Abstract
Plasma cell differentiation is orchestrated by the transcriptional repressor B lymphocyte-induced maturation protein-1 (Blimp-1), which silences the gene expression program of mature B cells. The molecular mechanism underlying Blimp-1 suppression of mature B-cell gene expression is not fully understood. Here we report that a proline-rich domain in Blimp-1 directly interacts with LSD1, a histone lysine demethylase. Both LSD1 knockdown and expression of Blimp-1 lacking the proline-rich domain derepressed the activities of Blimp-1-dependent luciferase reporters. Disruption of the Blimp-1 interaction with LSD1 or reduced LSD1 expression attenuated antibody production, demonstrating the biological significance of this interaction. Finally, using chromatin immunoprecipitation, we showed that Blimp-1 binding to its target sites is accompanied by LSD1 binding to those same sites and that LSD1 binding correlates with histone modifications of accessible chromatin. These findings provide further insights into the molecular mechanism of the silencing of mature B-cell genes by Blimp-1 in plasma cell differentiation.
Nucleosomes contain the four canonical histones, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 (26). The covalent posttranslational modification of histones, including acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, ubiquitylation, sumoylation, and ADP ribosylation, generates the epigenetic information of chromatin called the histone code, which is crucial for regulating DNA transcription (5, 7, 10, 15, 43). By recruiting enzymatic regulatory complexes or altering chromatin architecture, the combined effects of several posttranslational modifications of histones on specific amino acid residues determine the outcome of transcription, either activating or suppressing gene expression (5, 7, 10, 15). For example, methylation of histone H3 on lysine residue 9 (K9) or K27 and methylation of histone H4 on K20 or K59 are associated with gene silencing, whereas methylation of histone H3 on K4 (H3K4) or H3K36 is linked to active gene transcription (20, 28, 44). Methylation of arginine residues of H3 or H4 is also linked to active transcription (50).
The processes of addition and removal of acetyl groups to histones by histone acetyltransferases and histone deacetylases (HDACs), respectively, and histone methylation are both dynamic and reversible (15). The histone methyltransferases, which often contain a common SET domain (17), add one to three methyl groups to lysine residues of histones; histone demethylases remove methyl groups (18). Lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1), a nuclear amine oxidase homolog, specifically demethylates mono- or dimethyl groups on H3K4 (41, 42). It is associated with gene repression through an interaction with corepressor for RE1 silencing transcription factor/neural restrictive silencing factor (CoREST) and HDAC1/2 in a multiprotein complex (42). LSD1 also interacts with androgen receptors and acts as a coactivator for transcriptional activation by removal of a dimethyl group from H3K9 (31).
B-lymphocyte-induced maturation protein-1 (Blimp-1) is a transcriptional repressor whose five-zinc-finger motif confers DNA binding activity (14). Blimp-1 plays crucial roles during development of the embryo and in the homeostasis/differentiation of adult tissues (3, 13, 29, 32, 39), including regulating cascades of gene expression during plasma cell differentiation (38, 39). Blimp-1 suppresses the mature B-cell gene expression program in order to drive the formation of antibody-secreting cells. Several genes, such as c-myc, Pax5, CIITA, Id3, and Spi-B, are directly regulated by Blimp-1 (22, 24, 33, 38). Deletion of the Blimp-1 gene, Prdm1, in mouse B cells results in failure of the formation of preplasma memory B cells and antibody-secreting plasma cells after immunization (39). Long-lived plasma cells in bone marrow and transformed plasma cells express high levels of Blimp-1 (12, 38), whose continued expression appears to maintain plasma cells, likely by ensuring plasma cell survival (21, 40).
Although Blimp-1 contains a SET domain-like region, there is no evidence that Blimp-1 exhibits endogenous methyltransferase activity (8). The mechanism underlying Blimp-1-mediated gene suppression, at least partially, includes interaction with several proteins, including HDAC1/2 (49), Groucho family proteins (34), and G9a histone methyltransferase (8). Blimp-1 also interacts with the histone arginine methyltransferase, Prmt-5, during germ cell development (1). Here we provide evidence showing that LSD1 is involved in the Blimp-1-dependent repression of the mature B-cell gene expression program. Our findings further reveal the mode of action of Blimp-1 in regulating plasma cell differentiation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cells and reagents.
NCI-H929 human multiple myeloma cells, SKW 6.4 human lymphoblastoid cells, 293T, and 3T3 cells were maintained as described previously (21, 38). Stable transfectants of WI-L2 cells, a human mature lymphoblastoid cell line, were maintained as described previously (38), and Blimp-1-ERD protein was induced by 5 μM CdCl2 and 3 μM 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-OHT). Mouse splenic B cells were purified with anti-B220 microbeads (Miltenyi Biotec) from 6- to 8-week-old C57BL/6 mice (purchased from BioLasco Taiwan Co.) and Prdm1f/fCD19Cre+/+ or Prdm1f/fCD19+/+ mice as described previously (39). Purified splenic B cells (purity of >95%) were cultured and stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (2.5 μg/ml; Sigma). Primary human CD19+ B cells were purified and differentiated by addition of interleukin 21 (IL-21) (100 ng/ml; Biosource) and anti-CD40 (1 μg/ml; R&D Systems) at a cell density of 1 × 106/ml as described previously (6). CdCl2 and 4-OHT were purchased from Sigma.
Plasmids.
Detailed information on plasmid constructions, including FLAG-tagged Blimp-1 and its various FLAG-tagged deletions (Δ1-518, Δ491-789, Δ317-789, and Δ317-424) expressed by the pCMV promoter, DBD-Blimp-1 (wild type or Δ317-424), pGC-Blimp-1-yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) or pGC-Δ317-424-YFP, hemagglutinin (HA)-LSD1, and its various deletions, HA-HDAC1, HA-HDAC2, and Myc-G9a, are available upon request. The protocol for generating small hairpin RNA (shRNA) for Blimp-1 silencing or the negative control was essentially as described previously (46). The human LSD1 shRNA contained the sense targeting sequence, 5′-GGGAGAACATACGATCCGTAA-3′. The negative-control shRNA (Ctrli) contained scrambled nucleotides, as described previously (21).
Transfection and luciferase reporter assay.
