Abstract
Previous studies have demonstrated that some endocrine consequences of long-term caloric restriction persist after weight restoration in human subjects. Here we evaluate effects of chronic food restriction in rats that were restricted to 70% of control kcal for 4 wk and subsequently weight restored. Measures were taken from rats at 80% (chronically restricted; CR), 90% (partially weight restored; PR), 100% (fully weight restored; FR), and after 4 wk at 100% body weight of controls (extended weight restored; ER). Plasma insulin and leptin were decreased, and ghrelin was increased in CR compared with controls. Leptin and ghrelin normalized with weight restoration at PR, FR, and ER; however, baseline insulin was not normalized until the ER state. Hypothalamic mRNA expression levels for proopiomelanocortin (POMC), agouti-related protein (AgRP), and neuropeptide Y (NPY) revealed significantly less POMC mRNA expression in CR and PR rats, and significantly less arcuate NPY mRNA in PR and FR. In the dorsomedial hypothalamus, CR, PR, and FR rats had significantly increased NPY expression that was not normalized until the ER state. In response to a test meal, insulin and ghrelin release patterns were altered through the FR stage, and ghrelin remained affected at ER. Collectively, these data demonstrate that mere weight restoration is not sufficient to normalize hypothalamic gene expression levels and endocrine responses to a meal, and that meal-related ghrelin responses persist despite weight restoration for up to 4 wk.
Keywords: ghrelin, insulin, leptin, hypothalamus
hypothalamic peptide signaling and peripheral hormones play important roles in the control of food intake and regulation of body weight. Ideally, these systems work in concert to promote food intake and reduce energy expenditure when energy stores are low, and to inhibit food intake and promote energy expenditure when excess energy is stored. Changes in energy balance, both in cases of deficit and surplus, result in a number of neuroendocrine effects that act to restore energy homeostasis. Whereas many central and peripheral factors have been characterized for animals maintained on high-calorie, high-fat diets, the effects of chronic caloric restriction are less clear. Many studies investigating the effects of caloric restriction with regard to neuroendocrine controls of food intake have done so by evaluating a single time point after an acute fast or short-term (<2 wk) caloric restriction.
Insulin, leptin, and ghrelin provide signals about adiposity to the brain and affect food intake (27–29, 45, 46). The basal hypothalamus integrates these signals and provides outputs critical to the control of ingestive behavior and energy expenditure. Within the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus, neuropeptide Y (NPY)/agouti-related protein (AgRP) and proopiomelanocortin (POMC) neurons express leptin receptors (for review, see Ref. 24). Leptin inhibits NPY/AgRP neurons and suppresses expression of these orexigenic neuropeptides (31). Conversely, leptin has been shown to activate POMC neurons, resulting in increased synthesis and release of anorexigenic α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH) (5, 41). Neurons that co-express NPY and AgRP in the arcuate are also influenced by ghrelin. They express the ghrelin receptor, ghrelin administration stimulates expression of NPY and AgRP mRNA, and pharmacological blockade of either NPY or AgRP prevents the ghrelin-induced food intake (6, 8, 17, 25, 32, 42, 48). Collectively, these data demonstrate the involvement of NPY/AgRP and POMC in responding to anorexigenic and orexigenic signals that arise from the periphery to regulate food intake and body weight.
Recent work has demonstrated that human subjects who have undergone long-term caloric restriction associated with anorexia nervosa (AN) display altered endocrine responses to ingestion of a test meal that persist despite weight restoration (18). In the present experiments, we sought to evaluate how chronic food restriction and subsequent weight restoration would affect hypothalamic and peripheral feeding-related systems. Furthermore, we examined the effects of chronic food restriction and partial and full weight restoration on meal-induced insulin and ghrelin secretion. Because we found that many of the effects of chronic caloric restriction were not corrected on weight restoration, we evaluated an additional group of rats that experienced caloric restriction and subsequent weight restoration that was maintained for 4 wk beyond reaching 100% of control body weights.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Experiment 1
Animals and housing.
Male Long-Evans rats (Harlan, Indianapolis, IN) weighing 270.48 ± 0.89 g were maintained at a constant temperature (25°C) on a 12:12-h light-dark cycle in hanging wire cages. All rats had 24-h access to tap water during all portions of the experiment. After 1 wk of acclimation to the laboratory, rats were weight matched and placed into one of four experimental groups: control (n = 6), chronically restricted (CR; n = 7), partially weight restored (PR; n = 7), or fully weight restored (FR; n = 7). Rats in the control group had ad libitum access to rodent chow (Harlan Teklad 2018 18% protein diet) at all times, except where noted. The CR, PR, and FR rats were restricted in the number of calories allowed each day such that they received 70% of the number of calories consumed by the control group in the previous 24 h. Food was presented to CR, PR, and FR rats within the hour before the onset of the dark cycle each day. Rats were handled and weighed daily. The Purdue University Animal Care and Use Committee approved all procedures.
CR, PR, and FR rats were restricted to 70% of control intake for 4 wk. At this point, the mean CR body weight was 80% of control body weights, and CR rats were killed. The remaining rats were then pair fed the number of calories consumed by the controls in the previous 24 h. PR rats were killed when the mean body weight was 90% of the mean control body weight, and FR rats were killed when the mean body weight was 100% of that of controls.
Blood and tissue collection.
On the day of death, food was removed 12 h before the onset of the dark cycle. Two hours before the dark cycle, rats were deeply anesthetized by exposure to ether and rapidly decapitated. Brains were quickly removed, submerged into iced isopentane for 25 s, and immediately stored in dry ice. Trunk blood was collected into K+EDTA vacutainer tubes, briefly placed in ice, and then centrifuged at 4°C for 15 min at 2,000 rpm. Plasma was aspirated into Eppendorf tubes. Blood and brains were stored at −80°C until processing. Epidydimal fat pads were also removed and weighed.
Radioimmunoassay.
Radioimmunoassays (RIAs) (Linco Research) were used to determine baseline levels of plasma insulin, leptin, and ghrelin. The rat insulin RIA kit had a sensitivity of 0.1 ng/ml, the leptin RIA sensitivity was 0.5 ng/ml, and the ghrelin RIA sensitivity was 7.8 pg/ml. Volumes of 100 μl of plasma were used in duplicate samples for each assay, as directed by the manufacturer.
In situ hybridization.
Brains were coronally sectioned at 14 μm, mounted onto electrostatically charged Superfrost Plus slides (Fisher Scientific), and stored at −80°C. Brain slices were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and dehydrated with an ascending series of alcohols. Sections from each rat containing the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus and sections containing the dorsomedial hypothalamus (DMH) were selected and stored at −80°C for future processing. Plasmids of NPY, AgRP, and POMC were linearized with the appropriate restriction enzymes. Antisense riboprobes were labeled with 35S-labeled UTP (PerkinElmer), using in vitro transcription systems with appropriate polymerases (T3, SP6, and T3, respectively), according to protocols provided by the manufacturer (Promega). Probes were then purified using Quick Spin RNA columns (Roche Diagnostics).
