Abstract
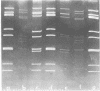
Antigenically distinct rotaviruses, i.e., viruses morphologically identical to conventional rotaviruses by electron microscopy, yet lacking the common group antigen(s) detected by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, were found in 2 of 51 fecal samples from Bulgarian infants with rotavirus gastroenteritis. These antigenically distinct viruses contained 11 segments of double-stranded RNA, but they demonstrated a unique RNA migration profile after electrophoresis of the genome RNA in polyacrylamide gels. This report confirms the presence of a new group of rotaviruses in humans. The significance of these viruses is currently unknown, and specific diagnostic tests must be developed for epidemiological studies to determine their role as human and veterinary pathogens and to evaluate their impact on proposed vaccine development programs.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bohl E. H., Saif L. J., Theil K. W., Agnes A. G., Cross R. F. Porcine pararotavirus: detection, differentiation from rotavirus, and pathogenesis in gnotobiotic pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):312–319. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.312-319.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt C. D., Kim H. W., Rodriguez W. J., Thomas L., Yolken R. H., Arrobio J. O., Kapikian A. Z., Parrott R. H., Chanock R. M. Comparison of direct electron microscopy, immune electron microscopy, and rotavirus enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of gastroenteritis viruses in children. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 May;13(5):976–981. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.5.976-981.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridger J. C., Clarke I. N., McCrae M. A. Characterization of an antigenically distinct porcine rotavirus. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1058–1062. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1058-1062.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung E. Y., Hnatko S. I., Gunning H., Wilson J. Comparison of Rotazyme and direct electron microscopy for detection of rotavirus in human stools. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):562–563. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.562-563.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Greenberg H. B., Espejo R. T., Flores J., Wyatt R. G., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Distinctive ribonucleic acid patterns of human rotavirus subgroups 1 and 2. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):958–961. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.958-961.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Wyatt R. G., Greenberg H. B., Kalica A. R., Kim H. W., Brandt C. D., Rodriguez W. J., Parrott R. H., Chanock R. M. Approaches to immunization of infants and young children against gastroenteritis due to rotaviruses. Rev Infect Dis. 1980 May-Jun;2(3):459–469. doi: 10.1093/clinids/2.3.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNulty M. S., Allan G. M., Todd D., McFerran J. B., McCracken R. M. Isolation from chickens of a rotavirus lacking the rotavirus group antigen. J Gen Virol. 1981 Aug;55(Pt 2):405–413. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-55-2-405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas J. C., Cohen J., Fortier B., Lourenco M. H., Bricout F. Isolation of a human pararotavirus. Virology. 1983 Jan 15;124(1):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90302-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Bishop R. F., Holmes I. H. Detection of a rotavirus-like agent associated with diarrhea in an infant. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Oct;16(4):724–726. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.4.724-726.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein A. S., Miller M. F. Comparison of an enzyme immunoassay with electron microscopic procedures for detecting rotavirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):938–944. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.938-944.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Bohl E. H., Theil K. W., Cross R. F., House J. A. Rotavirus-like, calicivirus-like, and 23-nm virus-like particles associated with diarrhea in young pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jul;12(1):105–111. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.1.105-111.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Inaba Y., Miura Y., Tokuhisa S., Matumoto M. Antigenic relationships between rotaviruses from different species as studied by neutralization and immunofluorescence. Arch Virol. 1982;73(1):45–50. doi: 10.1007/BF01341726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Bridger J. C., Jones J. M., Flewett T. H., Davies H. A., Davis H. A., White G. B. Morphological and antigenic relationships between viruses (rotaviruses) from acute gastroenteritis of children, calves, piglets, mice, and foals. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):804–810. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.804-810.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]