In general, we transfected 100 ng of luciferase reporter construct driven by CIITA promoter III (CIITA-Luc) (33), or 100 ng of thymidine kinase (tk) promoter harboring four Gal4 binding sites [(Gal4)4-tk-Luc; a gift from Hsiu-Ming Shih, Institute of Biomedical Sciences, Academia Sinica, Taipei, Taiwan] with various amounts [0.5 to 1 μg for CIITA-Luc or 1.5 μg for (Gal4)4-tk-Luc] of Blimp-1 expression vectors or the control vector, plus 4 ng of Renilla luciferase reporter driven by the tk promoter (RL-tk) into 293T cells, which were split into six-well plates at a density of 5 × 105 cells/well 1 day before transfection. The transfection procedure was performed by the polyethylenimine (PEI; Sigma) method. Briefly, DNA combined with PEI, at a concentration of 1 μg PEI/1 μg DNA in Opti-MEM, was added dropwise to the culture medium. After 4 h, an equal volume of culture medium was fed to the cells. After 48 h, cells were lysed and used for firefly luciferase and Renilla luciferase assays using the dual-luciferase reporter assay kit (Promega). The luminescence was measured by TopCount NXT. Repression was calculated by normalization of the firefly luciferase/Renilla luciferase ratios to the ratio obtained from empty vector control transfection.
Immunoprecipitation and immunoblot analysis.
293T cells were transfected with various amounts of expression plasmids (1 to 2 μg) by the PEI method as described above, or H929 cells were harvested and washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) twice. Nuclear extracts were prepared by lysing cells in buffer 1 (25 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.5], 25 mM KCl, 7.5 mM MgCl2, 30% sucrose, protease inhibitor cocktail [Sigma], 0.5% [wt/vol] NP-40), centrifuging them for 3 min at 3,000 × g, resuspending the nuclei in buffer 2 (20 mM HEPES [pH 7.9], 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM EGTA, 300 mM NaCl, protease inhibitor cocktail, 0.1% NP-40, 20% glycerol), and then centrifuging them for 15 min at 14,000 × g. Total lysates were prepared by lysing the cells in buffer 3 (20 mM HEPES [pH 7.9], 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM EGTA, 150 mM NaCl, protease inhibitor cocktail, 0.5% [wt/vol] NP-40). Precleared nuclear extracts or total extracts were immunoprecipitated by the indicated antibodies, followed by incubation with protein G or protein A beads (Santa Cruz Biotechnology). Precipitated protein complexes were eluted by boiling in Laemmli buffer, after they were washed four times in washing buffer (20 mM HEPES [pH 7.9], 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM EGTA, 150 mM NaCl, protease inhibitor cocktail, 0.1% [wt/vol] NP-40). The immunoblot analysis was performed essentially as described previously (23). The primary antibodies in this study are mouse anti-Blimp-1 antibody (1:500 dilution) (4), mouse anti-FLAG antibody (1: 2,000 dilution; Sigma), rabbit anti-HA antibody (1:1,000 dilution; Sigma), mouse anti-Myc antibody (1:1,000 dilution; LTK), rabbit anti-LSD1 antibody (1:1,000 dilution; Bethyl Laboratories), rabbit anti-HDAC2 (1:1,000 dilution; Santa Cruz), mouse anti-HDAC2 (1:1,000 dilution; Upstate Biotech), rabbit anti-PRMT5 (1:1,000 dilution; Upstate Biotech), goat anti-human μ heavy chain antibody (1:2,000 dilution; Bethyl Laboratories), and mouse anti-α-actin antibody (1:5,000 dilution; Sigma). Secondary antibodies used in this study are as described previously (21, 40). The immunoreactive proteins were detected by the enhanced chemiluminescence system (Amersham Biosciences) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Chemiluminescent signal images were captured using the Fujifilm LAS 3000 system.
Immunofluorescence staining.
H929 cells were washed with PBS twice and smeared on a glass slide and then subjected to fixation with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 min. Cells were permeabilized with ice-cold 0.1% (wt/vol) Triton X-100 for 5 min and then washed three times with PBS. After being blocked with 1% bovine serum albumin in PBS for 30 min, the cells were incubated with the primary antibodies: mouse antibody against HDAC2 (1:1,000 dilution; Upstate), mouse antibody against Blimp-1 (4), rabbit antibody against Blimp-1 (16), and rabbit anti-LSD1 (1:200 dilution; Bethyl Laboratories) in blocking buffer (1% bovine serum albumin in PBS) for 1 h. Cells were washed with PBS three times and incubated with the secondary antibodies anti-mouse IgG conjugated with Alexa Fluor 555 dye (Invitrogen) and anti-rabbit IgG conjugated with Alexa Fluor 488 dye (Invitrogen) along with Hoechst (Invitrogen) for 1 h. The entire staining procedure was done at room temperature. After three extensive washes with PBS, the slides were mounted with mounting buffer (Vector Laboratories) and the fluorescent images were examined with a confocal microscope (Leica SP2).
GST pull-down assay.
Glutathione S-transferase (GST)-Blimp-1, GST-Δ317-424, and GST-295-433 were generated by subcloning full-length Blimp-1, Δ317-424, and 295-433 cDNA, respectively, into pGEX-4T3 (Amersham Biosciences). His6-LSD1 was generated by subcloning full-length LSD1 into pRSET-b (Invitrogen). Recombinant GST fusion proteins were expressed in Escherichia coli strain BL21 and then purified with immobilized glutathione. Recombinant His6-LSD1 was purified by Ni-nitrilotriacetic acid (Ni-NTA) agarose by following the supplier-provided protocol (Novagen). Recombinant proteins for the GST pull-down assay were prepared essentially as described previously (25). GST agarose beads from the assay were washed three times with binding buffer (for full-length Blimp-1 and Δ317-424, 20 mM Tris [pH 7.4], 300 mM NaCl, 1% [wt/vol] NP-40, and protease inhibitor cocktails; for 295-433, 20 mM HEPES [pH 7.9], 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM EGTA, 150 mM NaCl, 0.1% [wt/vol] NP-40, and protease inhibitor cocktails), analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis using 10% gels, and then transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride membrane for immunoblot analysis. Anti-His antibody (1:1,000 dilution; Bioman) and anti-GST (1:2,500 dilution; Amersham Biosciences) were used for immunoblot analysis.
Generation of retroviral and lentiviral vectors and virus transduction.
We prepared retroviral and lentiviral vectors as described in references 38 and 21, respectively. Splenic B cells, H929, WI-L2 stable transfectants, primary human CD19+ B cells, and SKW cells were infected with virus at a multiplicity of infection of 2 to 20 in the presence of 5 μg/ml Polybrene. The percentage of cells expressing GFP in transduced populations reached over 95%, as determined by a fluorescence-activated cell sorter, after 3 days of infection in H929 cells, WI-L2 stable transfectants, and SKW cells. Virus was added to primary cell cultures that were stimulated for 12 h; the transduced YFP+ mouse splenic B cells or GFP+ primary human B cells were sorted at day 3 and day 6 of infection, respectively, for further analysis.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and ELISPOT assay.
