Abstract
Since creatinine excretion reflects a continuous loss of creatine and creatine phosphate, there is a need for creatine replacement, from the diet and/or by de novo synthesis. Creatine synthesis requires three amino acids, methionine, glycine, and arginine, and two enzymes, l-arginine:glycine amidinotransferase (AGAT), which produces guanidinoacetate acid (GAA), and guanidinoacetate methyltransferase (GAMT), which methylates GAA to produce creatine. In the rat, high activities of AGAT are found in the kidney, whereas high activities of GAMT occur in the liver. Rat hepatocytes readily convert GAA to creatine; this synthesis is stimulated by the addition of methionine, which increases cellular S-adenosylmethionine concentrations. These same hepatocytes are unable to produce creatine from methionine, arginine, and glycine. 15N from 15NH4Cl is readily incorporated into urea but not into creatine. Hepatic uptake of GAA is evident in vivo by livers of rats fed a creatine-free diet but not when rats were fed a creatine-supplemented diet. Rats fed the creatine-supplemented diet had greatly decreased renal AGAT activity and greatly decreased plasma [GAA] but no decrease in hepatic GAMT or in the capacity of hepatocytes to produce creatine from GAA. These studies indicate that hepatocytes are incapable of the entire synthesis of creatine but are capable of producing it from GAA. They also illustrate the interplay between the dietary provision of creatine and its de novo synthesis and point to the crucial role of renal AGAT expression in regulating creatine synthesis in the rat.
Keywords: interorgan metabolism, in vivo hepatic fluxes, S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase, methylation demand
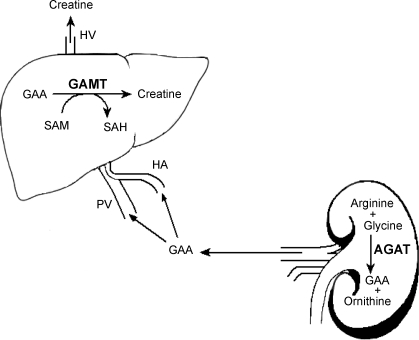
in vertebrates, creatine and creatine phosphate function as buffers for ATP in tissues, maintaining ATP levels when energy demand is transiently greater than the rate of ATP synthesis. They also serve in an energy shuttle between the sites of ATP synthesis and utilization (2). Creatine can be obtained from the diet and/or synthesized de novo in the body from the amino acids arginine, glycine, and methionine. The entire pathway of creatine synthesis consists of just two enzyme-catalyzed reactions (Fig. 1). First, the amidino group from arginine is transferred to the amino group of glycine, yielding ornithine and guanidinoacetic acid (GAA). This is catalyzed by the enzyme l-arginine:glycine amidinotransferase (AGAT). GAA can then be methylated on the original glycine nitrogen using S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) as the methyl donor. This reaction yields creatine and S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH) and is catalyzed by the enzyme guanidinoacetate N-methyltransferase (GAMT) (31).
Fig. 1.
Creatine biosynthetic pathway. HA, h′epatic artery; PV, portal vein; HV, hepatic vein; SAM, S-adenosylmethionine; SAH, S-adenosylhomocysteine; GAMT, guanidinoacetate N-methyltransferase; AGAT, L-arginine:glycine amidinotransferase; GAA, guanidinoacetate acid.
The need to synthesize creatine arises from the fact that under physiological conditions creatine and creatine phosphate are spontaneously converted to creatinine, which is subsequently lost to the urine. Daily creatinine loss is estimated to be on the order of 1.7% of the total body creatine pool or around 2 g/day in a young 70-kg human male (31). Since the total body pool of creatine is constant, the lost creatine must be replaced from either the diet or de novo synthesis. Humans on a typical Western diet obtain about one-half of their creatine by synthesis and one-half from the diet. Vegetarians obtain very little dietary creatine so that endogenous synthesis is their major source (25).
In the rat, AGAT is highly active in the kidneys, whereas GAMT is highly active in the liver. This has given rise to the idea that GAA is synthesized primarily in the kidney and then transported to the liver where it is methylated to form creatine (31). Evidence to date strongly suggests that AGAT is a critical control step in creatine synthesis, and it has been shown that creatine supplementation downregulates, whereas the growth hormone upregulates, AGAT expression (12, 16). The mechanisms by which creatine and growth hormone affect the regulation of AGAT expression have not been identified, but it is known that they affect AGAT synthesis at the pretranslational level (12, 16). On the other hand, GAMT isolated from pig or rat liver is not inhibited by creatine but is competitively inhibited by SAH, as are the other methyltransferases (8, 11). In addition to its role in creatine synthesis, GAMT should maintain low [GAA], since it has been shown that high GAA levels result in neurotoxicity (17). There is evidence that the regulation of creatine biosynthesis in humans is similar to that in the rat. Dietary creatine supplementation with a 4 g/kg diet (similar to the content of red meat) in rats results in a reduction of renal AGAT activity by 86% and plasma GAA levels by 70% compared with control rats fed a creatine-free diet (10). Creatine ingestion by humans lowers plasma GAA levels, which is consistent with the downregulation of AGAT activity (9).
