Abstract
Acting through a number of distinct pathways, many G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) activate the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade. Recently, it has been shown that in some cases, clathrin-mediated endocytosis is required for GPCR activation of the ERK/MAPK cascade, whereas in others it is not. Accordingly, we compared ERK activation mediated by a GPCR that does not undergo agonist-stimulated endocytosis, the α2A adrenergic receptor (α2A AR), with ERK activation mediated by the β2 adrenergic receptor (β2 AR), which is endocytosed. Surprisingly, we found that in COS-7 cells, ERK activation by the α2A AR, like that mediated by both the β2 AR and the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), is sensitive to mechanistically distinct inhibitors of clathrin-mediated endocytosis, including monodansylcadaverine, a mutant dynamin I, and a mutant β-arrestin 1. Moreover, we determined that, as has been shown for many other GPCRs, both α2A and β2 AR-mediated ERK activation involves transactivation of the EGFR. Using confocal immunofluorescence microscopy, we found that stimulation of the β2 AR, the α2A AR, or the EGFR each results in internalization of a green fluorescent protein-tagged EGFR. Although β2 AR stimulation leads to redistribution of both the β2 AR and EGFR, activation of the α2A AR leads to redistribution of the EGFR but the α2A AR remains on the plasma membrane. These findings separate GPCR endocytosis from the requirement for clathrin-mediated endocytosis in EGFR transactivation-mediated ERK activation and suggest that it is the receptor tyrosine kinase or another downstream effector that must engage the endocytic machinery.
Many G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) have been shown to activate the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade. Recently, it was discovered that for some GPCRs, events associated with the termination of receptor signaling are also involved in signaling to the MAPK cascade (1). Receptor phosphorylation, β-arrestin recruitment, and clathrin-mediated endocytosis have all been implicated in GPCR-mediated MAPK activation. Among GPCRs, the involvement of clathrin-mediated endocytosis in MAPK activation was first established for the β2 adrenergic receptor (β2 AR) (2). Specifically, dominant-negative forms of dynamin I and of β-arrestin 1, which inhibit clathrin-mediated endocytosis of the β2 AR, also block isoproterenol-stimulated MAPK activation.
Additional studies addressing the role of clathrin-mediated endocytosis in GPCR-mediated ERK activation have yielded often conflicting results. In addition to the β2 AR, our laboratory has reported that blocking receptor endocytosis attenuates MAPK signaling by endogenously expressed lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), thrombin, and bombesin receptors in Rat-1 fibroblasts (3) and by the 5-HT1A receptor expressed in 293 cells (4). MAPK activation by the m1 muscarinic receptor (5), and the μ, δ, and κ opioid receptors (6, 7) are also reported to be sensitive to inhibitors of endocytosis, whereas MAPK signaling by the α2A, α2B, and α2C adrenergic receptors (8, 9), the CB1 cannabinoid receptor (10), the m3 muscarinic receptor (11), the CXCR2 (12), the κ opioid receptor (13), and the B2 bradykinin receptor (14) have been shown to be independent of GPCR endocytosis. In some cases, notably the κ opioid receptor, MAPK signaling has been shown to be both sensitive and insensitive to inhibitors of clathrin-mediated endocytosis (6, 13).
One major pathway of GPCR-mediated MAPK activation converges with the pathway used by many receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) (15) (Scheme 1). This pathway, known as RTK “transactivation,” has been demonstrated for many GPCRs, including the LPA receptor, the thrombin receptor, and the endothelin receptor (16–18). In this pathway, GPCR stimulation leads to the release of Gβγ subunits, which, through unknown effectors, leads to activation and tyrosine phosphorylation of RTKs, such as the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) (16). Subsequent to RTK phosphorylation, the steps involved in GPCR-mediated and RTK-mediated ERK activation are indistinguishable (Scheme 1) (19, 20).
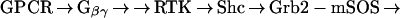 |
 |
Scheme 1.