SKW supernatants were harvested for enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to determine the amount of IgM as described previously (23). Enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT) analysis for detecting IgM-secreting mouse splenic YFP+ B cells or for detecting IgG-secreting human GFP+ B cells was performed by essentially following a previously reported procedure (6, 22). Photomicrographs of the spots were enumerated and analyzed by the AID ELISPOT reader system (AID Autoimmun Diagnostika GmbH).
Flow cytometry.
B cells were harvested and washed in PBS once and then further suspended in PBS plus 2% fetal bovine serum at a density of 106 cells/ml. A total of 105 cells were used for each staining. Antibodies used in this study were phycoerythrin-conjugated anti-mouse CD138/syndecan-1 (clone 281-2) (BD PharMingen), allophycocyanin-conjugated anti-mouse CD45R/B220 (clone RA3-6B2), phycoerythrin-conjugated anti-human IgD (clone IA6-2), and allophycocyanin-conjugated anti-human CD38 (clone HB7). Cells were then analyzed by FACSCanto (Becton Dickinson) and FCS Express 3.0 software.
ChIP assay.
The chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays for detection of histone modifications were performed essentially according to the Upstate Biotechnology protocol and to a described procedure (22). Briefly, 2.5 × 106 H929 or WI-L2 cells were used per histone modification ChIP assay. Antibodies for detection of histone modifications were purchased from Upstate Biotechnology (anti-H3Ac, anti-H3K4me2, and anti-H3K9me2) and Abcam (anti-H3K4me1 and anti-H3K4me3). The immunoprecipitated DNA was quantified by quantitative PCR (QPCR) with the SYBR green method on an ABI Prism 7300 system (Applied Biosystems). The ChIP assays were performed as described previously for detection of Blimp-1 binding (27) and LSD1 and FLAG-Blimp-1 binding in vivo (41). The anti-Blimp-1 sera were described in reference 16. A total of 1 × 107 H929 or WI-L2 cells were used per LSD1, FLAG, or Blimp-1 ChIP assay. Immunoprecipitated chromatin samples were quantified by QPCR using primers that specifically amplified fragments encompassing the Blimp-1 binding site or within 100 bp of the Blimp-1 binding site at each individual gene locus. Values obtained from immunoprecipitated samples were normalized to that of their corresponding input samples. For histone modifications, the ratio was further normalized to the IP/input ratio of the GAPDH promoter. The primer sequences for the ChIP assay were as follows: SPI-B forward, 5′-GTGCGTGAATGTCCCTTTG-3′, reverse, 5′-AAGCCCGGAGAAGACTCAGAT-3′; SPI-B exon 5 forward, 5′-TGGTTCCCCCGGCATAT-3, reverse, 5′-AGGGCAGGGCTGTCCAA-3′; PAX-5 forward, 5′-CCACAGCCACATTTCCGATT-3′, reverse, 5′-CGGCAACTGGACATCACATATC-3′; PAX5 exon 6 forward, 5′-GACTTCCTCCGGAAGCAGATG-3′, reverse, 5′-TGAGTAGTGCTGCCTCTCAAACA-3′; CIITA forward, 5′-GCCACCTTGCAGGGAGAGT-3′, reverse, 5′-AAGCTAAGCCAACATGCAAAGAA-3′; CIITA 3′UTR forward, 5′-CCATCATGTCTGGCTAATTTTTCA-3′, reverse, 5′-GGATCACCTGAGGTCAAGAGTTTG-3′; GAPDH forward, 5′-GGGCTCCGGCTCCAATT-3′, reverse, 5′-ACCCTTACACGCTTGGATGAA-3′; and α-satellite forward, 5′-GGACATTTGGAGCGCTTTCA-3′, reverse, 5′-TCTGCCTAGTTGTTATTGGGAAGA-3′.
RNA isolation and RT-QPCR analysis.
Total RNA isolation, cDNA synthesis, and subsequent reverse transcription (RT)-QPCR analysis in an ABI Prism 7300 sequence detection system were performed according to published protocols (23). Total RNA was isolated on an RNeasy spin column (Qiagen), and total RNA (250 ng) was used for cDNA synthesis with a high-capacity cDNA reverse transcriptase kit (ABI) used according to the manufacturer's instructions. RT-QPCR analysis of the cDNA was carried out using the following TaqMan primer sets or primers for the SYBR green method. The primer sequences used were the following: LSD1 forward, 5′-GTGCAGTACCTCAGCCCAAAG-3′, reverse, 5′-CCGAGCCCAGGGATCAG-3′; PRDM1(Blimp-1) forward, 5′-CGAAATGCCCTTCTACCCTG-3′, reverse, 5′-GCGTTCAAGTAAGCGTAGGAGT-3′; SPI-B forward, 5′-GGCCACACTTCAGCTGTCTGTA-3′, reverse, 5′-AGGAGCCCCCTCTGAATCAG-3′; PAX5 forward, 5′-GACTTCCTCCGGAAGCAGATG-3′, reverse, 5′-TGAGTAGTGCTGCCTCTCAAACA-3′; CIITA forward, 5′-CCAGGGAGGCTTATGCCAAT-3′, reverse, 5′-GCTGGGAGTCCTGGAAGACA-3′; and GAPDH forward, 5′-CGGGAAACTGTGGCGTGATG-3′, reverse, 5′-TGGAGGAGTGGGTGTCGCTGTT-3′.
RESULTS
The proline-rich domain in Blimp-1 is essential for Blimp-1-dependent gene repression and plasma cell differentiation.
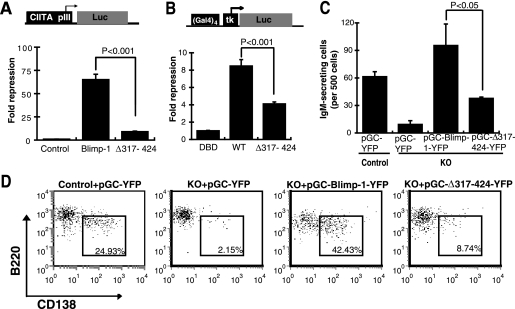
The proline-rich domain of Blimp-1 has been implicated as a repression domain (34). However, a more recent microarray study showed the discrepant result that the Blimp-1 proline-rich domain is dispensable for gene regulation and immunoglobulin production in a murine mature B lymphoma line (37). We first verified whether the proline-rich domain is required for Blimp-1-mediated gene repression and function. We found that Blimp-1 lacking the proline-rich domain (Δ317-424) was less able to transcriptionally repress CIITA promoter III activity (Fig. 1A). Likewise, in a Gal4 fusion protein assay, the repression of the activity of a tk promoter containing four Gal4 binding sites, (Gal4)4-tk, by a Gal4 DNA-binding domain/full-length Blimp-1 fusion protein was attenuated by deletion of the Blimp-1 proline-rich domain (Fig. 1B). Furthermore, the lack of IgM secretion and plasma cell surface marker CD138 induction in Prdm1-deficient B cells stimulated with LPS (39) could be restored by reintroduction of full-length Blimp-1, but not by Δ317-424 (Fig. 1C and D), convincingly showing the biological significance of the Blimp-1 proline-rich domain.