For processing, slides were warmed and rinsed in triethylamine (TEA) buffer (pH 8.0) and TEA with acetic anhydride. Sections were incubated in hybridization buffer composed of 50% formamide, 0.3 M NaCl, 10 mM Tris·HCl (pH 8.0), 1 nM EDTA (pH 8.0), 1× Denhardt's solution (Eppendorf), 10% dextran sulfate, 10 mM DTT, 500 μg/ml yeast tRNA, and 35S-UTP and incubated overnight in a 56°C humid chamber. After hybridization, sections were washed three times in 2× SSC followed by one wash in 2× SSC + DTT at 56°C. Slides were then treated with 20 μg/ml RNase A (Sigma) in buffer containing 5 M NaCl, 0.5 M EDTA, 1 M Tris, pH 7.5, and double-distilled H2O. Sections were washed twice in 2× SSC + DTT and then twice in 0.1× SSC + DTT and dehydrated in an ascending series of alcohols. Slides were exposed to Kodak Biomax film for 2 days. Autoradiographic images were then scanned and quantified with Scion Image software (National Institutes of Health), using autoradiographic 14C-labeled microscales (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech) as a standard. Data for each animal were means of the product of hybridization area × density, with the background density subtracted from the three sections, reflecting the region-specific levels of gene expression. Data for each animal were normalized to controls as 100% and are expressed as means ± SE.
Statistical analyses.
Differences were first analyzed by one-way ANOVA. Post hoc comparisons were made with Tukey's honestly significant difference (HSD) tests. Differences were deemed significant when P value was <0.05.
Experiment 2
Animals and dietary maintenance.
Sixteen male Long-Evans rats (338.71 ± 14.38 g; Harlan) were maintained on a 12:12-h light-dark cycle at a constant temperature (25°C) in Plexiglas tub cages. All rats had 24-h access to tap water during all portions of the experiment. During an acclimation period of 2 wk, all rats had ad libitum access to the standard laboratory chow described in Experiment 1. After acclimation, rats were weight matched and divided into two groups. The control group (n = 7) had ad libitum access to chow except where noted. The restricted group (n = 9) was given 70% of the number of calories consumed by the controls in the previous 24 h. Rats were maintained in the restricted (CR) state for 4 wk and then trained and tested in a meal testing paradigm as described below.
After the meal test, CR rats were allowed access to the same number of calories as were consumed by controls in the previous 24 h until body weights reached 90% of control body weight. At this time, rats were meal tested (PR). Access to 100% of the number of calories consumed by controls was continued until rats reached 100% of control body weights, at which time a final meal test was conducted (FR). Food intake and body weights were recorded daily.
Surgical procedures.
Before experimentation, all rats had catheters implanted into the central branch of the jugular vein. The catheter, constructed of silastic tubing (inner diameter, 0.508 mm; outer diameter, 0.940 mm), was placed 42 mm into the vein, such that the tip minimally entered the heart. The catheter was exteriorized, attached to a bent and blunted 21G needle, and fixed to the top of the skull with dental cement. Catheters were flushed daily, and a lock solution composed of heparin and glycerol was used to maintain patency of the catheter.
Acute meal test.
Rats were given access to vanilla-flavored Ensure on three separate training sessions before testing. For training, food and water were removed 3 h before the onset of the dark cycle, and a preweighed bottle of Ensure was placed on the cage when the lights were turned off. Access was allowed for 1 h, after which the bottle was removed, intake was recorded, and food and water were replaced on the cage. For testing, food and water were removed 3 h before the onset of the dark cycle. Blood was drawn via the jugular catheter immediately before rats gained access to Ensure (baseline) and then 15 min, 30 min, 1 h, and 2 h after the first lick. At each time point, 200 μl of blood were collected via a luer-lock syringe attached to the catheter while the rat was freely moving and feeding. The blood was then transferred into sterile vacutainer tubes containing K+EDTA and placed on ice for the remainder of the test. Once all samples were collected, blood was centrifuged at 4°C for 15 min at 2,000 rpm; plasma was transferred into sterile 1.5-ml Eppendorf tubes and stored at −80°C for further processing. The Ensure was weighed at baseline, 15 min after the first lick, and then at 30 min and 1 h, at which time the Ensure was removed. Food and water were replaced after the 2-h blood draw.
RIA.
Insulin, ghrelin, and leptin were assayed using commercially available RIA kits (Linco Research) as described for Experiment 1. All samples were processed in duplicate and according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Statistical analyses.
Baseline plasma hormone levels were analyzed by one-way ANOVA. Post hoc comparisons of statistical differences were performed using Tukey's HSD. Meal-related changes in plasma hormone levels were made by repeated measures ANOVA. Statistical significance was deemed at P < 0.05.
Experiment 3
Animals and analyses.
Given persistent differences in hypothalamic and endocrine responses following chronic restriction and weight restoration, an additional set of rats were calorie restricted to 80% body weight of controls, maintained at 80% body weight for 2 wk, and then pair fed to control food intake until weight was restored to 100% for a period of 4 wk (extended weight restored; ER). Sixteen male Long-Evans rats (Harlan) weighing 302 ± 2.6 g were maintained as described in Experiment 1. Before the start of restriction, rats were weight matched and divided into two groups. Controls (n = 8) were allowed ad libitum access to food and water, except where described, and ER rats (n = 8) received 70% of the calories consumed by controls over the previous 24 h. After ER body weights reached 80% of control body weights, rats were given the same number of calories per day as were consumed by controls to restore body weight in a controlled manner. Matched calorie access was continued for 4 wk beyond the point when the ER rats reached 100% body weight of controls. At this time, all rats were killed, and blood and brains were collected and processed precisely as described in Experiment 1, such that plasma insulin, leptin, and ghrelin were analyzed by RIA, and hypothalamic gene expression levels were quantified for arcuate NPY, AgRP, POMC, and DMH NPY.
Statistical analyses.
Differences were first analyzed by one-way ANOVA. Post hoc comparisons were made with Tukey's HSD tests. Differences were deemed significant when P value was <0.05.
