Abstract
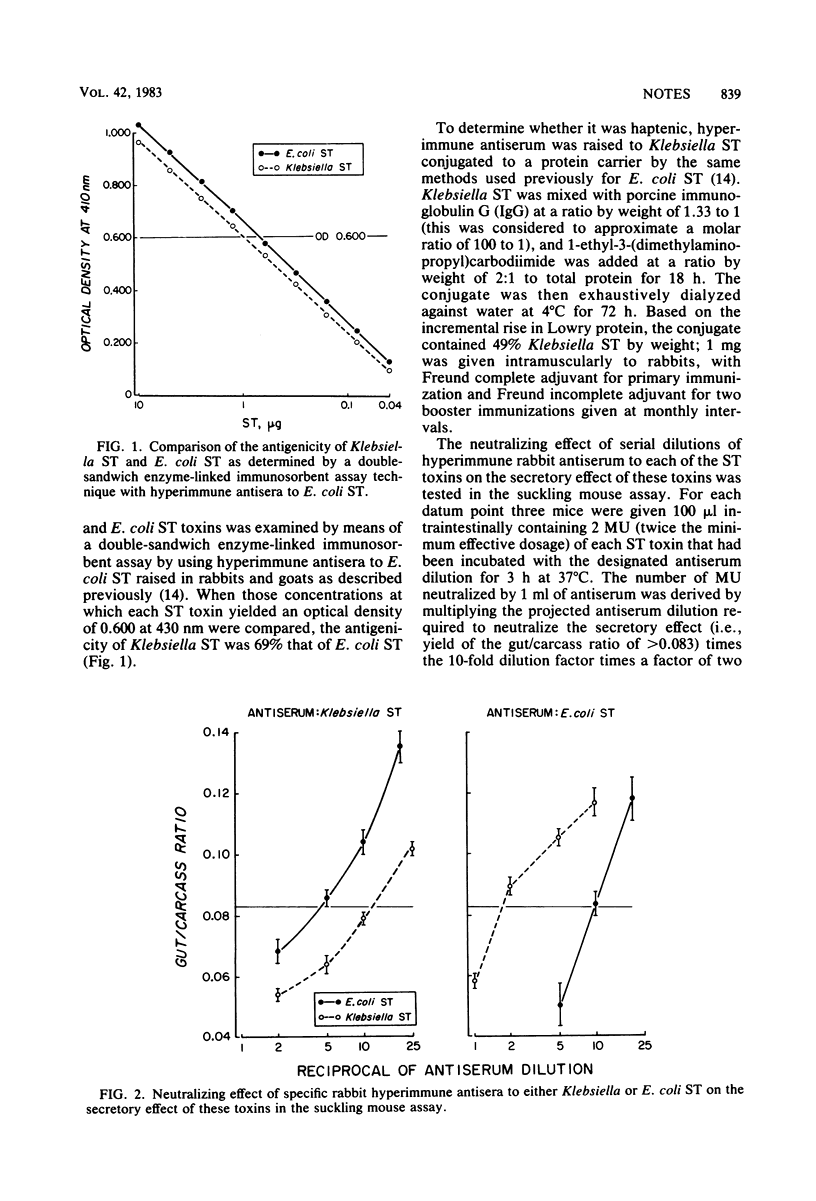
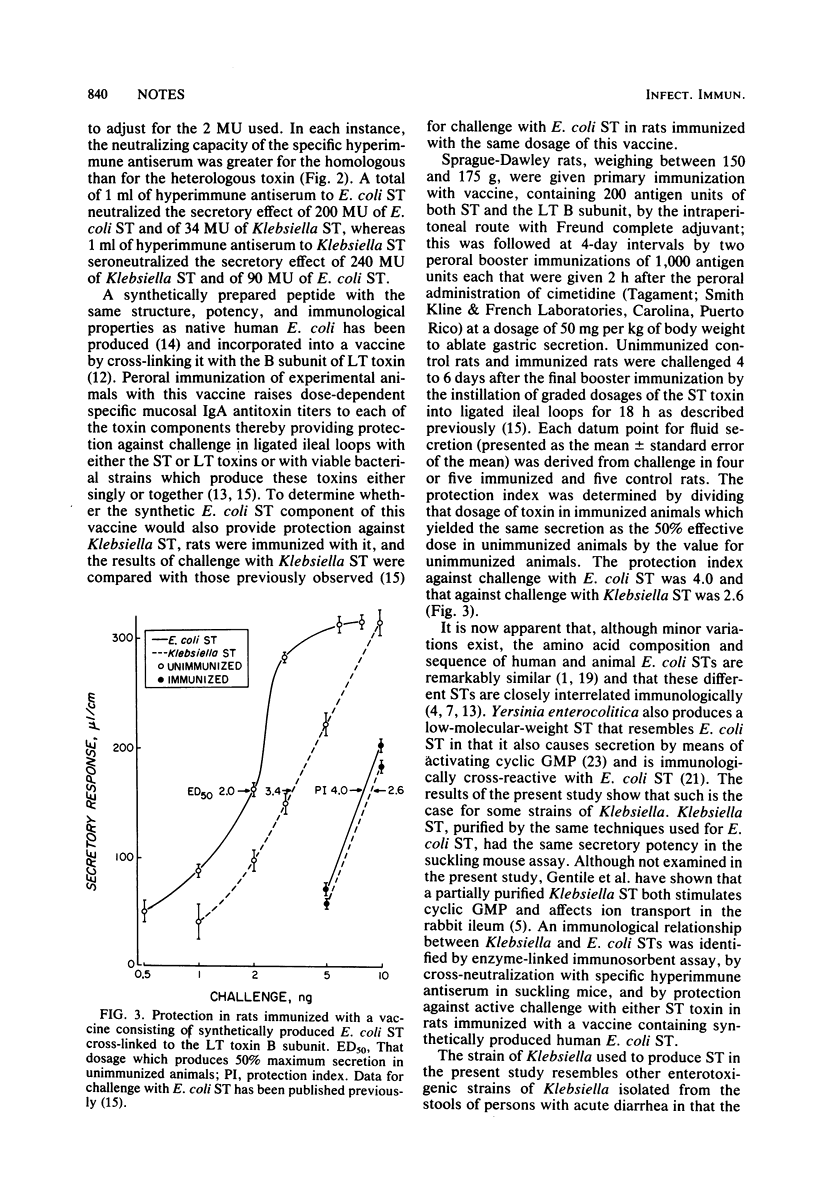
Klebsiella pneumoniae heat-stable enterotoxin was purified to apparent homogenicity by the same techniques used to purify Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin. The two toxins had the same potency in the suckling mouse assay and showed immunological cross-reactivity in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, neutralization of secretory activity by specific hyperimmune antisera, and protection against active challenge in rats immunized with a vaccine containing synthetically produced E. coli heat-stable enterotoxin.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aimoto S., Takao T., Shimonishi Y., Hara S., Takeda T., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Amino-acid sequence of a heat-stable enterotoxin produced by human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec 15;129(2):257–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bäck E., Jonsson M., Wadström T. Enterotoxin-producing bacteria stools from Swedish United Nations soldiers in Cyprus. Infection. 1978;6(3):116–120. doi: 10.1007/BF01642259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb M., Bhujwala R. A., Shriniwas, Singh M. Klebsiella pneumoniae as the possible cause of an outbreak of diarrhoea in a neonatal special care unit. Indian J Med Res. 1980 Mar;71:359–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frantz J. C., Robertson D. C. Immunological properties of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxins: development of a radioimmunoassay specific for heat-stable enterotoxins with suckling mouse activity. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):193–198. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.193-198.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Drake K. W., Luttrell M. Development of a radioimmunoassay for Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin: comparison with the suckling mouse bioassay. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):186–192. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.186-192.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A. Suckling mouse model for detection of heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin: characteristics of the model. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):95–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.95-99.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Dickens M. D., Wenzel R. P., Kapikian A. Z. Toxigenic bacterial diarrhea: nursery outbreak involving multiple bacterial strains. J Pediatr. 1976 Dec;89(6):885–891. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80591-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Moore R. A., Kirschenfeld P. M., Sande M. A. Role of toxigenic and invasive bacteria in acute diarrhea of childhood. N Engl J Med. 1975 Sep 18;293(12):567–572. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197509182931201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jhanjee A., Asnani P. J. Klebsiella pneumoniae enterotoxin. I. Effect of aeration on production and toxicity assay in animals. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1982;29(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F., Clements J. D., Houghten R. A. Protection against human and porcine enterotoxigenic strains of Escherichia coli in rats immunized with a cross-linked toxoid vaccine. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):924–929. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.924-929.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F., Clements J. D., Houghten R. A. Vaccine for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli based on synthetic heat-stable toxin crossed-linked to the B subunit of heat-labile toxin. J Infect Dis. 1983 Feb;147(2):318–326. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.2.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F., Houghten R. A. Properties of synthetically produced Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):117–121. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.117-121.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F., Houghten R. A. Protection in rabbits immunized with a vaccine of Escherichia coli heat-stable toxin cross-linked to the heat-labile toxin B subunit. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):888–893. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.888-893.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F. Purification and properties of Klebsiella pneumoniae heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1976 Feb;13(2):373–381. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.2.373-381.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Guerrant R. L., Wells J. G., Short H. B., Engert R. F. Comparison of assay of coliform enterotoxins by conventional techniques versus in vivo intestinal perfusion. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):146–152. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.146-152.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Holdeman L. V., Corcino J. J., Moore W. E. Enterotoxigenic intestinal bacteria in tropical sprue. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Nov;79(5):632–641. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-5-632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Horowitz I. R., Engert R. F., Schnenk E. A. Effect of Klebsiella pneumoniae enterotoxin on intestinal transport in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):799–807. doi: 10.1172/JCI108158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lallier R., Bernard F., Gendreau M., Lazure C., Seidah N. G., Chrétien M., St-Pierre S. A. Isolation and purification of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin of porcine origin. Anal Biochem. 1982 Dec;127(2):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90171-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao M. C., Guandalini S., Laird W. J., Field M. Effects of heat-stable enterotoxin of Yersinia enterocolitica on ion transport and cyclic guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate metabolism in rabbit ileum. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):875–878. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.875-878.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoub B. D., Greeff A. S., Lecatsas G., Prozesky O. W., Hay I. T., Prinsloo J. G., Ballard R. C. A microbiological investigation of acute summer gastroenteritis in black South African infants. J Hyg (Lond) 1977 Jun;78(3):377–385. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400056278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staples S. J., Asher S. E., Giannella R. A. Purification and characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by a strain of E. coli pathogenic for man. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4716–4721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T., Aust-Kettis A., Habte D., Holmgren J., Meeuwisse G., Möllby R., Söderlind O. Enterotoxin-producing bacteria and parasites in stools of Ethiopian children with diarrhoeal disease. Arch Dis Child. 1976 Nov;51(11):865–870. doi: 10.1136/adc.51.11.865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcock B. P. Experimental Klebsiella and Salmonella infection in neonatal swine. Can J Comp Med. 1979 Apr;43(2):200–206. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