FIG. 1.
The proline-rich domain is required for Blimp-1-mediated gene repression and function. (A) Plasmids encoding full-length Blimp-1, proline-rich-domain-deleted Blimp-1 (Δ317-424), or empty vector alone (Control) together with a firefly luciferase reporter driven by CIITA promoter III (CIITA pIII-Luc) and a Renilla luciferase reporter plasmid (RL-tk) were cotransfected into 293T cells for 2 days and then measured for luciferase activity. (B) Plasmids encoding a full-length Blimp-1/Gal4 DNA binding domain (DBD), fusion protein (WT), proline-rich-domain-deleted Blimp-1/Gal4 DBD fusion protein (Δ317-424), or Gal4 DBD alone (DBD), together with (Gal4)4-tk-Luc and RL-tk, were transfected into 293T cells. Two days later, cell lysates were harvested for a luciferase activity assay. (A and B) Results are means ± standard deviations from three experiments. (C and D) Purified splenic Prdm1f/fCD19Cre+/+ (KO) and Prdm1f/fCD19+/+ (Control) B cells stimulated with LPS overnight were transduced with the indicated retroviral vectors. (C) ELISPOT results of the number of IgM-secreting cells from sorted YFP+ cells. (D) Flow cytometric analysis of surface expression of CD138 and B220 on YFP+ cells at day 3 of culture. Values shown indicate the percentages of B220lowCD138+ plasma cells. (C and D) Results are data from one representative experiment of three independent experiments.
LSD1 interacts with the Blimp-1 proline-rich domain and is required for Blimp-1-dependent gene suppression.
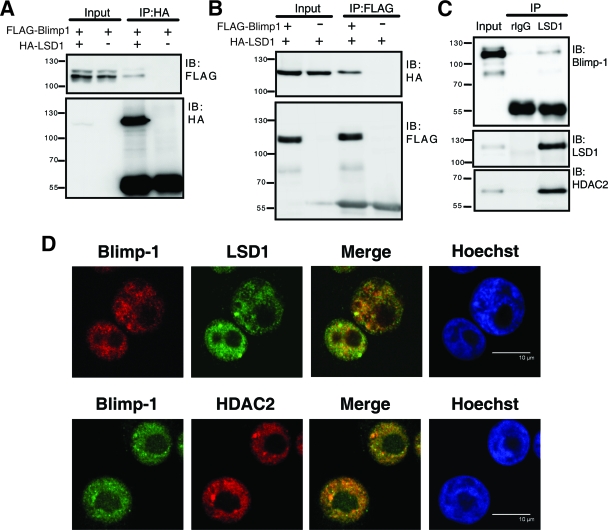
The proline-rich domain of Blimp-1 interacts with HDAC1/2 (49). Because LSD1 was initially purified in a multiprotein complex with HDAC1/2 (42), we asked whether LSD1 also interacts with Blimp-1. Indeed, when 293T cells were transfected with FLAG-Blimp-1 and HA-LSD1 expression vectors, Blimp-1 was coimmunoprecipitated from the lysates by an antibody against the HA epitope (Fig. 2A). Likewise, HA-LSD1 was coimmunoprecipitated by anti-FLAG (Fig. 2B). Endogenous Blimp-1 interacts with LSD1, as shown by the fact that endogenous Blimp-1 was present in the anti-LSD1 immunoprecipitate, but not in the isotype control antibody immunoprecipitate, from nuclear extracts of H929 cells, a human plasma cell line (Fig. 2C). As a positive control, HDAC2 was coimmunoprecipitated by anti-LSD1 in the same immunoprecipitates (Fig. 2C). Immunofluorescence staining further demonstrated that a portion of Blimp-1 colocalized with LSD1 in the nucleus of H929 cells (Fig. 2D). Consistent with their known interaction (49), Blimp-1 also colocalized with HDAC2 in the nucleus of H929 cells (Fig. 2D).
FIG. 2.
Blimp-1 interacts with LSD1. (A and B) FLAG-tagged Blimp-1 expression vector was cotransfected with an HA-tagged LSD1 expression vector or empty vector into 293T cells for 2 days. Immunoblot (IB) analysis was performed with the indicated antibodies on either lysate (Input), anti-HA immunoprecipitates (IP) (A), or anti-FLAG IP (B). (C) Immunoblot (IB) analysis was performed with the indicated antibodies on either H929 nuclear extract (Input) or IP with the LSD1 antibody or an isotype rabbit IgG (rIgG). Protein molecular weight markers (in thousands) are indicated to the left of each blot. (D) Immunofluorescence images of H929 cells stained with antibodies against Blimp-1, LSD1, and HDAC2. Nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst. Scale bar, 10 μm.
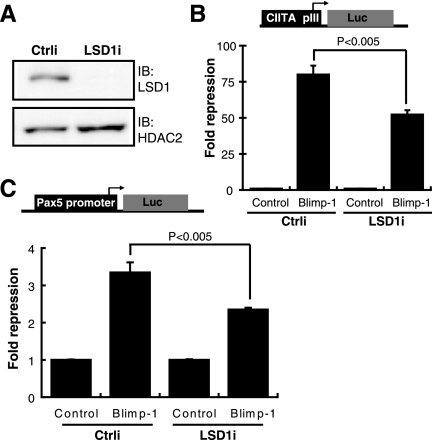
To demonstrate the molecular relevance of LSD1 in Blimp-1-dependent gene suppression, we depleted LSD1 by shRNA delivered by a lentiviral vector, LSD1i (Fig. 3A). LSD1 depletion significantly reduced Blimp-1-dependent repression of the reporter CIITA promoter III (Fig. 3B). Similar results were observed in Blimp-1-dependent repression of the activities of the Pax5 promoter (Fig. 3C). These data indicate that Blimp-1-dependent gene repression requires LSD1.
FIG. 3.
