Abstract
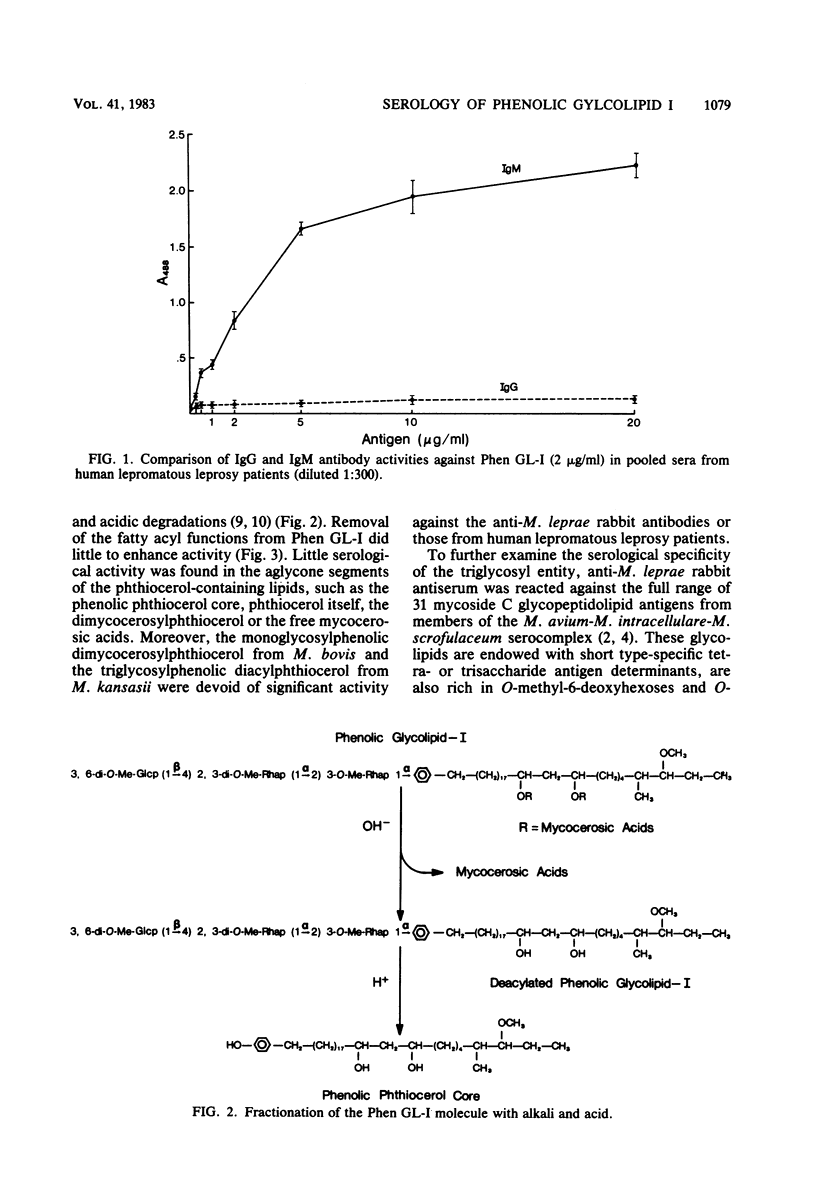
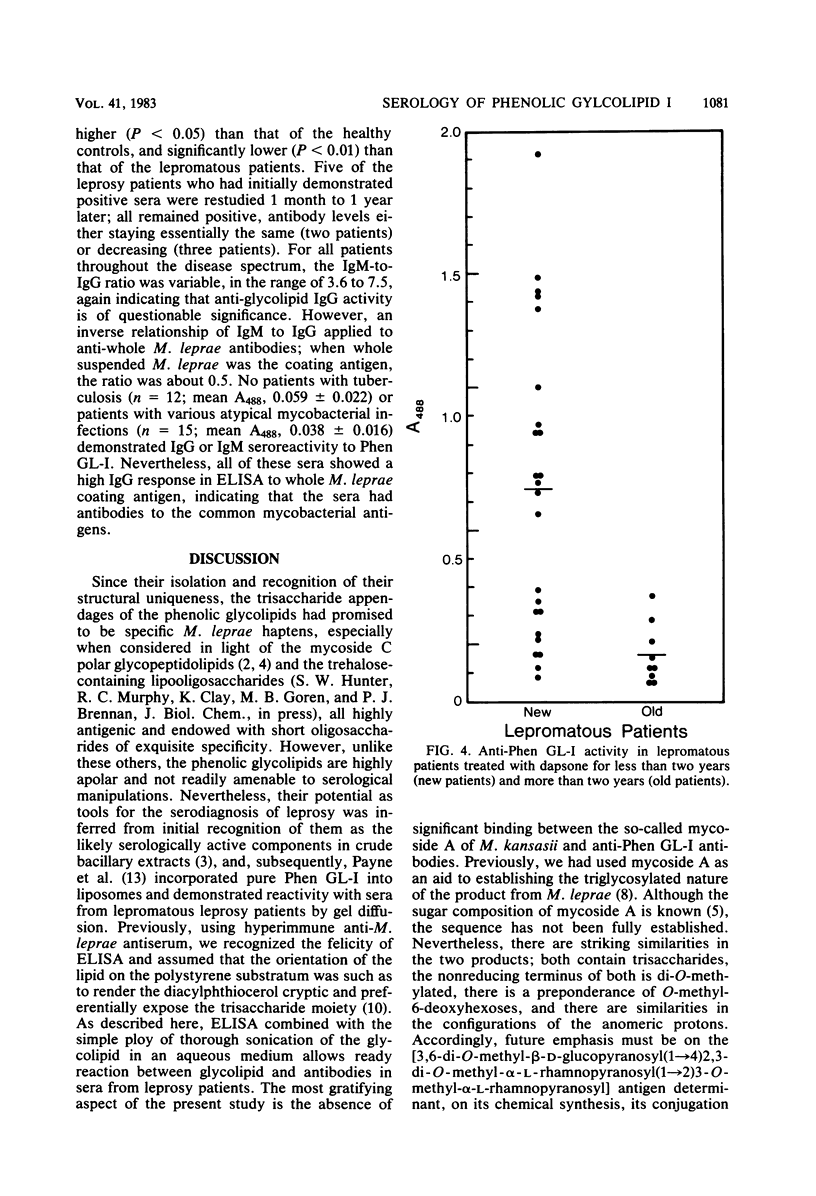
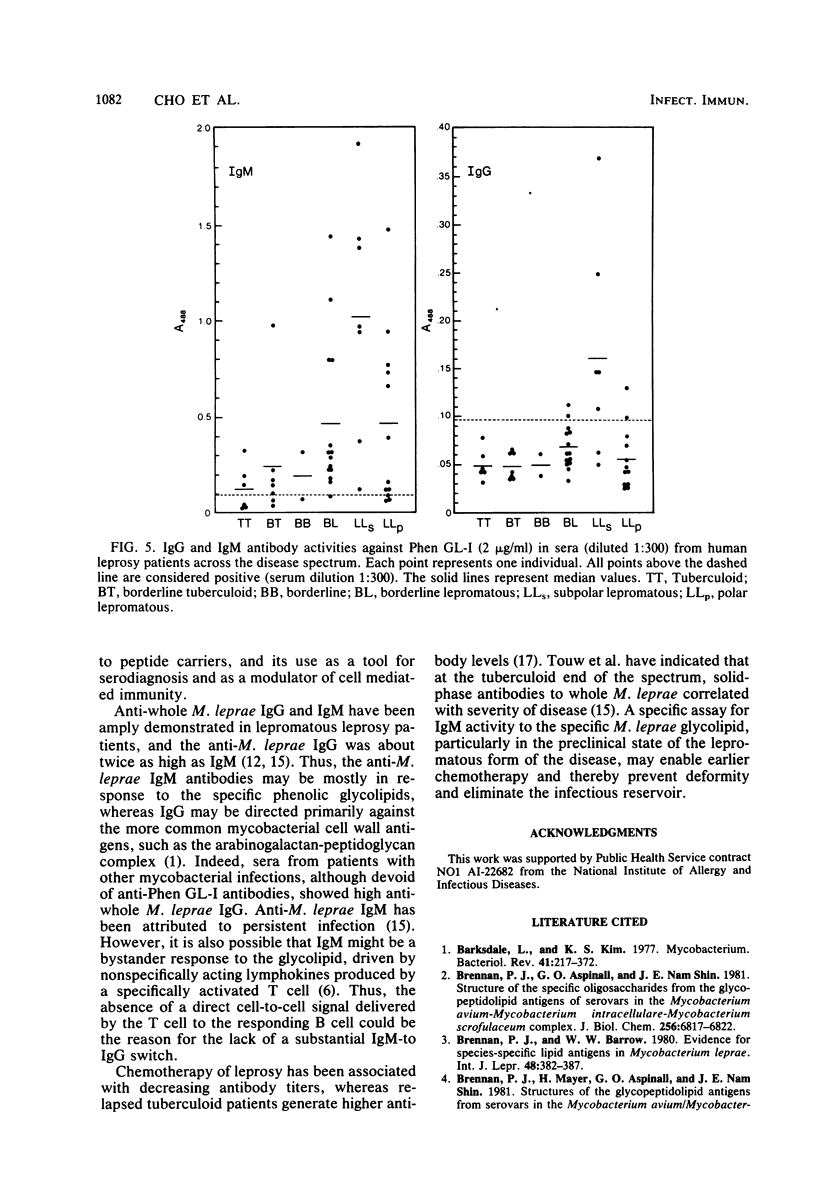
The serological activities of the specific phenolic glycolipid I from Mycobacterium leprae, its dissected parts, and related glycolipids from other mycobacteria were examined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay against hyperimmune anti-M. leprae rabbit antiserum and sera from patients with leprosy and other mycobacterial diseases. High anti-phenolic glycolipid I immunoglobulin M antibodies were found in 23 of 24 (96%) of lepromatous leprosy patients on short term chemotherapy and in 8 of 13 tuberculoid leprosy patients (62%). Sera from patients with tuberculosis or atypical mycobacterial infections were devoid of anti-phenolic glycolipid I activity. The structurally related phenolic glycolipids from Mycobacterium kansasii and Mycobacterium bovis and the aglycone segments of the M. leprae product showed no significant activity. Thus, the trisaccharide determinant of phenolic glycolipid I is specific in its structure, serological activity, and, to a lesser extent, the antibody class it evokes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barksdale L., Kim K. S. Mycobacterium. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Mar;41(1):217–372. doi: 10.1128/br.41.1.217-372.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan P. J., Aspinall G. O., Shin J. E. Structure of the specific oligosaccharides from the glycopeptidolipid antigens of serovars in the Mycobacterium avium-Mycobacterium intracellulare-Mycobacterium scrofulaceum complex. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6817–6822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan P. J., Barrow W. W. Evidence for species-specific lipid antigens in Mycobacterium leprae. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1980 Dec;48(4):382–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEMARTEAU-GINSBURG H., LEDERER E. SUR LA STRUCTURE CHIMIQUE DU MYCOSIDE B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 27;70:442–451. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90774-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endres R. O., Kushnir E., Kappler J. W., Marrack P., Kinsky S. C. A requirement for nonspecific T cell factors in antibody responses to "T cell independent" antigens. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):781–784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis T. P., Buchanan T. M. Production and partial characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Mycobacterium leprae. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):172–178. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.172-178.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter S. W., Brennan P. J. A novel phenolic glycolipid from Mycobacterium leprae possibly involved in immunogenicity and pathogenicity. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):728–735. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.728-735.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter S. W., Brennan P. J. Further specific extracellular phenolic glycolipid antigens and a related diacylphthiocerol from Mycobacterium leprae. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7556–7562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter S. W., Fujiwara T., Brennan P. J. Structure and antigenicity of the major specific glycolipid antigen of Mycobacterium leprae. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):15072–15078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. B., Jr, Libby R. Separation of immunoglobulin M (IgM) essentially free of IgG from serum for use in systems requiring assay of IgM-type antibodies without interference from rheumatoid factor. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):451–454. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.451-454.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. N., Draper P., Rees R. J. Serological activity of purified glycolipid from Mycobacterium leprae. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1982 Jun;50(2):220–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley D. S., Jopling W. H. Classification of leprosy according to immunity. A five-group system. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1966 Jul-Sep;34(3):255–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touw J., Langendijk E. M., Stoner G. L., Belehu A. Humoral immunity in leprosy: immunoglobulin G and M antibody responses to Mycobacterium leprae in relation to various disease patterns. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):885–892. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.885-892.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoder L., Naafs B., Harboe M., Bjune G. Antibody activity against Mycobacterium leprae antigen 7 in leprosy: studies on variation in antibody content throughout the spectrum and on the effect of DDS treatment and relapse in BT leprosy. Lepr Rev. 1979 Jun;50(2):113–121. doi: 10.5935/0305-7518.19790017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