Experiment 4
To evaluate whether the meal-related effects of caloric restriction persisted beyond attainment of 100% body weight of controls, rats that were previously restricted, weight restored, and maintained at 100% body weight of controls for 4 wk were meal tested, as described in Experiment 2. Eight control and eight ER rats with indwelling jugular catheters were given three 1-h training sessions with Ensure. For training, food and water were removed 3 h before the onset of the dark cycle, and a preweighed bottle of Ensure was placed on the cage when the lights were turned off. Access was allowed for 1 h, after which the bottle was removed, intake was recorded, and food and water were replaced on the cage. For testing, food and water were removed 3 h before the onset of the dark cycle. Blood was drawn via the jugular catheter immediately before rats gained access to Ensure (baseline) and then 15 min, 30 min, 1 h, and 2 h after the first lick. Blood was treated and processed for plasma levels of insulin and ghrelin, as described in Experiment 2. Food and water were replaced after the 2-h blood draw.
Statistical analyses.
Baseline plasma hormone levels were analyzed by one-way ANOVA. Post hoc comparisons of statistical differences were performed using Tukey's HSD. Meal-related changes in plasma hormone levels were made by repeated measures ANOVA. Statistical significance was deemed at P < 0.05.
RESULTS
Experiment 1: peripheral and central effects of chronic caloric restriction and partial and full weight restoration.
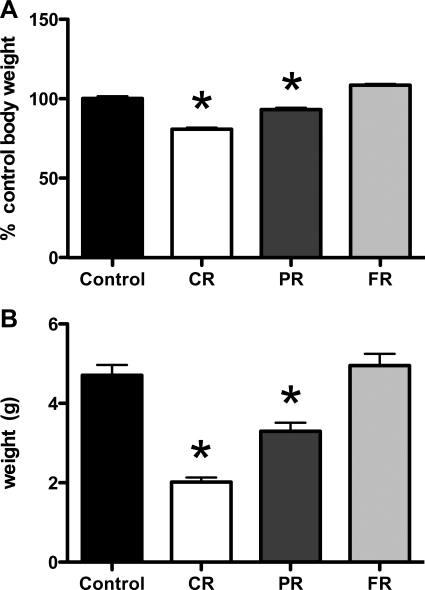
As depicted in Fig. 1A, chronic food restriction resulted in reduced body weight compared with controls, and access to food following the restriction period resulted in weight gain to the level of controls. After 4 wk of restriction to 70% of the calories consumed by controls, CR body weights were 81.0% of control body weights (P < 0.001). One-third of the CR rats were killed at this time for subsequent analysis of plasma hormones and hypothalamic gene expression levels. The remaining two-thirds were allowed access to 100% of the calories consumed by controls for 2 wk, such that their body weights were restored to ∼90% of control body weights. One-half of the rats were then killed for the previously described analyses (see materials and methods). Body weights of the PR group at death were 93.3% (P < 0.01). The FR group mean body weight was 104% of that of controls.
Fig. 1.
Body weight and fat pad weight during and after chronic caloric restriction. Rats were allowed access to 70% of the daily kcal consumed by controls for 4 wk (chronically restricted; CR), which resulted in significantly lower body weight. A: after 4 wk, rats were pair fed to the amount of kcal consumed by controls [partially weight restored (PR) and fully weight restored (FR)] before death. At PR, body weights remained significantly lower than for controls (P < 0.05). B: epidydimal fat pad weights were significantly lower in CR and PR compared with controls. At the FR stage of weight restoration, epidydimal fat weight was restored to that of controls. *P < 0.05.
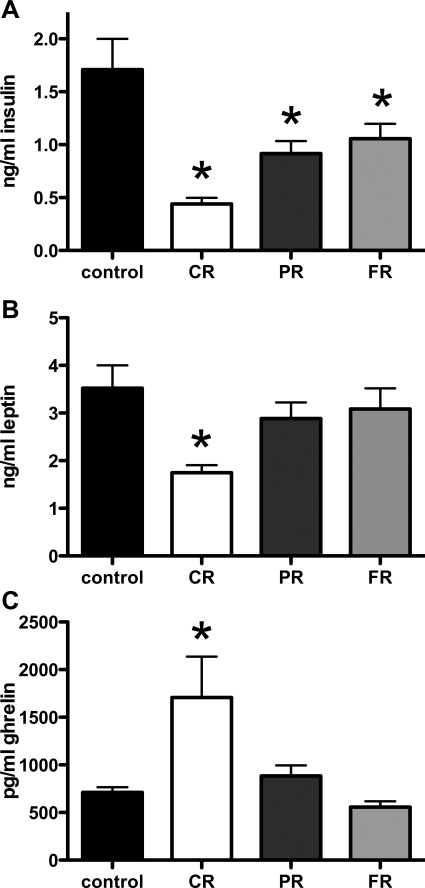
Epidydimal fat mass was significantly less in CR and PR rats compared with controls (P < 0.01 and P < 0.05, respectively). There was no difference between control and FR fat pad weight (Fig. 1B). As depicted in Fig. 2A, baseline plasma insulin levels were significantly lower than in controls in all groups, regardless of weight status (P < 0.05 in all cases). Although plasma insulin remained significantly lower in CR, PR, and FR rats despite weight restoration, leptin levels were only significantly lower in CR rats compared with controls (Fig. 2B). At the PR and FR weight stages, leptin was not different than in control animals. Baseline plasma ghrelin levels were significantly elevated in CR compared with controls (P < 0.05 for CR; Fig. 2C). At the PR and FR stages of weight restoration, ghrelin levels were not different from controls.
Fig. 2.
Basal insulin, leptin, and ghrelin during and after chronic caloric restriction. A: baseline plasma insulin levels were significantly lower in all groups regardless of weight status compared with controls (P < 0.05 in all cases). B: leptin levels were only significantly lower in CR rats compared with controls. C: baseline plasma ghrelin levels were significantly elevated in CR rats compared with controls (P < 0.05 for CR). At the PR and FR stages of weight restoration, ghrelin levels were not different from controls. *P < 0.05.
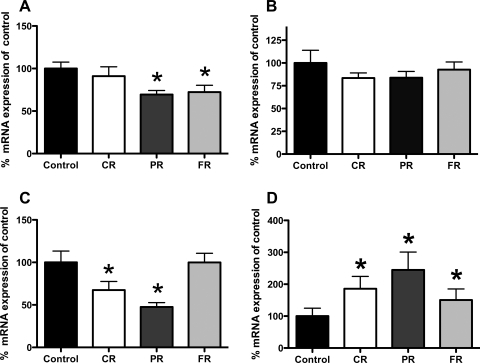
Analysis of hypothalamic gene expression levels revealed unexpected differences in NPY mRNA in the arcuate between control and CR, PR, or FR rats. As depicted in Fig. 3A, arcuate NPY mRNA expression levels were not different from those of controls in CR but were significantly lower in PR and FR (69.4 and 72.3%, respectively; P < 0.05 for both cases). Figure 3B demonstrates no differences in AgRP mRNA expression in any groups compared with controls. POMC mRNA expression was significantly lower in CR (67.8%) and PR (47.6%) rats compared with controls (P < 0.05 for all comparisons; Fig. 3C).