Because direct EGF-induced ERK activation has been shown to depend on clathrin-mediated endocytosis (21), we hypothesized that the sensitivity of GPCR-mediated ERK activation might correlate with signaling via EGFR transactivation. That is, we hypothesized that, in cells in which GPCRs activate MAPK via transactivation of the EGFR, ERK activation would be sensitive to inhibitors of endocytosis, regardless of whether the GPCR itself underwent agonist-induced internalization. To test this hypothesis, we have examined the role of clathrin-mediated endocytosis in ERK activation via internalizing β2 ARs and noninternalizing α2A ARs in COS-7 cells, a cell type in which both receptors stimulate MAPK primarily via EGFR transactivation.
Materials and Methods
Materials.
Tyrphostin AG1478 and recombinant EGF were from Calbiochem, monodansylcadaverine (MDC) was from Sigma, and pertussis toxin was from List Biological Laboratories (Campbell, CA). Anti-phospho-MAPK antibodies were from New England Biolabs, the total ERK 1/2 antibody and the EGFR antibodies were from Upstate Biotechnology (Lake Placid, NY), and the anti-phosphotyrosine antibody was from Transduction Laboratories (Lexington, KY). The unlabeled and rhodamine-labeled 12CA5 antibodies were from Roche Biochemicals, and the M2 Flag antibody was from Sigma. The anti-hemagglutinin (HA) affinity beads were from Covance (Princeton, NJ). Secondary antibodies were from Jackson ImmunoResearch (Indianapolis). All other reagents were standard laboratory grade.
Plasmids.
HA-α2A was obtained from Brian Kobilka (Stanford Univ.), β-arrestin 1 318–419 from J. L. Benovic (Thomas Jefferson Univ.), EGFR–green fluorescent protein (GFP) from A. Sorkin (University of Colorado Health Sciences Center), and HA-ERK-1 from J. Pouyssegur (Univ. of Nice). All other plasmids were constructed in our laboratory.
Tissue Culture.
COS-7 cells were maintained in DMEM containing 10% fetal bovine serum and 100 μg/ml gentamicin. HEK293 cells were maintained in modified Eagle's medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum and 100 μg/ml gentamicin. Cells were transiently transfected by using Lipofectamine as described (16). Experiments were performed 2–3 days posttransfection, and in all cases, cells were serum starved overnight in medium containing 10 mM Hepes, 0.1% BSA, and 100 μg/ml gentamicin.
Sequestration Assays.
COS-7 cells transiently expressing HA epitope-tagged α2A ARs or Flag epitope-tagged β2 ARs were exposed to isoproterenol (10 μM) or UK14304 (10 μM), respectively, for 30 min at 37°C. Cell-surface receptors were labeled with a 12CA5 monoclonal antibody (Roche) or an M2 Flag monoclonal antibody (Sigma) by using FITC-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG as a secondary antibody. Receptor sequestration was quantified as loss of cell-surface receptors in agonist-treated cells measured by flow cytometry (22).
Immunoprecipitation.
Serum-starved transfected cells were exposed to agonist at 37°C, washed once with ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline, lysed in glycerol lysis buffer [5 mM Hepes, 250 mM NaCl, 10% (vol/vol) glycerol, 0.5% Nonidet P-40, 2 mM EDTA, 100 μM Na3VO4, 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, 10 μg/ml leupeptin, 10 μg/ml aprotinin], clarified by centrifugation, and immunoprecipitated by using the appropriate antibodies. HA–ERK-1 was immunoprecipitated by using 20 μl of anti-HA affinity beads and rotated for 4 hr at 4°C, the immune complexes were washed twice with cold glycerol lysis buffer, denatured in 2× Laemmli sample buffer, and electrophoresed on SDS/PAGE gels. The proteins were transferred to poly(vinylidene difluoride) and probed for both phospho-ERK 1/2 and total ERK 1/2 as described below. Immunoprecipitation and detection of tyrosine phosphorylation of the EGFR was performed as described (16).
ERK 1/2 Phosphorylation.
