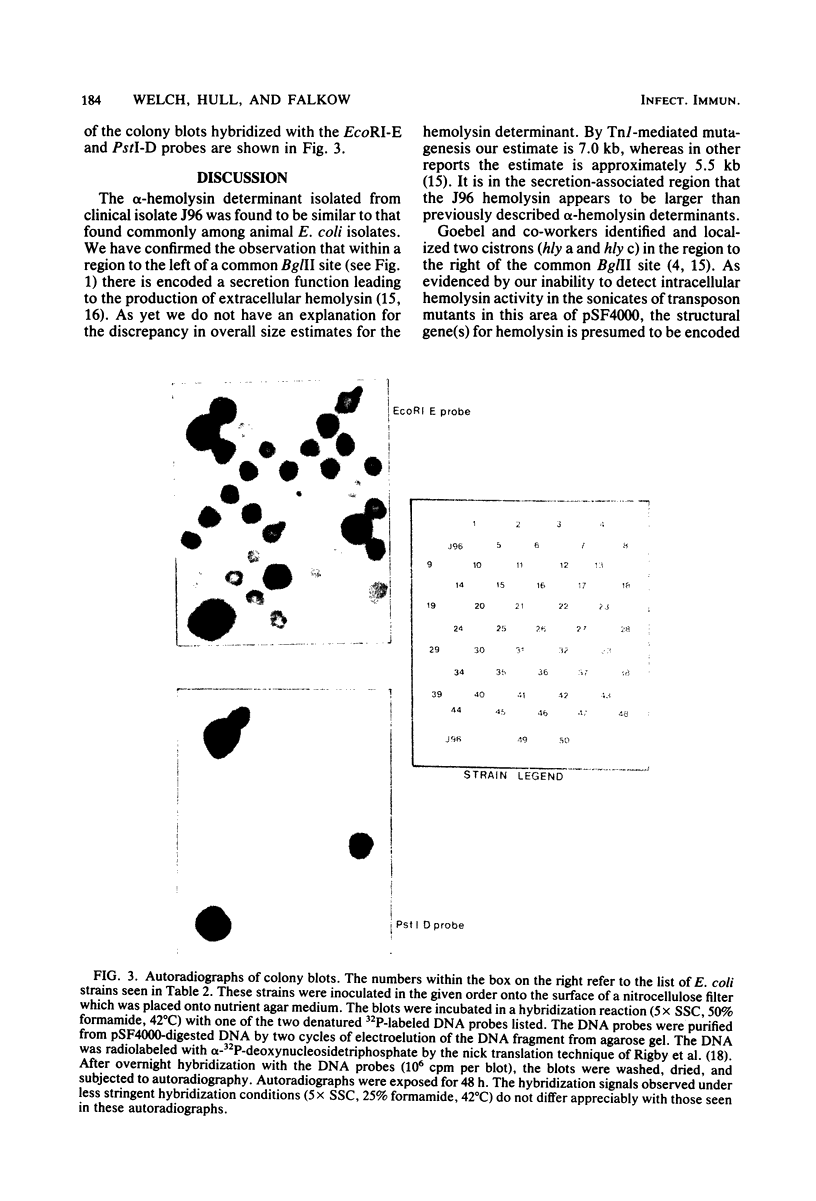
Abstract
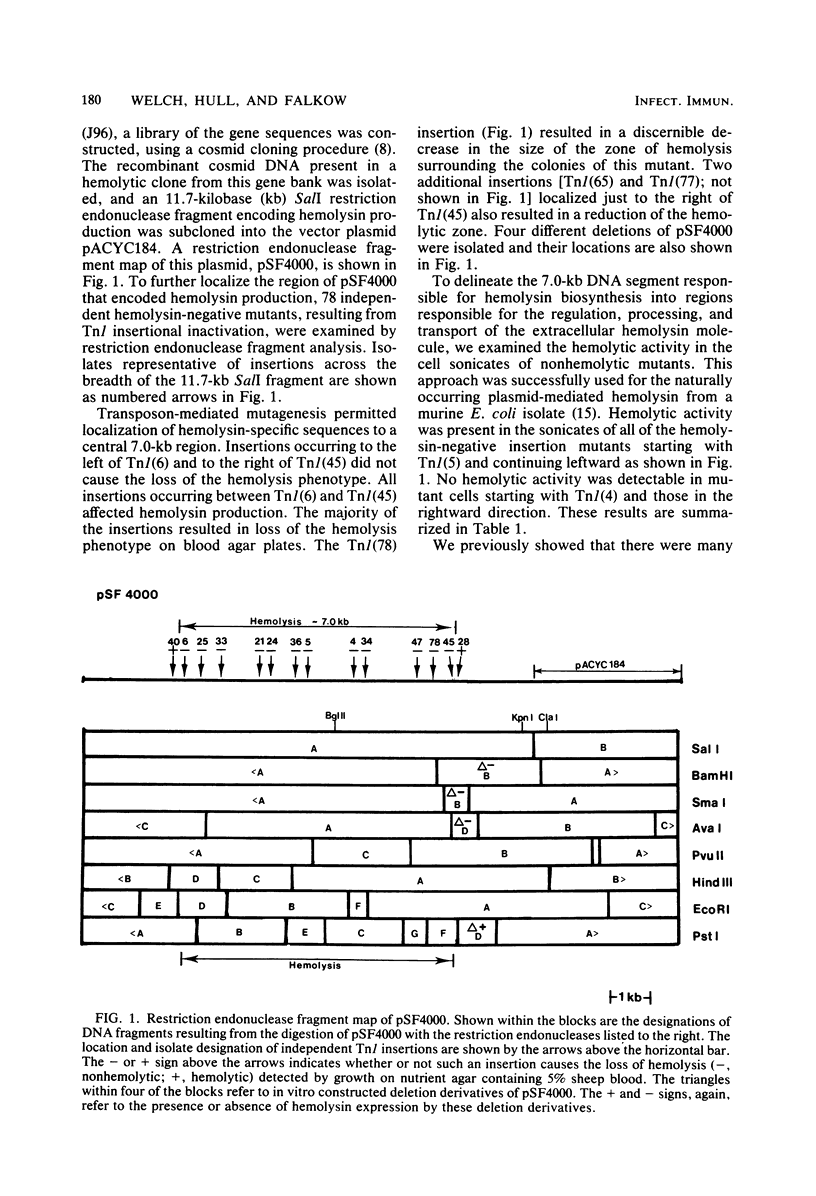
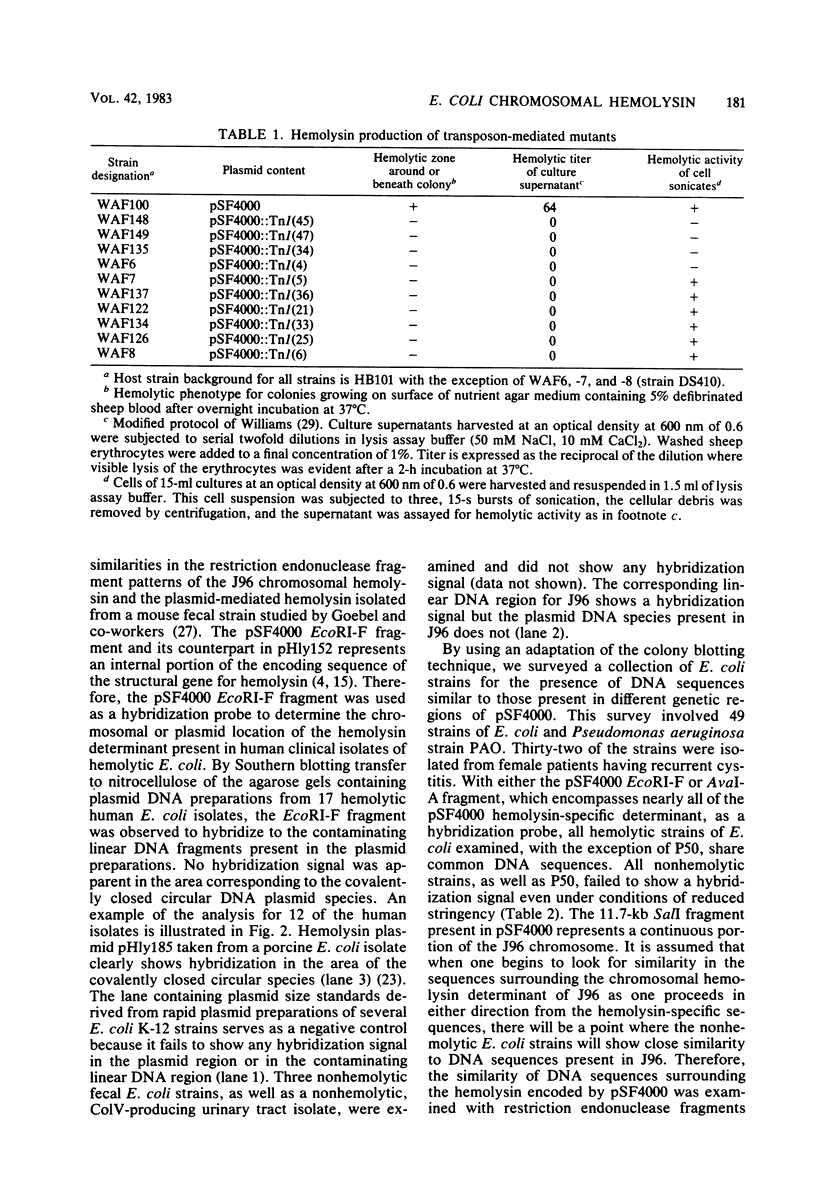
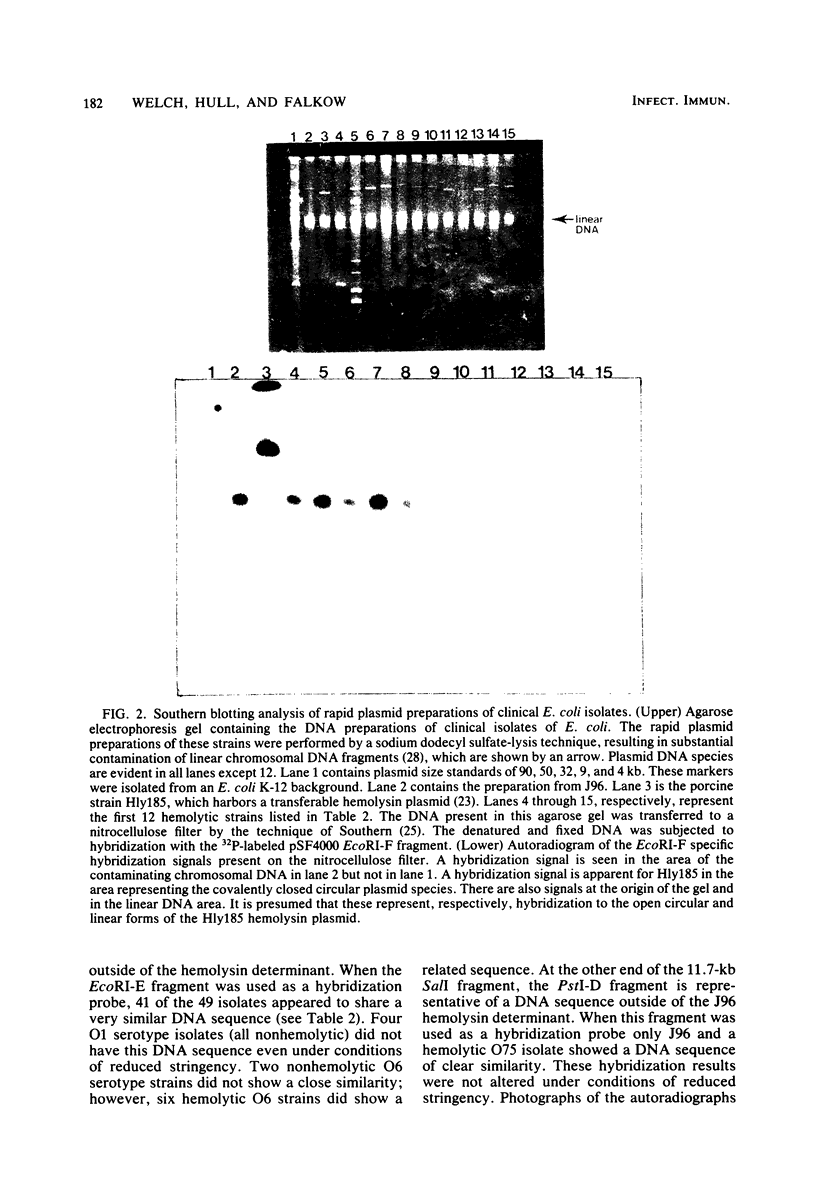
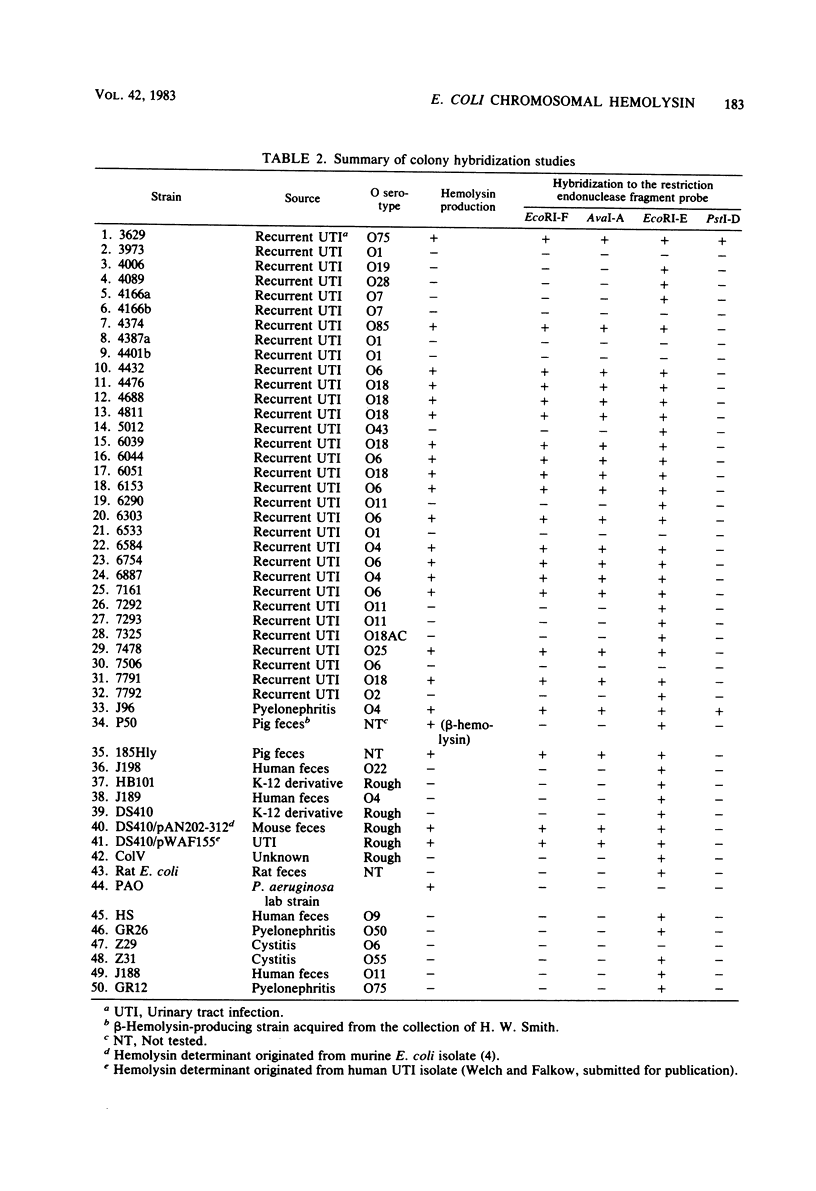
A chromosomal hemolysin determinant was isolated in the form of recombinant plasmid pSF4000 from a human urinary tract isolate. Escherichia coli J96. A restriction endonuclease fragment map of pSF4000 was constructed. The ampicilin resistance transposon Tn/ was used as a site-specific mutagen in conjunction with in vitro derived deletions to localize the hemolysin determinant to a 7.0-kilobase region of pSF4000. Seventeen hemolytic E. coli isolates from human urinary tract infections were found to share similar DNA sequences with J96 hemolysin sequences, using a hemolysin-specific restriction endonuclease fragment as a hybridization probe. In all 17 hemolytic E. coli strains the hemolysin gene sequences were localized to the bacterial chromosome. The hemolysin-specific gene sequences can be found only in hemolytic strains by colony blot hybridization, suggesting that in the evolutionary sense the hemolysin-specific genetic sequences have only recently been introduced into the E. coli chromosome. Evidence is also presented that in the regions neighboring the J96 chromosomal hemolysin there are additional unique DNA sequences not commonly found in other E. coli isolates.