Fig. 3.
Hypothalamic gene expression levels. A: arcuate neuropeptide Y (NPY) mRNA expression levels were not different from controls in the CR stage; however, they were significantly reduced in PR (69.4%) and FR (72.3%) compared with control values (P < 0.05 in both cases). B: analysis of agouti-related protein (AgRP) mRNA revealed no effect of body weight status. C: there were reductions in proopiomelanocortin (POMC) mRNA levels in CR (67.8%), PR (47.6%), and FR (74.4%). All differences were significantly different from controls (P < 0.05 in all cases). D: CR rats had significantly elevated NPY mRNA in the dorsomedial hypothalamus (DMH) compared with controls (451.6% increase in CR; P < 0.05). This difference persisted in PR and FR rats, such that PR rat DMH NPY mRNA expression levels were 399.07% and those of FR rats were 240.83% of control levels. *P < 0.05 compared with controls.
Chronic caloric restriction also affected NPY mRNA expression levels in the DMH. CR rats had significantly elevated NPY mRNA in the DMH compared with controls (451.6% increase in CR; P < 0.05), and this difference persisted in PR and FR rats such that PR rat DMH NPY mRNA expression levels were 399.07% and FR levels were 240.83% of control levels (P < 0.05 in both cases; Fig. 3D).
Experiment 2: meal-related plasma insulin and ghrelin after chronic caloric restriction and subsequent weight restoration.
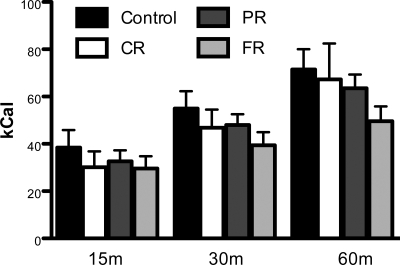
Following a period of chronic caloric restriction, rats were allowed to consume Ensure at the start of the dark cycle for 60 min on three separate occasions to accustom them to the procedure. During a fourth access period, intake was measured and blood was sampled. As depicted in Fig. 4, Ensure intake was similar among groups at all time points.
Fig. 4.
Test meal intake. Following a period of chronic caloric restriction, rats were trained to consume Ensure at the start of the dark cycle for 60 min. During the test session, Ensure intake was similar among groups at all time points.
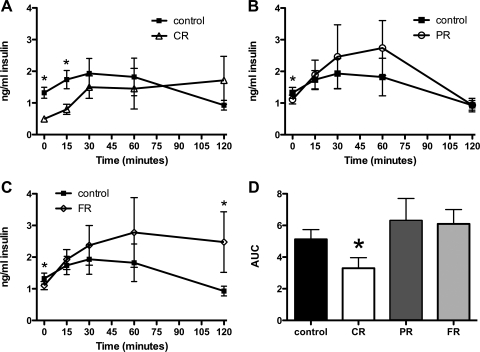
Chronic caloric restriction resulted in altered patterns of plasma insulin in rats that had undergone chronic restriction and weight restoration. In control rats, plasma insulin was significantly increased 30 min after the onset of the test meal (P < 0.05). It remained significantly elevated through the 60-min time point and returned to a value that was not different from baseline at the 120-min measurement. As depicted in Fig. 5A, plasma insulin was significantly lower in CR rats compared with controls at baseline, and the difference between CR insulin at baseline and CR insulin at 15 min was significantly greater (P < 0.05). It remained elevated throughout the testing period such that at the 120-min time point, CR plasma insulin was greater than CR baseline plasma insulin (P < 0.01). Comparison of the area under the curve (AUC) for control compared with CR insulin revealed a significant difference such that the AUC for CR rats was less than that of control rats (P < 0.05; Fig. 5D).
Fig. 5.
Plasma insulin in response to a test meal. Chronic caloric restriction resulted in altered patterns of plasma insulin in rats that had undergone chronic restriction and weight restoration. A: baseline plasma insulin levels were significantly lower in CR compared with control rats. In controls, plasma insulin was significantly increased 30 min after the onset of the test meal (P < 0.05). It remained significantly elevated through the 60-min time point and returned to a value that was not different from baseline at the 120-min measurement. CR insulin was significantly elevated compared with CR baseline at 15 min (P < 0.05) and remained so for the entirety of the test session. B: PR insulin was significantly elevated compared with baseline PR insulin at the 30-min time point, remained so at 60 min, and returned to baseline levels at 120 min. C: FR insulin was increased compared with FR baseline insulin 15 min after the start of the meal and remained elevated for the duration of the test session (P < 0.05). FR insulin at 120 min was also significantly higher than control insulin at this time point. D: the area under the curve (AUC) for CR rats was significantly lower than for controls (P < 0.05). *P < 0.05 compared with controls.
The pattern of insulin release in PR rats was similar to that of controls. At baseline, PR insulin was lower than control baseline insulin (P < 0.05), and PR insulin was significantly elevated compared with baseline PR insulin at the 30-min time point. It remained elevated at 60 min and returned to baseline levels at the 120-min measurement (Fig. 5B). Interestingly, the FR insulin values rose more quickly than those of controls or PR rats such that at 15 min, FR insulin was increased compared with FR baseline insulin (P < 0.05). It remained elevated with respect to the baseline FR level for the duration of the test session such that it was significantly elevated at 120 min. FR insulin at 120 min was also significantly higher than control insulin at this time point (Fig. 5C). Despite the prolonged elevation, the AUC for the FR group was not different from that of controls.
