Abstract
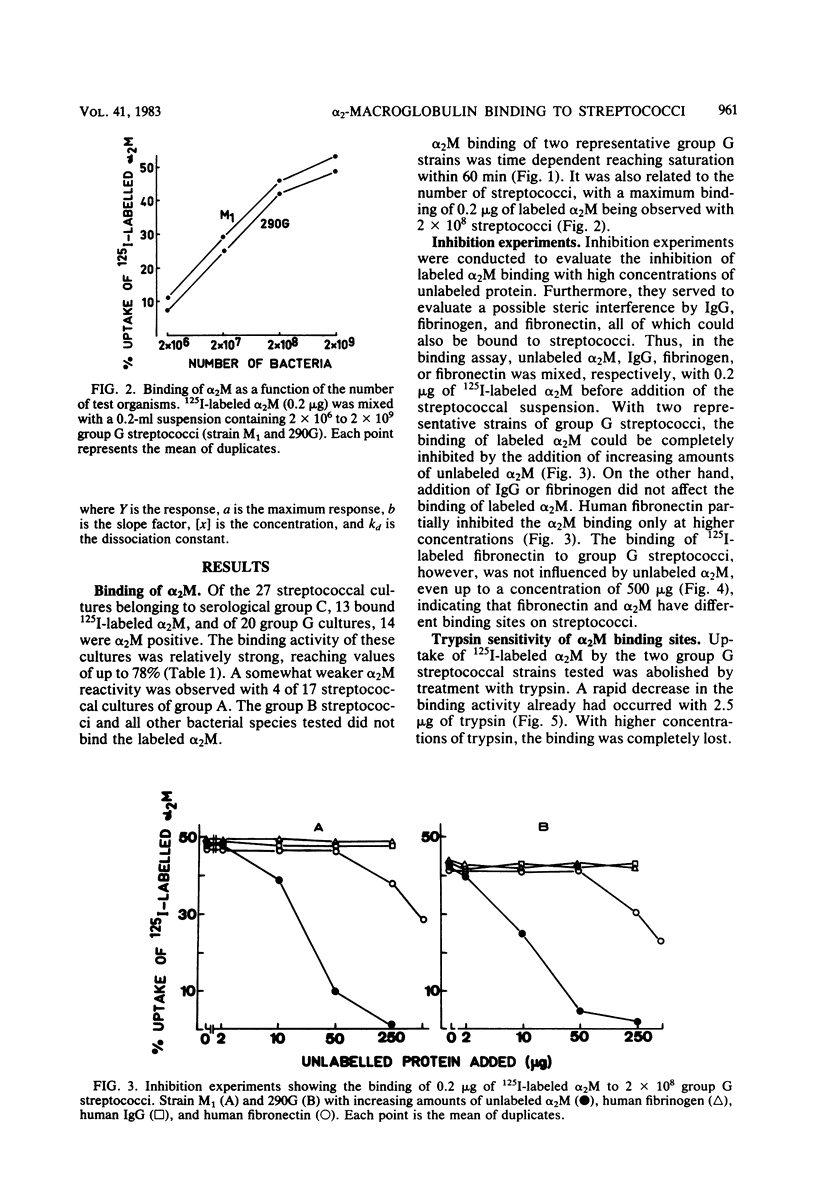
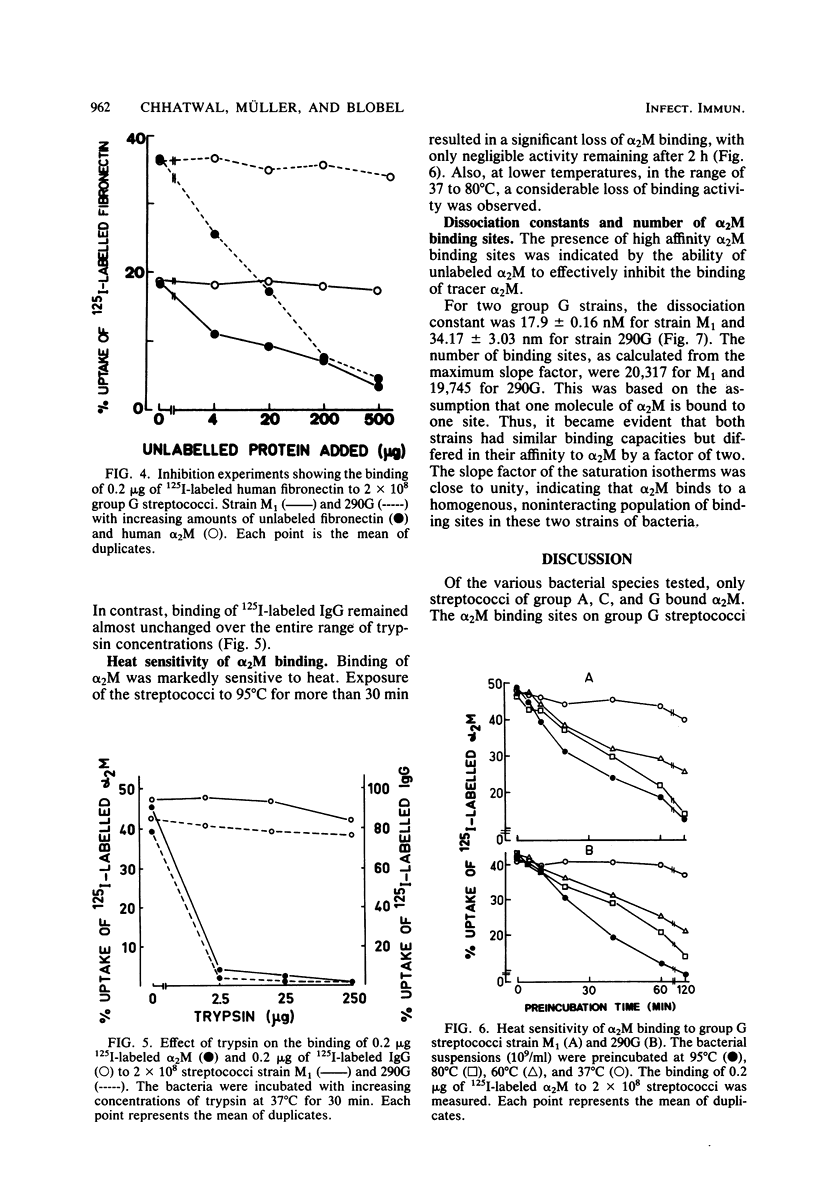
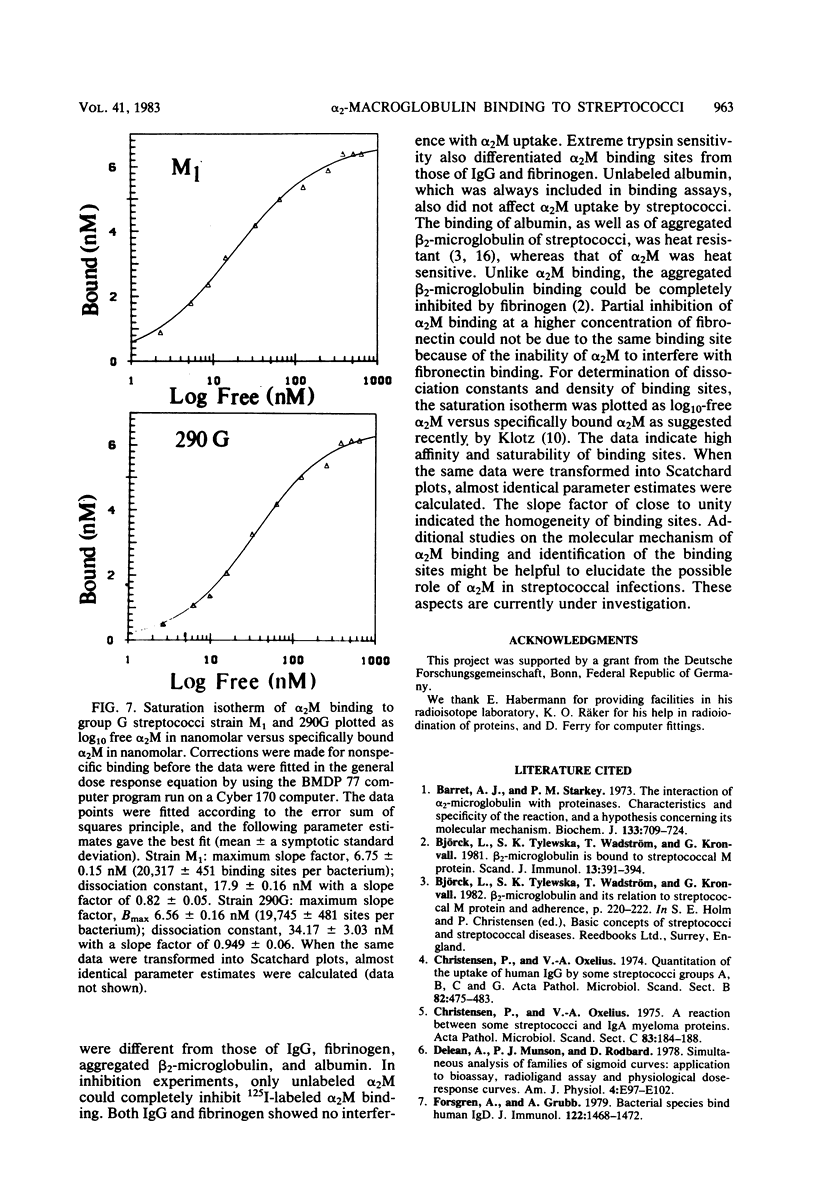
An interaction was observed between human alpha 2-macroglobulin (alpha 2M) and streptococci belonging to group A, C, and G. Of 27 group C and 19 group G streptococcal cultures, 13 and 14, respectively, bound 125I-labeled alpha 2M. Some group A streptococci also interacted with alpha 2M. A number of other bacterial species tested did not react with alpha 2M. The binding of 125I-labeled alpha 2M to group G streptococci was time dependent, saturable, and could be inhibited by unlabeled alpha 2M. Inhibition experiments indicated that the streptococcal binding site for alpha 2M differed from the receptors for immunoglobulin G, fibrinogen, aggregated beta 2-microglobulin, albumin, and fibronectin. The alpha 2M binding activity was remarkably sensitive to trypsin and heat treatment indicating its protein nature. Kinetic analysis indicated a homogenous population of binding sites. The number of binding sites per bacterial cell was estimated to be approximately 20,000.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett A. J., Starkey P. M. The interaction of alpha 2-macroglobulin with proteinases. Characteristics and specificity of the reaction, and a hypothesis concerning its molecular mechanism. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;133(4):709–724. doi: 10.1042/bj1330709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björck L., Tylewska S. K., Wadström T., Kronvall G. beta 2-Microglobulin is bound to streptococcal M protein. Scand J Immunol. 1981;13(4):391–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1981.tb00149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen P., Oxelius V. A. Quantitation of the uptake of human IgG by some streptococci groups A, B, C, and G. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Aug;82(4):475–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb02356.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLean A., Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Simultaneous analysis of families of sigmoidal curves: application to bioassay, radioligand assay, and physiological dose-response curves. Am J Physiol. 1978 Aug;235(2):E97–102. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.2.E97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Grubb A. O. Many bacterial species bind human IgD. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1468–1472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz I. M. Numbers of receptor sites from Scatchard graphs: facts and fantasies. Science. 1982 Sep 24;217(4566):1247–1249. doi: 10.1126/science.6287580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G. A surface component in group A, C, and G streptococci with non-immune reactivity for immunoglobulin G. J Immunol. 1973 Nov;111(5):1401–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Myhre E. B., Björck L., Berggård I. Binding of aggregated human beta2-microglobulin to surface protein structure in group A, C, and G streptococci. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):136–142. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.136-142.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskowski M., Jr, Kato I. Protein inhibitors of proteinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:593–626. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt G. C., Egerton J. R., Loi J. S. Inhibition of Fusiformis nodosus protease and bovine trypsin by serum alpha macroglobulin. J Comp Pathol. 1971 Jul;81(3):353–358. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(71)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myhre E. B., Kronvall G. Demonstration of specific binding sites for human serum albumin in group C and G streptococci. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):6–14. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.6-14.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myhre E. B., Kronvall G. Heterogeneity of nonimmune immunoglobulin Fc reactivity among gram-positive cocci: description of three major types of receptors for human immunoglobulin G. Infect Immun. 1977 Sep;17(3):475–482. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.3.475-482.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller H. P., Blobel H. Absorption of human alpha 2-macroglobulin with selected strains of streptococci. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1983;172(1):33–39. doi: 10.1007/BF02123675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prokop O., Köhler W., Geserick G. Untersuchungen zu den Beziehungen zwischen Haptoglobintyp und Streptokokken der Gruppe G. Z Immunitatsforsch Immunobiol. 1977 Dec;153(5):457–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. A., Hasty D. L., Mason J. M., Beachey E. H. Fibronectin-mediated binding of group A streptococci to human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):805–810. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.805-810.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switalski L. M., Ljungh A., Rydén C., Rubin K., Hök M., Wadström T. Binding of fibronectin to the surface of group A, C, and G streptococci isolated from human infections. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Dec;1(6):381–387. doi: 10.1007/BF02019939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