Serum-starved transfected cells grown in 12-well dishes were stimulated with agonist for 5 minutes at 37°C, the media aspirated, and the cells lysed in 100 μl of 2× Laemmli sample buffer. The samples were then electrophoresed on SDS/PAGE gels and transferred to poly(vinylidene difluoride). Phospho-ERK 1/2 was detected by using a 1:3,000 dilution of a rabbit polyclonal phospho-ERK 1/2-specific antibody (New England Biolabs), and total ERK 1/2 was detected by using a 1:1,000 dilution of an ERK 1/2 antibody (Upstate Biotechnology). Blots were probed with a 1:7,000 dilution of a donkey anti-rabbit horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody. Blots were visualized by using ECL (enhanced chemiluminescence reagent; Amersham Pharmacia) and quantitated by using a scanning laser densitometer.
Immunofluorescence Microscopy.
HEK-293 cells transiently expressing HA epitope-tagged α2A ARs or β2 ARs together with an EGFR–GFP fusion protein (23) were grown on sterile coverslips. Before stimulation, epitope-tagged receptors were labeled with a 1:100 dilution of a rhodamine-conjugated anti-HA antibody (Roche). Cells were then stimulated for 30 min at 37°C in the absence or presence of UK14304 (10 μM), isoproterenol (10 μM), or EGF (10 ng/ml) and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde. Confocal microscopy was performed on a Zeiss LSM-510 laser scanning microscope by using a Zeiss 100× oil-immersion lens. Fluorescent signals were collected by using the Zeiss LSM software in the line switching mode by using dual excitation (488, 568 nm) and emission (515–540 nm, 590–610 nm) filter sets. Specificity of labeling and absence of signal crossover were established by examination of single-labeled samples.
Results and Discussion
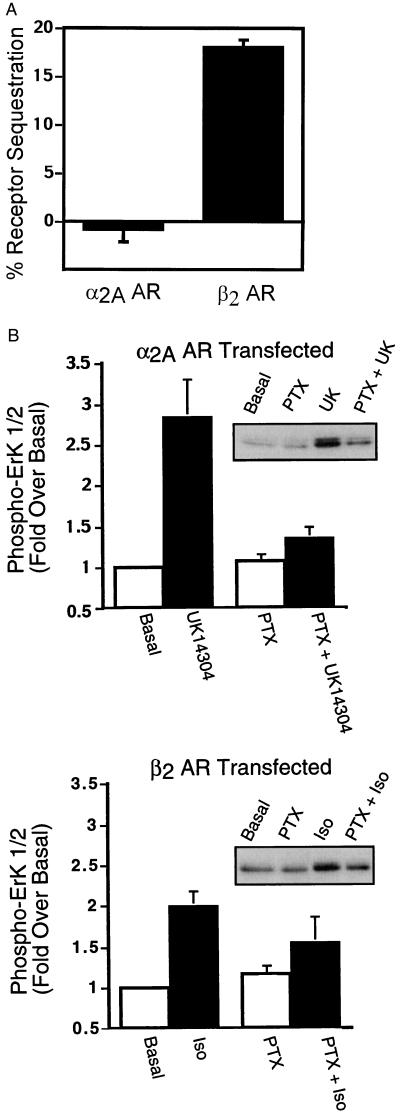
As shown in Fig. 1A, when expressed in COS-7 cells, the β2 AR undergoes agonist-driven internalization, whereas the α2A AR does not. These data are consistent with previous studies that demonstrated that the α2A AR exhibits little or no agonist-induced sequestration in either HEK293 (9, 24) or COS-1 (8) cells. In addition, as shown in Fig. 1B, activation of MAPK by both receptors is significantly dependent on the activation of pertussis toxin-sensitive G proteins.
Figure 1.