Blimp-1-dependent gene suppression partly relies on LSD1. (A) Immunoblot showing that LSD1 is depleted after transduction by a lentiviral vector containing LSD1 shRNA (LSD1i) in 293T cells cotransfected with LSD1 and HDAC2 expression vectors. HDAC2 is a transfection control. (B) 293T cells were transduced with either LSD1i or a negative Ctrli together with plasmids encoding Blimp-1 or an empty vector (Control), CIITA pIII-Luc and RL-tk and then luciferase activity was measured after 3 days. (C) 293T cells were transduced with either LSD1i or Ctrli together with plasmids encoding Blimp-1 or an empty vector (Control), Pax5 p-Luc (22), and RL-tk, and then luciferase activity was measured after 3 days. Results are means ± standard deviations from three experiments.
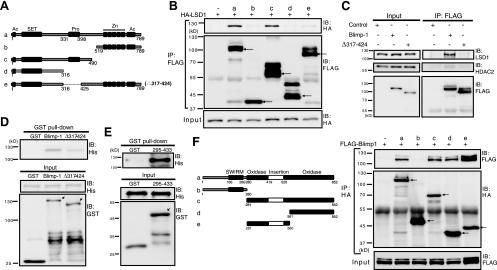
We next investigated whether the proline-rich domain of Blimp-1 is the region that interacts with LSD1. Indeed, Blimp-1 constructs lacking the proline-rich domain (Fig. 4A, rows b, d, and e) failed to interact with LSD1 in cell lysates of 293T cells transfected with HA-LSD1 (Fig. 4B). Moreover, endogenous LSD1 coimmunoprecipitated with exogenously expressed full-length Blimp-1, but not exogenously expressed Δ317-424, in 293T transfectants (Fig. 4C), confirming the requirement for the proline-rich domain. Notably, we also found that Blimp-1 and LSD1 interact directly, as shown by a GST pulldown assay. Bacterially expressed His6-LSD1 was pulled down by glutathione-agarose when incubated with bacterially expressed GST-Blimp-1 (Fig. 4D). As anticipated, the direct interaction depended on the proline-rich domain, as the amount of His6-LSD1 pulled down by GST-Δ317-424 was much lower in comparison (Fig. 4D). In addition, the GST-Blimp-1 proline-rich domain fusion protein, GST-295-433, was sufficient to interact with His6-LSD1 (Fig. 4E). We also mapped the region in LSD1 for Blimp-1 interaction. LSD1 essentially comprises a SWIRM domain, insertion tower domain, and oxidase domain (45) (Fig. 4F), and we found that the oxidase domain and tower domain appear to be important for interaction with Blimp-1 (Fig. 4F).
FIG. 4.
The Blimp-1 proline-rich domain is essential for interaction with LSD1. (A) Linear domain structure maps of full-length Blimp-1 (a) and various Blimp-1 deletion mutants (b to e). Known motifs: Ac, acidic domain; SET, PR domain resembling SET domain; Pro, proline-rich domain; Zn, five-zinc-finger motifs. (B) Blimp-1 or various mutated Blimp-1 expression constructs or empty vector (−) was cotransfected with expression vector HA-LSD1 into 293T cells for 2 days. Cell lysates were then harvested for immunoprecipitation (IP) and then immunoblot (IB) analysis. Arrows indicate Blimp-1 proteins. (C) Expression vectors encoding FLAG-tagged Blimp-1 or FLAG-tagged Δ317-424 or empty vector (Control) was transfected into 293T cells. Cells were harvested 2 days later, and the input and IP samples that were immunoprecipitated by anti-FLAG were analyzed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies. (D) Pull-down assay for GST-Blimp-1, GST-Δ317-424, or GST alone with His6-LSD1. (E) Pull-down assay for GST-295-433 or GST alone with His6-LSD1. Arrows indicate fusion proteins. (F) The oxidase domain containing the insertion tower domain in LSD1 is required for Blimp-1 interaction. Linear domain structures of LSD1 and its deletion mutants are illustrated at the left. Expression vectors encoding Blimp-1, LSD1, or various LSD1 mutants were cotransfected into 293T cells. Cell lysates were harvested after 2 days and subjected to co-IP. Arrows indicate LSD1 proteins. Molecular mass markers are indicated to the left of each blot.
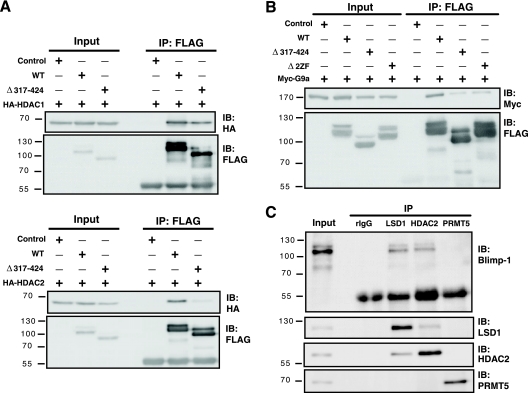
Blimp-1 interacts with HDAC1/2, G9a, and Prmt5 (1, 8, 49). We sought to delineate the interplay among these Blimp-1-interacting proteins. Two mouse Blimp-1 regions are required for association with HDAC2: one located within residues 557 to 715 and the other located within the proline-rich domain (49). The first two zinc fingers (2ZF) are crucial for Blimp-1 interaction with G9a (8). We found that the Blimp-1 construct Δ317-424 (lacking the proline-rich region) could interact with HDAC1 (Fig. 5A, top) but failed to interact with HDAC2 (Fig. 5A, bottom). Unexpectedly, both the mutant lacking the first two zinc fingers, Δ2ZF, and the mutant Δ317-424 interacted poorly with G9a (Fig. 5B), suggesting that the proline-rich domain also helps mediate the G9a interaction. Thus, the proline-rich domain is essential for Blimp-1 repression due to its ability to interact with HDAC2, G9a, and LSD1. However, in H929 cells, Blimp-1 failed to interact with endogenous PRMT5, although it associated with endogenous LSD1 and HDAC2 (Fig. 5C).
FIG. 5.
The proline-rich domain in Blimp-1 associates with multiple chromatin modifiers. (A) 293T cells were cotransfected with FLAG-tagged Blimp-1 expression vector, FLAG-tagged Δ317-424 expression vector, or empty vector along with HA-tagged HDAC1 (top) or HA-tagged HDAC2 (bottom) expression vectors. Immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-FLAG was performed 2 days later, and then immunoblotting (IB) was performed with the indicated antibodies. (B) 293T cells were cotransfected with a vector expressing FLAG-tagged Blimp-1, FLAG-tagged Δ317-424, or FLAG-tagged Blimp-1 lacking the first two zinc fingers (Δ2ZF) or empty vector along with a Myc-tagged G9a expression vector. Two days later, immunoprecipitation was performed using anti-FLAG antibodies, and then immunoblotting was performed. (C) Nuclear extracts from H929 cells were subjected to immunoprecipitation with the indicated antibodies and then immunoblotting was performed using the indicated antibodies. Molecular weight markers (in thousands) are indicated to the left of each blot.