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Goebel W., Hedgpeth J. Cloning and functional characterization of the plasmid-encoded hemolysin determinant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1290–1298. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1290-1298.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebel W., Royer-Pokora B., Lindenmaier W., Bujard H. Plasmids controlling synthesis of hemolysin in Escherichia coli: molecular properties. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):964–973. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.964-973.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebel W., Schrempf H. Isolation and characterization of supercoiled circular deoxyribonucleic acid from beta-hemolytic strains of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 May;106(2):311–317. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.2.311-317.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R. A., Gill R. E., Hsu P., Minshew B. H., Falkow S. Construction and expression of recombinant plasmids encoding type 1 or D-mannose-resistant pili from a urinary tract infection Escherichia coli isolate. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):933–938. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.933-938.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull S. I., Hull R. A., Minshew B. H., Falkow S. Genetics of hemolysin of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):1006–1012. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.1006-1012.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz D., Burke J. F. Rapid and efficient cosmid cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):2989–2998. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linggood M. A., Ingram P. L. The role of alpha haemolysin in the virulence of Escherichia coli for mice. J Med Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(1):23–30. doi: 10.1099/00222615-15-1-23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minshew B. H., Jorgensen J., Counts G. W., Falkow S. Association of hemolysin production, hemagglutination of human erythrocytes, and virulence for chicken embryos of extraintestinal Escherichia coli isolates. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):50–54. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.50-54.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Huq I., Alim A. R., So M., Samadpour-Motalebi M., Falkow S. Detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by DNA colony hybridization. J Infect Dis. 1980 Dec;142(6):892–898. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.6.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noegel A., Rdest U., Goebel W. Determination of the functions of hemolytic plasmid pHly152 of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):233–247. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.233-247.