Abstract
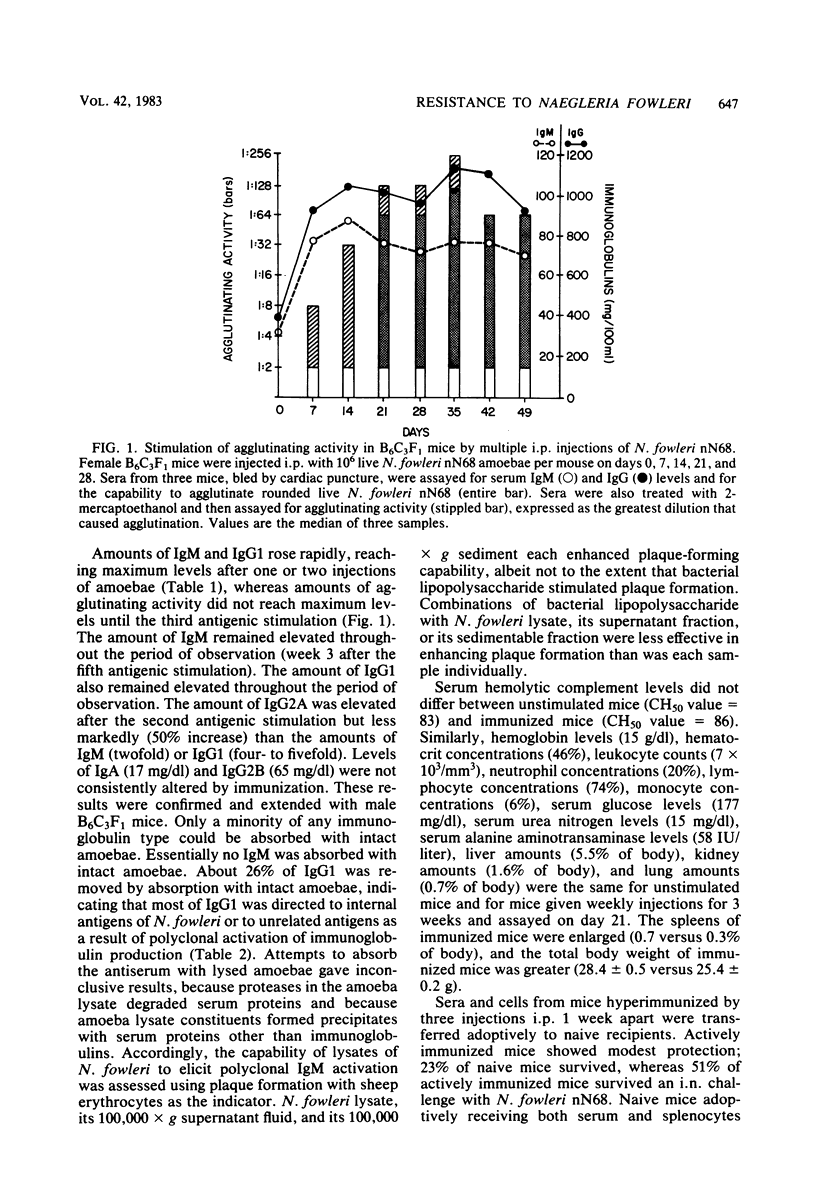
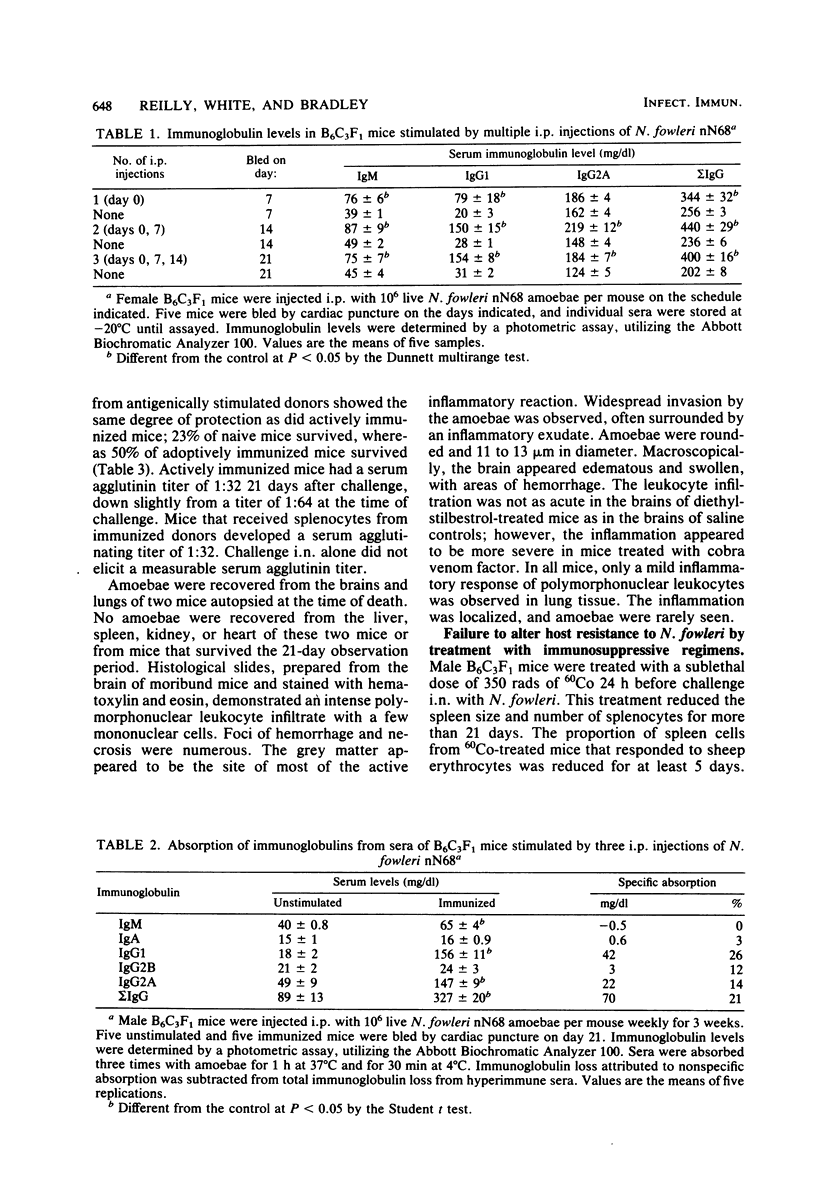
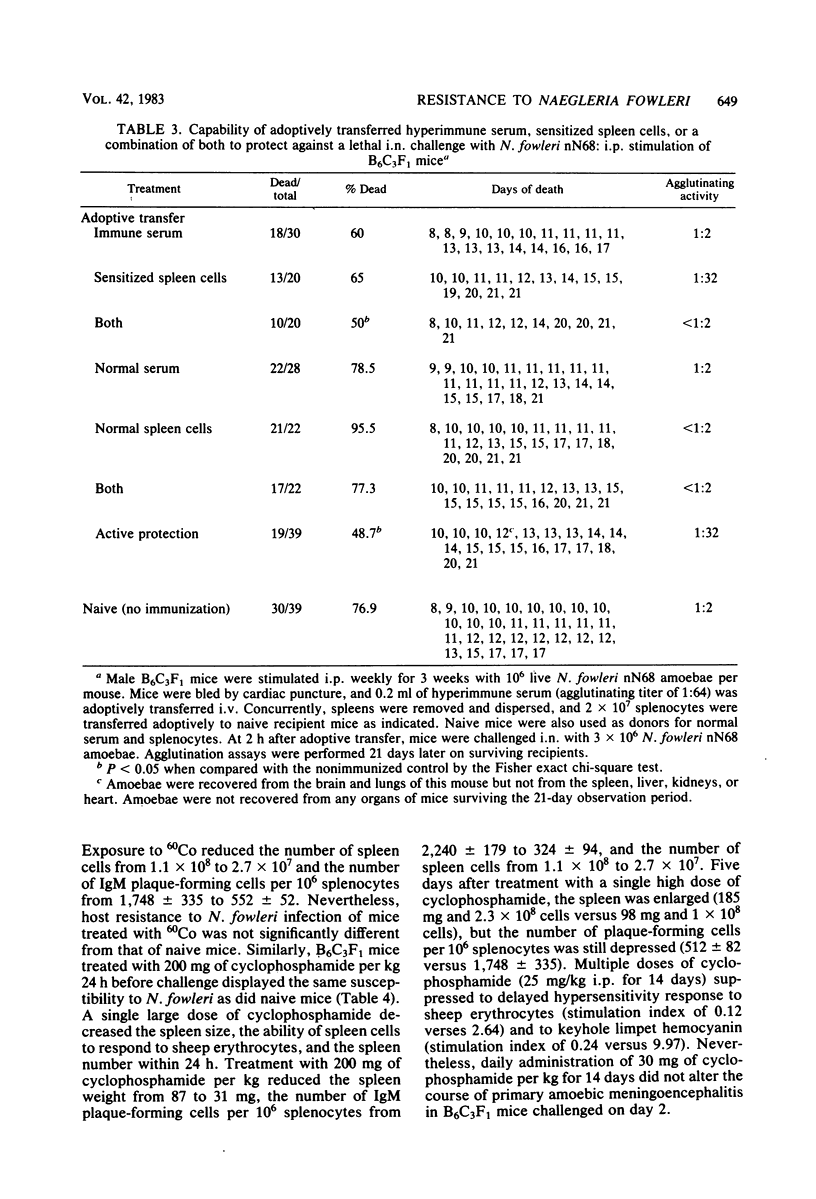
Naegleria fowleri is an etiological agent of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis in humans and laboratory animals. The determinative factors in host resistance of mice to N. fowleri infections have not been fully characterized. Male or female B6C3F1 mice stimulated by intraperitoneal administration of 10(6) amoebae of N. fowleri nN68 per mouse produced agglutinating activity and markedly elevated levels of serum and immunoglobulins M and G. Despite a marked humoral response, protective immunity was increased only marginally by active immunization. Host resistance was not impaired by prior treatment with 350 rads of 60Co radiation or 200 mg of cyclophosphamide per kg or by concurrent daily treatment with 30 mg of cyclophosphamide per kg for 14 days. Moreover, host resistance was not impaired by daily treatment with 4 mg of diethylstilbestrol per kg for 14 days, with challenge on day 2 of drug exposure or 24 h after the last drug treatment. Mice depleted of hemolytic complement by cobra venom factor were more susceptible to N. fowleri infection than were untreated mice.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams A. C., John D. T., Bradley S. G. Modification of resistance of mice to Naegleria fowleri infections. Infect Immun. 1976 May;13(5):1387–1391. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.5.1387-1391.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K., Jamieson A. Agglutination test for the investigation of the genus Naegleria. Pathology. 1972 Oct;4(4):273–278. doi: 10.3109/00313027209068953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley S. G., Bond J. S. Toxicity, clearance, and metabolic effects of pactamycin in combination with bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1975 Feb;31(2):208–221. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(75)90157-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter R. F. Description of a Naegleria sp. isolated from two cases of primary amoebic meningo-encephalitis, and of the experimental pathological changes induced by it. J Pathol. 1970 Apr;100(4):217–244. doi: 10.1002/path.1711000402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline M., Marciano-Cabral F., Bradley S. G. Comparison of Naegleria fowleri and Naegleria gruberi cultivated in the same nutrient medium. J Protozool. 