Abstract
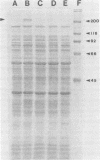
Transposon Tn5 was used to isolate mutants of Bordetella pertussis. Strains with Tn5 insertions were screened for loss of virulence-associated factors, including filamentous hemagglutinin, hemolysin, and pertussis toxin. Several mutants deficient for hemolysin production were obtained. All produced dermonecrotic toxin, pertussis toxin, and filamentous hemagglutinin, but were found to vary with respect to adenylate cyclase production. One hemolysin mutant had no detectable adenylate cyclase activity; others had 0.6% or 16% wild-type activity, whereas a fourth seemed to be unaffected in terms of adenylate cyclase activity. Mutants deficient in the ability to hemagglutinate sheep erythrocytes were also isolated. These mutants either failed to synthesize or produced reduced amounts of three protein species of 200,000, 130,000, and 100,000 daltons, all of which reacted with antiserum to filamentous hemagglutinin. Pertussis toxin mutants were identified by screening culture supernatants for failure to induce a clustered growth pattern in Chinese hamster ovary cells, and identification was confirmed by the standard histamine-sensitizing assay in mice. These mutants will be useful to determine the relative contribution of each virulence factor to pathogenicity as well as to determine the identity of the antigens important in protective immunity.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J., Low K. B. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 6. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Mar;44(1):1–56. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.1.1-56.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassford P., Beckwith J. Escherichia coli mutants accumulating the precursor of a secreted protein in the cytoplasm. Nature. 1979 Feb 15;277(5697):538–541. doi: 10.1038/277538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg D. E., Weiss A., Crossland L. Polarity of Tn5 insertion mutations in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):439–446. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.439-446.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A., Berg D. E., Botstein D., Lederberg E. M., Novick R. P., Starlinger P., Szybalski W. Nomenclature of transposable elements in prokaryotes. Gene. 1979 Mar;5(3):197–206. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chumley F. G., Menzel R., Roth J. R. Hfr formation directed by tn10. Genetics. 1979 Apr;91(4):639–655. doi: 10.1093/genetics/91.4.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cody C. L., Baraff L. J., Cherry J. D., Marcy S. M., Manclark C. R. Nature and rates of adverse reactions associated with DTP and DT immunizations in infants and children. Pediatrics. 1981 Nov;68(5):650–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Falkow S. Protein antigens from Staphylococcus aureus strains associated with toxic-shock syndrome. Science. 1981 Feb 20;211(4484):842–844. doi: 10.1126/science.7466361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Confer D. L., Eaton J. W. Phagocyte impotence caused by an invasive bacterial adenylate cyclase. Science. 1982 Sep 3;217(4563):948–950. doi: 10.1126/science.6287574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowell J. L., Hewlett E. L., Manclark C. R. Intracellular localization of the dermonecrotic toxin of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):896–901. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.896-901.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figurski D. H., Helinski D. R. Replication of an origin-containing derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett E. L., Manclark C. R., Wolff J. Adenyl cyclase in Bordetella pertussis vaccines. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S216–S219. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett E. L., Roberts C. O., Wolff J., Manclark C. R. Biphasic effect of pertussis vaccine on serum insulin in mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):137–144. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.137-144.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett E. L., Sauer K. T., Myers G. A., Cowell J. L., Guerrant R. L. Induction of a novel morphological response in Chinese hamster ovary cells by pertussis toxin. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1198–1203. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1198-1203.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett E. L., Urban M. A., Manclark C. R., Wolff J. Extracytoplasmic adenylate cyclase of Bordetella pertussis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1926–1930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett E., Wolff J. Soluble adenylate cyclase from the culture medium of Bordetella pertussis: purification and characterization. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):890–898. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.890-898.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R. A., Gill R. E., Hsu P., Minshew B. H., Falkow S. Construction and expression of recombinant plasmids encoding type 1 or D-mannose-resistant pili from a urinary tract infection Escherichia coli isolate. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):933–938. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.933-938.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KASUGA T., NAKASE Y., UKISHIMA K., TAKATSU K. Studies on Haemophilus pertussis. I. Antigen structure of H. pertussis and its phases. Kitasato Arch Exp Med. 1953 Nov;26(2-3):121–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Ui M. Direct modification of the membrane adenylate cyclase system by islet-activating protein due to ADP-ribosylation of a membrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3129–3133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai Y., Moribayashi A. Characteristic lipids of Bordetella pertussis: simple fatty acid composition, hydroxy fatty acids, and an ornithine-containing lipid. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):996–1005. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.996-1005.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai Y., Moribayashi A., Yano I. Ornithine-containing lipid of Bordetella pertussis that carries hemagglutinating activity. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):907–910. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.907-910.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N. Transposable elements in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:341–404. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. L., Ross E. M., Alderslade R., Bellman M. H., Rawson N. S. Pertussis immunisation and serious acute neurological illness in children. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 May 16;282(6276):1595–1599. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6276.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peppler M. S. Isolation and characterization of isogenic pairs of domed hemolytic and flat nonhemolytic colony types of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):840–851. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.840-851.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman M., Furman B. L., Wardlaw A. C. Bordetella pertussis respiratory tract infection in the mouse: pathophysiological responses. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jul;142(1):56–66. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.1.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman M. Pertussis toxin: the cause of the harmful effects and prolonged immunity of whooping cough. A hypothesis. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 May-Jun;1(3):401–412. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.3.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A., Irons L. I. Synergistic effect of Bordetella pertussis lymphocytosis-promoting factor on protective activities of isolated Bordetella antigens in mice. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):523–528. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.523-528.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein S. J., Jorgensen R. A., Postle K., Reznikoff W. S. The inverted repeats of Tn5 are functionally different. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):795–805. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80055-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvkun G. B., Ausubel F. M. A general method for site-directed mutagenesis in prokaryotes. Nature. 1981 Jan 1;289(5793):85–88. doi: 10.1038/289085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura M., Nogimori K., Murai S., Yajima M., Ito K., Katada T., Ui M., Ishii S. Subunit structure of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, in conformity with the A-B model. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5516–5522. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., Nakase Y. Mutant of Bordetella pertussis which lacks ability to produce filamentous hemagglutinin. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1018–1023. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1018-1023.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Falkow S. Plasmid transfer to Bordetella pertussis: conjugation and transformation. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):549–552. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.549-552.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Falkow S. Transposon insertion and subsequent donor formation promoted by Tn501 in Bordetella pertussis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):304–309. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.304-309.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff J., Cook G. H., Goldhammer A. R., Berkowitz S. A. Calmodulin activates prokaryotic adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3841–3844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]