Abstract
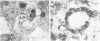
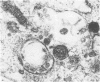
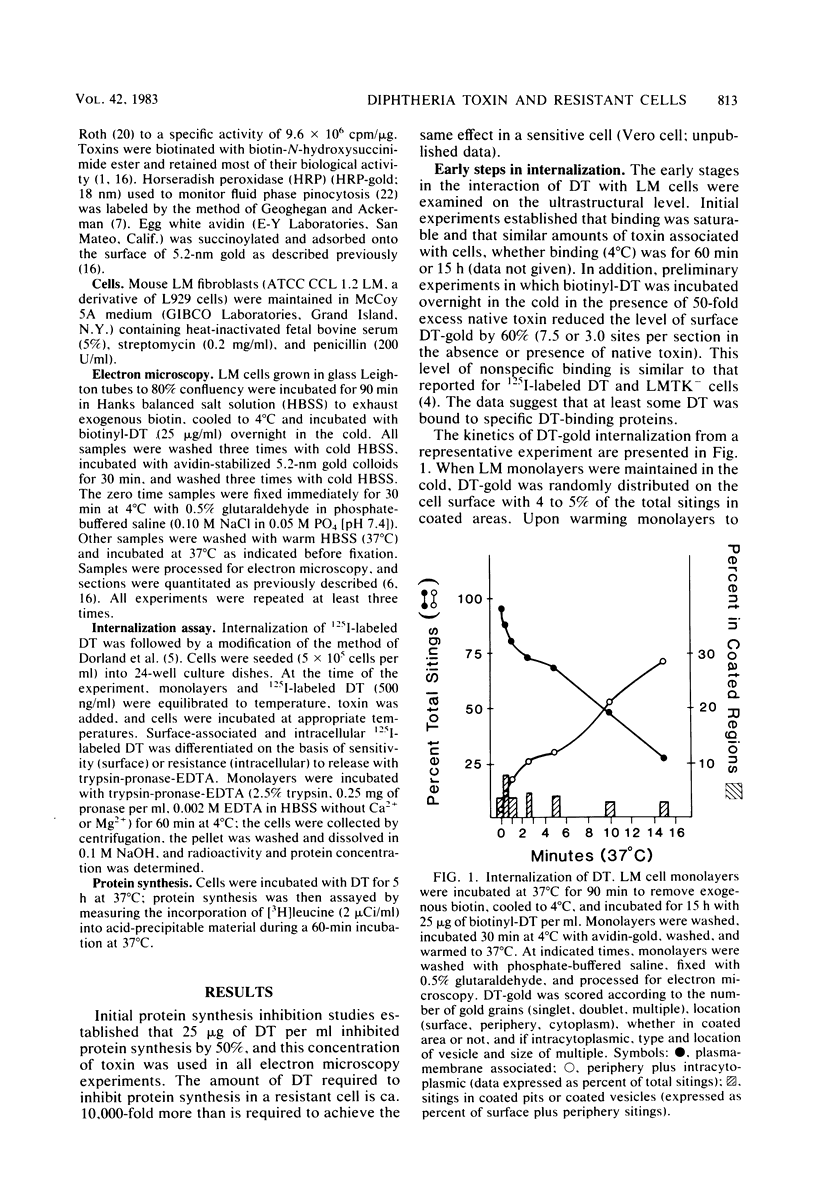
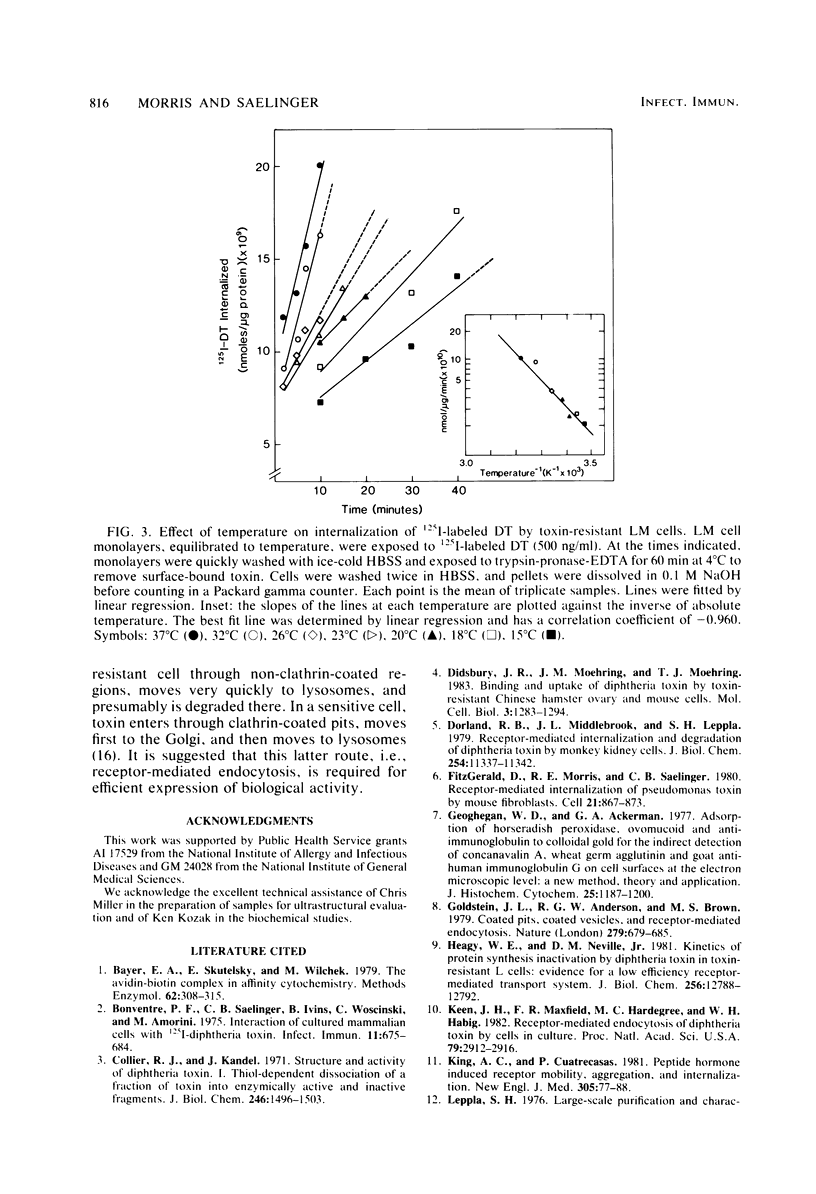
Diphtheria toxin (DT) and pseudomonas toxin are two distinct microbial toxins which inhibit protein synthesis in an identical manner, i.e., by the inactivation of cytoplasmic elongation factor 2. Although murine cells bind both toxins, they are 10,000-fold less sensitive to DT than to pseudomonas toxin. This suggests that the level of resistance resides at some event after binding. We have previously shown that pseudomonas toxin enters mouse LM fibroblasts by receptor-mediated endocytosis, a process in which ligand is internalized via specialized clathrin-coated pits and moves to the Golgi region and then to the lysosomes. Here, we visually follow the entry and trafficking of DT by resistant mouse fibroblasts. A biotinyl-toxin-avidin-gold system was used to visualize DT on the ultrastructural level. DT entered resistant cells through non-clathrin-coated regions of the plasma membrane and within 2.5 to 5 min was seen in lysosomes. Only rarely was DT seen in coated pits or in the Golgi region. Furthermore, the temperature dependence of internalization of 125I-labeled horseradish peroxidase and 125I-labeled DT by LM cells was similar. On the basis of these observations, we postulate that DT does not enter DT-resistant LM cells by receptor-mediated endocytosis and that receptor-mediated endocytosis is required for efficient expression of toxicity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayer E. A., Skutelsky E., Wilchek M. The avidin-biotin complex in affinity cytochemistry. Methods Enzymol. 1979;62:308–315. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)62235-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre P. F., Saelinger C. B., Ivins B., Woscinski C., Amorini M. Interaction of cultured mammalian cells with [125I] diphtheria toxin. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):675–684. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.675-684.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J., Kandel J. Structure and activity of diphtheria toxin. I. Thiol-dependent dissociation of a fraction of toxin into enzymically active and inactive fragments. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1496–1503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Didsbury J. R., Moehring J. M., Moehring T. J. Binding and uptake of diphtheria toxin by toxin-resistant Chinese hamster ovary and mouse cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;3(7):1283–1294. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.7.1283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorland R. B., Middlebrook J. L., Leppla S. H. Receptor-mediated internalization and degradation of diphtheria toxin by monkey kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11337–11342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FitzGerald D., Morris R. E., Saelinger C. B. Receptor-mediated internalization of Pseudomonas toxin by mouse fibroblasts. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):867–873. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90450-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geoghegan W. D., Ackerman G. A. Adsorption of horseradish peroxidase, ovomucoid and anti-immunoglobulin to colloidal gold for the indirect detection of concanavalin A, wheat germ agglutinin and goat anti-human immunoglobulin G on cell surfaces at the electron microscopic level: a new method, theory and application. J Histochem Cytochem. 1977 Nov;25(11):1187–1200. doi: 10.1177/25.11.21217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G., Brown M. S. Coated pits, coated vesicles, and receptor-mediated endocytosis. Nature. 1979 Jun 21;279(5715):679–685. doi: 10.1038/279679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heagy W. E., Neville D. M., Jr Kinetics of protein synthesis inactivation by diphtheria toxin in toxin-resistant L cells. Evidence for a low efficiency receptor-mediated transport system. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12788–12792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen J. H., Maxfield F. R., Hardegree M. C., Habig W. H. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of diphtheria toxin by cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2912–2916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. C., Cuatrecasas P. Peptide hormone-induced receptor mobility, aggregation, and internalization. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jul 9;305(2):77–88. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198107093050206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppla S. H. Large-scale purification and characterization of the exotoxin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):1077–1086. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.1077-1086.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook J. L., Dorland R. B., Leppla S. H. Association of diphtheria toxin with Vero cells. Demonstration of a receptor. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7325–7330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehring T. J., Moehring J. M. Interaction of diphtheria toxin and its active subunit, fragment A, with toxin-sensitive and toxin-resistant cells. Infect Immun. 