Abstract
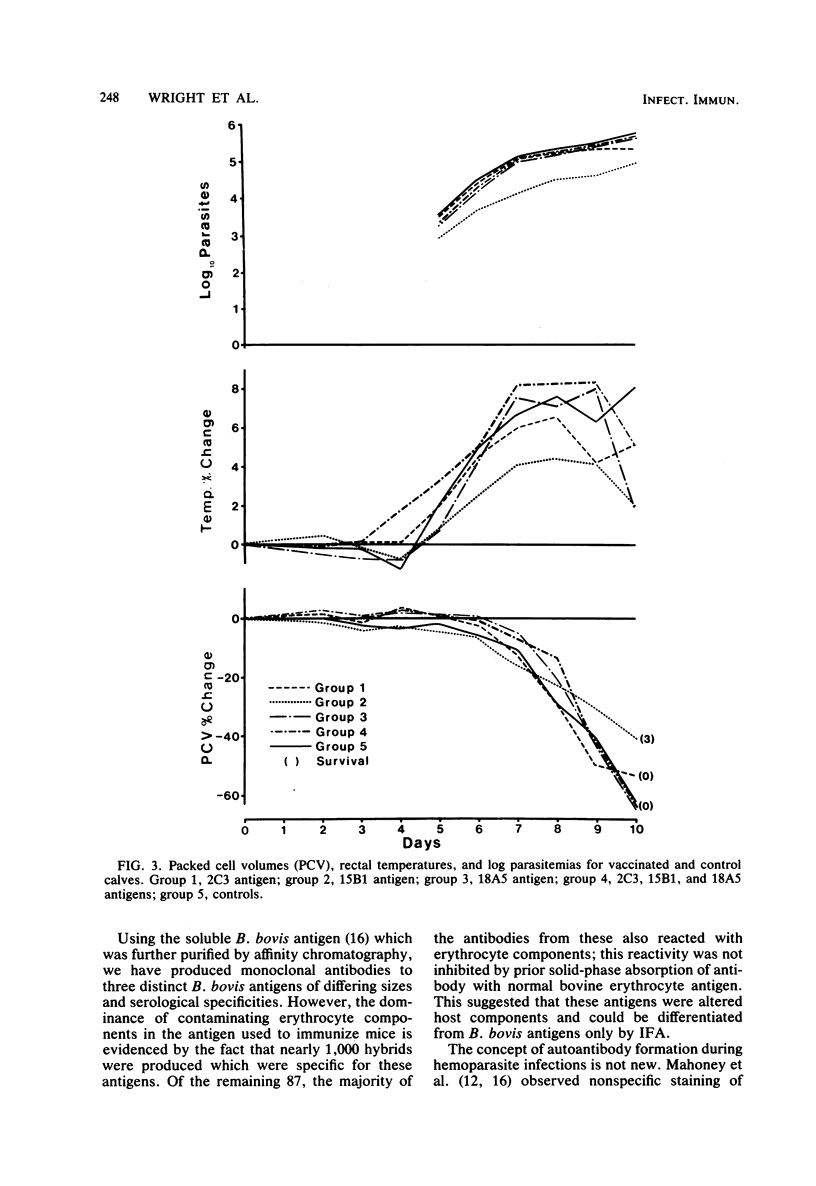
Three distinct monoclonal antibody-producing hybridomas have been produced against a partly purified protective fraction of Babesia bovis. All three stain the parasite or infected erythrocytes or both in precise and different manners when fluorescent-antibody techniques are used. The relevant antigens for each monoclonal antibody were isolated by immunoadsorption, their native molecular weights being 1.3 X 10(6), 180 X 10(3), and 44 X 10(3). Each antigen reacted in serological assays with homologous and heterologous bovine antisera to B. bovis. Susceptible splenectomized calves were immunized twice, 4 weeks apart, with the respective antigens and were challenged with virulent homologous organisms 2 weeks later. Strong protective immunity was induced by the antigen with a molecular weight of 44 X 10(3), but no significant protection was induced by either of the other two antigens.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bittle J. L., Houghten R. A., Alexander H., Shinnick T. M., Sutcliffe J. G., Lerner R. A., Rowlands D. J., Brown F. Protection against foot-and-mouth disease by immunization with a chemically synthesized peptide predicted from the viral nucleotide sequence. Nature. 1982 Jul 1;298(5869):30–33. doi: 10.1038/298030a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfre G., Howe S. C., Milstein C., Butcher G. W., Howard J. C. Antibodies to major histocompatibility antigens produced by hybrid cell lines. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):550–552. doi: 10.1038/266550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodger B. V. Babesia argentina: intraerythrocytic location of babesial antigen extracted from parasite suspensions. Int J Parasitol. 1973 May;3(3):387–391. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(73)90118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodger B. V. Babesia argentina: observations on the immunogenicity of the cryofibrinogen complex. Z Parasitenkd. 1977 Aug 25;53(1):47–52. doi: 10.1007/BF00383114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodger B. V., Wright I. G., Mahoney D. F. The use of pathophysiological reactions to assess the efficacy of the immune response to Babesia bovis in cattle. Z Parasitenkd. 1981;66(1):41–48. doi: 10.1007/BF00941944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOREJSI J., SMETANA R. The isolation of gamma globulin from blood-serum by rivanol. Acta Med Scand. 1956 Jun 30;155(1):65–70. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1956.tb14351.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Niday E., Gordon J. A dot-immunobinding assay for monoclonal and other antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90677-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder A. A., Freeman R. R. Immunization against blood-stage rodent malaria using purified parasite antigens. Nature. 1981 Nov 26;294(5839):361–364. doi: 10.1038/294361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney D. F. Bovine babesiosis: preparation and assessment of complement fixing antigens. Exp Parasitol. 1967 Apr;20(2):232–241. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(67)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney D. F., Wright I. G., Goodger B. V. Bovine babesiosis: the immunization of cattle with fractions of erythrocytes infected with Babesia bovis (syn B. argentina). Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1981 Apr;2(2):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(81)90046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney D. F., Wright I. G., Goodger B. V. Immunity in cattle to Babesia bovis after single infections with parasites of various origin. Aust Vet J. 1979 Jan;55(1):10–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1979.tb09535.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J. An enzymic method for the trace iodination of immunoglobulins and other proteins. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(2):299–305. doi: 10.1042/bj1130299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAAL J. R. GIEMSA STAIN FOR THE DIAGNOSIS OF BOVINE BABESIOSIS. II. CHANGES IN ERYTHROCYTES INFECTED WITH BABESIA BIGEMINA AND B. ARGENTINA. J Protozool. 1964 Nov;11:582–585. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1964.tb01802.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]