Recent work from our laboratory has shown that the renal output of GAA in rats fed a creatine-free diet is equal to the renal loss of creatinine, indicating that renal GAA production is sufficient to replace creatine and creatine phosphate lost to creatinine formation (10). This implies that in this species extrarenal tissue(s) must convert the GAA released by the kidney to creatine. In humans, however, the renal production of GAA appears to represent only 20% of the daily loss of creatinine, suggesting that GAA must be synthesized in other tissues. It has been proposed by Brosnan and Brosnan (6) that the entire creatine synthetic pathway may occur in the liver. They coined the term arginine bicycle to illustrate a situation where arginine could be acted upon by either arginase to form urea or by AGAT to form GAA; in either case, ornithine would be formed and metabolized via the urea cycle enzyme ornithine transcarbamoylase. There is also evidence for the appreciable expression of AGAT mRNA in human liver (32). Despite past failures to measure AGAT activity under standard assay conditions in rat liver, there is immunohistochemical evidence for the AGAT protein in the cytosol of rat hepatocytes (15). The goal of this article is to examine creatine synthesis by the rat liver both in vivo and in vitro. We also sought to establish whether AGAT is functionally active in this tissue. Our results show a brisk production of creatine from GAA by hepatocytes in vitro, as well as an hepatic uptake of GAA in vivo. We could find no evidence for a functional AGAT in the liver despite using very sensitive methods.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Reagents.
HPLC-grade methanol was obtained from Fisher Scientific (Ontario, Canada). 15NH4Cl was obtained from Cambridge Isotope. All other chemicals and reagents were obtained from Sigma.
Animals.
Male Sprague-Dawley rats (250–350 g) were used for all experiments. Animals were housed on a 12:12-h light-dark cycle and fed Purina Rodent Chow 5001 ad libitum. Rats used for the determination of hepatic fluxes of GAA and creatine were fed a purified AIN-93G diet either free of creatine or supplemented with 0.4% creatine monohydrate, by weight, in place of an equivalent amount of corn starch. Rats were anesthetized with pentobarbital sodium, intraperitoneally, at a dose of 6 mg/100 g body wt. All procedures were approved by Memorial University of Newfoundland Institutional Animal Care Committee and were in accordance with the Guidelines of the Canadian Council of Animal Care.
Isolated hepatocytes.
Rat hepatocytes were prepared as described by Seglen (23). The viability of hepatocytes was measured by Trypan blue exclusion. Average viability was 95%. All hepatocyte incubations were carried out at 37°C in a shaking water bath using 25-ml glass Erlenmeyer flasks with rubber stoppers. Substrates were prepared in Krebs-Henseleit medium (containing 1.3 mM calcium) and gassed with 95% O2-5% CO2. Incubations were begun by the addition of aliquots of hepatocyte suspension to the Krebs-Henseleit medium containing the substrates. Each flask was gassed with 95% O2-5% CO2 for 20 s after the hepatocytes were added and then stopped. Incubations were carried out in triplicate. Incubations were stoppered with the addition of 100 μl of ice-cold 30% (wt/vol) perchloric acid. Precipitated protein was pelleted at 10,000 g for 10 min at room temperature. The supernatants (700 μl) were removed and neutralized with 20 μl of universal indicator, 40 μl of 50% K2CO3, and 20% KOH until the pH was between 6 and 8. After the samples stood in ice for 15 min, precipitated salts were removed by centrifugation at 10,000 g for 5 min at room temperature. Supernatants were then assayed for creatine as described in Creatine, GAA, SAM, and SAH measurement. Hepatocytes incubated for SAM and SAH measurement were pelleted at 3,000 g for 2 min at room temperature and flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen after the removal of the supernatant.
Hepatic blood sampling.
Blood sampling was performed while rats were under anesthesia. Blood was drawn into chilled heparinized syringes and centrifuged for 15 min at 4,000 g at room temperature, and plasma was removed and stored at −20°C until analysis. Samples were drawn from the hepatic vein, the hepatic portal vein, and the abdominal aorta. The hepatic vein was accessed via cannulation of the right jugular vein with polyethylene 50 tubing. The position of the catheter tip was visually confirmed before and after blood was withdrawn. Hepatic uptake and output were calculated from the concentrations in these three vessels by assuming that the portal vein accounted for 75% of hepatic blood flow and the hepatic artery accounted for 25% (20).
Creatine, GAA, SAM, and SAH measurement.