Agonist-promoted α2A AR and β2 AR sequestration and ERK 1/2 phosphorylation in COS-7 cells. (A) COS-7 cells transiently expressing either HA-epitope tagged α2A ARs or Flag epitope-tagged β2 ARs were serum-starved overnight and exposed to UK14304 (10 μM) or isoproterenol (10 μM), respectively, for 30 min at 37°C. Cell-surface receptors were labeled with an 12CA5 monoclonal antibody or an M2 Flag monoclonal antibody, by using FITC-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG as the secondary antibody. Receptor sequestration, quantified as the percent loss of cell-surface fluorescence in agonist-treated cells, was measured by using flow cytometry. The data are expressed as the mean ± SEM of four independent experiments performed in triplicate. (B) Appropriately transfected COS-7 cells were serum-starved overnight in the presence or absence of pertussis toxin (100 ng/ml) before stimulation with 1 μM UK14304 (Upper) or 1 μM isoproterenol (Lower) for 5 min. Aliquots of whole-cell lysate (approximately 30 μg of protein per lane) were resolved by SDS/PAGE, and ERK 1/2 phosphorylation was detected by protein immunoblotting by using rabbit polyclonal phospho-MAPK-specific IgG. Data are expressed as the fold ERK 1/2 phosphorylation over the basal value in appropriately transfected cells. The data are expressed as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments.
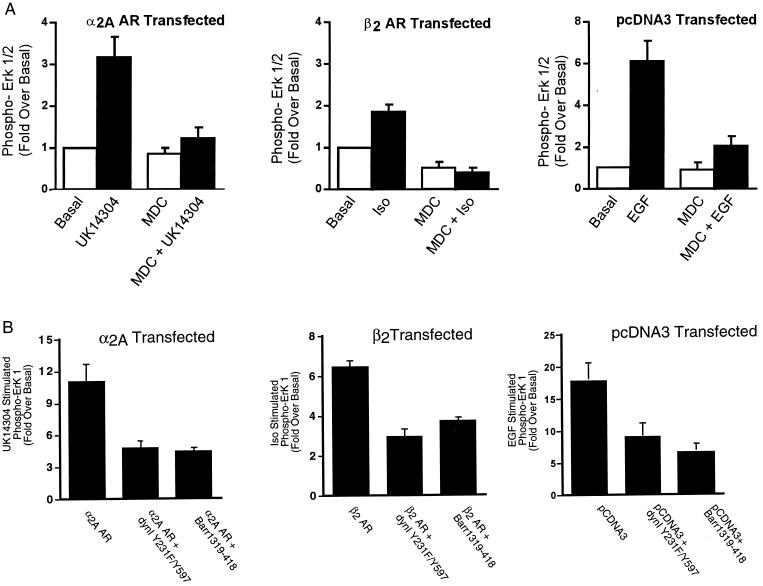
Because both the α2A AR- and the β2 AR-mediated activation of ERK is pertussis toxin-sensitive, but the β2 AR internalizes whereas the α2A AR does not, this is an ideal system to examine the requirement for clathrin-mediated endocytosis in ERK activation. Our previous studies have suggested that for the β2 AR, inhibitors of clathrin-mediated endocytosis block MAPK downstream of β2 AR internalization (2). Moreover, in addition to a role for clathrin-mediated endocytosis in ERK activation by GPCRs, Vieira et al. (21) have suggested that clathrin-mediated endocytosis is involved in ERK activation mediated by the EGFR. Thus, we tested whether ERK activation by the α2A AR, the β2 AR, and the EGFR was sensitive to inhibitors of clathrin-mediated endocytosis. The effects of three mechanistically distinct inhibitors of clathrin-mediated endocytosis, MDC, Y231F/Y597F dynamin I, and β-arrestin 1 318–419, were determined. MDC inhibits clathrin-mediated endocytosis by stabilizing clathrin cages and has been shown to inhibit insulin-like growth factor-I (25) as well as LPA-mediated ERK activation (3). Y231F/Y597F dynamin I is a dominant inhibitory form of dynamin I that cannot be phosphorylated by c-src (26), and β-arrestin 1 318–419 is a truncated form of β-arrestin 1 that interferes with GPCR sequestration through interactions with clathrin (27). MDC, Y231F/Y597F dynamin I, and β-arrestin 1 318–419 all inhibited agonist-stimulated internalization of the β2 AR and the EGFR by 45–75% measured either by flow cytometry (β2 AR) or by 125I-labeled EGF-induced EGFR internalization (data not shown). As shown in Fig. 2A, MDC inhibited ERK 1/2 phosphorylation by the α2A AR (Left), the β2 AR (Center), and the EGFR (Right). Similarly, the dominant inhibitory forms of both dynamin I and of β-arrestin 1 significantly attenuated α2A AR (Fig. 2B, Left), β2 AR (Fig. 2B, Center) and EGFR-mediated (Fig. 2B, Right) MAPK activation. Thus, even though the α2A AR itself does not internalize, the activation of MAPK by UK14304, like the activation by isoproterenol, is sensitive to all three inhibitors of clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Although consistent with a role for clathrin-mediated endocytosis in GPCR-mediated ERK activation, these data clearly dissociate sequestration of the GPCR from ERK activation. They also suggest that the Gi-dependent ERK signaling cascades used by the β2 and α2A ARs as well as the pathway used by the EGFR in COS-7 cells all depend on clathrin-mediated endocytosis.
