Abstract
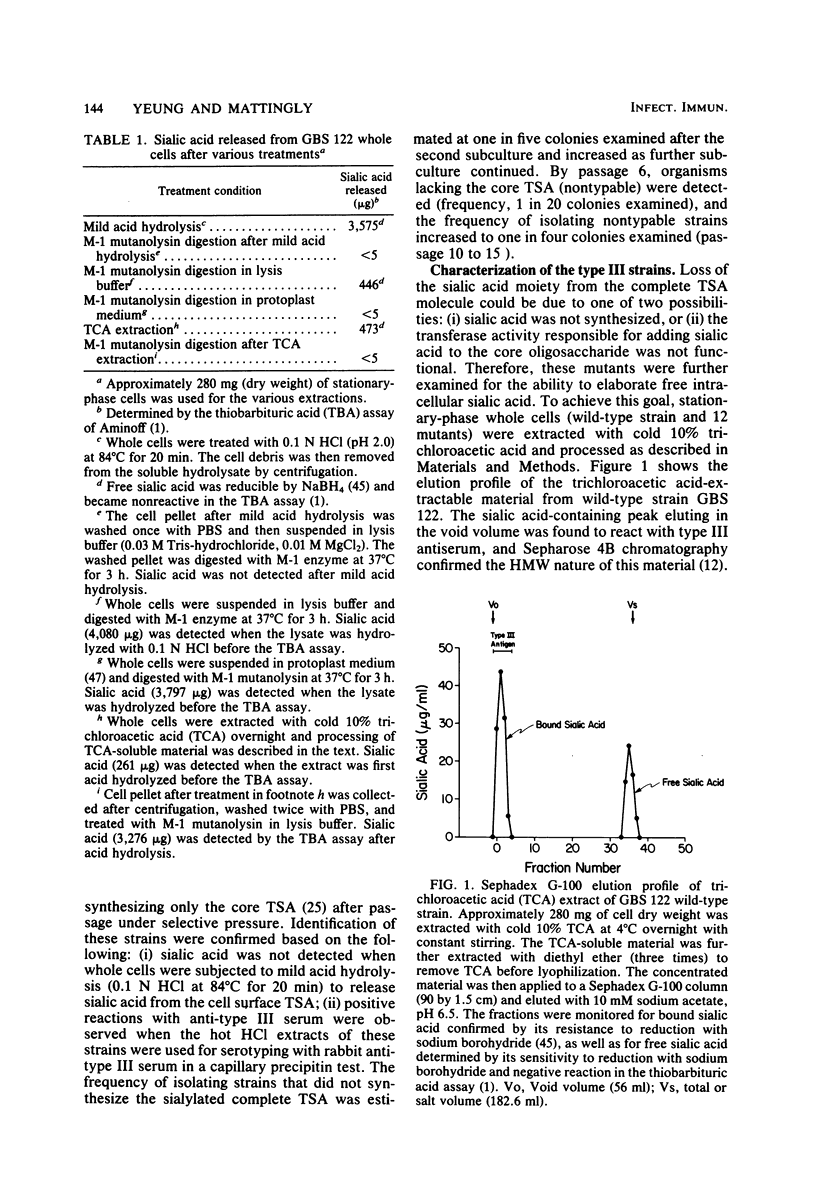
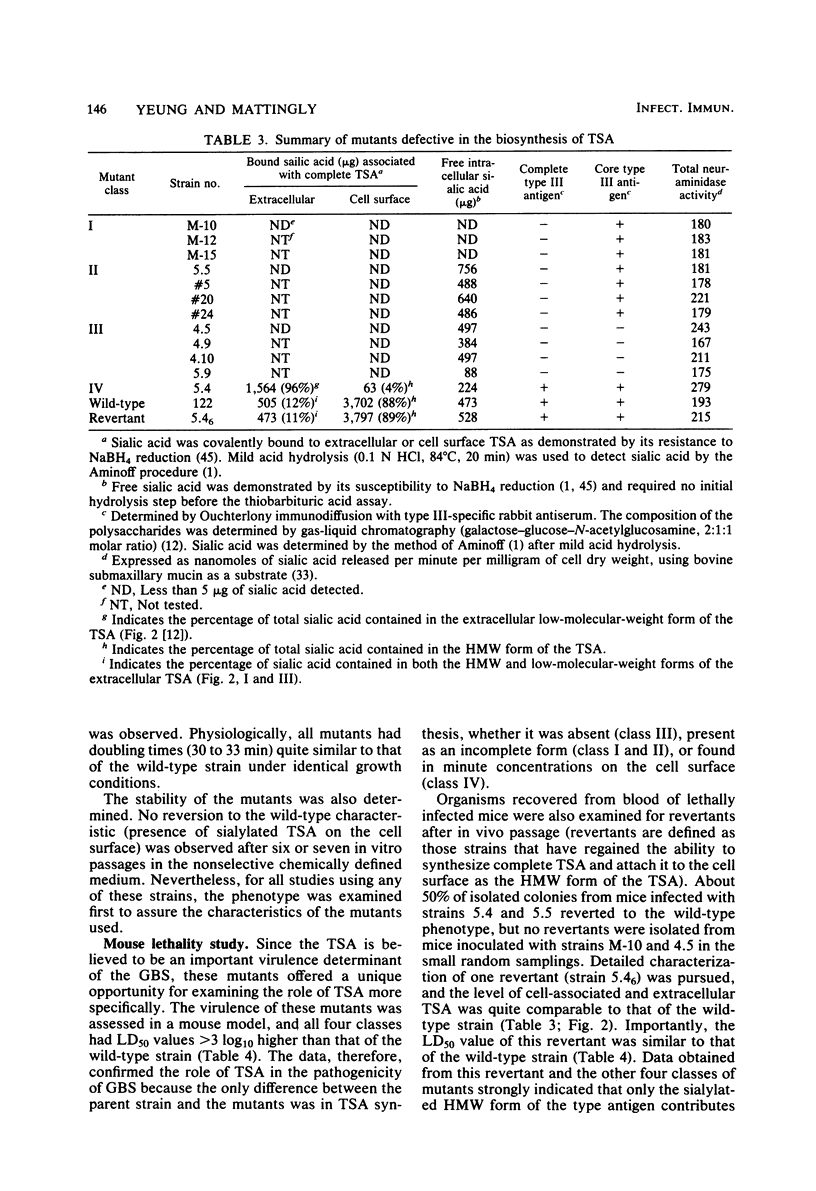
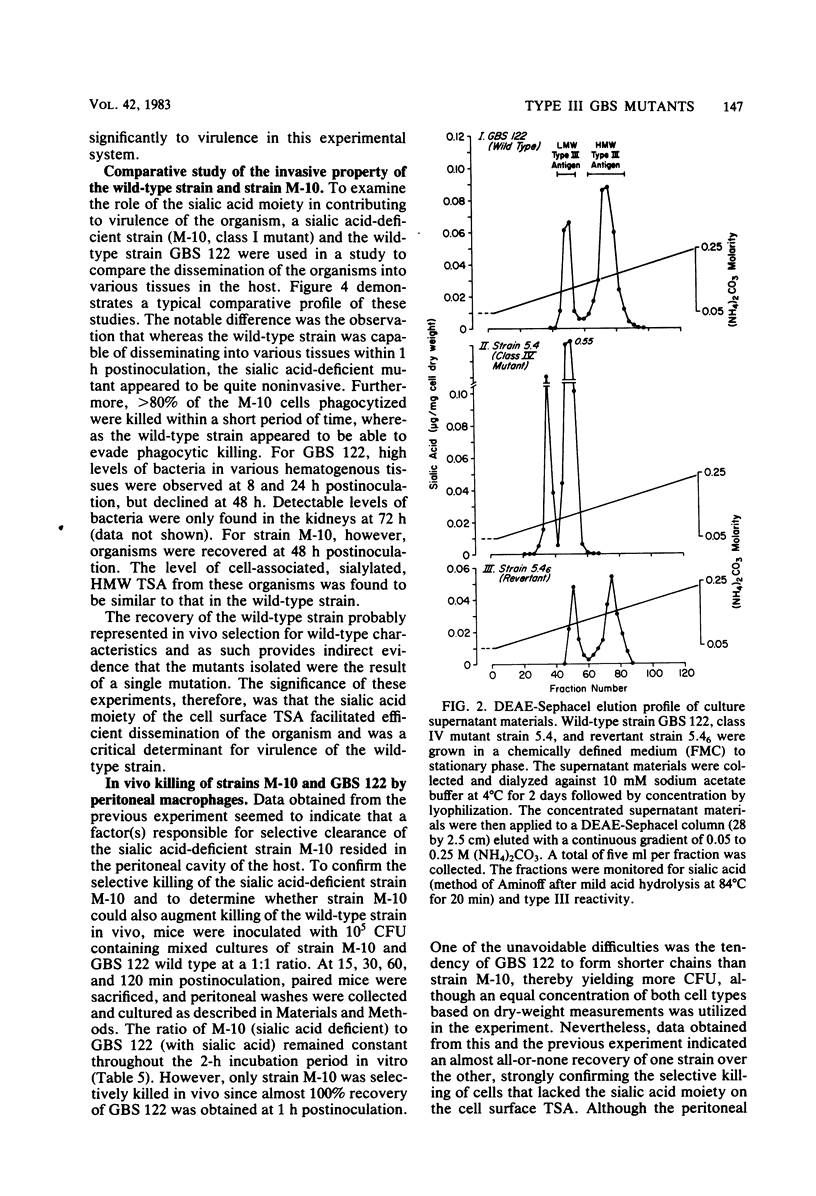
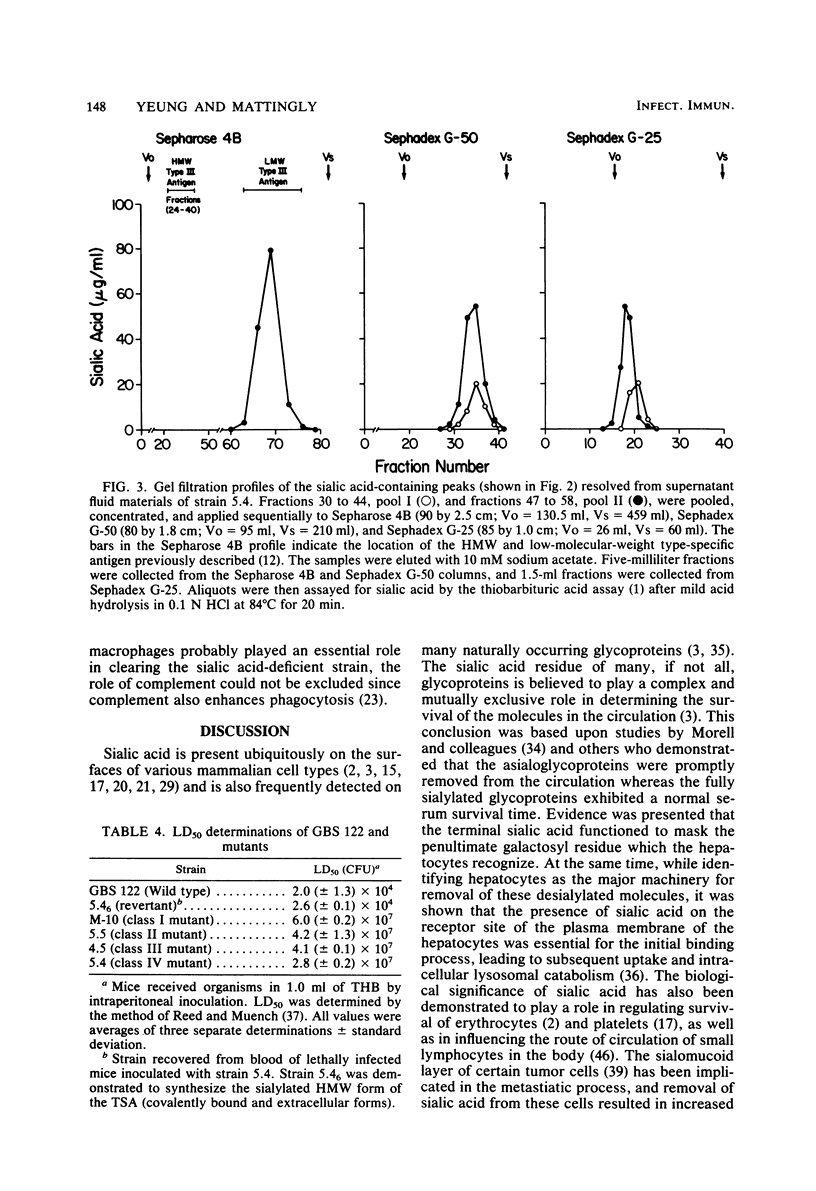
Four classes of mutants of type III group B streptococcus were isolated by serial subculture of the wild-type strain in the presence of type III-specific rabbit antiserum. Class I mutants no longer synthesized sialic acid but still elaborated the core antigen. Class II mutants maintained the ability to synthesize sialic acid but could not attach it to the core antigen. Class III mutants did not produce the core antigen but still synthesized intracellular sialic acid. Class IV mutants synthesized the complete antigen; however, only approximately 4% of the antigen synthesized was found associated with the cell wall peptidoglycan (in the wild-type strain greater than 85% of the antigen synthesized is covalently attached to the cell wall peptidoglycan), whereas greater than 90% of the antigen was secreted into the growth medium. Production of other components (CAMP factor, group B antigen, beta-hemolysin, neuraminidase) by these mutants appeared similar to those of the wild-type strain. Mouse lethality studies of these strains indicated that all four classes have greater than 3 log10-higher 50% lethal dose values than that of the wild-type strain. To understand the basis for this variation, the invasive ability of the wild-type strain and the sialic acid-deficient mutant strain M-10 (class I) was examined. Mice received 10(5) CFU of each organism; they were then sacrificed at various times postinoculation, and viable group B streptococci from different organs were enumerated. Mice were able to clear M-10 more efficiently, with greater than 80% of M-10 cells being phagocytized by macrophages within 1 h, whereas the wild-type strain was able to evade phagocytic killing and disseminate to other tissues. These data, therefore, strongly indicate that the sialic acid moiety greatly enhances the virulence of the type III antigen. In addition, the level of cell-associated type-specific antigen appears to contribute significantly to the pathogenicity of the organism.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMINOFF D. Methods for the quantitative estimation of N-acetylneuraminic acid and their application to hydrolysates of sialomucoids. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:384–392. doi: 10.1042/bj0810384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aminoff D., Bell W. C., Fulton I., Ibgebrigtsen N. Effect of sialidase on the viability of erythrocytes in circulation. Am J Hematol. 1976;1(4):419–432. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830010407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashwell G., Morell A. G. The role of surface carbohydrates in the hepatic recognition and transport of circulating glycoproteins. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1974;41(0):99–128. doi: 10.1002/9780470122860.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRY G. T. Colominic acid, a polymer of N-acetylneuraminic acid. J Exp Med. 1958 Apr 1;107(4):507–521. doi: 10.1084/jem.107.4.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS S. N., KRAUSE R. M. ANTIGENIC RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN GROUPS B AND G STREPTOCOCCI. J Exp Med. 1964 Oct 1;120:629–637. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.4.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey R. B., Eisenstein T. K., Shockman G. D., Greber T. F., Swenson R. M. Soluble group- and type-specific antigens from type III group B Streptococcus. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):195–203. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.195-203.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleat P. H., Coid C. R. Phagocytic and bactericidal activity of human neutrophils against two isolates of Group B streptococci Type Ic of differing pathogenicity. Br J Exp Pathol. 1981 Aug;62(4):393–397. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Cueninck B. J., Shockman G. D., Swenson R. M. Group B, type III streptococcal cell wall: composition and structural aspects revealed through endo-N-acetylmuramidase-catalyzed hydrolysis. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):572–581. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.572-581.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doran T. I., Mattingly S. J. Association of type- and group-specific antigens with the cell wall of serotype III group B streptococcus. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1115–1122. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1115-1122.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doran T. I., Straus D. C., Mattingly S. J. Factors influencing release of type III antigens by group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):615–623. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.615-623.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durham D. L., Mattingly S. J., Doran T. I., Milligan T. W., Straus D. C. Correlation between the production of extracellular substances by type III group B streptococcal strains and virulence in a mouse model. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):448–454. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.448-454.