LSD1 binds to Blimp-1 target genes in vivo and is involved in suppression of endogenous Blimp-1 target genes.
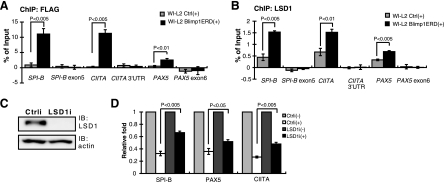
We next asked if LSD1 binds to Blimp-1 target sites in vivo and if this binding is important for suppression and for histone modification of Blimp-1 targets. We previously used stable WI-L2 transfectants expressing a FLAG-Blimp-1-ERD (estrogen ligand binding domain) fusion protein under the control of the heavy metal-inducible metallothionein promoter to show the direct binding of Blimp-1 to endogenous targets upon induction by CdCl2 and 4-OHT (38). Here, we used this system along with a ChIP assay to assess whether LSD1 associates Blimp-1 DNA binding sites upon Blimp-1 induction. Figure 6A shows that, after induction, Blimp-1 bound to endogenous CIITA, PAX5, and SPI-B promoter sites but not to the 3′ untranslated region or exonic regions of these genes. LSD1 exhibited low-level binding to the promoter sites but not to the 3′ untranslated region or exonic regions of these genes at steady-state, although the biological relevance of this binding is unclear (Fig. 6B). However, upon Blimp-1 induction, LSD1 bound significantly stronger to the CIITA, PAX5, and SPI-B promoter loci (Fig. 6B), suggesting that Blimp-1 recruits or stabilizes LSD1 binding to mature B-cell gene targets. We depleted endogenous LSD1 by LSD1i (Fig. 6C) and examined the effect on Blimp-1-mediated target gene repression. Blimp-1 induction led to suppression of SPI-B, PAX5, and CIITA mRNA levels; interestingly, the mRNA levels of these genes were derepressed when LSD1 was depleted (Fig. 6D), consistent with the notion that LSD1 is involved in Blimp-1-dependent gene repression.
FIG. 6.
LSD1 binding to Blimp-1 target genes in vivo upon induction of Blimp-1. (A and B) Chromatin samples prepared from WI-L2 Blimp1ERD cells or WI-L2 ERD cells (WI-L2 Ctrl) induced by CdCl2 (5 μM) and 4-OHT (3 μM) for 10 h were immunoprecipitated with either anti-FLAG (A) or anti-LSD1 (B) for subsequent ChIP analysis. Regions encompassing or adjacent to Blimp-1 binding sites in the indicated gene loci were amplified by QPCR. A region located in each gene's 3′ untranslated region (UTR) or exonic region was amplified as a negative-control site. Input DNA amplified by QPCR was used to normalize data for the individual gene sites. Results are means ± standard errors of the mean from four independent experiments. (C) Immunoblot analysis showing the efficient knockdown of endogenous LSD1 in Blimp-1-ERD WI-L2 cells. (D) WI-L2 Blimp1ERD cells were either transduced with Ctrli or LSD1i for 5 days, and then CdCl2 and 4-OHT (+) were added or the cells were left untreated (−). After 48 h, cells were prepared for RT-QPCR analysis. Transcript levels of each indicated gene from untreated Ctrli or untreated LSD1i cells were set as 1 for normalization. Results are means ± standard deviations from three independent experiments.
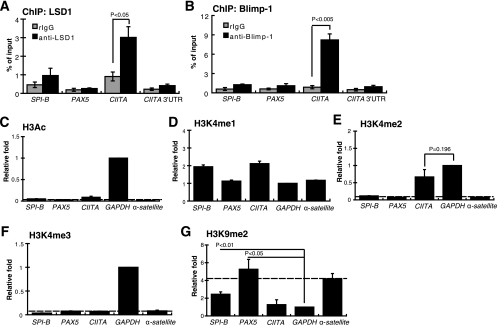
Because Blimp-1 is not only induced during plasma cell differentiation but also continuously expressed in plasma cells, we next investigated whether LSD1 binds to Blimp-1 target gene loci in a plasma cell line, H929, by ChIP assay using an LSD1-specific antibody. Except for the CIITA site, LSD1 did not bind to Blimp-1 target sites, like SPI-B and PAX5 sites, in H929 cells (Fig. 7A), consistent with the result that Blimp-1 binds only to the CIITA site in H929 cells (Fig. 7B). The relationship between the binding of LSD1 and the local chromatin architecture in Blimp-1 target sites in H929 cells was examined by ChIP assay using antibodies against acetylated histone H3 (H3Ac); mono-, di-, and trimethylated K4 on histone H3 (H3K4me1, H3K4me2, and H3K4me3, respectively); or dimethylated K9 on histone H3 (H3K9me2). The α-satellite locus and GAPDH locus were used as controls for heterochromatin and active chromatin, respectively. Figure 7C shows that, in H929 cells, Blimp-1 target sites and the α-satellite locus showed significantly lower H3Ac levels than the GAPDH locus. However, there was no good correlation of H3K4me1 levels between active gene loci, such as the GAPDH locus and inactive gene loci, such as PAX5 and SPI-B in H929 cells (Fig. 7D). Like the α-satellite locus, the PAX5 and SPI-B sites had dramatically lower H3K4me2 levels than the GAPDH locus, whereas at the CIITA promoter III locus, H3K4me2 levels were comparable to that of the GAPDH locus (Fig. 7E). With regard to H3K4me3 modification, only the GAPDH locus was decorated by H3K4me3, whereas the other gene loci were negative for this modification (Fig. 7F). Finally, the H3K9me2 levels at the PAX5 and SPI-B sites, like the α-satellite locus, were much higher than that of the GAPDH locus (Fig. 7G). Because methylation of H3K9 is the hallmark of heterochromatin (2), this result suggests that PAX5 and SPI-B are located within heterochromatin in plasma cells.
FIG. 7.
Context of histone modifications and LSD1 binding in Blimp-1 target loci in H929 cells. (A and B) Chromatin prepared from H929 plasma cells was subjected to ChIP analysis using an antibody specific to LSD1 (A) or to Blimp-1 (B) or an isotype control rabbit IgG (rIgG). Input DNA was used for normalization. (C to G) ChIP analyses using antibodies against H3Ac (C), H3K4me1 (D), H3K4me2 (E), H3K4me3 (F), or H3K9me2 (G) of chromatin prepared from H929 plasma cells at the indicated gene loci. For each gene locus (C to G), QPCR values obtained from immunoprecipitated samples were normalized to input samples and then were further normalized to the GAPDH locus IP/input ratio, which was set as 1. All data are means ± standard errors of means from three independent experiments.
