Abstract
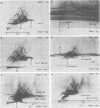
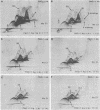
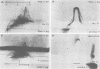
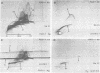
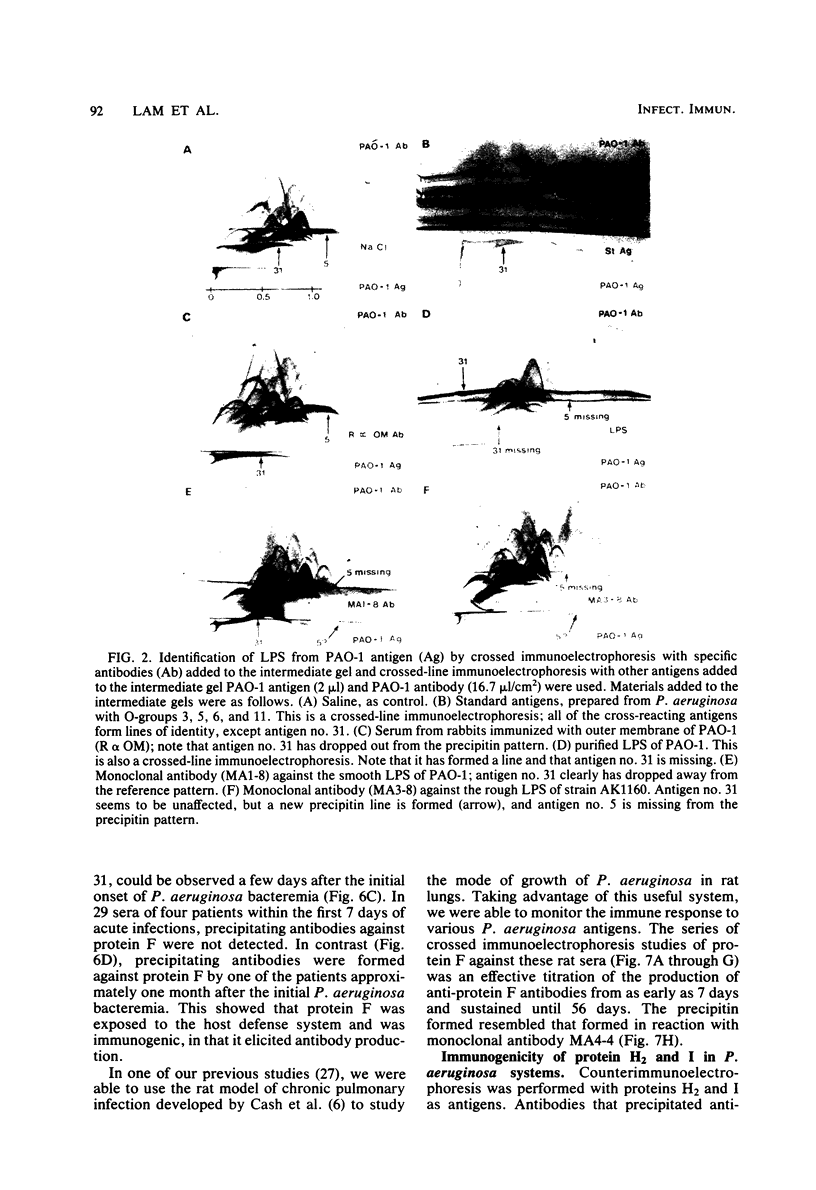
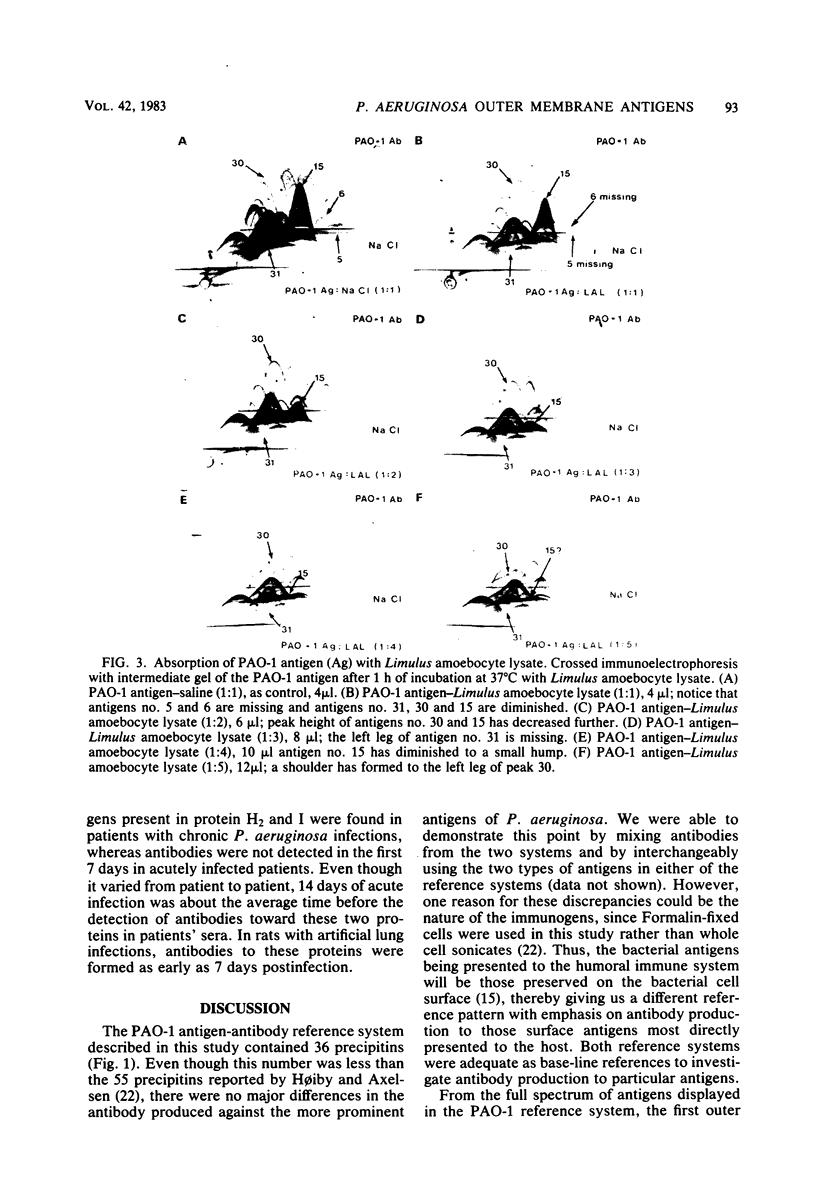
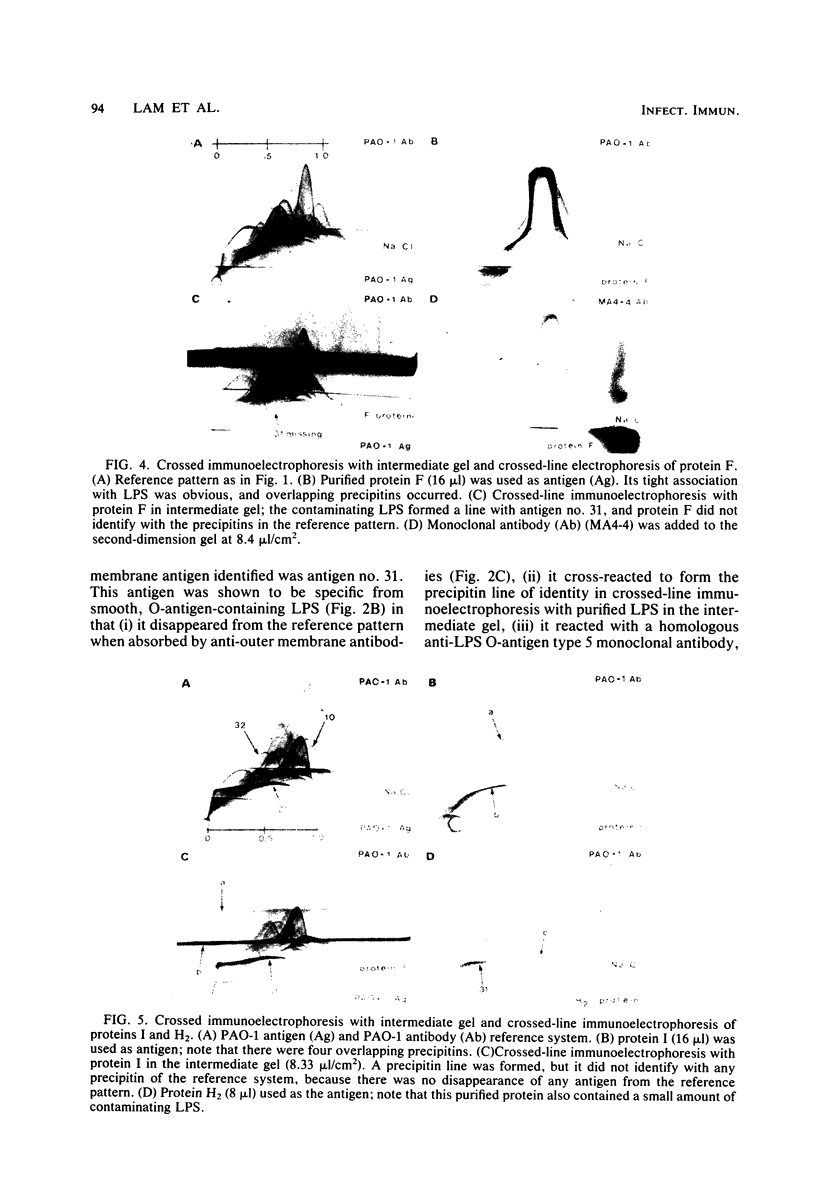
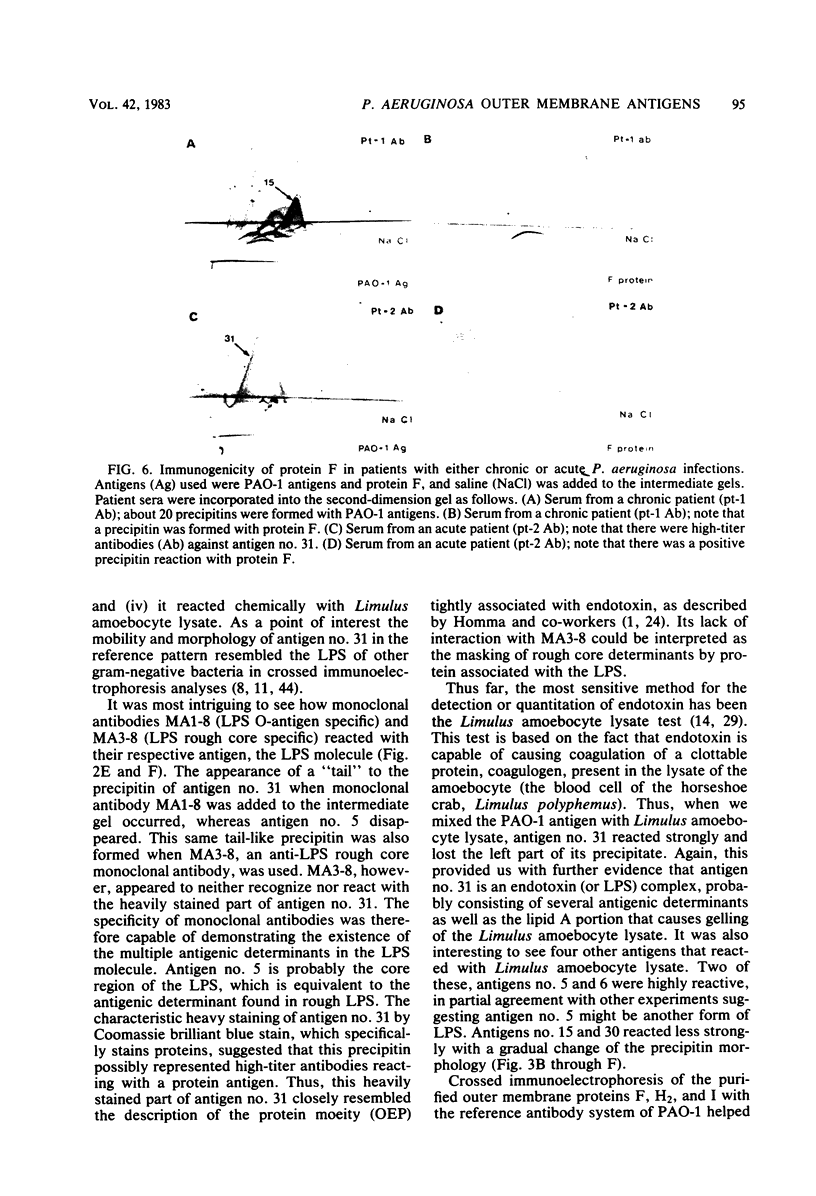
By crossed immunoelectrophoresis 36 different anode-migrating antigens were demonstrated in sonicated antigen preparations of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. We numbered these antigens to establish a reference precipitin pattern. Antigen no. 31 was identified as the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) antigen, because it was found to be responsible for the O-group specificity and because it reacted with anti-LPS monoclonal antibodies and with Limulus amoebocyte lysate. Purified outer membrane proteins F (porin), H2, and I used as antigens formed precipitins with the reference antibodies, thus establishing their antigenicity. LPS that copurified with protein F and slightly contaminated protein H2 was detectable as an extra precipitin (antigen no. 31). The use of monoclonal antibodies specific for smooth LPS and rough LPS revealed different antigenic determinants in the LPS molecule and suggested that antigen no. 5 could be the core region of the LPS which is equivalent to the rough LPS. Antibodies against these outer membrane antigens were detected in patients with chronic P. aeruginosa pneumonia and in patients with acute P. aeruginosa bacteremia. Antibodies with the same specificity were also found in rats chronically infected with P. aeruginosa 7 days postinfection. This demonstrates the surface accessibility and antigenic reactivity of outer membrane antigens.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe C., Tanamoto K. I., Homma J. Y. Infection protective property of the common antigen (OEP) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its chemical composition. Jpn J Exp Med. 1977 Oct;47(5):393–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adamus G., Mulczyk M., Witkowska D., Romanowska E. Protection against keratoconjunctivitis shigellosa induced by immunization with outer membrane proteins of Shigella spp. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):321–324. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.321-324.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P., Bolivar R., Fainstein V., Jadeja L. Infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Mar-Apr;5(2):279–313. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.2.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P. Epidemiological studies of Pseudomonas species in patients with leukemia. Am J Med Sci. 1970 Aug;260(2):82–89. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197008000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan T. M., Pearce W. A., Schoolnik G. K., Arko R. J. Protection against infection with Neisseria gonorrhoeae by immunization with outer membrane protein complex and purified pili. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S132–S137. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cash H. A., Woods D. E., McCullough B., Johanson W. G., Jr, Bass J. A. A rat model of chronic respiratory infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Mar;119(3):453–459. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.3.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. H., Hancock R. E., Mishell R. I. Mitogenic effects of purified outer membrane proteins from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):178–184. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.178-184.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. T., Cho S. N., Høiby N., Espersen F., Baek L., Reif J. S. Crossed immunoelectrophoretic analysis of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 antigens. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1428–1440. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1428-1440.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe K. E., Bass J. A., Young V. M., Straus D. C. Antibody response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoproducts in cancer patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jan;15(1):115–122. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.1.115-122.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espersen F., Hertz J. B., Høiby N., Mogensen H. H. Quantitative immunoelectrophoretic analysis of Salmonella typhi antigens and of corresponding antibodies in human sera. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1980 Aug;88(4):237–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb02634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes P. B., Kim C., Cundy K. R., Haung N. N. Antibodies to cell envelope proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis patients. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):527–532. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.527-532.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardi A., Arpagaus G. R. Improved microtechnique for endotoxin assay by the Limulus amebocyte lysate test. Anal Biochem. 1980 Dec;109(2):382–385. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90664-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Carey A. M. Outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: heat- 2-mercaptoethanol-modifiable proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):902–910. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.902-910.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Decad G. M., Nikaido H. Identification of the protein producing transmembrane diffusion pores in the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA01. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 5;554(2):323–331. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90373-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Wieczorek A. A., Mutharia L. M., Poole K. Monoclonal antibodies against Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane antigens: isolation and characterization. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):166–171. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.166-171.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoff G. E., Frasch C. E. Outer membrane antigens of Neisseria meningitidis group B serotype 2 studied by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):849–856. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.849-856.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiby N., Axelsen N. H. Identification and quantitation of precipitins against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with cystic fibrosis by means of crossed immunoelectrophoresis with intermediate gel. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Jun;81(3):298–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiby N. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis. Diagnostic and prognostic significance of pseudomonas aeruginosa precipitins determined by means of crossed immunoelectrophoresis. A survey. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand Suppl. 1977;(262):1–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll J. Crossed-line immunoelectrophoresis (73, 76). Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:79–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusi N., Nurminen M., Saxen H., Valtonen M., Mäkelä P. H. Immunization with major outer membrane proteins in experimental salmonellosis of mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):857–862. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.857-862.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam J., Chan R., Lam K., Costerton J. W. Production of mucoid microcolonies by Pseudomonas aeruginosa within infected lungs in cystic fibrosis. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):546–556. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.546-556.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J. The reaction between bacterial endotoxin and amebocyte lysate. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1979;29:131–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackie E. B., Brown K. N., Lam J., Costerton J. W. Morphological stabilization of capsules of group B streptococci, types Ia, Ib, II, and III, with specific antibody. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):609–617. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.609-617.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelsen O. S. Serotyping of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. 2. Results of an O group classification. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1970;78(2):163–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicas T. I., Hancock R. E. Outer membrane protein H1 of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: involvement in adaptive and mutational resistance to ethylenediaminetetraacetate, polymyxin B, and gentamicin. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):872–878. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.872-878.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J. STUDIES ON THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL. I. EVIDENCE FOR THE ROLE OF 2-KETO- 3-DEOXYOCTONATE IN THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:499–506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimpff S. C., Greene W. H., Young V. M., Wiernik P. H. Pseudomonas septicemia: incidence, epidemiology, prevention and therapy in patients with advanced cancer. Eur J Cancer. 1973 Jun;9(6):449–455. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(73)90110-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimpff S. C., Moody M., Young V. M. Relationship of colonization with Pseudomonas aeruginosa to development of Pseudomonas bacteremia in cancer patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1970;10:240–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiøtz P. O., Høiby N., Hertz J. B. Cross-reactions between Haemophilus influenzae and nineteen other bacterial species. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1979 Dec;87(6):337–344. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1979.tb02448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth C. J., Siegel J., Salton M. R., Owen P. Immunochemical analysis of inner and outer membranes of Escherichia coli by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):306–319. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.306-319.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitecar J. P., Jr, Luna M., Bodey G. P. Pseudomonas bacteremia in patients with malignant diseases. Am J Med Sci. 1970 Oct;60(4):216–223. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197010000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Mandrell R. E., Altieri P., Berman S., Lowenthal J., Artenstein M. S. Safety and immunogenicity of a Neisseria meningitidis type 2 protein vaccine in animals and humans. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jun;137(6):728–739. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.6.728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]