1983 May;30(2):387–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1983.tb02936.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham D. S., Kuhn R. E. Trypanosoma cruzi-induced suppressor substance III. Activation of suppressor cells. J Parasitol. 1980 Dec;66(6):881–887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cursons R. T., Brown T. J., Keys E. A., Moriarty K. M., Till D. Immunity to pathogenic free-living amoebae: role of cell-mediated immunity. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):408–410. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.408-410.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cursons R. T., Brown T. J., Keys E. A., Moriarty K. M., Till D. Immunity to pathogenic free-living amoebae: role of humoral antibody. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):401–407. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.401-407.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Thong Y. H. Antibody induced capping and endocytosis of surface antigens in Naegleria fowleri. Int J Parasitol. 1979 Dec;9(6):599–601. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(79)90018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haggerty R. M., John D. T. Innate resistance of mice to experimental infection with Naegleria fowleri. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):73–77. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.73-77.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haggerty R. M., John D. T. Serum agglutination and immunoglobulin levels of mice infected with Naegleria fowleri. J Protozool. 1982 Feb;29(1):117–122. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1982.tb02892.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haight J. B., John D. T. Growth of Naegleria fowleri in several axenic media. Folia Parasitol (Praha) 1980;27(3):207–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook T. W., Boackle R. J., Parker B. W., Vesely J. Activation of the alternative complement pathway by Naegleria fowleri. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):58–61. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.58-61.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John D. T. Primary amebic meningoencephalitis and the biology of Naegleria fowleri. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:101–123. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John D. T., Weik R. R., Adams A. C. Immunization of mice against Naegleria fowleri infection. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):817–820. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.817-820.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIM Y. B., BRADLEY S. G., WATSON D. W. CHARACTERIZATION OF EARLY 19 S AND LATE 7 S IMMUNOGLOBULINS IN THE MOUSE. J Immunol. 1964 Nov;93:798–806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karch H., Gmeiner J., Nixdorff K. Alteration of the immunoglobulin G subclass responses in mice to lipopolysaccharide: effects of nonbacterial proteins and bacterial membrane phospholipids or outer membrane proteins of Proteus mirabilis. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):157–165. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.157-165.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leijh P. C., van den Barselaar M. T., Daha M. R., van Furth R. Participation of immunoglobulins and complement components in the intracellular killing of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli by human granulocytes. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):714–724. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.714-724.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luster M. I., Boorman G. A., Dean J. H., Luebke R. W., Lawson L. D. The effect of adult exposure to diethylstilbestrol in the mouse: alterations in immunological functions. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1980 Dec;28(6):561–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciano-Cabral F. M., Patterson M., John D. T., Bradley S. G. Cytopathogenicity of Naegleria fowleri and Naegleria gruberi for established mammalian cell cultures. J Parasitol. 1982 Dec;68(6):1110–1116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez A. J., Nelson E. C., Duma R. J. Animal model of human disease. Primary amebic meningoencephalitis, Naegleria meningoencephalitis, CNS protozoal infection. Am J Pathol. 1973 Nov;73(2):545–548. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez J., Duma R. J., Nelson E. C., Moretta F. L. Experimental naegleria meningoencephalitis in mice. Penetration of the olfactory mucosal epithelium by Naegleria and pathologic changes produced: a light and electron microscope study. Lab Invest. 