Abstract
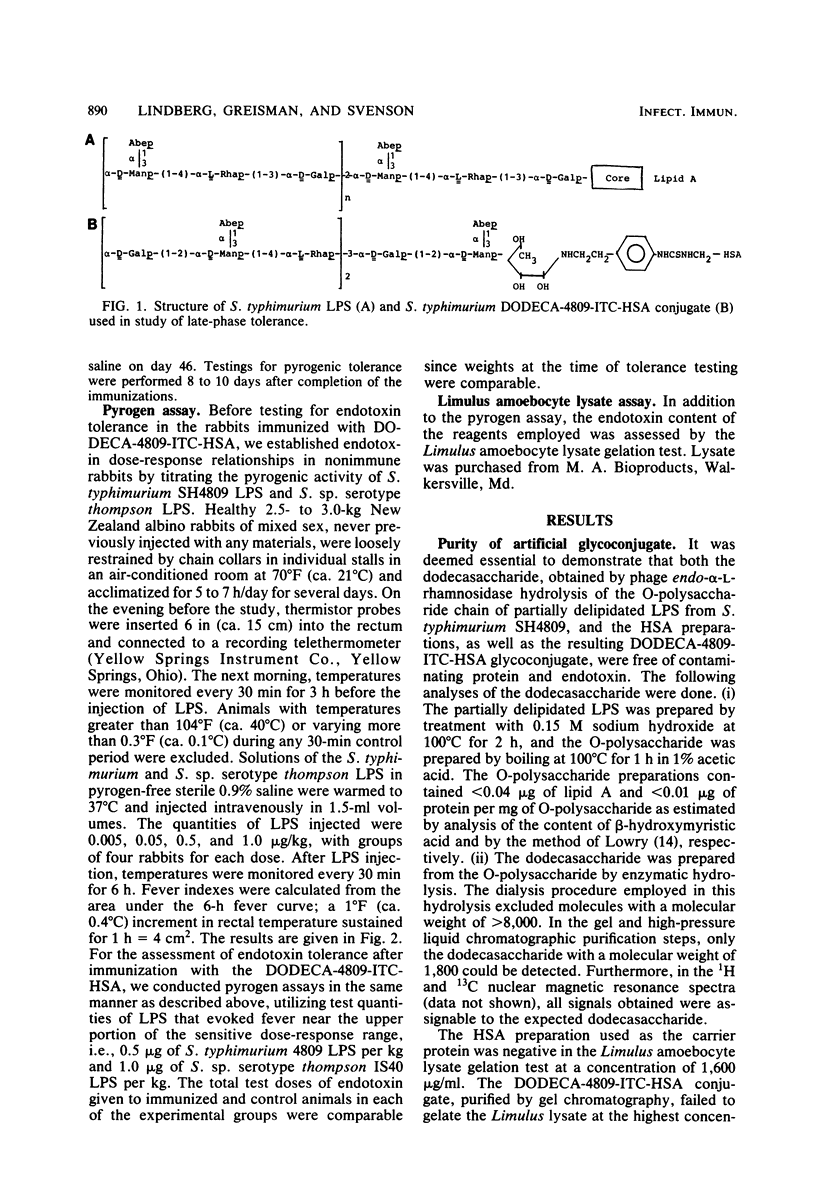
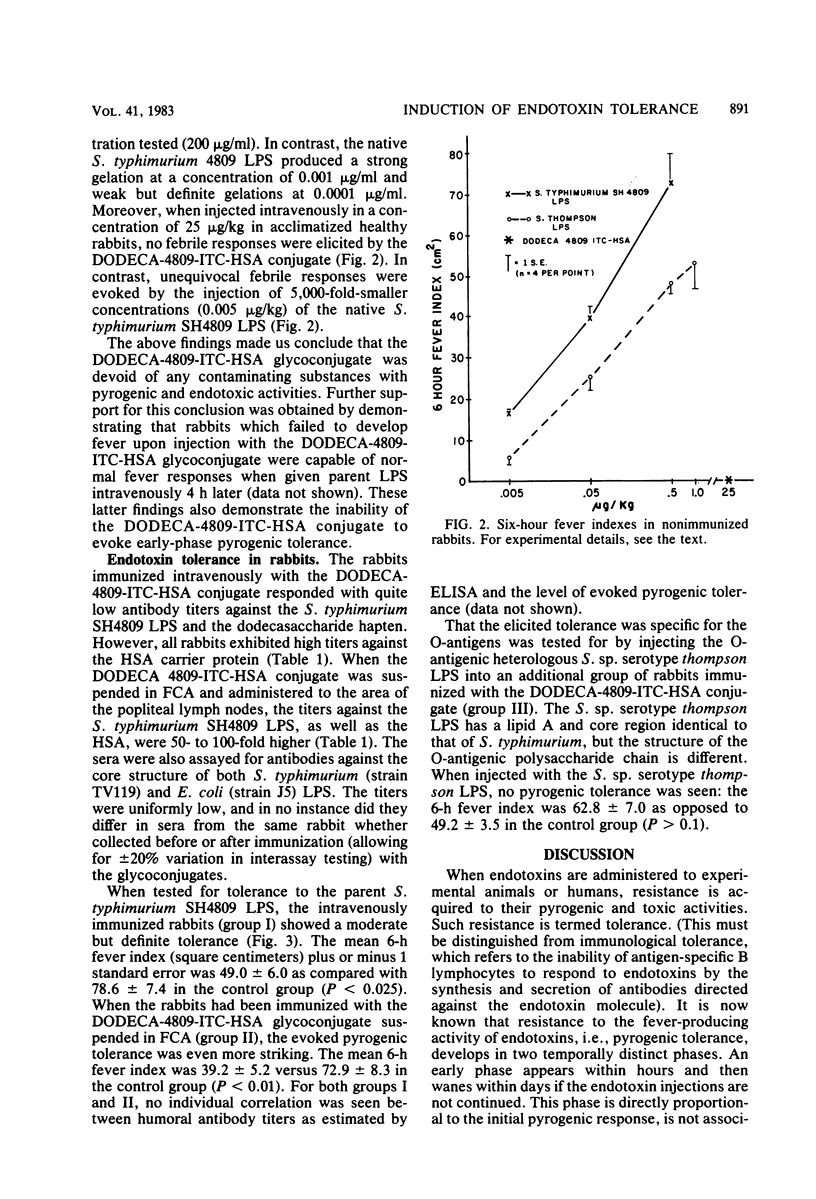
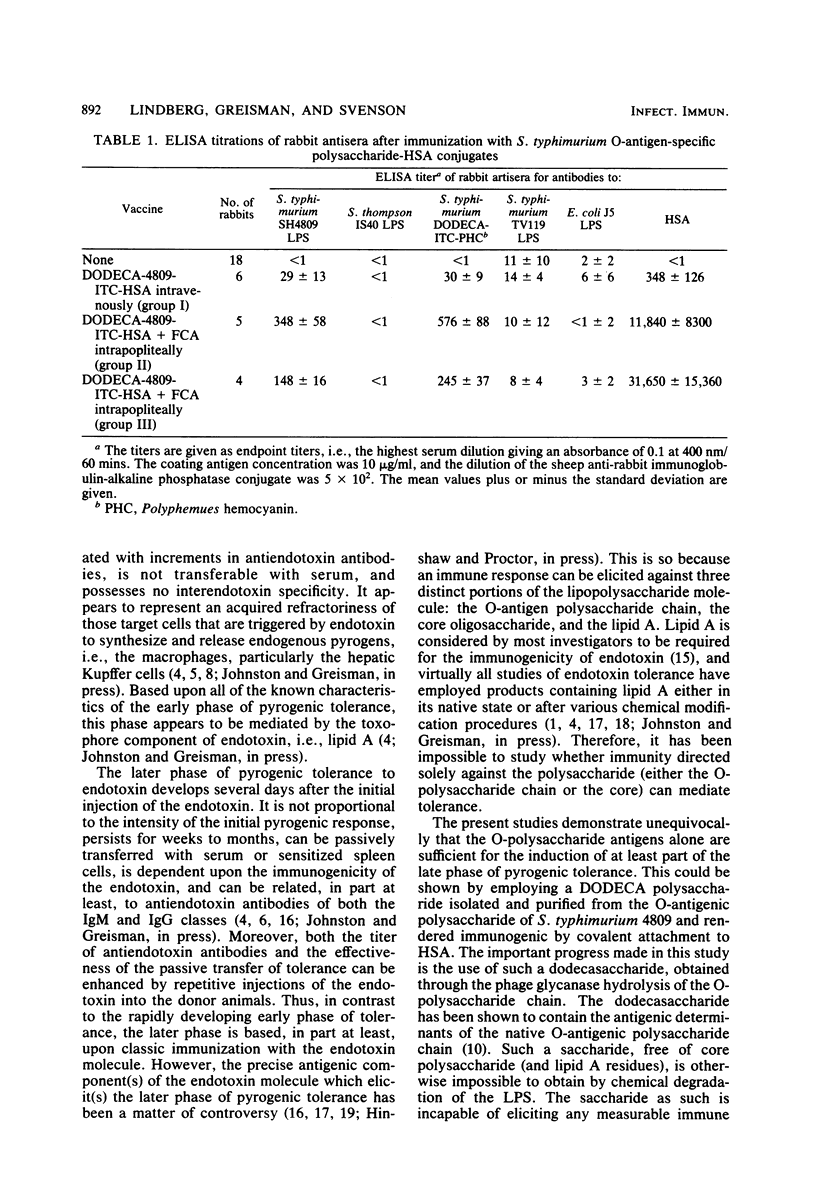
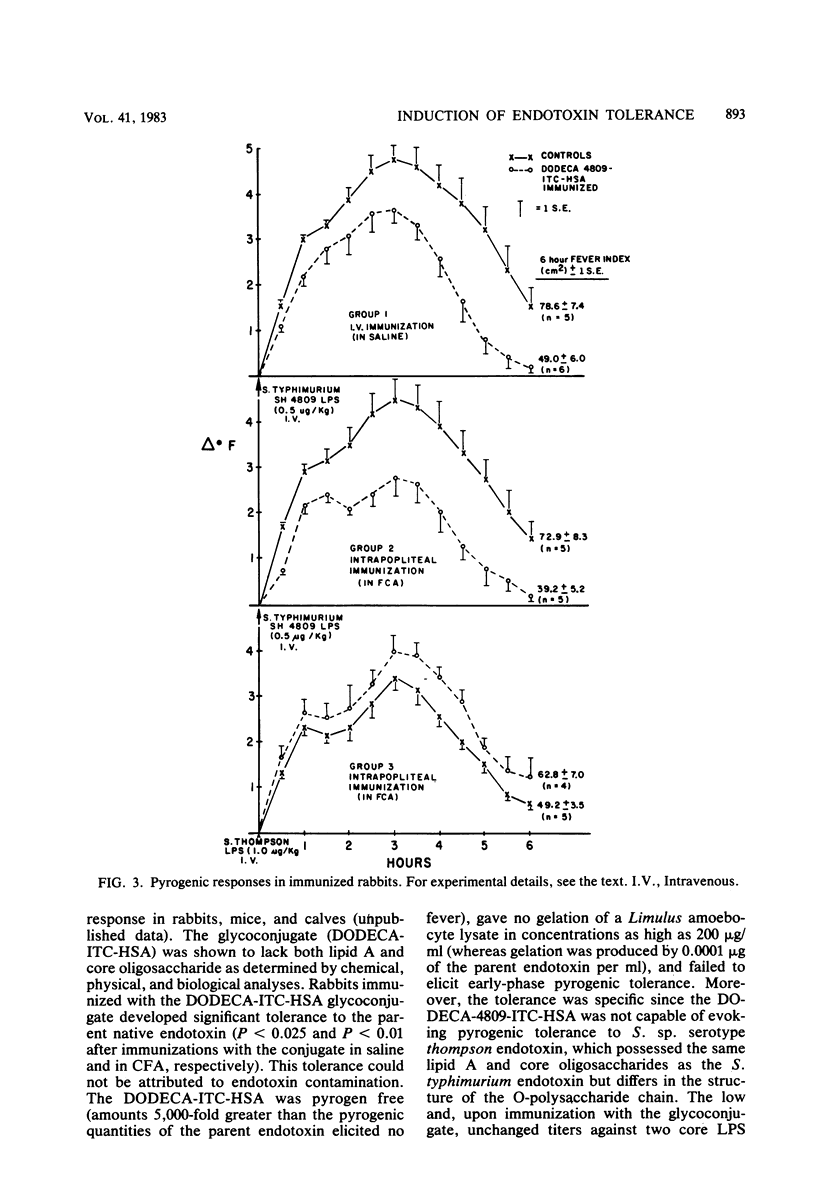
We prepared a dodecasaccharide, specific for the O-antigenic polysaccharide chain of Salmonella typhimurium (O-antigens 4 and 12), by the partial hydrolysis of the O-polysaccharide chain, utilizing bacteriophage 28B endo-alpha-L-rhamnosidase. The dodecasaccharide was shown by chemical and spectroscopical analyses to be totally devoid of lipid A and core oligosaccharide. By coupling this dodecasaccharide to human serum albumin, a glycoconjugate (DODECA-4809-ITC-HSA) was prepared and found to be (i) nonpyrogenic, (ii) unable to gelate a Limulus amoebocyte lysate, and (iii) unable to induce early-phase pyrogenic tolerance to endotoxin. Rabbits immunized either intravenously (with the glycoconjugate suspended in saline) or intrapopliteally (with the glycoconjugate suspended in Freund complete adjuvant) developed a significant although modest pyrogenic tolerance against challenge with the O-antigenic homologous S. typhimurium lipopolysaccharide (P less than 0.025 and P less than 0.01 for immunized and control rabbits, respectively). The evoked tolerance was O-antigen specific since no pyrogenic tolerance against challenge with lipopolysaccharide from S. thompson (possessing identical lipid A and core oligosaccharide structures but differing in the O-antigen polysaccharide chain) could be seen (P greater than 0.1). These results demonstrate that a nonpyrogenic O-antigenic polysaccharide hapten, when coupled to an immunogenic carrier protein, evokes immune responses which mediate significant, although modest, late-phase tolerance and is capable of partly reducing the pyrogenic activity of the O-antigenic homologous lipopolysaccharide.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdelnoor A. M., Johnson A. G., Anderson-Imbert A., Nowotny A. Immunization against bacteria- and endotoxin-induced hypotension. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1093–1099. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1093-1099.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson H. E., Lindberg A. A., Hammarström S. Titration of antibodies to salmonella O antigens by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):703–708. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.703-708.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOIS M., GILLES K., HAMILTON J. K., REBERS P. A., SMITH F. A colorimetric method for the determination of sugars. Nature. 1951 Jul 28;168(4265):167–167. doi: 10.1038/168167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greisman S. E., Hornick R. B. Mechanisms of endotoxin tolerance with special reference to man. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jul;128(Suppl):265–276. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.supplement_1.s265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greisman S. E., Young E. J., Carozza F. A., Jr Mechanisms of endotoxin tolerance. V. Specificity of the early and late phases of pyrogenic tolerance. J Immunol. 1969 Dec;103(6):1223–1236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greisman S. E., Young E. J., DuBuy B. Mechanisms of endotoxin tolerance. 8. Specificity of serum transfer. J Immunol. 1973 Nov;111(5):1349–1360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greisman S. E., Young E. J., Woodward W. E. Mechanisms of endotoxin tolerance. IV. Specificity of the pyrogenic refractory state during continuous intravenous infusions of endotoxin. J Exp Med. 1966 Nov 1;124(5):983–1000. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.5.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jörbeck H. J., Svenson S. B., Lindberg A. A. Immunochemistry of Salmonella O-antigens: specificity of rabbit antibodies against the O-antigen 4 determinant elicited by whole bacteria and O-antigen 4 specific saccharide-protein conjugates. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1376–1381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVIN J., BANG F. B. A DESCRIPTION OF CELLULAR COAGULATION IN THE LIMULUS. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1964 Oct;115:337–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A., Holme T. Evaluation of some extraction methods for the preparation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides for structural analysis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(5):751–759. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00203.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz O., Staub A. M., Westphal O. Immunochemistry of O and R antigens of Salmonella and related Enterobacteriaceae. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Mar;30(1):192–255. doi: 10.1128/br.30.1.192-255.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOLL H., BRAUDE A. I. Preparation and biological properties of a chemically modified Escherichia coli endotoxin of high immunogenic potency and low toxicity. J Clin Invest. 1961 Nov;40:1935–1951. doi: 10.1172/JCI104419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowotny A., Behling U. H., Chang H. L. Relation of structure to function in bacterial endotoxins. VIII. Biological activities in a polysaccharide-rich fraction. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):199–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietschel E. T., Galanos C. Lipid A antiserum-mediated protection against lipopolysaccharide- and lipid A-induced fever and skin necrosis. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):34–49. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.34-49.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertsson J. A., Fossum C., Svenson S. B., Lindberg A. A. Salmonella typhimurium infection in calves: specific immune reactivity against O-antigenic polysaccharide detectable in in vitro assays. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):728–736. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.728-736.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertsson J. A., Svenson S. B., Lindberg A. A. Salmonella typhimurium infection in calves: delayed specific skin reactions directed against the O-antigenic polysaccharide chain. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):737–748. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.737-748.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenson S. B., Lindberg A. A. Artificial Salmonella vaccines: Salmonella typhimurium O-antigen-specific oligosaccharide-protein conjugates elicit protective antibodies in rabbits and mice. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):490–496. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.490-496.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenson S. B., Lindberg A. A. Immunochemistry of Salmonella O-antigens: preparation of an octasaccharide-bovine serum albumin immunogen representative of Salmonella serogroup B O-antigen and characterization of the antibody response. J Immunol. 1978 May;120(5):1750–1757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenson S. B., Lönngren J., Carlin N., Lindberg A. A. Salmonella bacteriophage glycanases: endorhamnosidases of Salmonella typhimurium bacteriophages. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):583–592. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.583-592.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenson S. B., Nurminen M., Lindberg A. A. Artificial Salmonella vaccines: O-antigenic oligosaccharide-protein conjugates induce protection against infection with Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):863–872. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.863-872.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