Creatine was assayed enzymatically and by HPLC. The enzymatic method was performed as previously described (14) except that the assay was scaled down for use in 96-well microplates. The absorbance was measured in a Molecular Devices SpectraMAX 190 spectrophotometer, using Softmax Pro software, version 3.1.1. The creatine concentration was determined by reference to a standard curve. Both GAA and creatine were assayed by the HPLC method of Buchberger and Ferdig (7). GAA and creatine were derivatized with ninhydrin, and the product was separated on a C18 reverse phase YMC column (3-μm particle size and 12-nm pore size; Waters) employing a Waters 600E solvent delivery system and a Waters 717 autosampler. The derivatized products were detected by means of a Shimadzu RF-535 fluorescence detector using an excitation wavelength at 390 nm and an emission wavelength at 470 nm. SAM and SAH were assayed by HPLC using a previously described method (13). SAM and SAH were extracted by adding 3 vol of 8% TCA to cell pellets, which were then centrifuged at 12,000 g for 10 min at room temperature; supernatants were filtered through a 0.45-μm nylon membrane and injected onto the column.
GAMT and AGAT assays.
GAMT was assayed using a modification of the previously described method of Ogawa et al. (19). Fresh rat livers were homogenized in 4 vol of a buffer containing 0.25 M sucrose, 10 mM HEPES, and 1 mM EDTA. Liver homogenates were centrifuged at 100,000 g at 4°C for 1 h, and the supernatants were assayed for GAMT activity. The assay contained 35 mM Tris buffer (pH 7.4), 7 mM 2-mercaptoethanol, 50 μM SAM, and 0.2 mM GAA. After a 10-min preincubation of all the constituents of the assay except GAA, the assay was started by the addition of GAA. The blanks did not contain GAA. Homogenates were incubated at 37°C and were stopped with 75 μl of 15% (wt/vol) TCA. This was followed by immediate neutralization with 72 μl of 1 M Tris (pH 7.4). Precipitated protein was pelleted at 10,000 g for 5 min at room temperature, and creatine was assayed via the HPLC method described in Creatine, GAA, SAM, and SAH measurement. AGAT was assayed as previously described (28). Total protein was assayed using the Biuret method.
GC-MS.
Approximately 500 μl of the neutralized perchloric acid extract of hepatocytes were added into vials containing saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate (50 μl), toluene (600 μl), and hexafluoroacetylacetone (50 μl). The mixture was incubated for 2 h at 80°C under continuous stirring, then allowed to cool, and centrifuged at 3,000 g for 4 min, and ∼500 μl of the upper toluene phase were transferred to another vial and dried under nitrogen flow. This solid was suspended in 50 μl of t-butyldimethylsilyl (t-BDMS) and incubated for 30 min at 60°C to form the t-BDMS derivatives. The mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) 344, 345, 346, and 347 ions of the GAA t-BDMS derivative and the m/z 360, 361, 362, and 363 ions of the creatine t-BDMS derivative were monitored. Sample preparation for 15N-labeled urea and amino acids was carried out as described (5). GC-MS measurements of 15N isotopic enrichment were performed on either a Hewlett-Packard 5970 Mass Selective Detector (MSD) or a 5971 MSD, coupled with a 5890 HP-GC, GC-MS Agilent System (6890 GC-5973 MSD) or Hewlett-Packard (HP-5970 MSD), using electron impact ionization with an ionizing voltage of −70 eV and an electron multiplier set to 2,000 V.
Data and statistical analysis.
The linearity of creatine and urea production by isolated hepatocytes was tested using linear regression. Creatine production by hepatocytes as a function of [GAA] was fitted to a curve using nonlinear regression. Plasma values for GAA and creatine were analyzed using paired t-tests, pairing different plasma samples from the same animal. SAM and SAH data were analyzed using a two-way ANOVA with a Newman-Keuls posttest. All other data were analyzed using unpaired Student's t-tests. All statistical analyses employed Prism Graph Pad software version 3.02.
RESULTS
Creatine production by isolated rat hepatocytes.
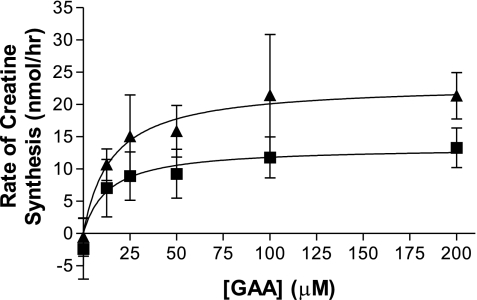
Creatine synthesis in hepatocytes was linear with time, for up to 90 min, and with tissue dry mass, up to 13 mg dry wt/ml. All subsequent studies were carried out within these linear ranges. The effect of GAA concentration on the rate of creatine synthesis was also examined (Fig. 2). The data fitted well to a rectangular hyperbola, and half-maximal GAA concentrations (13.3 μM) and maximal rates of creatine synthesis (2.1 nmol·h−1·mg dry wt−1) were calculated. The addition of 0.5 mM methionine to these incubations nearly doubled the maximal rate (3.6 nmol·h−1·mg dry wt−1) without affecting the half-maximal concentration of GAA.
