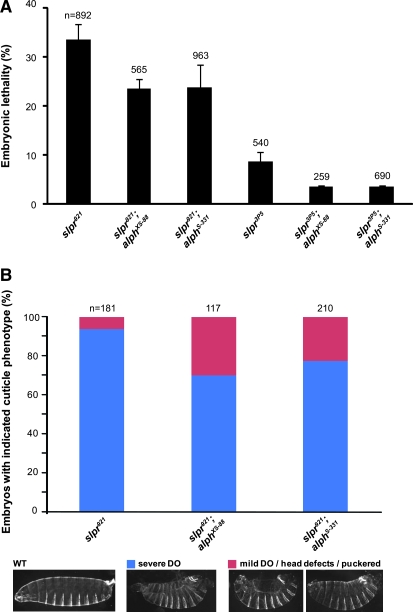
Figure 2.—
alph alleles suppress the dorsal open phenotype of mutant slpr embryos. (A) Embryonic lethality expressed as the mean percentage (%) ± standard deviation is shown for two slpr alleles tested either alone or in combination with two alph alleles. The total number (n) of embryos analyzed per genotype is indicated on top of its respective bar. Statistical significance was confirmed by conducting a two-tailed Student's t-test where P-values were at least <0.007. (B) Dead embryos of the indicated genotypes were scored for dorsal open (DO) phenotypes and head defect/puckered phenotypes, which are characteristic of impaired JNK signaling. The number of severe DO (blue) embryos were then compared to those that have mild DO or minor head defects and puckering (red). The relative proportion of the two categories per genotype is displayed as a percentage. (Bottom) Representative embryonic phenotypes compared to those of wild type (WT). The total number (n) of embryos analyzed per genotype is indicated on top of their respective bar. A Student's t-test confirmed the statistical significance of the difference between slpr921 alone and slpr921;alph alleles: P < 0.025.