Figure 2.
The effect of chemical and transfectable inhibitors of clathrin-mediated endocytosis on α2A AR- and β2 AR-mediated ERK 1/2 phosphorylation. (A) Cells transiently expressing the α2A AR-, the β2 AR-, or vector-transfected cells were pretreated with 300 μM MDC before a 5-minute stimulation with 1 μM UK14304 (Left), 1 μM isoproterenol (Center), or 10 ng/ml EGF (Right). Aliquots of whole-cell lysate (approximately 30 μg of protein per lane) were resolved by SDS/PAGE, and ERK 1/2 phosphorylation was detected by protein immunoblotting by using rabbit polyclonal phospho-MAP kinase-specific IgG. Data are expressed as the fold ERK 1/2 phosphorylation over the basal value in appropriately transfected cells. The data shown are the mean ± SEM of four independent experiments. (B) Cells in 100-mm dishes were transiently transfected with a HA-tagged ERK-1 plasmid (0.5 μg) together with the α2A AR (2 μg, Left), the β2 AR (2 μg, Center), or pCDNA3 (Right) alone or with either dynamin I Y231F/Y597F (7.5 μg) or β-arrestin 1 318–419 (7.5 μg). One day after transfection, cells were split into two 100-mm dishes and serum-starved overnight. After stimulation for 5 minutes with either 100 nM UK14304 (α2A AR), 1 μM isoproterenol (β2 AR), or 1 ng/ml EGF (EGFR), cell lysates were prepared, and the HA–ERK-1 was immunoprecipitated. Immunoblots were probed with both an anti-phospho-ERK 1/2 and a total ERK 1/2 antibody. Under each condition, data are expressed as the fold ERK 1/2 phosphorylation over the unstimulated. Data shown are the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments.
One pathway by which many GPCRs have been shown to activate ERK is via transactivation of RTKs, including the EGFR. For instance, the ET-1, LPA, and thrombin receptors in Rat-1 cells (17, 18) the LPA (20), and the β3 adrenergic receptors (28) in COS-7 cells each activate MAPK via transactivation of RTKs. To establish whether, in COS-7 cells, the α2A AR- and β2 AR-mediated activation of ERK 1/2 proceeds via a transactivation-dependent mechanism, we performed two experiments. First, we measured the ability of UK14304 and isoproterenol to stimulate increased tyrosine phosphorylation of the EGFR in cells expressing the α2A AR or the β2 AR. As previously reported for several GPCRs including the α2A AR, the LPA receptor, and the thrombin receptor (16), UK14304, isoproterenol, and EGF stimulation each increases tyrosine phosphorylation of the EGFR (Fig. 3A). Second, we measured the ability of tyrphostin AG1478, a selective EGFR inhibitor, to block α2A AR-, β2 AR-, and EGFR-induced ERK 1/2 phosphorylation. As shown in Fig. 3B, in appropriately transfected cells, tyrphostin AG1478 pretreatment attenuates the UK14304-, isoproterenol-, and EGF-induced ERK 1/2 phosphorylation. These data suggest that, in COS-7 cells, activation of the MAPK cascade by the α2A AR, the β2 AR, and the EGFR proceeds via a common mechanism, involving both clathrin-mediated endocytosis and activation of the EGFR.
