Abstract
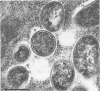
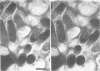
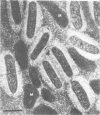
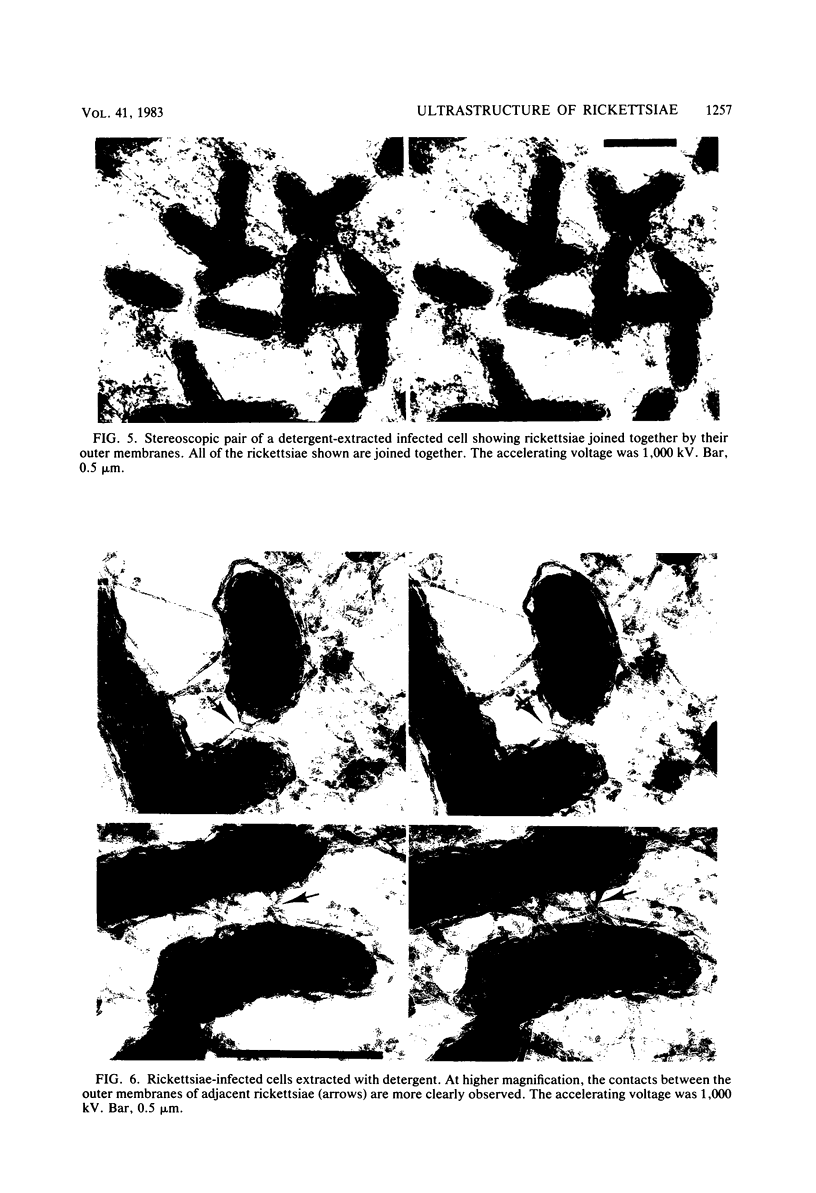
The ultrastructural appearance of the "halozone" formed at the interface between the spotted fever agent Rickettsia rickettsii and the cytoplasm of persistently infected cultured vole cells (Microtus pennsylvanicus) was studied by transmission electron microscopy. In sections of epoxy-embedded specimens stained with uranyl acetate and lead citrate, the halozone appeared clear and devoid of ultrastructural features. However, when unembedded preparations of whole infected cells were examined at 1,000 kV, fine structural features were observed within the halozone. These features, associated with the rickettsial outer membrane, were more clearly detectable when the infected cells were extracted with the detergent Triton X-100 before fixation. Under such conditions, long extensions of the rickettsial outer membrane, microfilament-like structures attached to that membrane, and extensive attachments between adjacent rickettsiae were seen. The fine structural features within the rickettsial halozone were also seen at 75 kV when unembedded sections were prepared from polyethylene glycol-embedded specimens. Thus, epoxy-embedding medium obscures the fine structural features within the halozone surrounding the rickettsiae in infected cells.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anacker R. L., Pickens E. G., Lackman D. B. Details of the ultrastructure of Rickettsia prowazekii grown in the chick yolk sac. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):260–262. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.260-262.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Cooney J. C., Mavros A. J., Jellison W. L., Maser C. The role of cottontail rabbits (Sylvilagus spp.) in the ecology of Rickettsia rickettsii in the United States. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1980 Jul;29(4):686–690. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1980.29.686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes S. F., Burgdorfer W. Reactivation of Rickettsia rickettsii in Dermacentor andersoni ticks: an ultrastructural analysis. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):779–785. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.779-785.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazia D., Schatten G., Sale W. Adhesion of cells to surfaces coated with polylysine. Applications to electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1975 Jul;66(1):198–200. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.1.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman D. J., Wisseman C. L., Jr Comparative ultrastructural study on the cell envelopes of Rickettsia prowazekii, Rickettsia rickettsii, and Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):1020–1023. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.1020-1023.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman D. J., Wisseman C. L., Jr, Waddell A. D., Jones M. External layers of Rickettsia prowazekii and Rickettsia rickettsii: occurrence of a slime layer. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):233–246. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.233-246.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolosewick J. J. The application of polyethylene glycol (PEG) to electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1980 Aug;86(2):675–661. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.2.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]