Abstract
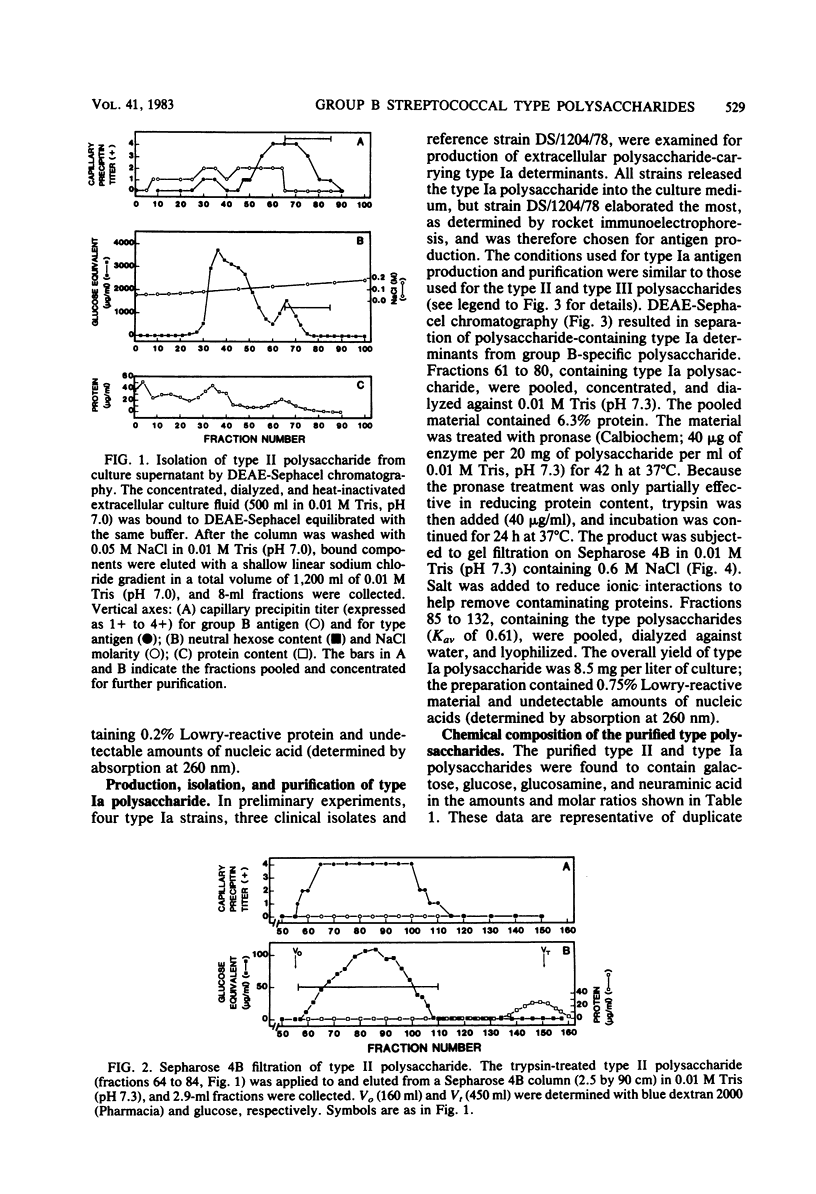
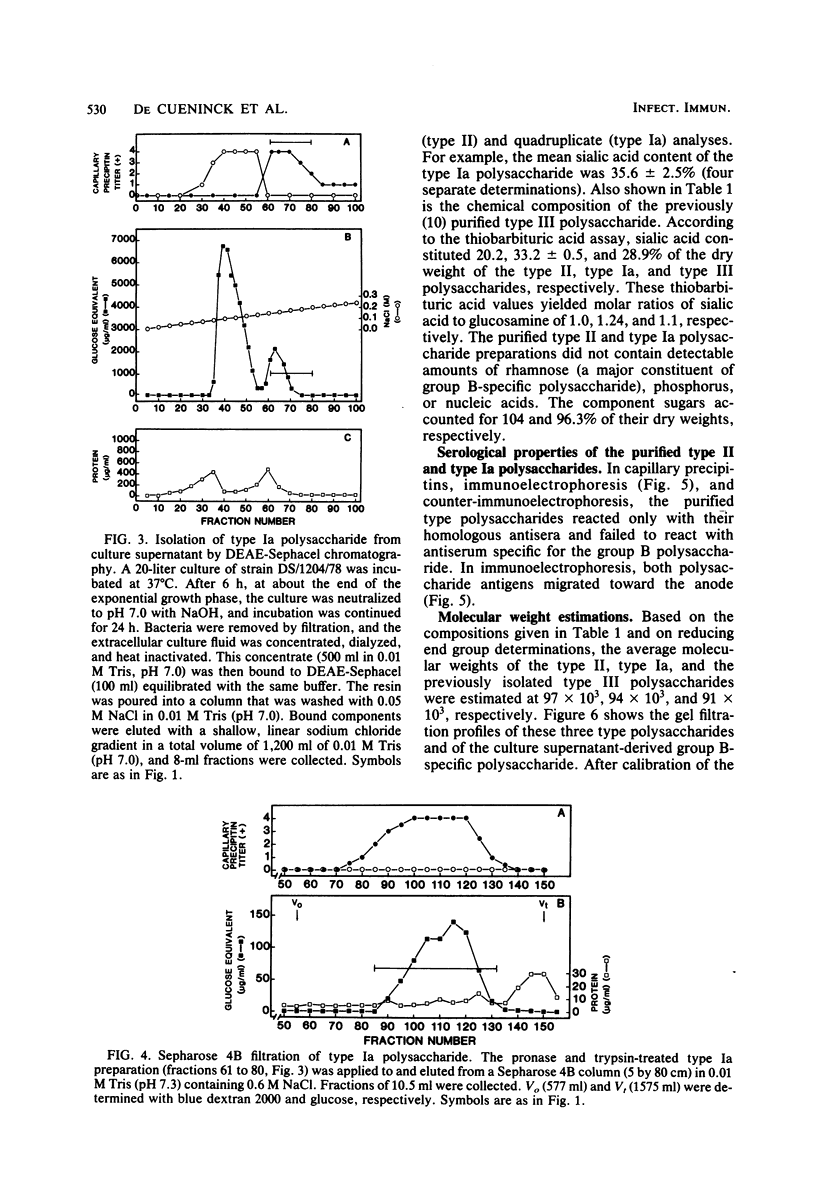
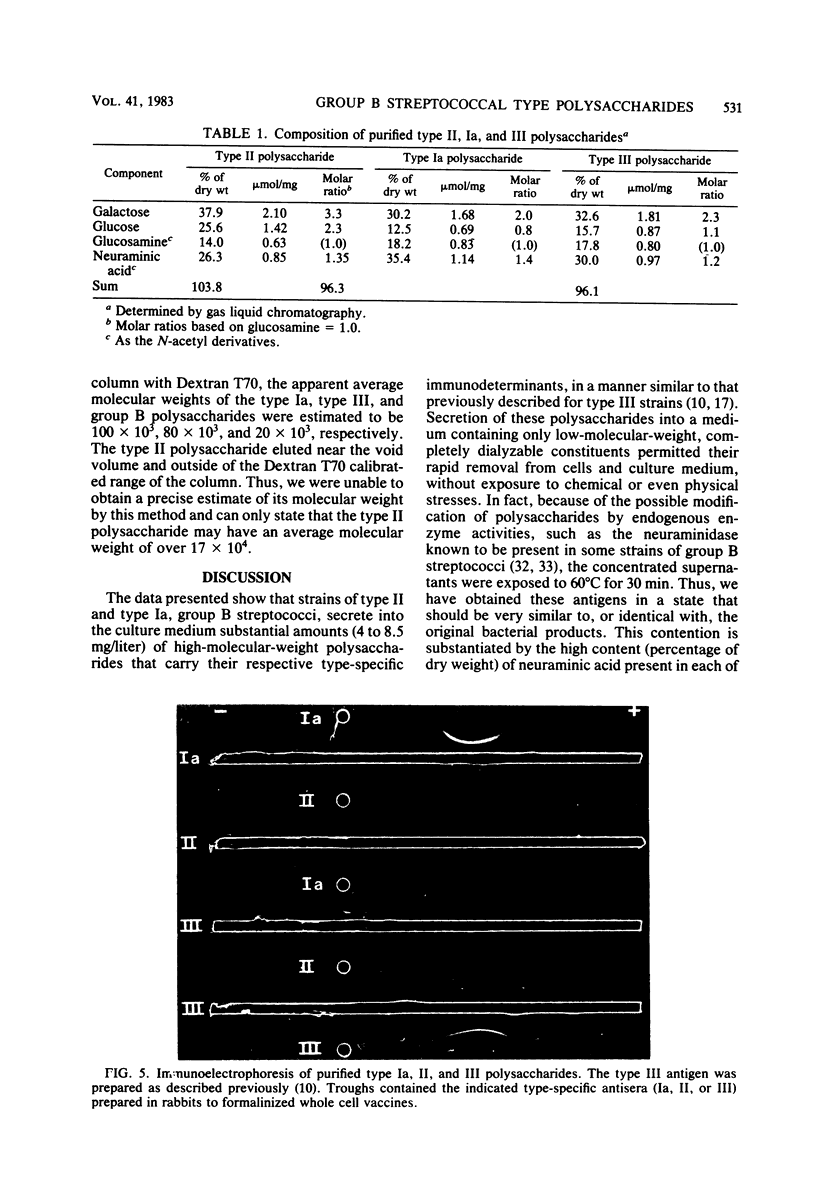
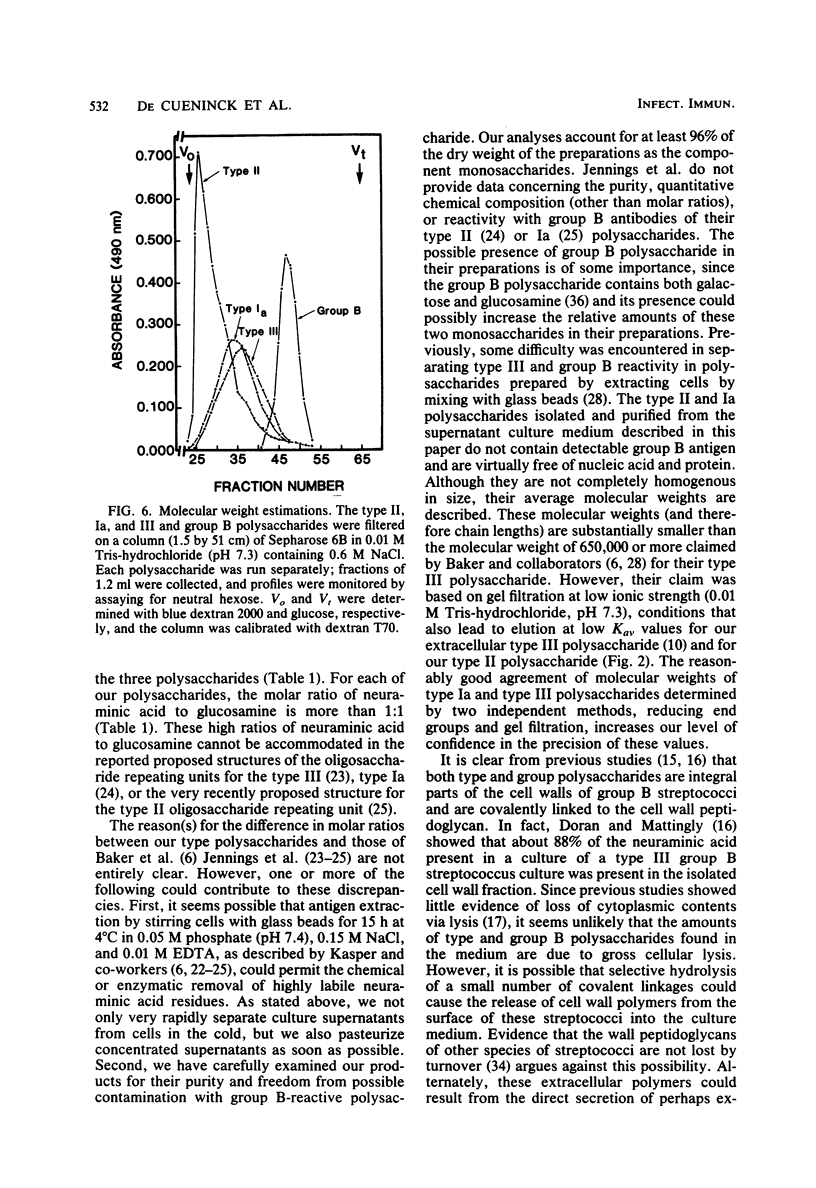
Polysaccharides carrying the type II- and type Ia-specific determinants of Lancefield group B streptococci were isolated and purified by anion-exchange chromatography and gel filtration from the supernatant culture medium after growth of strain 18RS21/67/1 (type II) and strain DS/1204/78 (type Ia), respectively. The average molecular weights of these polysaccharides were 97,000 (type II) and 94,000 (type Ia), as determined by reducing end group analyses. These molecular weights were in reasonably good agreement with molecular weights determined by gel filtration at high ionic strength on calibrated columns. The polysaccharides did not cross-react with antisera specific for the other type-specific determinants or with group B-specific antisera. Their content of galactose, glucose, glucosamine, and neuraminic acid (the last two calculated as N-acetyl derivatives) accounted for over 96% of their dry weight. The two polysaccharides differed from each other (and from type III polysaccharide) in their relative content of these monosaccharides. The molar ratios of galactose, glucose, and neuraminic acid to glucosamine were 3.3:2.3:1.35:1.0 for the type II polysaccharide and 2.0:0.8:1.4:1.0 for the type Ia polysaccharides. The results obtained indicate that these extracellular type II and Ia polysaccharides contain larger amounts of neuraminic acid than can be accounted for by previously proposed structures of their repeating units.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthony B. F. Immunity to the group B streptococci: interaction of serum and macrophages with types Ia, Ib, and Ic. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1186–1198. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Edwards M. S., Kasper D. L. Immunogenicity of polysaccharides from type III, group B Streptococcus. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):1107–1110. doi: 10.1172/JCI109011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Kasper D. L. Correlation of maternal antibody deficiency with susceptibility to neonatal group B streptococcal infection. N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 1;294(14):753–756. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197604012941404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Kasper D. L., Davis C. E. Immunochemical characterization of the "native" type III polysaccharide of group B Streptococcus. J Exp Med. 1976 Feb 1;143(2):258–270. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.2.258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Kasper D. L. Identification of sialic acid in polysaccharide antigens in group B Streptococcus. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):284–288. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.284-288.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Kasper D. L. Microcapsule of type III strains of group B Streptococcus: production and morphology. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):189–194. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.189-194.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Kasper D. L., Tager IRAB, Paredes A., Alpert S., McCormack W. M., Goroff D. Quantitative determination of antibody to capsular polysaccharide in infection with type III strains of group B Streptococcus. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):810–818. doi: 10.1172/JCI108703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore R. S., Kasper D. L., Baker C. J., Goroff D. K. Antigenic specificity of opsonophagocytic antibodies in rabbit anti-sera to group B streptococci. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):673–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore R. S., Kasper D. L., Vecchitto J. Mouse protection test for group B Streptococcus type III. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jul;140(1):81–88. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey R. B., Eisenstein T. K., Shockman G. D., Greber T. F., Swenson R. M. Soluble group- and type-specific antigens from type III group B Streptococcus. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):195–203. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.195-203.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clamp J. R., Bhatti T., Chambers R. E. The determination of carbohydrate in biological materials by gas-liquid chromatography. Methods Biochem Anal. 1971;19:229–344. doi: 10.1002/9780470110386.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleat P. H., Coid C. R. Protection of mice against group B Streptococcus type Ia by IgG components of a rabbit antiserum. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1980;169(1):9–14. doi: 10.1007/BF02123707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Cueninck B. J., Eisenstein T. K., McIntosh T. S., Shockman G. D., Swenson R. M. Type-specific protection of neonatal rats from lethal group B streptococcal infection by immune sera obtained from human volunteers vaccinated with type III-specific polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):961–965. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.961-965.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Cueninck B. J., Shockman G. D., Swenson R. M. Group B, type III streptococcal cell wall: composition and structural aspects revealed through endo-N-acetylmuramidase-catalyzed hydrolysis. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):572–581. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.572-581.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doran T. I., Mattingly S. J. Association of type- and group-specific antigens with the cell wall of serotype III group B streptococcus. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1115–1122. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1115-1122.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doran T. I., Straus D. C., Mattingly S. J. Factors influencing release of type III antigens by group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):615–623. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.615-623.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards M. S., Nicholson-Weller A., Baker C. J., Kasper D. L. The role of specific antibody in alternative complement pathway-mediated opsonophagocytosis of type III, group B Streptococcus. J Exp Med. 1980 May 1;151(5):1275–1287. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.5.1275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer G. W., Lowell G. H., Crumrine M. H., Bass J. W. Demonstration of opsonic activity and in vivo protection against group B streptococci type III by Streptococcus pneumoniae type 14 antisera. J Exp Med. 1978 Sep 1;148(3):776–786. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.3.776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freimer E. H. Type-specific polysaccharide antigens of group B streptococci. II. The chemical basis for serological specificity of the type II HCl antigen. J Exp Med. 1967 Mar 1;125(3):381–392. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemming V. G., Hall R. T., Rhodes P. G., Shigeoka A. O., Hill H. R. Assessment of group B streptococcal opsonins in human and rabbit serum by neutrophil chemiluminescence. J Clin Invest. 1976 Dec;58(6):1379–1387. doi: 10.1172/JCI108593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H. J., Lugowski C., Kasper D. L. Conformational aspects critical to the immunospecificity of the type III group B streptococcal polysaccharide. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 4;20(16):4511–4518. doi: 10.1021/bi00519a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H. J., Rosell K. G., Kasper D. L. Structural determination and serology of the native polysaccharide antigen of type-III group B Streptococcus. Can J Biochem. 1980 Feb;58(2):112–120. doi: 10.1139/o80-016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H. J., Rosell K. G., Kasper D. L. Structure and serology of the native polysaccharide antigen of type Ia group B streptococcus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2931–2935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H. J., Rosell K. G., Katzenellenbogen E., Kasper D. L. Structural determination of the capsular polysaccharide antigen of type II group B Streptococcus. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1793–1798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. A., Karakawa W. W. Multiple polysaccharide antigens of group B streptococcus, type Ia: emphasis on a sialic acid type-specific polysaccharide. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):2155–2160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper D. L., Baker C. J., Baltimore R. S., Crabb J. H., Schiffman G., Jennings H. J. Immunodeterminant specificity of human immunity to type III group B streptococcus. J Exp Med. 1979 Feb 1;149(2):327–339. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper D. L., Goroff D. K., Baker C. J. Immunochemical characterization of native polysaccharides from group B streptococcus: the relationship of the type III and group B determinants. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):1096–1105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruyssen F. J., de Boer W. R., Wouters J. T. Cell wall metabolism in Bacillus subtilis subsp. niger: effects of changes in phosphate supply to the culture. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):867–876. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.867-876.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancefield R. C., Freimer E. H. Type-specific polysaccharide antigens of group B streptococci. J Hyg (Lond) 1966 Jun;64(2):191–203. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400040456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancefield R. C., McCarty M., Everly W. N. Multiple mouse-protective antibodies directed against group B streptococci. Special reference to antibodies effective against protein antigens. J Exp Med. 1975 Jul 1;142(1):165–179. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan T. W., Mattingly S. J., Straus D. C. Purification and partial characterization of neuraminidase from type III group B streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):164–171. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.164-171.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mychajlonka M., McDowell T. D., Shockman G. D. Conservation of cell wall peptidoglycan by strains of Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):65–73. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.65-73.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK J. T., JOHNSON M. J. A submicrodetermination of glucose. J Biol Chem. 1949 Nov;181(1):149–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai J. Y., Gotschlich E. C., Lancefield R. C. Isolation of type-specific polysaccharide antigen from group B type Ib streptococci. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):58–66. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W. Immunochemistry of purified polysaccharide type antigens of group B streptococcal types Ia, Ib, and Ic. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):845–852. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.845-852.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer W., Kruyssen F. J., Wouters J. T. Cell wall metabolism in Bacillus subtilis subsp. niger: accumulation of wall polymers in the supernatant of chemostat cultures. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):877–884. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.877-884.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




