Abstract
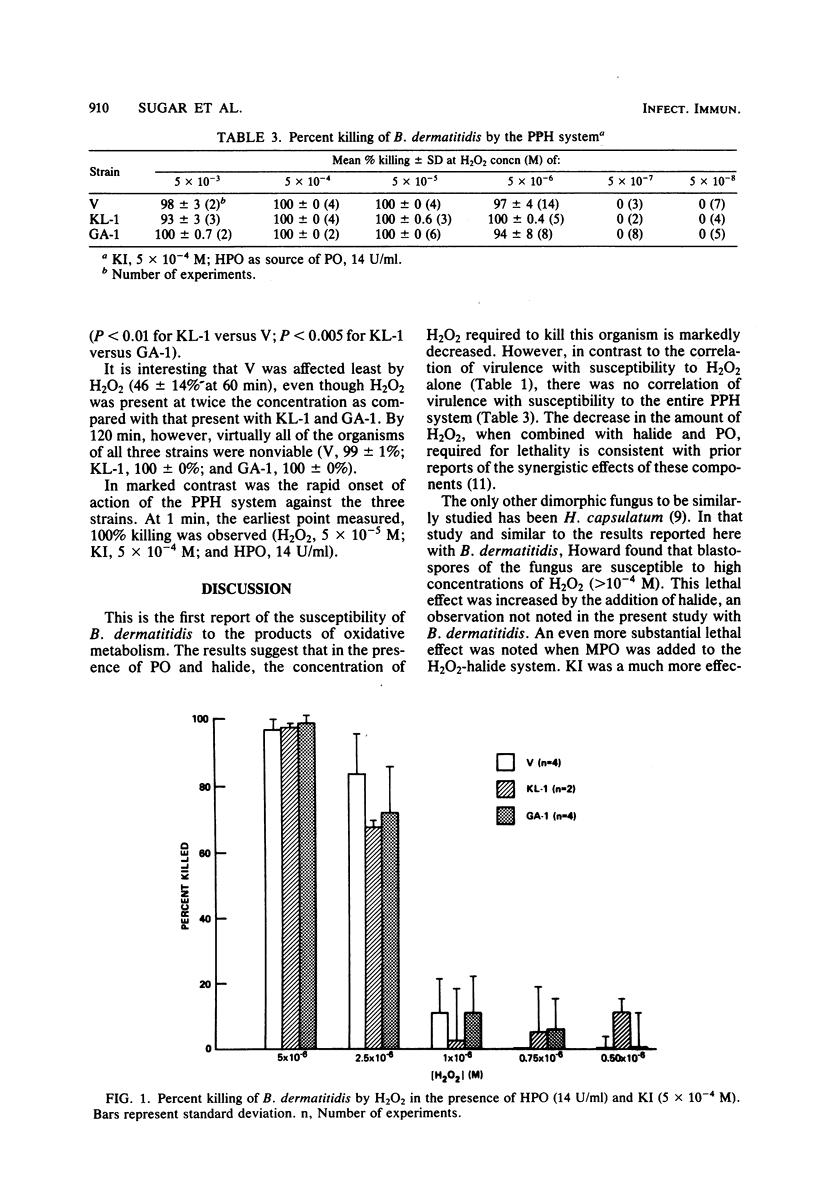
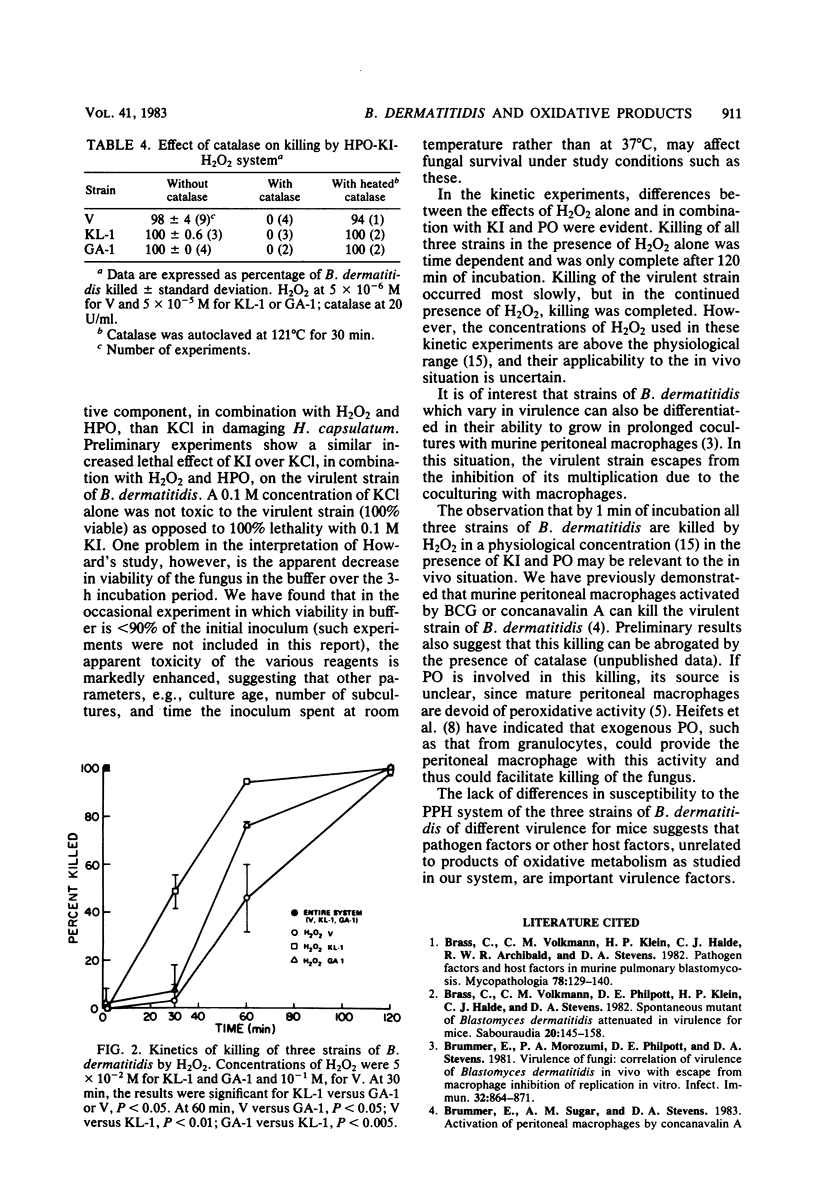
Three strains of Blastomyces dermatitidis which differ in their virulence for mice were exposed in their yeast form to various components of the peroxidase-hydrogen peroxide-halide system. Susceptibility to H2O2 alone correlated with virulence, with the most virulent strain (ATCC 26199) least susceptible (50% lethal dose, greater than 50 mM) and an avirulent strain (ATCC 26197) most susceptible (50% lethal dose less than 3.3 mM). A strain of intermediate virulence (ATCC 26198) was of intermediate susceptibility (50% lethal dose, 11.5 mM). The addition of a nontoxic concentration of KI (5 X 10(-4) M) did not increase H2O2 toxicity. However, the addition of either myeloperoxidase or horseradish peroxidase and KI markedly decreased the amount of H2O2 required to kill the organisms, with 100 +/- 0% of all strains killed at 5 X 10(-5) M H2O2 and 97 +/- 4, 100 +/- 0, and 94 +/- 8% of ATCC 26199, ATCC 26198, and ATCC 26197 killed, respectively, at 5 X 10(-6) M H2O2. Kinetic studies with H2O2 alone revealed a delayed onset of killing, but virtually 100% of organisms were killed by 120 min of exposure in all strains. By comparison, the peroxidase-hydrogen peroxide-halide system was 100% lethal for all strains at 1 min. The relatively high concentrations of H2O2 required to kill the yeast phase of B. dermatitidis suggest that H2O2 alone does not account for host resistance to the organism. However, the rapidly lethal effect of the peroxidase-hydrogen peroxide-halide system at physiologically relevant concentrations suggests that this may be one mechanism of host defense to B. dermatitidis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brass C., Volkmann C. M., Klein H. P., Halde C. J., Archibald R. W., Stevens D. A. Pathogen factors and host factors in murine pulmonary blastomycosis. Mycopathologia. 1982 Jun 18;78(3):129–140. doi: 10.1007/BF00466066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass C., Volkmann C. M., Philpott D. E., Klein H. P., Halde C. J., Stevens D. A. Spontaneous mutant of Blastomyces dermatitidis attenuated in virulence for mice. Sabouraudia. 1982 Jun;20(2):145–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brummer E., Morozumi P. A., Philpott D. E., Stevens D. A. Virulence of fungi: correlation of virulence of Blastomyces dermatitidis in vivo with escape from macrophage inhibition of replication in vitro. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):864–871. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.864-871.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., Clark R. A., Haudenschild C. C. Damage to Candida albicans hyphae and pseudohyphae by the myeloperoxidase system and oxidative products of neutrophil metabolism in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):908–917. doi: 10.1172/JCI109958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heifets L., Imai K., Goren M. B. Expression of peroxidase-dependent iodination by macrophages ingesting neutrophil debris. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1980 Oct;28(4):391–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard D. H. Comparative sensitivity of Histoplasma capsulatum conidiospores and blastospores to oxidative antifungal systems. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):381–387. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.381-387.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackett P. S., Aber V. R., Lowrie D. B. Virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and susceptibility to peroxidative killing systems. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Aug;107(2):273–278. doi: 10.1099/00221287-107-2-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Myeloperoxidase-halide-hydrogen peroxide antibacterial system. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2131–2138. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2131-2138.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I. The fungicidal mechanisms of human monocytes. I. Evidence for myeloperoxidase-linked and myeloperoxidase-independent candidacidal mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 1975 Feb;55(2):338–346. doi: 10.1172/JCI107937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Aley S. B., Scott W. A. Susceptibility of Entamoeba histolytica to oxygen intermediates. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1981 Oct;3(6):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(81)90038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Cohn Z. A. Macrophage oxygen-dependent antimicrobial activity. I. Susceptibility of Toxoplasma gondii to oxygen intermediates. J Exp Med. 1979 Oct 1;150(4):938–949. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.4.938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Brukner L. H., Silverstein S. C., Cohn Z. A. Extracellular cytolysis by activated macrophages and granulocytes. I. Pharmacologic triggering of effector cells and the release of hydrogen peroxide. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):84–99. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsan M. F., Douglass K. H., McIntyre P. A. Hydrogen peroxide production and killing of Staphylococcus aureus by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Blood. 1977 Mar;49(3):437–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Slivka A. Monocyte and granulocyte-mediated tumor cell destruction. A role for the hydrogen peroxide-myeloperoxidase-chloride system. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):255–262. doi: 10.1172/JCI110447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