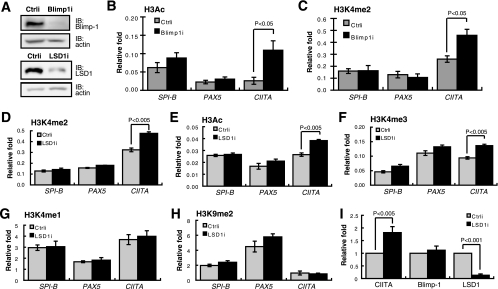
The correlation between LSD1 binding and higher H3K4me2 levels at the CIITA site prompted us to ask whether altering LSD1 binding leads to changes in histone modification—because the local chromatin environment could still be accessible. Thus, to examine potential changes in histone modifications, endogenous Blimp-1 or endogenous LSD1 was depleted in H929 cells (Fig. 8A). Blimp-1 knockdown resulted in increased H3Ac and H3K4me2 levels at the CIITA site (Fig. 8B and C) but did not change these two modifications at the PAX5 and SPI-B sites (Fig. 8B and C), supporting our hypothesis that LSD1 binding is associated with gene loci whose histone marks are still accessible to chromatin-modifying enzymes. Likewise, the H3K4me2 level at the CIITA site was increased by knockdown of LSD1 in H929 cells (Fig. 8D). As anticipated, the H3Ac and H3K4me3 levels increased upon LSD1 knockdown (Fig. 8E and F), which is consistent with previous results showing that the functions of LSD1 and HDAC are linked (19) and that depletion of LSD1 results in increased H3K4me3 in growth factor independence (Gfi)-1b targets in erythroleukemia MEL cells (36). However, LSD1 depletion did not change the levels of H3K4me1 (Fig. 8G) or H3K9me2 (Fig. 8H) at the CIITA site. In support of our hypothesis of the formation of heterochromatin in PAX5 and SPI-B loci, all the histone modifications in these two gene loci were insensitive to LSD1 depletion in H929 cells (Fig. 8D to H). Of note, changes in the above-mentioned histone modifications by LSD1 knockdown in H929 cells were associated with derepression of endogenous CIITA mRNA levels (Fig. 8I).
FIG. 8.
Accessible changes in H3Ac and H3K4me2 chromatin modifications in the CIITA locus upon depletion of Blimp-1 or LSD1. (A) Immunoblot analysis showing efficient depletion of Blimp-1 and LSD1 by Blimp-1i or LSD1i, respectively. (B and C) H929 cells, transduced with Ctrli or Blimp-1 shRNA (Blimp1i) for 3 days, were subjected to ChIP analysis using an antibody against H3Ac (B) or H3K4me2 (C). Immunoprecipitated genomic DNA was subjected to QPCR analysis of the histone modification in each indicated gene locus. (D to H) H929 cells were transduced with Ctrli or LSD1i for 2 days and then subjected to ChIP analysis using anti-H3K4me2 (D), anti-H3Ac (E), anti-H3K4me3 (F), anti-H3K4me1 (G), or anti-H3K9me2 (H). For each gene locus (B to H), the relative increase was calculated as described in the legend for Figure 7. (I) Derepression of CIITA mRNA by depletion of LSD1 in H929 cells. H929 cells were transduced with Ctrli or LSD1i for 2 days and then subjected to RT-QPCR analysis to determine the level of the indicated transcripts. All data are means ± standard errors of the means from three independent experiments.
LSD1 is required for the formation of antibody-secreting cells.
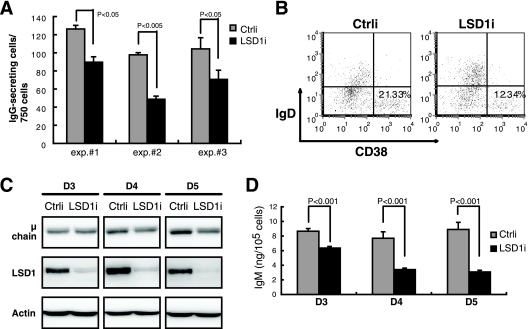
Finally, because LSD1 is important for Blimp-1 function, we asked if LSD1 is required for plasma cell differentiation. Indeed, the induction of IgG-secreting cells (Fig. 9A) and cells with plasma cell surface marker CD38hiIgDlo (Fig. 9B) at day 6 after treatment of human peripheral B-cell cultures with IL-21 and anti-CD40 was reduced by LSD1i compared with that of Ctrli-transduced cells. Additionally, the IgM-producing human lymphoblastoid line SKW 6.4 (SKW) was transduced with LSD1i to validate that secretion of IgM was reduced by LSD1 depletion. Consistently, we found that the expression of immunoglobulin μ heavy chain and the secretion of IgM were significantly reduced in a time course-dependent manner upon LSD1 knockdown in SKW cells (Fig. 9C and D). These combined data suggest that LSD1 is required for the formation of antibody-secreting cells.
FIG. 9.
Inhibition of LSD1 activity or expression blocks plasma cell formation. (A) ELISPOT for determining IgG-secreting cells from three sorted Ctrli- or LSD1i-transduced, GFP+ human peripheral B-cell cultures treated with IL-21 plus anti-CD40 for 6 days. (B) Flow cytometric analysis of cell surface expression of CD38 and IgD as described for panel A. Results are representative of three independent experiments. Values shown indicate the percentage of CD38hiIgDlo cells. (C) Immunoblot analysis of the indicated protein expression in SKW cells transduced with Ctrli or LSD1i for the indicated days (transduction rate of >95%). (D) Culture supernatants harvested from the experiment described for panel C were subjected to enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to determine IgM levels. (A and D) Results are means ± standard deviations from three samples.
DISCUSSION
We report here for the first time that LSD1 is involved in Blimp-1's mode of action in plasma cell differentiation. LSD1 has been implicated in regulating various lineages in development/differentiation by its ability to activate or repress gene expression, depending on its interaction with coactivators or corepressors in a context-dependent manner (48). For example, Drosophila LSD1 controls gene silencing in primordial germ cells (35). LSD1 deletion in mice revealed a role for LSD1 in late pituitary development and terminal differentiation (48). In the hematopoietic lineage, depletion of LSD1 by shRNA impairs the differentiation of primary erythroid progenitors, the megakaryoblastic cell line L8057, and the erythroleukemia cell line MEL but enhances spontaneous granulocytic differentiation in the myeloid cell line 32D.4 (36). We report that depletion of LSD1 reduced the generation of antibody-secreting cells (Fig. 9), indicating that LSD1 affects the gene expression program for plasma cell formation. One function of LSD1 during plasma cell differentiation may be to contribute to the activity of the Blimp-1-dependent repression complex, not to influence Blimp-1 expression, as Blimp-1 mRNA levels were not changed by LSD1 knockdown in H929 cells (Fig. 8I). Further characterization of the gene expression profiles regulated specifically by LSD1 during plasma cell differentiation and in antibody-secreting cells is still awaited.