1976 May;13(5):1426–1432. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.5.1426-1432.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehring T. J., Moehring J. M. Selection and characterization of cells resistant to diphtheria toxin and pseudomonas exotoxin A: presumptive translational mutants. Cell. 1977 Jun;11(2):447–454. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris R. E., Manhart M. D., Saelinger C. B. Receptor-mediated entry of Pseudomonas toxin: methylamine blocks clustering step. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):806–811. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.806-811.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Diphtheria toxin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:69–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I. H., Willingham M. C. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of hormones in cultured cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1981;43:239–250. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.43.030181.001323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. R., Peng S. S., Marshall J. L. Mutant Chinese hamster ovary cells pleiotropically defective in receptor-mediated endocytosis. J Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;96(4):1064–1071. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.4.1064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. Methods for assessing immunologic and biologic properties of iodinated peptide hormones. Methods Enzymol. 1975;37:223–233. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)37018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salisbury J. L., Condeelis J. S., Satir P. Receptor-mediated endocytosis: machinery and regulation of the clathrin-coated vesicle pathway. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1983;24:1–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Mellman I. S., Muller W. A., Cohn Z. A. Endocytosis and the recycling of plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;96(1):1–27. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Silver J. M., Cohn Z. A. Pinocytosis in fibroblasts. Quantitative studies in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1974 Dec;63(3):949–969. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.3.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel P. H., Oka J. A. Temperature dependence of endocytosis mediated by the asialoglycoprotein receptor in isolated rat hepatocytes. Evidence for two potentially rate-limiting steps. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2615–2617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]