Fig. 2.
Effect of [GAA] on creatine synthesis. Hepatocytes were incubated with varying [GAA], with (▴) or without (▪) 0.5 mM methionine. Each flask contained an average of 6.5 mg dry mass of cells and was incubated at 37°C for 60 min (n = 4). Data are expressed as means ± SD and fit to a curve using nonlinear regression.
The stimulation of creatine synthesis by methionine is likely due to increased provision of SAM. Incubation of hepatocytes with methionine resulted in 2.9- and 2.6-fold increases in SAM over controls in the presence and absence of GAA, respectively (Table 1). In these same incubations, SAH increased by 3.4- and 3.8-fold, respectively. The addition of methionine or GAA significantly lowered the ratio of SAM to SAH compared with the control; however, incubations with both methionine and GAA did not result in a further lowering of this ratio.
Table 1.
Effect of added methionine and GAA on hepatocyte SAM and SAH levels and on the SAM-to-SAH ratio
| GAA | Control | Methionine | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAM | − | 63.4±13.1 | 167.9±24.4* |
| SAH | − | 10.2±2.4 | 38.5±3.7* |
| SAM-to-SAH | − | 6.3±1.1† | 4.4±0.8* |
| SAM | + | 54.7±6.7 | 156.5±17.4* |
| SAH | + | 12.6±2.7 | 42.6±5.4* |
| SAM-to-SAH | + | 4.5±0.8 | 3.7±0.6 |
Data are expressed in nanomoles per gram wet mass of liver cells as means ± SD; n = 4 hepatocyte preparations. Hepatocytes were incubated for 60 min at 37°C and incubated 0.5 mM methionine and 125 μM guanidinoacetate acid (GAA). P < 0.05.
Significant difference from the control;
significant difference from corresponding incubations with GAA. SAM, S-adenosylmethionine; SAH, S-adenosylhomocysteine.
Creatine synthesis in the intact rat.
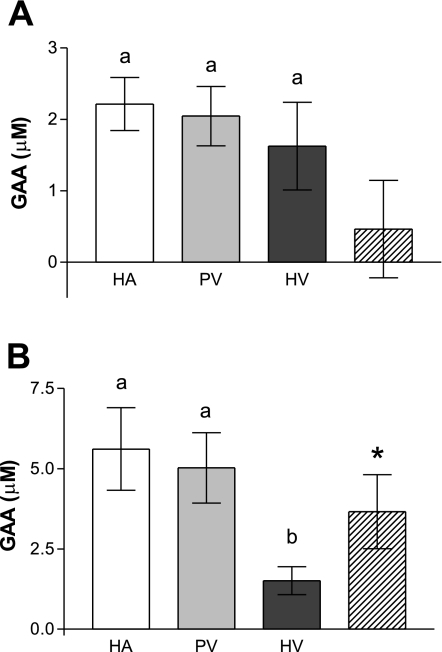
We next examined the fluxes of GAA and of creatine across the liver in rats fed both creatine-free and creatine-supplemented diets (Figs. 3 and 4). Creatine supplementation had a marked effect on circulating GAA concentrations, which were decreased by about 60% compared with those of the rats fed the creatine-free diets. There was no difference between the GAA concentrations of any of the vessels serving the liver in rats fed the creatine-supplemented diet. Hence, in these animals, there was no significant hepatic uptake or output of GAA (Fig. 3A). In contrast, there was a significant hepatic uptake of GAA in the rats fed the creatine-free diet (Fig. 3B). The net concentration difference across the liver, around 3.7 μM, was quite appreciable, amounting to more than 70% of the GAA available in the portal vein and hepatic artery.
Fig. 3.
Differences in plasma GAA concentration across the liver of rats fed a diet supplemented with 0.4% creatine (A) and rats fed a diet free of creatine (B). Plasma values are represented as follows: HA (white), PV (light gray), HV (dark gray), and concentration difference across liver (hatched). The different letters (a and b) indicate a statistically significant difference (P < 0.05) between the different blood vessels. *Significant difference (P < 0.05) between the vascular inflow and outflow values. The hepatic inflow was calculated as described in Hepatic blood sampling. Data are expressed as means ± SD (n = 6).