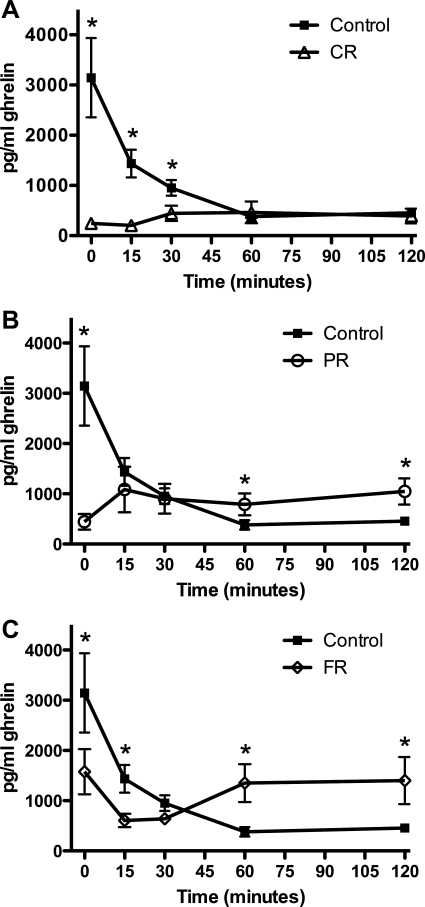
Plasma ghrelin levels in response to the test meal were also affected by chronic caloric restriction. Whereas CR rats had significantly elevated ghrelin levels in the baseline condition of Experiment 1 (Fig. 2C), the baseline measure in the meal testing paradigm was significantly lower than that of controls (P < 0.01). Figure 6A depicts the meal-induced changes in plasma ghrelin levels in controls compared with CR rats. Controls displayed the expected meal-related decrease in plasma ghrelin such that by 15 min after the start of the meal, ghrelin levels were significantly reduced compared with baseline. This pattern was not observed in CR rats. There was no preprandial elevation in this group, nor did consuming the meal affect ghrelin at any time point measured. In addition to lower preprandial ghrelin in CR rats, ghrelin levels were significantly lower than those of controls at 15, 30, and 120 min of testing (P < 0.05 in all cases).
Fig. 6.
Plasma ghrelin in response to a test meal. A: CR ghrelin was significantly lower than for controls at the start of the test session (P < 0.01). In control rats, plasma ghrelin decreased within 15 min of the start of the meal and remained depressed throughout the test session. Ghrelin levels in CR rats did not change from baseline. B: PR baseline ghrelin was significantly lower than for controls, and ingestion of Ensure did not result in any measurable changes from baseline PR ghrelin levels. At 60 and 120 min, PR ghrelin levels were significantly greater than those of controls (P < 0.05 in both cases). C: FR ghrelin was less than that of controls at baseline (P < 0.05). FR ghrelin was decreased from FR baseline 15 and 30 min after the onset of the test meal (P < 0.05). FR rats had significantly higher ghrelin levels than controls at 60 and 120 min (P < 0.05). *P < 0.05 compared with controls.
Similarly, PR baseline ghrelin was significantly lower than control ghrelin (Fig. 6B; P < 0.01). Ingestion of Ensure did not result in any measurable changes from baseline PR ghrelin levels; however, at 60 and 120 min, PR ghrelin levels were significantly greater than those of control rats (P < 0.05 in both cases). In the FR rats, baseline plasma ghrelin was less than that of controls (P < 0.05), but unlike CR and PR rats, ghrelin levels decreased in FR rats 15 min after the onset of the test meal (P < 0.05 compared with FR baseline; Fig. 6C). At this time point, FR ghrelin levels were lower than control levels. The lower FR ghrelin level persisted at the 30-min time point; however, as was the case for the PR rats, FR rats had significantly higher ghrelin levels than controls at 60 and 120 min (P < 0.05).
Experiment 3: peripheral and central effects of prior caloric restriction after extended weight restoration.
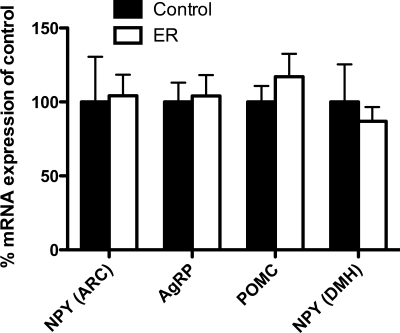
After 4 wk at the weight-restored state, body weights and epidydimal fat pad weights were indistinguishable between controls and ER rats (Table 1). Additionally, baseline levels of plasma insulin, leptin, and ghrelin were not different between groups. Analysis of hypothalamic gene expression levels revealed that, while levels of NPY mRNA in the arcuate remained altered in FR, after 4 wk at the weight-restored state, there were no longer differences between groups (Fig. 7). Similarly, AgRP, POMC, and DMH NPY levels in ER rats were found to be similar to those of controls.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of control and ER rats after ER rats were maintained at 100% body weight of controls for 4 wk
| Control | ER | |
|---|---|---|
| %Body wt of controls | 100±1.4 | 99.6±1.8 |
| Epidydimal fat, g | 4.7±0.3 | 5.2±0.6 |
| Plasma values | ||
| Insulin, ng/ml | 0.61±0.02 | 0.64±0.07 |
| Leptin, ng/ml | 8.0±2.12 | 9.40±3.30 |
| Ghrelin, pg/ml | 874±112.0 | 1021±109.6 |
Data are expressed as means ± SE. ER, extended weight restored.
Fig. 7.
Hypothalamic gene expression levels after extended weight restoration (ER). There were no differences in levels of mRNA for NPY, AgRP, or POMC in the arcuate nucleus, nor was there a difference between controls and ER with regard to NPY mRNA in the DMH.
Experiment 4: meal-related plasma insulin and ghrelin after 4 wk at the weight-restored state.
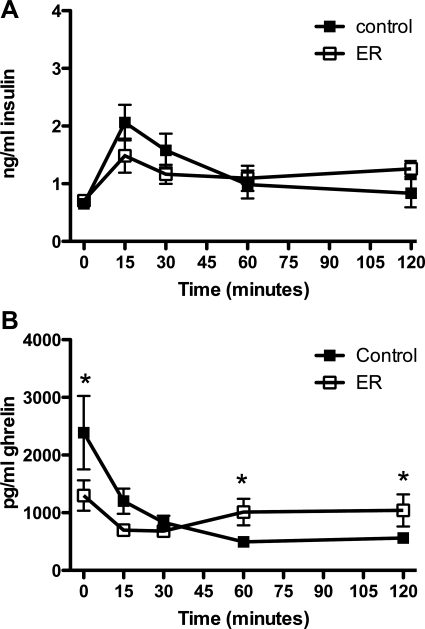
As depicted in Fig. 8A, insulin responses to a test meal in ER rats resembled those of controls. Insulin levels rose significantly in both groups compared with baseline levels and remained similar to one another for the duration of the test session.
Fig. 8.
Plasma insulin and ghrelin in response to a test meal after extended weight restoration. Four weeks at the weight-restored stage normalized insulin, but not ghrelin, responses to a test meal in ER rats. A: baseline plasma insulin levels were similar in controls and ER rats. There were no differences between the 2 groups throughout the testing session. B: ER ghrelin was significantly lower at baseline than in controls. Fifteen minutes after the start of the meal, ghrelin levels in both groups were decreased significantly, and at 60 and 120 min, ER ghrelin was elevated compared with controls (P < 0.05). *P < 0.05 compared with controls.
Figure 8B depicts the ghrelin response to a meal in ER rats. As was the case with FR rats in Experiment 2, plasma ghrelin levels resembled those of controls but were significantly lower at baseline and at 15 min after the start of the meal and higher than control levels at 60 and 120 min.