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards M. S., Kasper D. L., Jennings H. J., Baker C. J., Nicholson-Weller A. Capsular sialic acid prevents activation of the alternative complement pathway by type III, group B streptococci. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1278–1283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer G. W., Hunter K. W., Wilson S. R. Type III group B streptococcal strain differences in susceptibility to opsonization with human serum. Pediatr Res. 1981 Dec;15(12):1525–1529. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198112000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J., Packham M. A., Cazenave J. P., Reimers H. J., Mustard J. F. Effects on platelet function of removal of platelet sialic acid by neuraminidase. Lab Invest. 1975 Apr;32(4):476–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastings M. J., Easmon C. S. Variations in the opsonic requirements of group B streptococcus type III. Br J Exp Pathol. 1981 Oct;62(5):519–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemming V. G., Hall R. T., Rhodes P. G., Shigeoka A. O., Hill H. R. Assessment of group B streptococcal opsonins in human and rabbit serum by neutrophil chemiluminescence. J Clin Invest. 1976 Dec;58(6):1379–1387. doi: 10.1172/JCI108593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henricks P. A., van Erne-van der Tol M. E., Verhoef J. Partial removal of sialic acid enhances phagocytosis and the generation of superoxide and chemiluminescence by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):745–750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. C., Palmer P. D., Sanford B. H. Factors involved in the cytotoxicity of normal guinea pig serum for cells of murine tumor TA3 sublines treated with neuraminidase. J Immunol. 1973 Oct;111(4):1071–1080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H. J., Rosell K. G., Kasper D. L. Structural determination and serology of the native polysaccharide antigen of type-III group B Streptococcus. Can J Biochem. 1980 Feb;58(2):112–120. doi: 10.1139/o80-016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr, Klemperer M. R., Alper C. A., Rosen F. S. The enhancement of bacterial phagocytosis by serum. The role of complement components and two cofactors. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1275–1290. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper D. L., Baker C. J., Baltimore R. S., Crabb J. H., Schiffman G., Jennings H. J. Immunodeterminant specificity of human immunity to type III group B streptococcus. J Exp Med. 1979 Feb 1;149(2):327–339. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper D. L., Baker C. J. Electron microscopic definition of surface antigens of group B Streptococcus. J Infect Dis. 1979 Feb;139(2):147–151. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.2.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazatchkine M. D., Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. Human alternative complement pathway: membrane-associated sialic acid regulates the competition between B and beta1 H for cell-bound C3b. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):75–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancefield R. C., McCarty M., Everly W. N. Multiple mouse-protective antibodies directed against group B streptococci. Special reference to antibodies effective against protein antigens. J Exp Med. 1975 Jul 1;142(1):165–179. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtman M. A., Weed R. I. Electrophoretic mobility and N-acetyl neuraminic acid content of human normal and leukemic lymphocytes and granulocytes. Blood. 1970 Jan;35(1):12–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu T. Y., Gotschlich E. C., Dunne F. T., Jonssen E. K. Studies on the meningococcal polysaccharides. II. Composition and chemical properties of the group B and group C polysaccharide. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4703–4712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchlewicz B. A., Duncan J. L. Properties of a hemolysin produced by group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):805–813. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.805-813.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSharry J. J., Pickering R. J., Caliguiri L. A. Activation of the alternative complement pathway by enveloped viruses containing limited amounts of sialic acid. Virology. 1981 Oct 30;114(2):507–515. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90230-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan T. W., Baker C. J., Straus D. C., Mattingly S. J. Association of elevated levels of extracellular neuraminidase with clinical isolates of type III group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):738–746. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.738-746.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A. G., Gregoriadis G., Scheinberg I. H., Hickman J., Ashwell G. The role of sialic acid in determining the survival of glycoproteins in the circulation. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1461–1467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A. G., Irvine R. A., Sternlieb I., Scheinberg I. H., Ashwell G. Physical and chemical studies on ceruloplasmin. V. Metabolic studies on sialic acid-free ceruloplasmin in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jan 10;243(1):155–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pricer W. E., Jr, Ashwell G. The binding of desialylated glycoproteins by plasma membranes of rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4825–4833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., McCracken G. H., Jr, Gotschlich E. C., Orskov F., Orskov I., Hanson L. A. Escherichia coli K1 capsular polysaccharide associated with neonatal meningitis. N Engl J Med. 1974 May 30;290(22):1216–1220. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197405302902202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanford B. H. An alteration in tumor histocompatibility induced by neuraminidase. Transplantation. 1967 Sep 5;5(5):1273–1279. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196709000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffer M. S., Oliveira E., Glode M. P., McCracken G. H., Jr, Sarff L. M., Robbins J. B. A review: relation between invasiveness and the K1 capsular polysaccharide of Escherichia coli. Pediatr Res. 1976 Feb;10(2):82–87. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197602000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terleckyj B., Willett N. P., Shockman G. D. Growth of several cariogenic strains of oral streptococci in a chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):649–655. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.649-655.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Den Hamer C. J., Morell A. G., Scheinberg I. H., Hickman J., Ashwell G. Physical and chemical studies on ceruloplasmin. IX. The role of galactosyl residues in the clearance of ceruloplasmin from the circulation. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 10;245(17):4397–4402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L., BLACKLOW R. S. The biosynthesis of cytidine 5'-monophospho-n-acetylneuraminic acid by an enzyme from Neisseria meningitidis. J Biol Chem. 1962 Nov;237:3527–3534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff J. J., Gesner B. M. The effect of neuraminidase on the fate of transfused lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1969 Mar 1;129(3):551–567. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.3.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung M. K., Mattingly S. J. Biosynthesis of cell wall peptidoglycan and polysaccharide antigens by protoplasts of type III group B Streptococcus. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):211–220. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.211-220.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Oss C. J. Phagocytosis as a surface phenomenon. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:19–39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