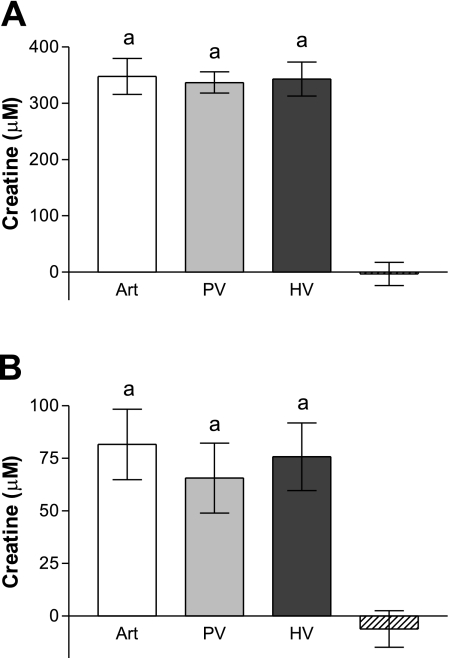
Fig. 4.
Differences in plasma creatine concentration across the liver of rats fed a diet supplemented with 0.4% creatine (A) and rats fed a diet free of creatine (B). Plasma values are represented as follows: arterial (Art; white), PV (light gray), HV (dark gray), and concentration difference across liver (hatched). aThere was no significant difference (P > 0.05) between the creatine concentrations in the different vessels. The data are expressed as means ± SD (n = 6).
We also measured creatine levels in the plasma samples (Fig. 4). Circulating creatine levels were about fourfold higher in the creatine-supplemented rats than in those fed creatine-free diet. There was no difference between the creatine levels in any of the three vessels in the rats fed either the creatine-free or creatine-supplemented diet (Fig. 4).
Enzyme activities for the enzymes of creatine synthesis.
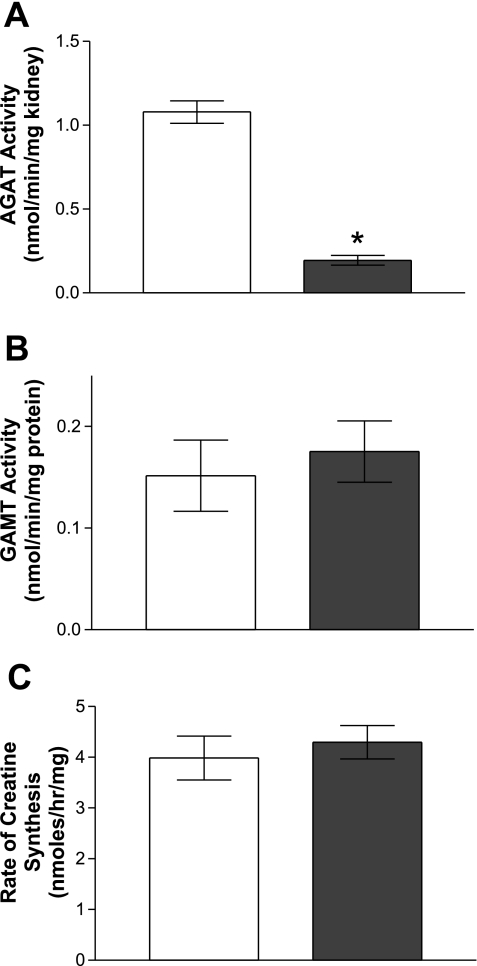
The activities of the enzymes involved in creatine synthesis were measured in rats that had been fed creatine-supplemented and creatine-free diets (Fig. 5). Renal AGAT activity was depressed by 84% in rats fed a diet supplemented with creatine. Hepatic GAMT activity did not differ between the rats fed creatine-free or creatine-supplemented diets. There was no difference in the rate of creatine synthesis from GAA between hepatocytes isolated from rats fed a creatine-free or creatine-supplemented diet.
Fig. 5.
Enzyme activities of AGAT and GAMT and creatine production by hepatocytes isolated from rats fed different diets. A: renal AGAT activity. B: hepatic GAMT activity. C: creatine synthesis in hepatocytes. White bars, rats fed the creatine-free diets; dark gray bars, rats fed the creatine-supplemented diets. Hepatocytes were incubated with 0.5 mM methionine and 125 μM GAA at 37°C for 60 min. All values are expressed as means ± SD. *Statistical significance P < 0.05 (n = 4).
Stable isotope analysis of creatine synthesis in rat hepatocytes.
Hepatocytes incubated with 15N-ammonium chloride as well as methionine and glycine, but without GAA, produced urea at a linear rate, under all substrate conditions. Incubations were performed both in the presence and absence of ornithine since it has been shown to inhibit the activity of AGAT (29). We were unable to detect creatine in these incubations using the enzymatic method, and we were only able to detect trace amounts of creatine, which were present at time 0, using the HPLC method. However, there was no increase in creatine after incubation. Isotopic analysis showed significant enrichment of both M + 1 and M + 2 isotopomers of urea; however, only trace enrichment was found in creatine (Table 2).
Table 2.
