Abstract
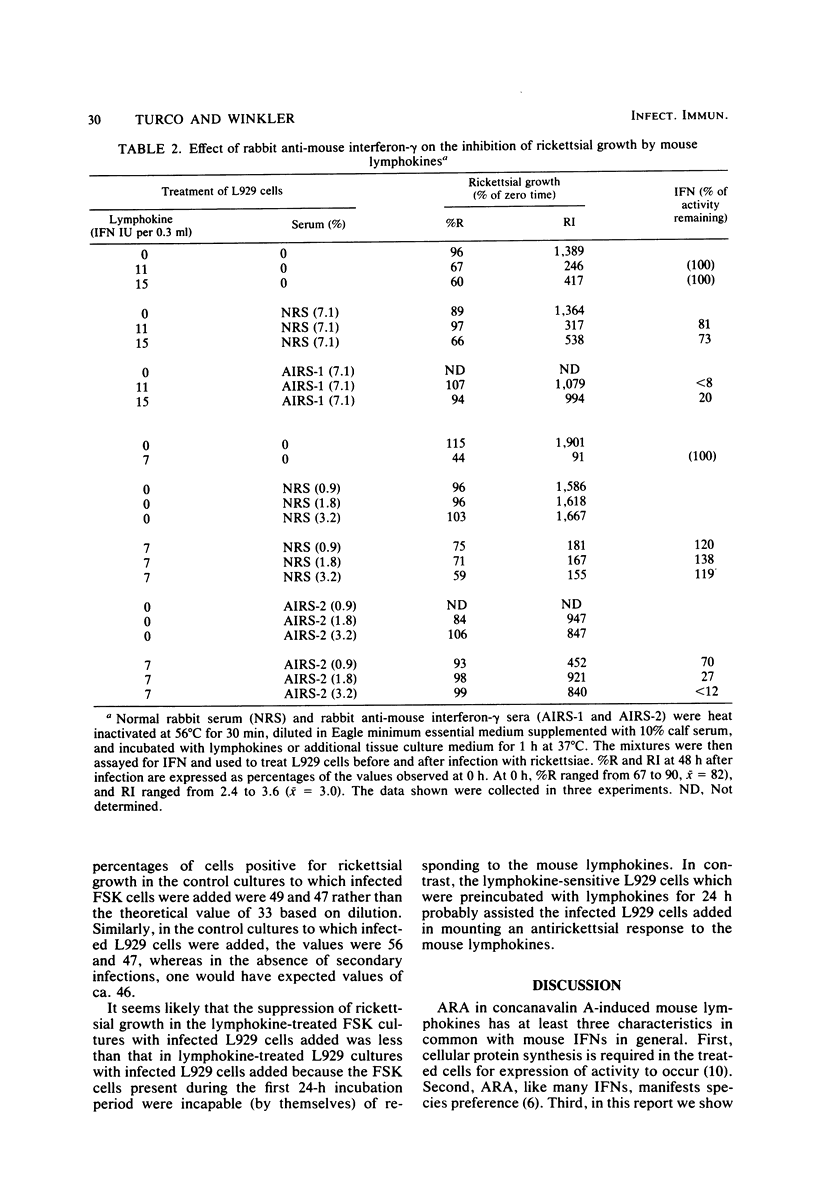
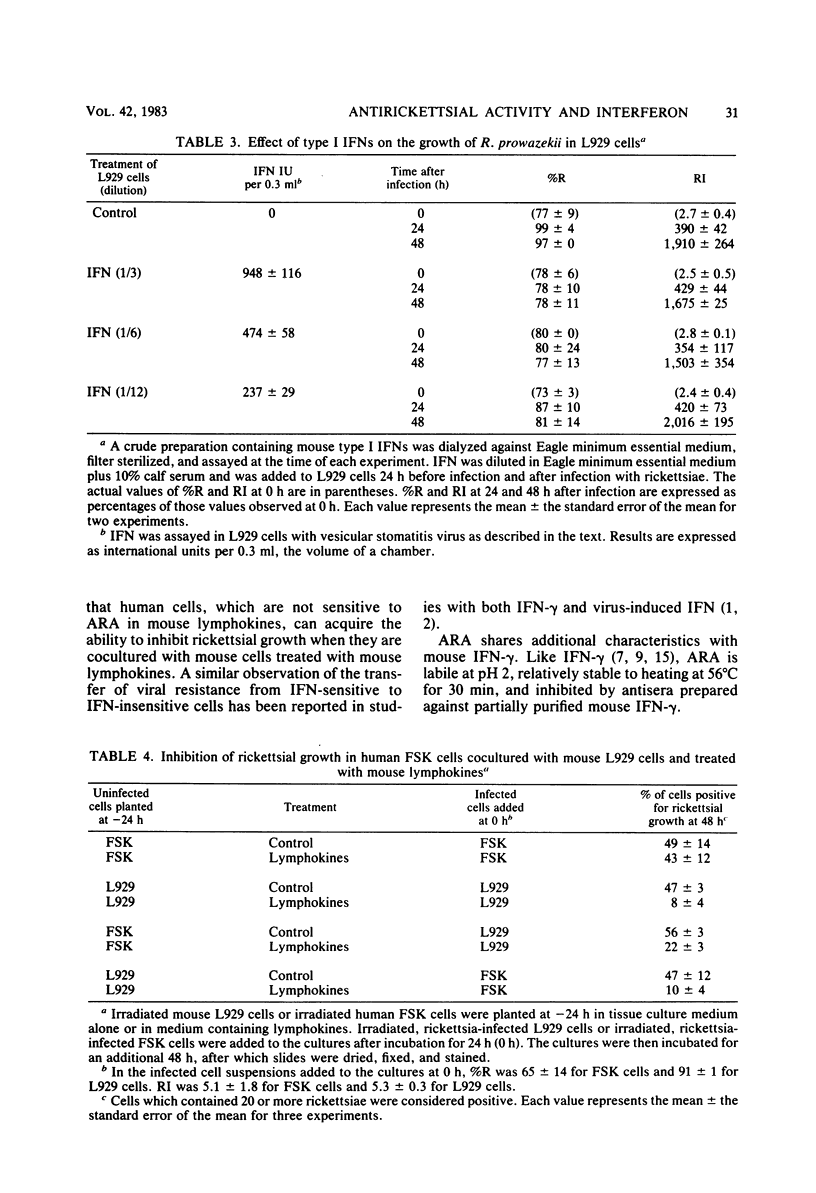
Certain properties of the antirickettsial activity and interferon in lymphokine preparations obtained from concanavalin A-stimulated mouse spleen cells were compared. Both the antirickettsial activity and interferon were relatively stable to heating at 56 degrees C, whereas both activities were destroyed by trypsin, by heating at 80 degrees C, or by exposure to pH 2 for 24 h. Both activities were likewise inhibited after incubation with rabbit antisera to partially purified murine interferon-gamma. In contrast to the mouse lymphokine preparations, which contained both interferon-gamma and antirickettsial activity, a preparation of virus-induced interferons (type I) had no detectable antirickettsial activity. Human foreskin fibroblasts, which were not sensitive to the antirickettsial activity in mouse lymphokines, acquired the ability to inhibit rickettsial growth when they were cocultured with sensitive mouse L929 cells treated with mouse lymphokines. These results are consistent with the idea that the antirickettsial activity in mouse lymphokines is due to interferon-gamma.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blalock J. E., Baron S. Interferon-induced transfer of viral resistance between animal cells. Nature. 1977 Sep 29;269(5627):422–425. doi: 10.1038/269422a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blalock J. E., Georgiades J., Johnson H. M. Immune-type interferon-induced transfer of viral resistance. J Immunol. 1979 Mar;122(3):1018–1021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A., Vilcek J. Production of high-titered interferon in cultures of human diploid cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Dec;2(6):476–484. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.6.476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson D. R., Joklik W. K. The mechanism of interferon induction by UV-irradiated reovirus. Virology. 1978 Dec;91(2):389–406. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90386-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Interferon nomenclature. Nature. 