Figure 3.
UK14304, Isoproterenol- and EGF-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of the EGFR and the effect of the EGFR-specific tyrphostin, AG1478, on α2A AR- and β2 AR-mediated ERK 1/2 phosphorylation. (A) Serum-starved COS-7 cells transiently expressing the α2A AR or β2 AR or pCDNA3 were stimulated with 1 μM UK14304, 1 μM isoproterenol, or 10 ng/ml EGF for 2 min. Monolayers were lysed in glycerol lysis buffer, and endogenous EGFRs were immunoprecipitated by using a sheep anti-human EGFR polyclonal antiserum. Immunoprecipitates were resolved by SDS/PAGE, and EGFR tyrosine phosphorylation was determined by immunoblotting by using a horseradish peroxidase-conjugated anti-phosphotyrosine monoclonal antiserum as described in Materials and Methods. (B) Cells transiently overexpressing the α2A AR-, the β2 AR-, or vector-transfected cells were preincubated for 15 min with tyrphostin AG1478 (125 nM) before stimulation with isoproterenol (1 μM), UK14304 (1 μM), or EGF (10 ng/ml) for 5 min. ERK 1/2 phosphorylation was determined from whole-cell lysates as described in Materials and Methods. Data shown are the mean ± SEM of four independent experiments and are normalized to the level of ERK 1/2 phosphorylation in untreated cells.
Because transactivated EGFRs serve as an intermediate for α2A AR and β2 AR-mediated ERK activation, our data support the hypothesis that endocytosis of the EGFR or of another downstream effector accounts for the sensitivity of the GPCR signals to inhibitors of clathrin-mediated endocytosis. To examine whether stimulation of the α2A AR and the β2 AR leads to internalization of transactivated EGFRs, we used confocal immunofluorescence microscopy to examine the localization of each of these receptors after agonist treatment. Fig. 4 shows that in unstimulated cells transfected with the β2 AR and the EGFR, both the β2 AR and the EGFR localize primarily to the cell surface (a–c). Isoproterenol treatment of these cells leads to an increase in the intracellular localization of both the β2 AR and the EGFR (d–f). EGF treatment of these cells, however, leads to an increase in EGFR localized inside the cells, whereas the β2 AR remains on the cell surface (g–i). As shown in Fig. 5, treatment of cells expressing both the α2A AR and the EGFR with either UK14304 (d–f) or EGF (g–i) leads to increased intracellular localization of the EGFR, whereas the α2A AR remains localized on the cell surface. Thus, although activation of the β2 AR leads to internalization of both the transactivated EGFR and the β2 AR, UK14304 treatment of cells expressing the α2A AR leads to internalization of the transactivated EGFR but not the α2A AR. Our data suggest that GPCR-mediated transactivation of an RTK can lead to internalization of either the RTK alone (as is the case for the α2A AR) or both the RTK and the GPCR (as is the case for the β2 AR).
Figure 4.
The effect of isoproterenol and EGF on the cellular distribution of epitope-tagged β2 ARs and EGFR–GFP. Confocal microscopic images depicting the cellular distribution of HA-tagged β2 AR (a, d, and g), and EGFR–GFP (23) (b, e, and h) before (NS; a–c) and after 30 min exposure to isoproterenol (d–f) or EGF (g, h, and i) in 293 cells. In the absence of agonist, both β2 AR and EGFR-GFP staining was predominantly confined to the plasma membrane (c). After exposure to isoproterenol, a portion of both receptor pools redistributed to an intracellular compartment (f). After exposure to EGF, redistribution of the EGFR–GFP, but not the β2 AR, was observed (i). Qualitatively similar results have been obtained in COS-7 cells.