Isotopic enrichment of urea and creatine in hepatocyte incubations with 15N-ammonium chloride
| Urea (M + 1) | Urea (M + 2) | Creatine (M + 1) | Creatine (M + 2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −Ornithine | 43.0±10.6 | 55.3±6.1 | 2.9±3.5 | 4.1±4.7 |
| +Ornithine | 38.3±7.9 | 61.3±6.0 | 1.9±1.8 | 5.9±5.9 |
Values are expressed as atom percent excess as means ± SD; n = 4 hepatocyte preparations. Incubations included 5 mg dry mass hepatocytes for 30 min at 37°C. Hepatocytes were incubated with (in mM) 1 15N-ammonium chloride, 2 pyruvate, 0.5 methionine, 1 glycine, and 1 ornithine where indicated. M, mass isotopomers of molecular weight 60 g/mol for urea and 130 g/mol for creatine. M + 1 and M + 2 are, respectively, 1 and 2 mass units heavier than M.
DISCUSSION
We have clearly demonstrated that rat hepatocytes can convert GAA to creatine. This is consistent with our previous finding that isolated hepatocytes released 50% more homocysteine when incubated with methionine and GAA compared with cells incubated with methionine alone (24). The average maximal rate for creatine synthesis of 3.08 nmol·h−1·mg dry mass−1 in hepatocytes found in this study corresponds well with the increase in the rate of homocysteine export reported by Stead et al. (24). Our data agree with the notion of methylation demand suggested by Stead et al. (24), i.e., that methylation is sensitive to increases in substrate concentration. In this regard, it should be noted that Stead et al. (24) found that feeding GAA to rats increased plasma homocysteine, whereas feeding creatine reduced plasma homocysteine.
How well can the synthesis of creatine by isolated hepatocytes account for creatine synthesis in vivo? The liver of a 250-g rat weighs about 10 g, of which 70% is water. Using our maximal rates of creatine synthesis by isolated hepatocytes (3.08 nmol·min−1·mg dry wt−1), we can calculate a maximum in vivo rate of hepatic creatine synthesis of 221 μmol·24 h−1·250 g rat−1. However, a more physiological estimate requires that we take into account the substrate levels that occur in vivo. The Km of GAMT for SAM has been reported to be 49 μM (8), and hepatic SAM levels were almost 200 nmol/g (1), so it may be assumed that in vivo SAM levels are not normally limiting. However, in vivo levels of GAA are certain to be a limiting factor. It is therefore necessary to take into account the [GAA] that is presented to the liver (about 5 μM) and the [GAA] required for half-maximal rates of creatine synthesis by isolated hepatocytes (about 13.3 μM). Using this data, we can predict an in vivo rate of hepatic creatine synthesis of about 60 μmol·24 h−1·250 g rat−1. We can compare this with the rate of hepatic GAA uptake in vivo by multiplying our [GAA] difference across the liver (3.7 μM) by the hepatic venous plasma flow rate (4.32 ml·min−1·100 g body wt−1) reported by Welbourne et al. (30). Such a calculation yields a rate of hepatic GAA uptake of 57 μmol·24 h−1·250 g rat−1. The close agreement between these two estimates reflects the physiological relevance of our in vitro experiments. We may also compare these data with the rate of urinary creatinine excretion from rats on creatine-free diets, about 55 μmol·24 h−1·250 g rat−1 (data not shown). It is probably somewhat fortuitous that these numbers are in such close agreement. Nevertheless, with the allowance for the assumptions required for these calculations, it is evident that the liver is the major producer of creatine in the rat and that our in vitro studies with hepatocytes are a good reflection of the situation in vivo. We do not, however, imply that the liver is the sole site of creatine synthesis. Both AGAT and GAMT occur in tissues other than kidney and liver. In particular, it is known that the brain can synthesize creatine (31). The central nervous system may even be considered as autonomous in creatine synthesis since there is evidence that the blood-brain barrier is poorly permeable to creatine (3).
Our results also show that rat liver in vivo can clear over half of the GAA presented to it; to our knowledge this is the first time this has been shown. Creatine output by livers of animals fed creatine-free diets in vivo did not attain statistical significance. However, given that plasma creatine in these animals is about 70 μM, the production of an additional 3.7 μM by the liver would be too small for us to reliably demonstrate. However, the clear uptake of GAA by the liver in vivo and the demonstration of creatine synthesis from GAA by isolated hepatocytes indicates that the liver produces creatine in vivo and thus would require a means by which creatine exits the liver. Creatine transporters have been described in muscle (18), brain, kidney, and intestine (4). These are Na+- and Cl−-dependent active transporters, which concentrate creatine intracellularly. Intracellular-to-extracellular creatine gradients of greater than 100 to 1 are known in skeletal muscle (4). However, such transporters seem inappropriate for the liver. We have found creatine levels to be ∼0.25 μmol/g in freeze-clamped rat liver (data not shown). Therefore, the concentration gradient in liver is outward. We suggest that hepatocytes may express a novel creatine transporter as well as a GAA transporter. These issues have not yet been explored.