DISCUSSION
The present data demonstrate that chronic food restriction affects peripheral and central systems involved in the control of food intake and regulation of energy balance, and that weight restoration alone does not fully reverse these effects. Restricted access to food resulted in reduced body weight gain, epidydimal fat mass, and leptin and insulin, with significantly greater baseline ghrelin levels than those measured in control animals. Meal-related insulin and ghrelin responses were also affected by chronic caloric restriction, and patterns of insulin and ghrelin release did not fully normalize to those of control animals despite weight restoration.
Baseline leptin and insulin were reduced in response to chronic food restriction. This is in agreement with previous studies that have demonstrated diminished levels of these two well-characterized adiposity hormones in animals that have undergone weight loss or have been prevented from gaining weight at the rate of normal ad libitum fed rats (2, 10, 21, 36, 44, 45). Restoration of body weight fully reversed the deficit in plasma leptin levels in PR, although rats at this stage of weight restoration continued to display decreased basal insulin. This effect remained through the FR stage such that, despite no differences in body weight, epidydimal fat, or plasma leptin levels, plasma insulin remained lower than control insulin levels. We have previously demonstrated that meal-related insulin secretion is altered in human subjects with AN, and weight restoration does not fully reverse the effects of AN on meal-related insulin secretion (18). It may be that insulin levels are more sensitive to food restriction than leptin and require more time at a weight-restored state to return to levels comparable to controls. This conclusion is supported by our present finding that after 4 wk at the weight-restored state, baseline insulin levels were no longer suppressed compared with controls.
The effects of chronic caloric restriction on plasma insulin levels are also evidenced in the meal feeding paradigm employed in our present studies. The CR, PR, and FR rats displayed decreased plasma insulin levels at baseline compared with controls. Plasma insulin levels in control rats peaked 30 min after the start of the test meal and returned to baseline by the end of the meal testing session (120 min). In CR rats, plasma insulin increased more rapidly, such that it was elevated compared with CR baseline 15 min after the start of the test meal. Unlike control insulin, CR insulin remained significantly elevated with respect to CR baseline insulin for the duration of the test session. With partial weight restoration, the pattern of insulin release in response to the test meal more closely resembled that of controls; however, while the initial (first 60 min) insulin responses in PR and FR rats were similar, insulin remained elevated in FR rats to 120 min. This difference is attenuated at the ER stage, suggesting that the extended elevation of insulin in response to the test meal at FR was related to the active process of weight restoration that is corrected when weight is maintained for a period of time.
In our present experiments, plasma ghrelin measured 2 h before the onset of the dark cycle was significantly increased in CR rats compared with controls, but not in PR or FR rats. This finding concurs with other demonstrations of a relationship between low body weight and increased plasma ghrelin, such as in cases of underfeeding associated with dietary restriction, AN, and cancer anorexia, among others (see Ref. 43 for review). Given the baseline measures in our study, the meal-related ghrelin responses were unexpected. Control plasma ghrelin was at its highest at the onset of the dark cycle and was significantly decreased 15 min after the start of the liquid test meal. For the rats that had undergone caloric restriction, regardless of weight status at testing, ghrelin levels were significantly lower than for controls at the start of the dark cycle. In CR and PR, ingestion of the test meal did not result in changes in plasma ghrelin levels compared with baseline at any time point. The FR and ER groups demonstrated decreased plasma ghrelin levels 15 min after the start of the meal, compared with baseline, in response to the test meal. Whereas control ghrelin levels remained significantly decreased 120 min after the start of the test meal, they were not different from baseline in any of the experimental groups at this time point.
It is possible that the discrepancies in ghrelin measured 2 h before the onset of the dark cycle (Experiments 1 and 3) and those measured at baseline for the meal test (at the onset of the dark cycle; Experiments 2 and 4) are related to the patterns of intake that developed after a history of experiencing chronic caloric restriction. Differences between the anticipation and the presentation of meals have been demonstrated to affect plasma ghrelin levels. Many studies have shown preprandial ghrelin release in rats that are fed ad libitum, as ghrelin peaks just before the end of the light period when they normally eat their largest meal of the day (15, 20, 34, 35, 37, 39, 47). While it is clear that ghrelin secretion is involved in stimulating food intake, ghrelin secretion may be entrained to the timing of habitual meal feeding. In rodents, Drazen et al. (9) demonstrated that both pre- and postprandial ghrelin can be entrained to meal feeding that is independent of whether the rats were fed or fasted. Scheduled access to food resulted in increased ghrelin just before food presentation. Similarly, plasma ghrelin levels peaked in ad libitum rats just before the onset of the dark cycle, when rats generally consume the majority of their food. The preprandial peak in ghrelin was absent in rats that were fasted and not on a scheduled meal feeding regimen, suggesting that the ghrelin surge can be learned and precede an expected meal. In our present studies, food was replenished each day 1–2 h before the onset of the dark cycle during the CR, PR, FR, and ER stages. In contrast to rats fed ad libitum, rats that are calorie restricted eat when the food is available regardless of the light cycle. We did not measure patterns of intake in this study, although, based on observation, the majority of food was consumed within the first 2 h of access. Characterization of meal patterns in this paradigm would allow further examination of the relationships between caloric restriction, timing of food intake, and plasma ghrelin levels. Given that differences in ghrelin responses to the test meal persisted in the ER group, future work could address issues pertaining to changes in patterns of intake following experience with chronic caloric restriction.
In the hypothalamus, we measured reduced POMC in CR and PR rats. It is known that elevated POMC is associated with decreased food intake and that leptin activates POMC neurons (4). Therefore, it follows that in CR, reduced levels of circulating leptin in conjunction with low body weight and adiposity would be associated with decreased activity of POMC neurons. Continued suppression of POMC during weight restoration, as seen in the PR stage, may lend to promoting this process. Differences in POMC were attenuated by the time of weight restoration (FR).