Figure 5.
The effect of UK14304 and EGF on the cellular distribution of epitope-tagged α2A ARs, and GFP–EGFR proteins. Confocal microscopic images depicting the cellular distribution of HA-tagged α2A AR (a, d, and g), and EGFR–GFP (b, e, and h) before (NS; a, b, and c) and after 30-min exposure to UK14304 (d–f) or EGF (g, h, and i) in 293 cells. In the absence of agonist, both α2A AR and GFP–EGFR staining was predominantly confined to the plasma membrane (c). After exposure to UK14304, the EGFR–GFP, but not the α2A AR redistributed to an intracellular compartment (f). A qualitatively similar pattern was observed after exposure to EGF, with redistribution of EGFR–GFP but not the α2A AR (i). Qualitatively similar results have been obtained in COS-7 cells.
Recently Whistler and von Zastrow (7) reported that MAPK activation by the noninternalizing μ-opioid receptor is attenuated by a dominant inhibitory form of dynamin I. Their interpretation was that dynamin plays a unique signal transduction role distinct from its role in clathrin-mediated endocytosis. However, an alternative possibility is that the μ-opioid receptor, like the α2A AR and the β2 AR, mediates an endocytosis-dependent signal via EGFR transactivation. Our data, which indicate that several mechanistically distinct inhibitors of clathrin-mediated endocytosis block GPCR-mediated ERK activation, are consistent with a more general role for the clathrin-mediated endocytic machinery in signal transduction.
RTK transactivation is but one mechanism of many by which GPCRs can activate the ERK cascade. We have previously demonstrated that the same GPCR can activate MAPK via multiple pathways and that the cellular context in which a receptor is expressed can determine the mechanism of GPCR-mediated MAPK activation (20). In addition to MAPK activation that proceeds via the transactivation pathway, a second major pathway involves calcium and the tyrosine phosphorylation of the focal adhesion kinase (FAK)-like scaffolding protein, PYK2. Depending on the cell type, the contribution of transactivation (17) to ERK activation varies dramatically (20). In some cells, such as Rat-1 fibroblasts, the transactivation-dependent pathway is the major pathway to ERK activation, whereas in other cells such as PC12 cells, the PYK2 pathway is the major pathway. For instance, LPA receptor-mediated ERK activation can range from completely EGFR-dependent in Rat-1 cells to completely EGFR-independent in PC-12 cells (20). In HEK 293 cells, ERK 1/2 activation via both endogenous LPA receptor activation (20) and transiently expressed α2A AR activation (data not shown) is only partially sensitive to tyrphostin AG1478. In these cells, the α2A AR primarily activates ERK via a calcium-dependent signal that is blocked by a dominant-inhibitory mutant of the calcium-activated FAK family tyrosine kinase PYK2 (29). Such heterogeneity in GPCR signaling among cell types may account for the variable effects of clathrin-mediated inhibitors on MAPK that have recently been reported (2–14).
Taken together, our data suggest a model in which MAPK activation that proceeds via EGFR transactivation involves engagement of the clathrin-mediated endocytic machinery. What remains to be determined is whether endocytosis of a multiprotein complex including the EGFR and Raf is essential for transactivation-dependent MAPK activation or whether instead clathrin-coated endocytic pits serve some other function such as that of a specialized microdomain wherein signaling occurs.