With respect to the question of whether the entire pathway of creatine synthesis occurs in rat hepatocytes, we must conclude that it does not. Using a highly sensitive HPLC method (limits of detection, 25 nM), we were unable to detect creatine production by isolated hepatocytes incubated with pyruvate (as a source of energy as well as a source of oxaloacetate for aspartate production) and 15N-ammonium chloride, methionine, and glycine. This was confirmed by the absence of significant isotopic enrichment of creatine from 15N-ammonium. In these same incubations, there was synthesis of urea together with substantial labeling of urea. A significant flux of arginine derived from the urea cycle into the creatine synthetic pathway would yield similarly labeled creatine. Thus we conclude that the entire creatine synthetic pathway does not occur in rat hepatocytes. We caution, however, that this may be a species-specific observation and that in other mammals the liver may contain functional AGAT activity and thus the entire creatine synthetic pathway. There is considerable variability in the tissue distribution of AGAT and GAMT activities among different species (27). As discussed in the introduction, renal production of GAA in humans is only 20% of creatinine loss and, thus, humans are likely candidates to have the entire creatine synthetic pathway in the liver. To our knowledge, there has been only one study by Sandberg et al. (21) that reported GAA uptake by human liver. However, we do not consider this result to be reliable because the reported plasma [GAA], of about 20 μM, is some four- to fivefold than reported by modern techniques (10, 22, 26). This discrepancy is likely due to the use of the older Sakaguchi colorimetric method, which is not specific for GAA; in particular, arginine interferes in this assay.
Finally, our results shed light on the regulation of creatine synthesis in the rat. The feeding of creatine decreased neither the hepatic GAMT activity nor the capacity for creatine synthesis by isolated hepatocytes. This contrasts vividly with the massive downregulation of renal AGAT in such animals (10, 16). We also confirmed the finding of Edison et al. (10) that creatine feeding markedly reduces circulating GAA levels, from about 5 μM to about 2 μM. Since the [GAA] for half-maximal rates of creatine synthesis in hepatocytes is about 13 μM, hepatic creatine synthesis should be almost directly proportional to circulating [GAA]. This, in turn, indicates that creatine synthesis in rats is primarily regulated in the kidney rather than the liver.
GRANTS
This work was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research Grants MOP-4643 and MOP-77628 (to J. T. Brosnan and M. E. Brosnan) and by National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Grant NIH-DK-53761 (to I. Nissim). R. P. da Silva thanks the School of Graduate Studies, Memorial University of Newfoundland, for the award of a fellowship.
Acknowledgments
We thank Beatrice Hall for assistance in the preparation of the hepatocytes.
The costs of publication of this article were defrayed in part by the payment of page charges. The article must therefore be hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. Section 1734 solely to indicate this fact.
REFERENCES
- 1.Balaghi M, Horne DW, Wagner C. Hepatic one-carbon metabolism in early folate deficiency in rats. Biochem J 291: 145–149, 1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bessman SP, Carpenter CL. The creatine-creatine phosphate energy shuttle. Annu Rev Biochem 54: 831–862, 1985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Braissant O, Henry H. AGAT, GAMT and SLC6A8 distribution in the central nervous system, in relation to creatine deficiency syndromes: a review. J Inherit Metab Dis 31: 230–239, 2008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Brosnan JT, Brosnan ME. Creatine: endogenous metabolite, dietary, and therapeutic supplement. Annu Rev Nutr 27: 241–261, 2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Brosnan JT, Brosnan ME, Yudkoff M, Nissim I, Daikhin Y, Lazarow A, Horyn O, Nissim I. Alanine metabolism in the perfused rat liver. Studies with 15N. J Biol Chem 276: 31876–31882, 2001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Brosnan ME, Brosnan JT. Renal arginine metabolism. J Nutr 134: 2791S–2795S, 2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Buchberger W, Ferdig M. Improved high-performance liquid chromatographic determination of guanidino compounds by precolumn dervatization with ninhydrin and fluorescence detection. J Sep Sci 27: 1309–1312, 2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Clarke S, Banfield K. S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferases. In: Homocysteine in Health and Disease, edited by Carmel R and Jacobsen D. New York: Cambridge University, 2001, p. 63–78.
