Abstract
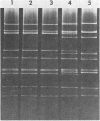
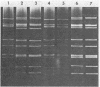
A rotavirus designated strain H-2 was isolated in primary African green monkey kidney cells from a foal with diarrhea. This cell culture-adapted strain was found to be similar, if not identical, to simian rotavirus (strains MMU18006 and SA-11) and canine rotavirus (strain CU-1) and, in addition, demonstrated a one-way antigenic relationship with five human rotavirus strains (P, B, no. 14, no. 15, and YO) of the third human rotavirus serotype by the plaque reduction neutralization test. This is the fifth example of an animal rotavirus which shares serotypic specificity with a human rotavirus. The H-2 strain is distinct from the H-1 strain (Y. Hoshino et al., J. Clin. Microbiol., in press) of equine rotavirus not only in serotypic specificity by neutralization but also in subgroup specificity, hemagglutinating activity, and RNA electrophoretic migration pattern, thus establishing the existence of a second equine rotavirus serotype. This H-2 isolate is also distinct by neutralization from three other human rotavirus serotypes, 1 (Wa), 2 (DS-1), and 4 (St. Thomas no. 4), as well as bovine (NCDV), and porcine (OSU) rotaviruses.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Conner M. E., Darlington R. W. Rotavirus infection in foals. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Oct;41(10):1699–1703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durham P. J., Stevenson B. J., Farquharson B. C. Rotavirus and coronavirus associated diarrhoea in domestic animals. N Z Vet J. 1979 Mar;27(3):30–32. doi: 10.1080/00480169.1979.34595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eugster A. K., Whitford H. W., Mehr L. E. Concurrent rotavirus and Salmonella infections in foals. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1978 Oct 1;173(7):857–858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukusho A., Shimizu Y., Ito Y. Isolation of cytopathic porcine rotavirus in cell roller culture in the presence of trypsin. Arch Virol. 1981;69(1):49–60. doi: 10.1007/BF01315265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaul S. K., Simpson T. F., Woode G. N., Fulton R. W. Antigenic relationships among some animal rotaviruses: virus neutralization in vitro and cross-protection in piglets. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):495–503. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.495-503.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Valdesuso J., van Wyke K., Midthun K., Walsh M., McAuliffe V., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., Flores J., Hoshino Y. Production and preliminary characterization of monoclonal antibodies directed at two surface proteins of rhesus rotavirus. J Virol. 1983 Aug;47(2):267–275. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.2.267-275.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Wyatt R. G., Kapikian A. Z., Kalica A. R., Flores J., Jones R. Rescue and serotypic characterization of noncultivable human rotavirus by gene reassortment. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):104–109. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.104-109.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H., McAuliffe V., Valdesuso J., Wyatt R., Flores J., Kalica A., Hoshino Y., Singh N. Serological analysis of the subgroup protein of rotavirus, using monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):91–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.91-99.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Wyatt R. G., Greenberg H. B., Kalica A. R., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z. Serological comparison of canine rotavirus with various simian and human rotaviruses by plaque reduction neutralization and hemagglutination inhibition tests. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):169–173. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.169-173.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Wyatt R. G., Scott F. W., Appel M. J. Isolation and characterization of a canine rotavirus. Arch Virol. 1982;72(1-2):113–125. doi: 10.1007/BF01314456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa H., Hirasawa K., Akiyama Y., Omori T. A sero-epizootiological survey on rotavirus infection in foals. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1982 Oct;44(5):819–821. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.44.819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Flores J., Greenberg H. B. Identification of the rotaviral gene that codes for hemagglutination and protease-enhanced plaque formation. Virology. 1983 Feb;125(1):194–205. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Garon C. F., Wyatt R. G., Mebus C. A., van Kirk D. H., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Differentiation of human and calf reoviruslike agents associated with diarrhea using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of RNA. Virology. 1976 Oct 1;74(1):86–92. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Cline W. L., Greenberg H. B., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., Banks C. E., James H. D., Jr, Flores J., Chanock R. M. Antigenic characterization of human and animal rotaviruses by immune adherence hemagglutination assay (IAHA): evidence for distinctness of IAHA and neutralization antigens. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):415–425. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.415-425.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Wyatt R. G., Greenberg H. B., Kalica A. R., Kim H. W., Brandt C. D., Rodriguez W. J., Parrott R. H., Chanock R. M. Approaches to immunization of infants and young children against gastroenteritis due to rotaviruses. Rev Infect Dis. 1980 May-Jun;2(3):459–469. doi: 10.1093/clinids/2.3.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson N. J., Fulton R. W., Issel C. J., Springer W. T. Prevalence of rotavirus antibody in chickens and horses in Louisiana, USA. Vet Rec. 1982 Jan 16;110(3):58–59. doi: 10.1136/vr.110.3.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Inaba Y., Shinozaki T., Fujii R., Matumoto M. Isolation of human rotavirus in cell cultures: brief report. Arch Virol. 1981;69(2):155–160. doi: 10.1007/BF01315159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaljohn A. L., Johnson E. D., Dalrymple J. M., Cole G. A. Non-neutralizing monoclonal antibodies can prevent lethal alphavirus encephalitis. Nature. 1982 May 6;297(5861):70–72. doi: 10.1038/297070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland K. L., Lenihan P., O'Connor M. G., Condon J. C. Diarrhoea in foals associated with rotavirus. Vet Rec. 1982 Oct 30;111(18):421–421. doi: 10.1136/vr.111.18.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studdert M. J., Mason R. W., Patten B. E. Rotavirus diarrhoea of foals. Aust Vet J. 1978 Jul;54(7):363–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1978.tb02499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi E., Inaba Y., Sato K., Kurogi H., Akashi H., Satoda K., Omori T. Antibody to rotavirus in various animal species. Natl Inst Anim Health Q (Tokyo) 1979 Summer;19(1-2):72–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thouless M. E., Beards G. M., Flewett T. H. Serotyping and subgrouping of rotavirus strains by the ELISA test. Arch Virol. 1982;73(3-4):219–230. doi: 10.1007/BF01318076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Walker M. Isolation of rotavirus from foals with diarrhoea. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1978 Aug;56(4):453–457. doi: 10.1038/icb.1978.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urasawa T., Urasawa S., Taniguchi K. Sequential passages of human rotavirus in MA-104 cells. Microbiol Immunol. 1981;25(10):1025–1035. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1981.tb00109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf J. L., Schreiber D. S. Viral gastroenteritis. Med Clin North Am. 1982 May;66(3):575–595. doi: 10.1016/S0025-7125(16)31408-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., Greenberg H. B., James W. D., Pittman A. L., Kalica A. R., Flores J., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Definition of human rotavirus serotypes by plaque reduction assay. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):110–115. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.110-115.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., James H. D., Jr, Pittman A. L., Hoshino Y., Greenberg H. B., Kalica A. R., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z. Direct isolation in cell culture of human rotaviruses and their characterization into four serotypes. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):310–317. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.310-317.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., Mebus C. A., Yolken R. H., Kalica A. R., James H. D., Jr, Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Rotaviral immunity in gnotobiotic calves: heterologous resistance to human virus induced by bovine virus. Science. 1979 Feb 9;203(4380):548–550. doi: 10.1126/science.216077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoden S., Kida H., Yanagawa R. An avian influenza virus of which infectivity is neutralized by antisera lacking hemagglutination-inhibition activity. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1982;74(2-3):205–210. doi: 10.1007/BF01314713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]