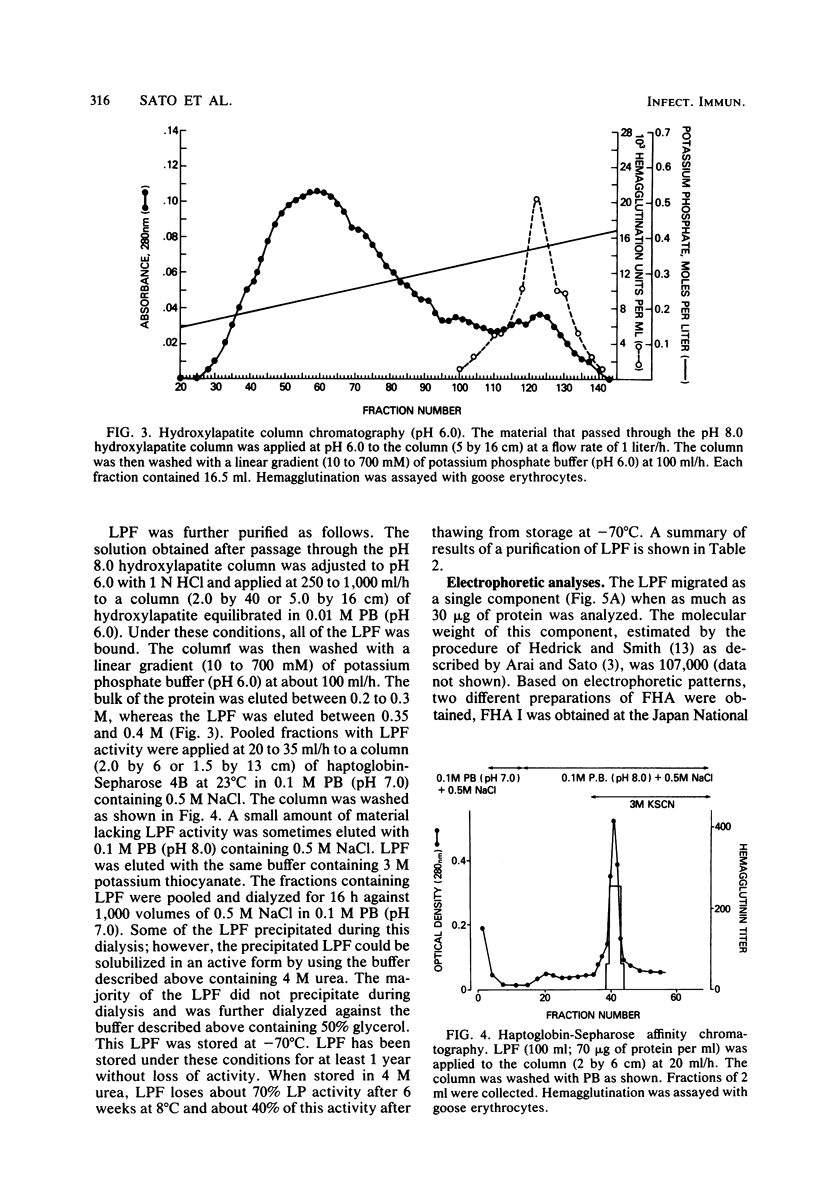
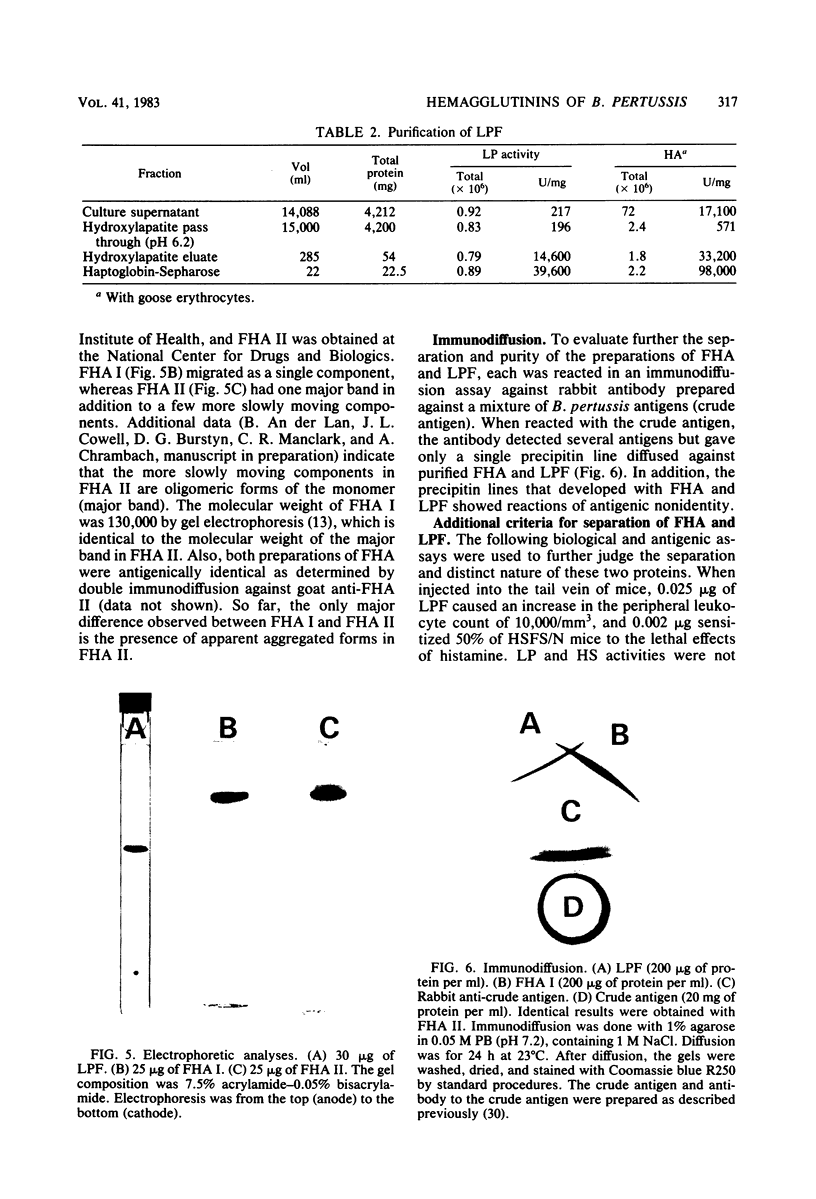
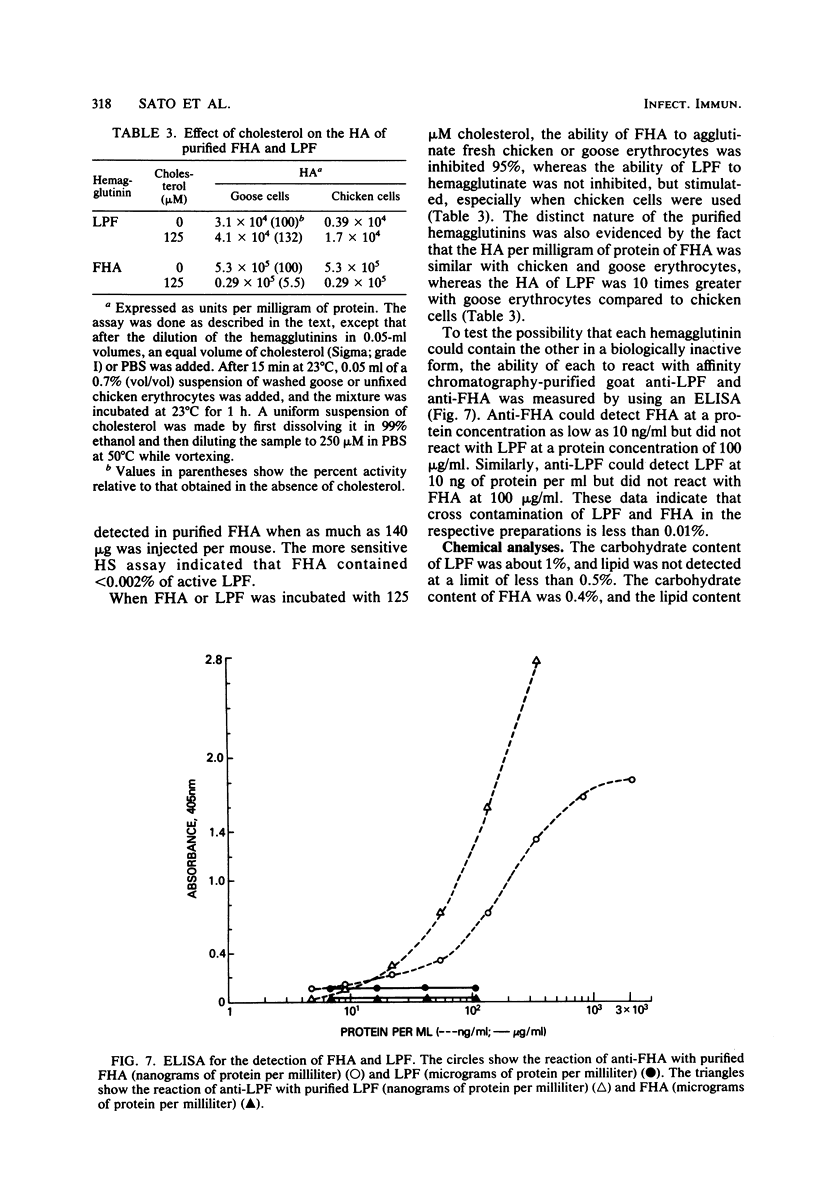
Abstract
The role of the filamentous hemagglutinin (FHA) and the lymphocytosis-promoting factor hemagglutinin (LPF) in pertussis pathogenesis and immunity is the subject of active investigation. To be certain of their role as protective antigens, the hemagglutinins must be pure and free of each other. This report describes procedures to separate and purify FHA and LPF from the culture supernatant of stationary cultures of Bordetella pertussis Tohama, using hydroxylapatite, haptoglobin-Sepharose, and Sepharose CL-6B filtration chromatography. Purified FHA contained less than 0.002% active LPF assayed by histamine-sensitizing activity, and both hemagglutinins contained less than 0.01% of each other based on antigenic activity measured by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, using affinity chromatography-purified antibody to each hemagglutinin. LPF and FHA were also shown to be antigenically distinct by immunodiffusion and were judged to be highly purified proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. In addition, the purification procedures yielded milligram amounts of each hemagglutinin with very good recovery of starting activities.
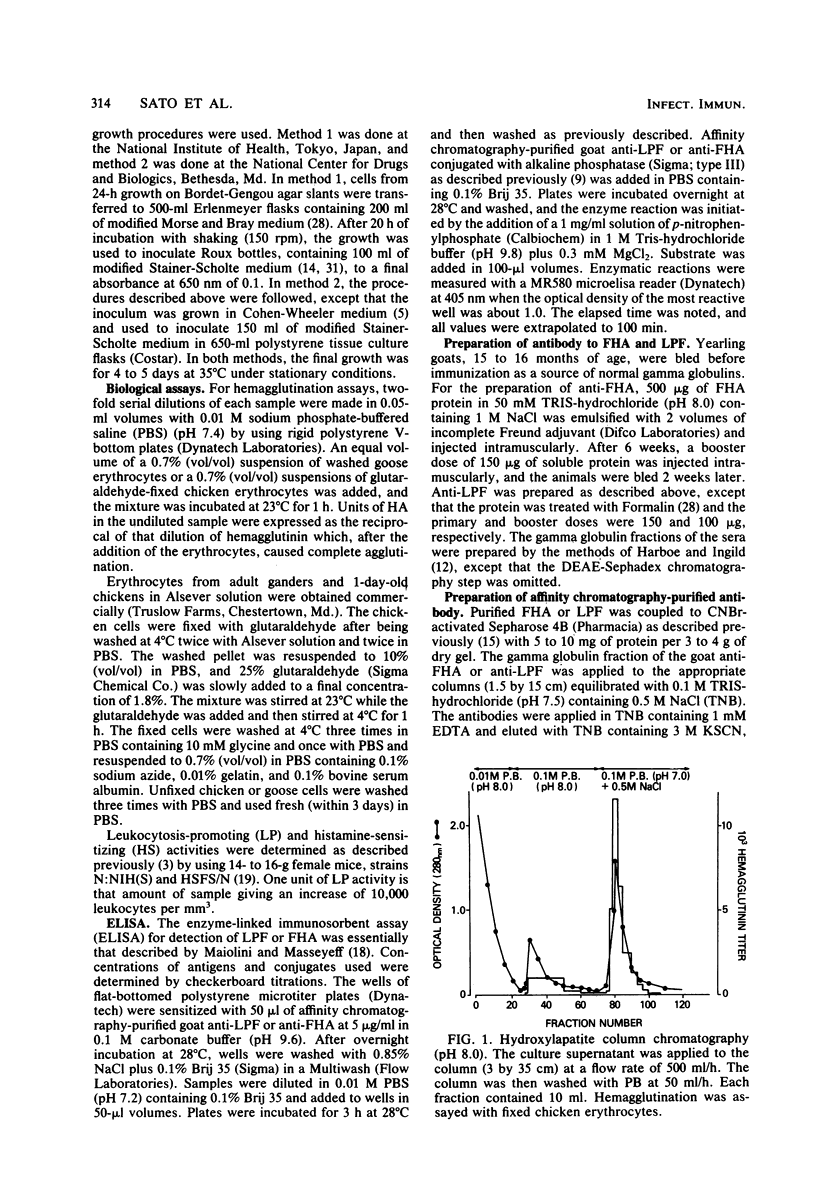
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai H., Munoz J. J. Crystallization of pertussigen from Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):495–499. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.495-499.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai H., Sato Y. Separation and characterization of two distinct hemagglutinins contained in purified leukocytosis-promoting factor from Bordetella pertussis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 22;444(3):765–782. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90323-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askelöf P., Gillenius P. Effect of lymphocytosis-promoting factor from Bordetella pertussis on cerebellar cyclic GMP levels. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):958–961. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.958-961.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONNELL G. E., SHAW R. W. The purification of haptoglobin. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1961 Jun;39:1013–1019. doi: 10.1139/o61-101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. M., Wheeler M. W. Pertussis Vaccine Prepared with Phase-I Cultures Grown in Fluid Medium. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1946 Apr;36(4):371–376. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick J. L., Smith A. J. Size and charge isomer separation and estimation of molecular weights of proteins by disc gel electrophoresis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jul;126(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90569-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett E., Wolff J. Soluble adenylate cyclase from the culture medium of Bordetella pertussis: purification and characterization. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):890–898. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.890-898.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irons L. I., MacLennan A. P. Isolation of the lymphocytosis promoting factor-haemagglutinin of Bordetella pertussis by affinity chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Sep 29;580(1):175–185. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maiolini R., Masseyeff R. A sandwich method of enzymoimmunoassay. I. Application to rat and human alpha-fetoprotein. J Immunol Methods. 1975 Sep;8(3):223–234. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(75)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manclark C. R., Hansen C. T., Treadwell P. E., Pittman M. Selective breeding to establish a standard mouse for pertussis vaccine bioassay. II. Bioresponses of mice susceptible and resistant to sensitization by pertussis vaccine HSF. J Biol Stand. 1975;3(4):353–363. doi: 10.1016/0092-1157(75)90060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. B., Weinstein D. B. Simple charring method for determination of lipids. J Lipid Res. 1966 Jul;7(4):574–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. I. Biologically active components and properties of Bordetella pertussis. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1976;20:9–26. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70106-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. I., Morse J. H. Isolation and properties of the leukocytosis- and lymphocytosis-promoting factor of Bordetella pertussis. J Exp Med. 1976 Jun 1;143(6):1483–1502. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.6.1483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz J. J., Arai H., Bergman R. K., Sadowski P. L. Biological activities of crystalline pertussigen from Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):820–826. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.820-826.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz J. J., Arai H., Cole R. L. Mouse-protecting and histamine-sensitizing activities of pertussigen and fimbrial hemagglutinin from Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):243–250. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.243-250.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Arai H., Suzuki K. Leukocytosis-promoting factor of Bordetella pertussis. 3. Its identity with protective antigen. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):801–810. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.801-810.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Izumiya K., Sato H., Cowell J. L., Manclark C. R. Role of antibody to leukocytosis-promoting factor hemagglutinin and to filamentous hemagglutinin in immunity to pertussis. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1223–1231. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1223-1231.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stainer D. W., Scholte M. J. A simple chemically defined medium for the production of phase I Bordetella pertussis. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Oct;63(2):211–220. doi: 10.1099/00221287-63-2-211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yajima M., Hosoda K., Kanbayashi Y., Nakamura T., Nogimori K., Mizushima Y., Nakase Y., Ui M. Islets-activating protein (IAP) in Bordetella pertussis that potentiates insulin secretory responses of rats. Purification and characterization. J Biochem. 1978 Jan;83(1):295–303. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yajima M., Hosoda K., Kanbayashi Y., Nakamura T., Takahashi I., Ui M. Biological properties of islets-activating protein (IAP) purified from the culture medium of Bordetella pertussis. J Biochem. 1978 Jan;83(1):305–312. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]