- 9.Derave W, Marescau B, Vanden Eede E, Eijnde BO, De Deyn PP, Hespel P. Plasma guanidino compounds are altered by oral creatine supplementation in healthy humans. J Appl Physiol 97: 852–857, 2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Edison EE, Brosnan ME, Meyer C, Brosnan JT. Creatine synthesis: production of guanidinoacetate by the rat and human kidney in vivo. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 293: F1799–F1804, 2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Fujioka M, Konishi K, Takata Y. Recombinant rat liver guanidinoacetate methyltransferase: reactivity and function of sulfhydryl groups. Biochemistry 27: 7658–7664, 1988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Guthmiller P, Van Pilsum JF, Boen JR, McGuire DM. Cloning and sequencing of rat kidney l-arginine:glycine amidinotransferase. Studies on the mechanism of regulation by growth hormone and creatine. J Biol Chem 269: 17556–17560, 1994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Jacobs RL, Stead LM, Devlin C, Tabas I, Brosnan ME, Brosnan JT, Vance DE. Physiological regulation of phospholipid methylation alters plasma homocysteine in mice. J Biol Chem 280: 28299–28305, 2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lowry OH, Passonneau JV. A Flexible System of Enzymatic Analysis. New York: Academic Press, 1972, p. 158–160.
- 15.McGuire DM, Gross MD, Elde RP, van Pilsum JF. Localization of l-arginine-glycine amidinotransferase protein in rat tissues by immunofluorescence microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem 34: 429–435, 1986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.McGuire DM, Gross MD, Van Pilsum JF, Towle HC. Repression of rat kidney l-arginine:glycine amidinotransferase synthesis by creatine at a pretranslational level. J Biol Chem 259: 12034–12038, 1984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mori A Biochemistry and neurotoxicology of guanidino compounds. History and recent advances. Pavlov J Biol Sci 22: 85–94, 1987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Murphy R, McConell G, Cameron-Smith D, Watt K, Ackland L, Walzel B, Wallimann T, Snow R. Creatine transporter protein content, localization, and gene expression in rat skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 280: C415–C422, 2001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ogawa H, Ishiguro Y, Fujioka M. Guanidoacetate methyltransferase from rat liver: purification, properties, and evidence for the involvement of sulfhydryl groups for activity. Arch Biochem Biophys 226: 265–275, 1983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Richter S, Olinger A, Hildebrandt U, Menger MD, Vollmar B. Loss of physiologic hepatic blood flow control (“hepatic arterial buffer response”) during CO2-pneumoperitoneum in the rat. Anesth Analg 93: 872–877, 2001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sandberg AA, Hecht HH, Tyler FH. Studies in disorders of muscle. X. The site of creatine synthesis in the human. Metabolism 2: 22–29, 1953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Schulze A, Mayatepek E, Bachert P, Marescau B, De Deyn PP, Rating D. Therapeutic trial of arginine restriction in creatine deficiency syndrome. Eur J Pediatr 157: 606–607, 1998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Seglen PO Preparation of isolated rat liver cells. Methods Cell Biol 13: 29–83, 1976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Stead LM, Au KP, Jacobs RL, Brosnan ME, Brosnan JT. Methylation demand and homocysteine metabolism: effects of dietary provision of creatine and guanidinoacetate. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 281: E1095–E1100, 2001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Stead LM, Brosnan JT, Brosnan ME, Vance DE, Jacobs RL. Is it time to reevaluate methyl balance in humans? Am J Clin Nutr 83: 5–10, 2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Stockler S, Marescau B, De Deyn PP, Trijbels JM, Hanefeld F. Guanidino compounds in guanidinoacetate methyltransferase deficiency, a new inborn error of creatine synthesis. Metabolism 46: 1189–1193, 1997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Van Pilsum JF, Stephens GC, Taylor D. Distribution of creatine, guanidinoacetate and enzymes for their biosynthesis in the animal kingdom. Implications for phylogeny. Biochem J 126: 325–345, 1972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Van Pilsum JF, Taylor D, Zakis B, McCormick P. Simplified assay for transamidinase activities of rat kidney homogenates. Anal Biochem 35: 277–286, 1970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Walker JB Creatine: biosynthesis, regulation, and function. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol 50: 177–242, 1979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Welbourne TC, Phromphetcharat V, Givens G, Joshi S. Regulation of interorganal glutamine flow in metabolic acidosis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 250: E457–E463, 1986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wyss M, Kaddurah-Daouk R. Creatine and creatinine metabolism. Physiol Rev 80: 1107–1213, 2000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Xu XR, Huang J, Xu ZG, Qian BZ, Zhu ZD, Yan Q, Cai T, Zhang X, Xiao HS, Qu J, Liu F, Huang QH, Cheng ZH, Li NG, Du JJ, Hu W, Shen KT, Lu G, Fu G, Zhong M, Xu SH, Gu WY, Huang W, Zhao XT, Hu GX, Gu JR, Chen Z, Han ZG. Insight into hepatocellular carcinogenesis at transcriptome level by comparing gene expression profiles of hepatocellular carcinoma with those of corresponding noncancerous liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 15089–15094, 2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]