Abstract
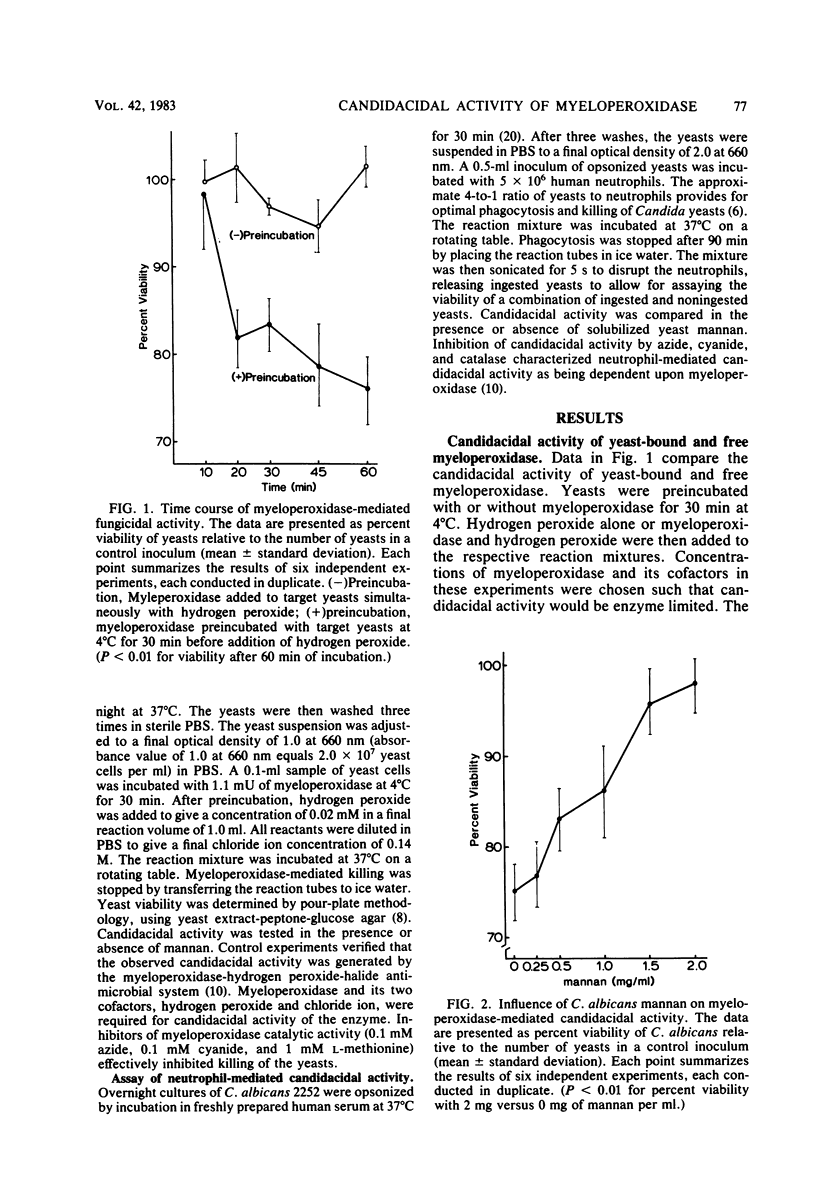
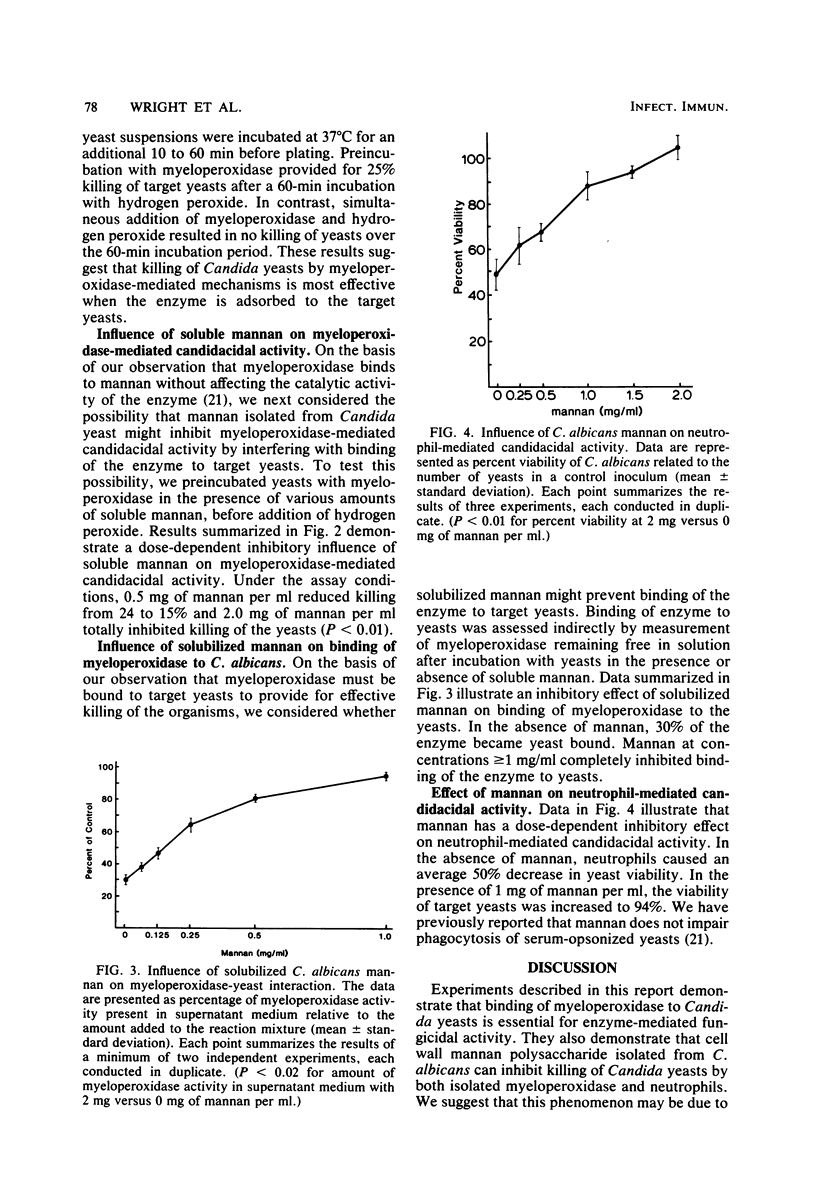
We have previously demonstrated the ability of human neutrophil myeloperoxidase to bind to mannan isolated from Candida albicans. Mannan may therefore be a primary component of the yeast cell wall which provides for binding of myeloperoxidase, a requirement potentially important for the candidacidal activity of the enzyme. In this report, we describe experiments to consider the relationship of the mannan-binding activity of myeloperoxidase to its candidacidal activity and the possibility that free mannan may inhibit myeloperoxidase-mediated candidacidal activity. We observed that binding of myeloperoxidase to the target yeasts was required for killing of C. albicans. We also observed that addition of soluble mannan significantly reduced myeloperoxidase-mediated killing of the yeasts in a dose-dependent manner by antagonizing binding of myeloperoxidase. Soluble mannan was demonstrated to have a similar dose-dependent inhibitory effect on neutrophil-mediated candidacidal activity without influencing phagocytosis of the organism. On the basis of these observations, we speculate that mannan solubilized in plasma and tissue fluid may interfere with neutrophil-mediated host defense against Candida infection.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. C., Krinsky N. I. The reductive cleavage of myeloperoxidase in half, producing enzymically active hemi-myeloperoxidase. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4211–4218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggiolini M., Hirsch J. G., De Duve C. Resolution of granules from rabbit heterophil leukocytes into distinct populations by zonal sedimentation. J Cell Biol. 1969 Feb;40(2):529–541. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P. Fungal infections complicating acute leukemia. J Chronic Dis. 1966 Jun;19(6):667–687. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(66)90066-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canales L., Middlemas R. O., 3rd, Louro J. M., South M. A. Immunological observations in chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis. Lancet. 1969 Sep 13;2(7620):567–571. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90264-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eickhoff T. C. Infectious complications in renal transplant recipients. Transplant Proc. 1973 Sep;5(3):1233–1238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Maallem H., Fletcher J. Effects of surgery on neutrophil granulocyte function. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):38–41. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.38-41.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Thong Y. H. A rapid one-step procedure for purification of mononuclear and polymorphonuclear leukocytes from human blood using a modification of the Hypaque-Ficoll technique. J Immunol Methods. 1978;24(3-4):389–393. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90143-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer A., Ballet J. J., Griscelli C. Specific inhibition of in vitro Candida-induced lymphocyte proliferation by polysaccharidic antigens present in the serum of patients with chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis. J Clin Invest. 1978 Nov;62(5):1005–1013. doi: 10.1172/JCI109204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Myeloperoxidase-halide-hydrogen peroxide antibacterial system. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2131–2138. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2131-2138.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laforce F. M., Mills D. M., Iverson K., Cousins R., Everett E. D. Inhibition of leukocyte candidacidal activity by serum from patients with disseminated candidiasis. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Oct;86(4):657–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I. Antifungal effects of peroxidase systems. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):361–365. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.361-365.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Cline M. J. Leukocyte myeloperoxidase deficiency and disseminated candidiasis: the role of myeloperoxidase in resistance to Candida infection. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1478–1488. doi: 10.1172/JCI106114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMurrough I., Rose A. H. Effect of growth rate and substrate limitation on the composition and structure of the cell wall of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem J. 1967 Oct;105(1):189–203. doi: 10.1042/bj1050189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R. L., Pazin G. J., Allen C. M. Disseminated candidiasis. Changes in incidence, underlying diseases, and pathology. Am J Clin Pathol. 1977 Jul;68(1):29–38. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/68.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacchi F., Cisternino M. A., Clivio A., Ferrari F. A., Fortunato A., Nespoli L., Beretta A., Siccardi A. G. Disorders of candidacidal activity and other neutrophil functions in three cases of chronic candidiasis. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1979;34(6):607–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraj R. J., Zgliczynski J. M., Paul B. B., Sbarra A. J. Enhanced killing of myeloperoxidase-coated bacteria in the myeloperoxidase-H2O2-Cl- system. J Infect Dis. 1978 Apr;137(4):481–485. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.4.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARDLAW A. C., PILLEMER L. The properdin system and immunity. V. The bactericidal activity of the properdin system. J Exp Med. 1956 May 1;103(5):553–575. doi: 10.1084/jem.103.5.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. D., Herron M. J., Gray G. R., Holmes B., Nelson R. D. Influence of yeast mannan on human neutrophil functions: inhibition of release of myeloperoxidase related to carbohydrate-binding property of the enzyme. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):731–738. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.731-738.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


