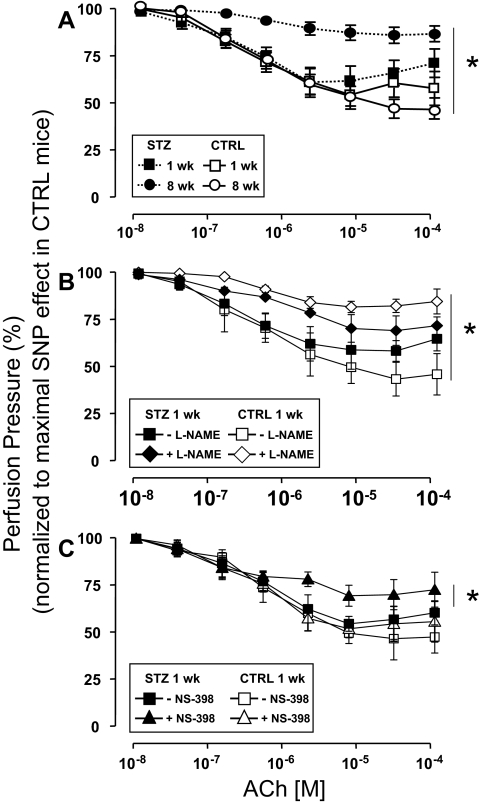
Figure 1.
Endothelial dysfunction in STZ-induced diabetes is unmasked by inhibition of COX-2. MVBs were isolated from mice treated with STZ (closed symbols) or vehicle CTRL (open symbols) and prepared as described in Materials and Methods. For these experiments, MVBs were contracted to about 80% of maximal vasoconstriction. To obtain comparable levels of precontraction with a perfusion pressure of about 100 mm Hg in MVBs from CTRL and STZ mice, 3 μm NA were used in MVBs from 1-wk STZ and 1-wk CTRL mice. A, Dose-response curves for ACh-induced vasorelaxation were obtained in MVBs from mice 1 wk (squares) or 8 wk (circles) after treatment with STZ or vehicle control. Results are mean ± sem of 11 (STZ) and eight (CTRL) independent experiments. ACh-mediated vasorelaxation was significantly impaired in MVBs from mice treated with STZ for 8 wk (vs. respective CTRL, P < 0.001). No significant difference was observed for ACh-induced vasodilation when results from 1-wk STZ and 8-wk CTRL were compared (P > 0.09). B, Dose-response curves for ACh-mediated vasorelaxation were obtained in MVBs from mice 1 wk after treatment with STZ or vehicle control in the absence (squares) or presence (diamonds) of pretreatment with the NO synthase antagonist L-NAME (100 μm, 30 min). Pretreatment with L-NAME significantly increased perfusion pressure to a similar extent (∼10 mm Hg) in MVBs from both CTRL and STZ-treated mice. Results are mean ± sem of five (STZ) and four (CTRL) independent experiments. Inhibition of NO synthase significantly reduced ACh-mediated vasorelaxation in MVBs from CTRL (vs. respective basal, P < 0.001) but not 1-wk STZ-treated mice. A statistical difference was observed in ACh-induced vasodilation when results from 1-wk CTRL + L-NAME and 1-wk STZ + L-NAME were compared (P < 0.05); no significant difference was observed in ACh-induced vasodilation when results from 1-wk CTRL without L-NAME and 1-wk STZ without L-NAME were compared (P > 0.12). C, Dose-response curves for ACh-mediated vasorelaxation were obtained in MVBs from mice 1 wk after treatment with STZ or vehicle control in the absence (squares) or presence (triangles) of pretreatment with the specific COX-2 inhibitor NS-398 (10 μm, 30 min). Results are mean ± sem of seven (STZ) and four (CTRL) independent experiments. ACh-mediated vasorelaxation was significantly impaired in MVBs from mice treated with STZ for 1 wk in the presence of NS-398 pretreatment (when compared with MVBs from 1 wk STZ in the absence of NS-398, P < 0.02). No significant difference was observed in ACh-induced vasodilation when results from 1-wk CTRL without NS-398 and 1-wk STZ without NS-398 were compared (P > 0.14). Asterisks refer to significant differences found between indicated curves assessed by two-way ANOVA for repeated measures.