Previous studies have demonstrated that acute food deprivation results in increased NPY mRNA expression levels in the arcuate (3, 12). This is also the case in studies in which rats have undergone food restriction for up to 14 days (2). Our results in chronically food-restricted rats are inconsistent with these findings. In the hypothalamus, chronic caloric restriction did not affect arcuate NPY gene expression in CR rats. This was an unanticipated finding, because not only was body weight reduced compared with controls, so were food intake and leptin levels. Given that leptin receptor mRNA is co-expressed with NPY in the arcuate (23), and leptin administration reduces arcuate NPY expression levels (30), we had predicted that NPY mRNA would be increased in the arcuate in CR rats. Compared with previous studies reported by others, one potentially important difference in our study is that rats were food restricted for 28 days. A potential explanation is that perhaps, with prolonged caloric restriction, adaptations occur such that NPY is normalized in CR. More surprising was the finding that arcuate NPY was significantly lower in PR and FR rats compared with controls. It is possible that this is related to the increases in plasma leptin levels during the weight restoration process. While there was no difference in plasma leptin levels between controls and PR/FR rats, there was a significant increase in PR/FR compared with CR. One possibility for the effects on NPY mRNA expression is that, during weight restoration, as plasma leptin levels rise, NPY neurons are responsive to the change in leptin, and that responsivity requires more than weight restoration (i.e., time) for normalization. Evaluation of sensitivity to leptin, in terms of effects on food intake and NPY mRNA expression, during the weight restoration process may provide insight into whether chronic restriction results in such effects.
A role for the DMH energy balance has long been suggested by studies demonstrating that DMH-lesioned animals develop hypophagia and show reduced body weight (1). Interestingly, paradigms of both an energy deficit (lactation, intense exercise, and chronic food restriction; Refs. 2, 16, 22, and 33) and excess [animal models of obesity, including the lethal yellow Ay, MC-4 receptor knockout, and diet-induced obesity (13, 14, 17a)] demonstrate increases in DMH NPY expression. The multiplicity of challenges to energy homeostasis that influence DMH NPY suggests an important role, the precise nature of which remains unknown. In our present experiments, we demonstrate that NPY in the DMH was elevated in rats at the CR, PR, and FR states. It was not until rats had been weight restored for 4 wk that levels of NPY resembled those of controls. This finding is consistent with the study of Bi et al. (2), in which rats were restricted to 70% of the calories consumed by control rats for 14 days, and provides further support for a role for DMH NPY in overall regulation of energy homeostasis (2, 40).
In conclusion, the present data indicate that chronic caloric restriction affects multiple factors involved in the control of food intake and regulation of energy balance. While some of these effects are abolished with weight restoration, the persistence of decreased basal plasma insulin and arcuate NPY, increased DMH NPY, and altered insulin and ghrelin responses to a test meal demonstrates that weight restoration alone is insufficient to fully reverse the effects of previous chronic caloric restriction. Indeed, the majority of parameters measured within these experiments were corrected after weight restoration, but only after weight had been restored for an extended period of time.
GRANTS
This work was supported by National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Grant DK-078654 (K. P. Kinzig).
Acknowledgments
We thank Terril Verplaetse, Brandon Davenport, and Thomas Getreu for assistance with data collection.
The costs of publication of this article were defrayed in part by the payment of page charges. The article must therefore be hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. Section 1734 solely to indicate this fact.
REFERENCES
- 1.Bernardis LL, Bellinger LL. The dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus revisited: 1998 update. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 218: 284–306, 1998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bi S, Robinson BM, Moran TH. Acute food deprivation and chronic food restriction differentially affect hypothalamic NPY mRNA expression. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 285: R1030–R1036, 2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Brady LS, Smith MA, Gold PW, Herkenham M. Altered expression of hypothalamic neuropeptide mRNAs in food-restricted and food-deprived rats. Neuroendocrinology 52: 441–447, 1990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cowley MA, Cone RD, Enriori P, Louiselle I, Williams SM, Evans AE. Electrophysiological actions of peripheral hormones on melanocortin neurons. Ann NY Acad Sci 994: 175–186, 2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cowley MA, Smart JL, Rubinstein M, Cerdan MG, Diano S, Horvath TL, Cone RD, Low MJ. Leptin activates anorexigenic POMC neurons through a neural network in the arcuate nucleus. Nature 411: 480–484, 2001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cowley MA, Smith RG, Diano S, Tschop M, Pronchuk N, Grove KL, Strasburger CJ, Bidlingmaier M, Esterman M, Heiman ML, Garcia-Segura LM, Nillni EA, Mendez P, Low MJ, Sotonyi P, Friedman JM, Liu H, Pinto S, Colmers WF, Cone RD, Horvath TL. The distribution and mechanism of action of ghrelin in the CNS demonstrates a novel hypothalamic circuit regulating energy homeostasis. Neuron 37: 649–661, 2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cummings DE, Purnell JQ, Frayo RS, Schmidova K, Wisse BE, Weigle DS. A preprandial rise in plasma ghrelin levels suggests a role in meal initiation in humans. Diabetes 50: 1714–1719, 2001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Dickson SL, Luckman SM. Induction of c-fos messenger ribonucleic acid in neuropeptide Y and growth hormone (GH)-releasing factor neurons in the rat arcuate nucleus following systemic injection of the GH secretagogue, GH-releasing peptide-6. Endocrinology 138: 771–777, 1997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Drazen DL, Vahl TP, D'Alessio DA, Seeley RJ, Woods SC. Effects of a fixed meal pattern on ghrelin secretion: evidence for a learned response independent of nutrient status. Endocrinology 147: 23–30, 2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dubuc PU Effects of limited food intake on the obese-hyperglycemic syndrome. Am J Physiol 230: 1474–1479, 1976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Faulconbridge LF, Cummings DE, Kaplan JM, Grill HJ. Hyperphagic effects of brainstem ghrelin administration. Diabetes 52: 2260–2265, 2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Grove KL, Chen P, Koegler FH, Schiffmaker A, Susan Smith M, Cameron JL. Fasting activates neuropeptide Y neurons in the arcuate nucleus and the paraventricular nucleus in the rhesus macaque. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 113: 133–138, 2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Guan XM, Yu H, Trumbauer M, Frazier E, Van der Ploeg LH, Chen H. Induction of neuropeptide Y expression in dorsomedial hypothalamus of diet-induced obese mice. Neuroreport 9: 3415–3419, 1998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Guan XM, Yu H, Van der Ploeg LH. Evidence of altered hypothalamic pro-opiomelanocortin/neuropeptide Y mRNA expression in tubby mice. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 59: 273–279, 1998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Horvath TL, Diano S, Tschop M. Ghrelin in hypothalamic regulation of energy balance. Curr Top Med Chem 3: 921–927, 2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kalra SP, Dube MG, Sahu A, Phelps CP, Kalra PS. Neuropeptide Y secretion increases in the paraventricular nucleus in association with increased appetite for food. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 10931–10935, 1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kamegai J, Tamura H, Shimizu T, Ishii S, Sugihara H, Wakabayashi I. Central effect of ghrelin, an endogenous growth hormone secretagogue, on hypothalamic peptide gene expression. Endocrinology 141: 4797–4800, 2000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17a.Kesterson RA, Huszar D, Lynch CA, Simerly RB, Cone RD. Introduction of neuropeptide Y gene expression in the dorsal medial hypothalamic nucleus in the two models of the agouti obesity syndrome. Mol Endocrinol 11: 630–637, 1997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kinzig KP, Coughlin JW, Redgrave GW, Moran TH, Guarda AS. Insulin, glucose, and pancreatic polypeptide responses to a test meal in restricting type anorexia nervosa before and after weight restoration. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 292: E1441–E1446, 2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kinzig KP, Scott KA, Hyun J, Bi S, Moran TH. Lateral ventricular ghrelin and fourth ventricular ghrelin induce similar increases in food intake and patterns of hypothalamic gene expression. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 290: R1565–R1569, 2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kissileff HR Free feeding in normal and “recovered lateral” rats monitored by a pellet-detecting eatometer. Physiol Behav 5: 163–173, 1970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Levin BE, Dunn-Meynell AA. Defense of body weight against chronic caloric restriction in obesity-prone and -resistant rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 278: R231–R237, 2000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lewis DE, Shellard L, Koeslag DG, Boer DE, McCarthy HD, McKibbin PE, Russell JC, Williams G. Intense exercise and food restriction cause similar hypothalamic neuropeptide Y increases in rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 264: E279–E284, 1993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Mercer JG, Hoggard N, Williams LM, Lawrence CB, Hannah LT, Trayhurn P. Localization of leptin receptor mRNA and the long form splice variant (Ob-Rb) in mouse hypothalamus and adjacent brain regions by in situ hybridization. FEBS Lett 387: 113–116, 1996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Munzberg H, Myers MG Jr. Molecular and anatomical determinants of central leptin resistance. Nat Neurosci 8: 566–570, 2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nakazato M, Murakami N, Date Y, Kojima M, Matsuo H, Kangawa K, Matsukura S. A role for ghrelin in the central regulation of feeding. Nature 409: 194–198, 2001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Proulx K, Seeley RJ. The regulation of energy balance by the central nervous system. Psychiatr Clin North Am 28: 25–38, vii, 2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Schwartz MW, Baskin DG, Kaiyala KJ, Woods SC. Model for the regulation of energy balance and adiposity by the central nervous system. Am J Clin Nutr 69: 584–596, 1999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Schwartz MW, Figlewicz DP, Baskin DG, Woods SC, Porte D Jr. Insulin in the brain: a hormonal regulator of energy balance. Endocr Rev 13: 387–414, 1992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Schwartz MW, Seeley RJ. The new biology of body weight regulation. J Am Diet Assoc 97: 54–58; quiz 59–60, 1997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Schwartz MW, Seeley RJ, Campfield LA, Burn P, Baskin DG. Identification of targets of leptin action in rat hypothalamus. J Clin Invest 98: 1101–1106, 1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Schwartz MW, Woods SC, Porte D Jr, Seeley RJ, Baskin DG. Central nervous system control of food intake. Nature 404: 661–671, 2000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Shintani M, Ogawa Y, Ebihara K, Aizawa-Abe M, Miyanaga F, Takaya K, Hayashi T, Inoue G, Hosoda K, Kojima M, Kangawa K, Nakao K. Ghrelin, an endogenous growth hormone secretagogue, is a novel orexigenic peptide that antagonizes leptin action through the activation of hypothalamic neuropeptide Y/Y1 receptor pathway. Diabetes 50: 227–232, 2001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Smith MS Lactation alters neuropeptide-Y and proopiomelanocortin gene expression in the arcuate nucleus of the rat. Endocrinology 133: 1258–1265, 1993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Strubbe JH, Keyser J, Dijkstra T, Prins AJ. Interaction between circadian and caloric control of feeding behavior in the rat. Physiol Behav 36: 489–493, 1986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Strubbe JH, Woods SC. The timing of meals. Psychol Rev 111: 128–141, 2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sucajtys-Szulc E, Goyke E, Korczynska J, Stelmanska E, Rutkowski B, Swierczynski J. Chronic food restriction differentially affects NPY mRNA level in neurons of the hypothalamus and in neurons that innervate liver. Neurosci Lett 433: 174–177, 2008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Tolle V, Kadem M, Bluet-Pajot MT, Frere D, Foulon C, Bossu C, Dardennes R, Mounier C, Zizzari P, Lang F, Epelbaum J, Estour B. Balance in ghrelin and leptin plasma levels in anorexia nervosa patients and constitutionally thin women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88: 109–116, 2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Tschop M, Smiley DL, Heiman ML. Ghrelin induces adiposity in rodents. Nature 407: 908–913, 2000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Tschop M, Wawarta R, Riepl RL, Friedrich S, Bidlingmaier M, Landgraf R, Folwaczny C. Post-prandial decrease of circulating human ghrelin levels. J Endocrinol Invest 24: RC19–RC21, 2001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wang Q, Bing C, Al-Barazanji K, Mossakowaska DE, Wang XM, McBay DL, Neville WA, Taddayon M, Pickavance L, Dryden S, Thomas ME, McHale MT, Gloyer IS, Wilson S, Buckingham R, Arch JR, Trayhurn P, Williams G. Interactions between leptin and hypothalamic neuropeptide Y neurons in the control of food intake and energy homeostasis in the rat. Diabetes 46: 335–341, 1997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Watanobe H, Habu S. Leptin regulates growth hormone-releasing factor, somatostatin, and alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone but not neuropeptide Y release in rat hypothalamus in vivo: relation with growth hormone secretion. J Neurosci 22: 6265–6271, 2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Willesen MG, Kristensen P, Romer J. Co-localization of growth hormone secretagogue receptor and NPY mRNA in the arcuate nucleus of the rat. Neuroendocrinology 70: 306–316, 1999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Williams DL, Cummings DE. Regulation of ghrelin in physiologic and pathophysiologic states. J Nutr 135: 1320–1325, 2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Woods SC, Chavez M, Park CR, Riedy C, Kaiyala K, Richardson RD, Figlewicz DP, Schwartz MW, Porte D Jr, Seeley RJ. The evaluation of insulin as a metabolic signal influencing behavior via the brain. Neurosci Biobehavioral Rev 20: 139–144, 1996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Woods SC, Seeley RJ. Adiposity signals and the control of energy homeostasis. Nutrition 16: 894–902, 2000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Woods SC, Seeley RJ, Porte D Jr, Schwartz MW. Signals that regulate food intake and energy homeostasis. Science 280: 1378–1383, 1998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Woods SC, Strubbe JH. The psychobiology of meals. Psychonomic Bull Rev 1: 141–155, 1994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wren AM, Small CJ, Abbott CR, Dhillo WS, Seal LJ, Cohen MA, Batterham RL, Taheri S, Stanley SA, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR. Ghrelin causes hyperphagia and obesity in rats. Diabetes 50: 2540–2547, 2001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]