1980 Jul 10;286(5769):110–110. doi: 10.1038/286110a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazar J., Krautwurst P. A., Gordon F. B. Effect of Interferon and Interferon Inducers on Infections with a Nonviral Intracellular Microorganism, Rickettsia akari. Infect Immun. 1971 Jun;3(6):819–824. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.6.819-824.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne L. C., Georgiades J. A., Johnson H. M. Classification of interferons with antibody to immune interferon. Cell Immunol. 1980 Jul 15;53(1):65–70. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90426-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirahata T., Shimizu K. Production and properties of immune interferon from spleen cell cultures of Toxoplasma-infected mice. Microbiol Immunol. 1980;24(11):1109–1120. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1980.tb02915.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanos S., Catinot L., Wietzerbin J., Falcoff E. Production of antibodies against mouse immune T (type II) interferon and their neutralizing properties. J Gen Virol. 1980 Sep;50(1):225–229. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-1-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Winkler H. H. Inhibition of the growth of Rickettsia prowazekii in cultured fibroblasts by lymphokines. J Exp Med. 1983 Mar 1;157(3):974–986. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.3.974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker T. S., Winkler H. H. Rickettsial hemolysis: rapid method for enumeration of metabolically active typhus rickettsiae. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 May;9(5):645–647. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.5.645-647.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisseman C. L., Jr, Waddell A. D., Walsh W. T. In vitro studies of the action of antibiotics on Rickettsia prowazeki by two basic methods of cell culture. J Infect Dis. 1974 Dec;130(6):564–574. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.6.564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngner J. S., Salvin S. B. Production and properties of migration inhibitory factor and interferon in the circulation of mice with delayed hypersensitivity. J Immunol. 1973 Dec;111(6):1914–1922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