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noegel A., Rdest U., Springer W., Goebel W. Plasmid cistrons controlling synthesis and excretion of the exotoxin alpha-haemolysin of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Oct 1;175(3):343–350. doi: 10.1007/BF00397234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennie R. P., Arbuthnott J. P. Partial characterisation of Escherichia coli haemolysin. J Med Microbiol. 1974 May;7(2):179–188. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M. K., Bennett P. M., Falkow S., Dodd H. M. Isolation of a temperature-sensitive derivative of RP1. Plasmid. 1980 May;3(3):343–347. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90047-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH H. W. The haemolysins of Escherichia coli. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1963 Jan;85:197–211. doi: 10.1002/path.1700850119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Halls S. The transmissible nature of the genetic factor in Escherichia coli that controls haemolysin production. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Apr;47(1):153–161. doi: 10.1099/00221287-47-1-153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Linggood M. A. Further observations on Escherichia coli enterotoxins with particular regard to those produced by atypical piglet strains and by calf and lamb strains: the transmissible nature of these enterotoxins and of a K antigen possessed by calf and lamb strains. J Med Microbiol. 1972 May;5(2):243–250. doi: 10.1099/00222615-5-2-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So M., Dallas W. S., Falkow S. Characterization of an Escherichia coli plasmid encoding for synthesis of heat-labile toxin: molecular cloning of the toxin determinant. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):405–411. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.405-411.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waalwijk C., van den Bosch J. F., MacLaren D. M., de Graaff J. Hemolysin plasmid coding for the virulence of a nephropathogenic Escherichia coli strain. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):32–37. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.32-37.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. A., Dellinger E. P., Minshew B., Falkow S. Haemolysin contributes to virulence of extra-intestinal E. coli infections. Nature. 1981 Dec 17;294(5842):665–667. doi: 10.1038/294665a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. A., Macrina F. L. Physical characterization of Bacteroides fragilis R plasmid pBF4. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):867–872. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.867-872.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Cruz F., Müller D., Ortiz J. M., Goebel W. Hemolysis determinant common to Escherichia coli hemolytic plasmids of different incompatibility groups. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):825–833. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.825-833.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





