Abstract
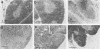
Thymocytes from mice 2 weeks after infection with Toxoplasma gondii resisted natural killer (NK) cell-mediated cytolysis in contrast to the high sensitivity of normal mouse thymocytes. The infected mouse thymocytes also failed to form conjugates with effector cells and to compete for cytolysis of NK sensitive targets. These effects were mediated, at least in part, by interferon-gamma because normal thymocytes became NK insensitive after incubation in the infected mouse serum which contained significant amount of interferon-gamma, and pH 2 treatment of the serum abolished the effect. An alternate possibility for the reduced NK sensitivity of the infected mouse thymocytes was the elimination of NK-sensitive cells from the thymus, since histopathological studies showed marked atrophy and clearance of NK-sensitive thymocytes in the cortex of thymuses of infected mice. Although T. gondii induced augmentation followed by suppression of the host splenic NK activity, it seems unlikely that this altered NK activity was responsible for the lowered NK sensitivity of the thymocytes.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biron C. A., Welsh R. M. Activation and role of natural killer cells in virus infections. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1982;170(3):155–172. doi: 10.1007/BF02298196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennert G., Yogeeswaran G., Yamagata S. Cloned cell lines with natural killer activity. Specificity, function, and cell surface markers. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):545–556. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djeu J. Y., Heinbaugh J. A., Holden H. T., Herberman R. B. Augmentation of mouse natural killer cell activity by interferon and interferon inducers. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):175–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson M., Kiessling R., Andersson B., Kärre K., Roder J. NK cell-sensitive T-cell subpopulation in thymus: inverse correlation to host NK activity. Nature. 1979 Mar 8;278(5700):174–176. doi: 10.1038/278174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson M., Kiessling R., Andersson B., Welsh R. M. Effect of interferon and interferon inducers on the NK sensitivity of normal mouse thymocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Nov;125(5):2225–2231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson M., Kärre K., Kiessling R., Roder J., Andersson B., Häyry P. Natural NK-cell targets in the mouse thymus: characteristics of the sensitive cell population. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):765–771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatcher F. M., Kuhn R. E., Cerrone M. C., Burton R. C. Increased natural killer cell activity in experimental American trypanosomiasis. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1126–1130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser W. E., Jr, Sharma S. D., Remington J. S. Natural killer cells induced by acute and chronic toxoplasma infection. Cell Immunol. 1982 May 15;69(2):330–346. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90076-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet C., Gresser I., Bandu M. T., Lindahl P. Increased binding of concanavalin A to interferon-treated murine leukemia L 1210 cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Oct;147(1):52–57. doi: 10.3181/00379727-147-38279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huldt G., Gard S., Olovson S. G. Effect of Toxoplasma gondii on the thymus. Nature. 1973 Aug 3;244(5414):301–303. doi: 10.1038/244301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiyama T., Hagiwara T. Augmented followed by suppressed levels of natural cell-mediated cytotoxicity in mice infected with Toxoplasma gondii. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):628–636. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.628-636.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai M., Leclerc J. C., McVay-Boudreau L., Shen F. W., Cantor H. Direct evidence that natural killer cells in nonimmune spleen cell populations prevent tumor growth in vivo. J Exp Med. 1979 May 1;149(5):1260–1264. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.5.1260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E., Jr, Korant B. D. A cell surface alteration in mouse L cells induced by interferon. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):707–713. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90360-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krahenbuhl J. L., Remington J. S. The role of activated macrophages in specific and nonspecific cytostasis of tumor cells. J Immunol. 1974 Aug;113(2):507–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl P., Gresser I., Leary P., Tovey M. Interferon treatment of mice: enhanced expression of histocompatibility antigens on lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1284–1287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oie H. K., Buckler C. E., Uhlendorf C. P., Hill D. A., Baron S. Improved assays for a variety of interferons. 1. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Sep;140(4):1178–1181. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojo-Amaize E. A., Salimonu L. S., Williams A. I., Akinwolere O. A., Shabo R., Alm G. V., Wigzell H. Positive correlation between degree of parasitemia, interferon titers, and natural killer cell activity in Plasmodium falciparum-infected children. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2296–2300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelster B., Piekarski G., Suzuki N. Zur Histopathologie des Thymus der weissen Maus bei einer Infektion mit Toxoplasma gondii. Z Parasitenkd. 1976 Apr 30;49(2):113–125. doi: 10.1007/BF00382418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisner Y., Linker-Israeli M., Sharon N. Separation of mouse thymocytes into two subpopulations by the use of peanut agglutinin. Cell Immunol. 1976 Jul;25(1):129–134. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90103-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riccardi C., Santoni A., Barlozzari T., Herberman R. B. In vivo reactivity of mouse natural killer (NK) cells against normal bone marrow cells. Cell Immunol. 1981 May 1;60(1):136–143. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90254-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roder J. C., Kiessling R., Biberfeld P., Andersson B. Target-effector interaction in the natural killer (NK) cell system. II. The isolation of NK cells and studies on the mechanism of killing. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2509–2517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland G. T., Ahmed A., Sell K. W. Blastogenic response of Toxoplasma-infected mouse spleen cells to T- and B-cell mitogens. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Oct;22(1):167–176. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland G. T., Sayles P. C. Depressed antibody responses to a thymus-dependent antigen in toxoplasmosis. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):184–190. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.184-190.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Granato D., Perussia B. Interferon-induced resistance of fibroblasts to cytolysis mediated by natural killer cells: specificity and mechanism. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):335–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Santoli D. Anti-viral activity induced by culturing lymphocytes with tumor-derived or virus-transformed cells. Enhancement of human natural killer cell activity by interferon and antagonistic inhibition of susceptibility of target cells to lysis. J Exp Med. 1978 May 1;147(5):1314–1333. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.5.1314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M., Karre K., Hansson M., Kunkel L. A., Kiessling R. W. Interferon-mediated protection of normal and tumor target cells against lysis by mouse natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):219–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogeeswaran G., Fujinami R., Kiessling R., Welsh R. M. Interferon-induced alterations in sialic acid and glycoconjugates of L-929 cells. Virology. 1982 Sep;121(2):363–371. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90174-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]