1973 Aug;29(2):121–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Playfair J. H. Effective and ineffective immune responses to parasites: evidence from experimental models. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;80:37–64. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66956-9_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly M. F., Bradley M. K., Bradley S. G. Agglutination of Naegleria fowleri by human serum. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1982 Jun;170(2):209–212. doi: 10.3181/00379727-170-41420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly M. F., Marciano-Cabral F., Bradley D. W., Bradley S. G. Agglutination of Naegleria fowleri and Naegleria gruberi by antibodies in human serum. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;17(4):576–581. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.4.576-581.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowan-Kelly B., Ferrante A., Thong Y. H. Activation of complement by Naegleria. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1980;74(3):333–336. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(80)90092-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simione F. P., Jr, Daggett P. M. Freeze preservation of pathogenic and nonpathogenic Naegleria species. J Parasitol. 1976 Feb;62(1):49–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thong Y. H., Ferrante A., Shepherd C., Rowan-Kelly B. Resistance of mice to Naegleria meningoencephalitis transferred by immune serum. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(6):650–652. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong M. M., Karr S. L., Jr, Balamuth W. B. Experimental infections with pathogenic free-living amebae in laboratory primate hosts: I (A) A study on susceptibility to Naegleria fowleri. J Parasitol. 1975 Apr;61(2):199–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodworth T. W., Keefe W. E., Bradley S. G. Characterization of proteins in flagellates and growing amebae of Naegleria fowleri. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1366–1374. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1366-1374.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


