:6035–40. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.McLean GW, Komiyama NH, Serrels B, et al. Specific deletion of focal adhesion kinase suppresses tumor formation and blocks malignant progression. Genes Dev. 2004;18:2998–3003. doi: 10.1101/gad.316304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Nath SK, Han S, Kim-Howard X, et al. A nonsynonymous functional variant in integrin-alpha(M) (encoded by ITGAM) is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet. 2008;40:152–4. doi: 10.1038/ng.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Harley JB, Alarcon-Riquelme ME, Criswell LA, et al. Genome-wide association scan in women with systemic lupus erythematosus identifies susceptibility variants in ITGAM, PXK, KIAA1542 and other loci. Nat Genet. 2008;40:204–10. doi: 10.1038/ng.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