Acknowledgments
We thank Donna Addison and Mary Holben for excellent secretarial assistance and W. E. Miller and S. Ahn for their helpful discussion. This work was supported in part by National Institutes of Health Grant HL16037 (R.J.L). R.J.L. is an Investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Abbreviations
- RTK
receptor tyrosine kinase
- LPA
lysophosphatidic acid
- ERK
extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- MAPK
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- AR
adrenergic receptor
- EGFR
epidermal growth factor receptor
- GPCR
G protein-coupled receptor
- MDC
monodansylcadaverine
- HA
hemagglutinin
- GFP
green fluorescent protein
References
- 1.Lefkowitz R J. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:18677–18880. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.30.18677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Daaka Y, Luttrell L M, Ahn S, Della Rocca G J, Ferguson S S, Caron M G, Lefkowitz R J. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:685–688. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.2.685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Luttrell L M, Daaka Y, Della Rocca G J, Lefkowitz R J. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:31648–31656. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.50.31648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Della Rocca G J, Mukhin Y V, Garnovskaya M N, Daaka Y, Clark G J, Luttrell L M, Lefkowitz R J, Raymond J R. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:4749–4753. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.8.4749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Vogler O, Nolte B, Voss M, Schmidt M, Jakobs K H, van Koppen C J. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:12333–12338. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.18.12333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ignatova E G, Belcheva M M, Bohn L M, Neuman M C, Coscia C J. J Neurosci. 1999;19:56–63. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-01-00056.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Whistler J L, von Zastrow M. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:24575–24578. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.35.24575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.DeGraff J L, Gagnon A W, Benovic J L, Orsini M J. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:11253–11259. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.16.11253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Schramm N L, Limbird L E. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:24935–24940. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.35.24935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Roche J P, Bounds S, Brown S, Mackie K. Mol Pharmacol. 1999;56:611–618. doi: 10.1124/mol.56.3.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Budd D C, Rae A, Tobin A B. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:12355–12360. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.18.12355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Yang W, Wang D, Richmond A. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:11328–11333. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.16.11328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Li J G, Luo L Y, Krupnick J G, Benovic J L, Liu-Chen L Y. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:12087–12094. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.17.12087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Blaukat A, Pizard A, Rajerison R M, Alhenc-Gelas F, Muller-Esterl W, Dikic I. FEBS Lett. 1999;451:337–341. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(99)00613-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Luttrell L M, Daaka Y, Lefkowitz R J. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1999;11:177–183. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(99)80023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Luttrell L M, Della Rocca G J, van Biesen T, Luttrell D K, Lefkowitz R J. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:4637–4644. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.7.4637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Daub H, Weiss F U, Wallasch C, Ullrich A. Nature (London) 1996;379:557–560. doi: 10.1038/379557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Daub H, Wallasch C, Lankenau A, Herrlich A, Ullrich A. EMBO J. 1997;16:7032–7044. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.23.7032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.van Biesen T, Hawes B E, Luttrell D K, Krueger K M, Touhara K, Porfiri E, Sakaue M, Luttrell L M, Lefkowitz R J. Nature (London) 1995;376:781–784. doi: 10.1038/376781a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Della Rocca G J, Maudsley S, Daaka Y, Lefkowitz R J, Luttrell L M. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:13978–13984. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.20.13978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Vieira A V, Lamaze C, Schmid S L. Science. 1996;274:2086–2089. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5295.2086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Barak L S, Tiberi M, Freedman N J, Kwatra M M, Lefkowitz R J, Caron M G. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:2790–2795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Carter R E, Sorkin A. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:35000–35007. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.52.35000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Daunt D A, Hurt C, Hein L, Kallio J, Feng F, Kobilka B K. Mol Pharmacol. 1997;51:711–720. doi: 10.1124/mol.51.5.711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chow J C, Condorelli G, Smith R J. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:4672–4680. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.8.4672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ahn S, Maudsley S, Luttrell L M, Lefkowitz R J, Daaka Y. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:1185–1188. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.3.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Krupnick J G, Santini F, Gagnon A W, Keen J H, Benovic J L. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:32507–32512. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.51.32507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Soeder K J, Snedden S K, Cao W H, Della Rocca G J, Daniel K W, Luttrell L M, Collins S. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:12017–12022. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.17.12017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Della Rocca G J, van Biesen T, Daaka Y, Luttrell D K, Luttrell L M, Lefkowitz R J. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:19125–19132. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.31.19125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]