Our data suggest that the Blimp-1 proline-rich domain is important for mediating gene repression, as the mutant Δ317-424 that lacks this domain showed decreased ability to suppress Blimp-1-dependent gene expression and was unable to rescue the failure to form antibody-secreting cells of Prdm1-deficient B cells (Fig. 1). The importance of the Blimp-1 proline-rich domain is in part due to its ability to associate with Blimp-1-interacting proteins, rather than to participate in regulating Blimp-1 DNA binding or nuclear localization (30). The proline-rich domain in Blimp-1 interacts with HDAC2 (49); our finding that this Blimp-1 domain is essential for association with LSD1 is consistent with a previous report that HDAC1/2 is present in LSD1-containing complexes (42). Unexpectedly, we found that the proline-rich domain is also involved in G9a association (Fig. 5B), suggesting that two regions in Blimp-1—the proline-rich domain and the first two zinc fingers—mediate G9a recruitment. Alternatively, association with G9a may require a prerequisite Blimp-1/HDACs/LSD1 complex. In addition to interacting with the above-mentioned chromatin modifiers, a temporal association of Blimp-1 and an arginine-specific histone methyltransferase, Prmt5, in mouse germ cell development has been reported (1). Blimp-1 and Prmt5 colocalize in the nucleus during the specification of mouse primordial germ cells (1). During the phase of extensive epigenetic reprogramming of germ cells, Blimp-1 and Prmt5 translocate to the cytoplasm, which allows Blimp-1 target genes, such as Dhx38, to be derepressed (1). However, despite moderate expression of PRMT5 in H929 cells, we did not detect an interaction between endogenous PRMT5 and endogenous Blimp-1 by coimmunoprecipitation (Fig. 5C), suggesting that the molecular mechanism of Blimp-1-dependent gene regulation by association with chromatin modifiers may be tissue specific. It is noteworthy that LSD1 may demethylate nonhistone proteins, like p53 (11). The direct interaction of LSD1 and p53 causes demethylation of p53 at residue K370, which in turn reduces the interaction between p53 and the coactivator p53 binding protein 1 (11). Although we found that LSD1 is recruited to Blimp-1 target loci in vivo, it remains to be determined whether LSD1 also regulates Blimp-1 transcriptional repression activity in a manner dependent on posttranslational modification.
Drosophila LSD1 colocalizes with H3K4me2 to subsequently initiate heterochromatin formation during early development (35). LSD1 expression results in reduced H3K4me2 and H3Ac levels for a given experimental target gene (19), and LSD1 depletion results in increased H3K4me2 and H3K4me3 levels of Gfi-1b targets that are located in accessible loci in MEL cells (36). Our data showing that LSD1 depletion led to increased H3Ac, H3K4me2, and H3K4me3 levels at the CIITA promoter III locus in H929 cells (Fig. 8D to F) and that Blimp-1 depletion, which may preclude LSD1 binding, resulted in increased H3Ac and H3K4me2 levels (Fig. 8B and C) are consistent with the reports that LSD1 functions in regulating histone modifications. Additionally, LSD1 depletion did not affect the H3K9me2 level at the CIITA site (Fig. 8H), indicating that LSD1 depletion is not sufficient to alter H3K9me2 modification mediated by G9a. This result is accordant with a recent report that LSD1 depletion does not change the H3K9me2 level in a p53-responsive element bound by p53 and LSD1 (47). Here, we found that H3K4me1 levels were neither sensitive to LSD1 depletion (Fig. 8G) nor correlated with active gene loci (Fig. 7D), which can be explained by the fact that higher H3K4me1 levels are found in gene enhancer regions (9). Furthermore, we found that, upon induction of Blimp-1, LSD1 binding to several Blimp-1 target gene loci increased significantly (Fig. 6B), indicating that LSD1 is recruited or stabilized to mature B-cell gene loci in differentiating B cells through the induction of Blimp-1. In contrast, in H929 plasma cells, LSD1 and Blimp-1 did not bind to PAX5 and SPI-B sites where heterochromatin forms (Fig. 8A and B), suggesting that the maintenance of heterochromatin at mature B-cell gene loci in terminally differentiated B cells may not require constitutive binding of LSD1 as well as Blimp-1.
In conclusion, we report that Blimp-1 interacts with LSD1. We propose that Blimp-1 orchestrates recruitment of the HDAC1/2 and LSD1 complex, then G9a binding to endogenous target sites to affect dynamic changes in histone modifications, and finally silencing of the mature B-cell gene expression program during plasma cell differentiation. In differentiated B cells, the Blimp-1-associated protein complex may not need to continuously occupy gene loci in heterochromatin.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by an intramural grant from the Genomics Research Center, Academia Sinica, by Summit Project II no. 5202402020-0 from Academia Sinica and by NSC96-3114-P-001-006-Y02 from the National Science Council.
We thank Ming-Daw Tsai for critical reading of the manuscript and Li-Wen Lo for excellent technical assistance.
Footnotes
Published ahead of print on 5 January 2009.
REFERENCES
- 1.Ancelin, K., U. C. Lange, P. Hajkova, R. Schneider, A. J. Bannister, T. Kouzarides, and M. A. Surani. 2006. Blimp1 associates with Prmt5 and directs histone arginine methylation in mouse germ cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 8623-630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bannister, A. J., P. Zegerman, J. F. Partridge, E. A. Miska, J. O. Thomas, R. C. Allshire, and T. Kouzarides. 2001. Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature 410120-124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Baxendale, S., C. Davison, C. Muxworthy, C. Wolff, P. W. Ingham, and S. Roy. 2004. The B-cell maturation factor Blimp-1 specifies vertebrate slow-twitch muscle fiber identity in response to hedgehog signaling. Nat. Genet. 3688-93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chang, D. H., G. Cattoretti, and K. L. Calame. 2002. The dynamic expression pattern of B lymphocyte induced maturation protein-1 (Blimp-1) during mouse embryonic development. Mech. Dev. 117305-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cohen-Armon, M., L. Visochek, A. Katzoff, D. Levitan, A. J. Susswein, R. Klein, M. Valbrun, and J. H. Schwartz. 2004. Long-term memory requires polyADP-ribosylation. Science 3041820-1822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ettinger, R., G. P. Sims, A. M. Fairhurst, R. Robbins, Y. S. da Silva, R. Spolski, W. J. Leonard, and P. E. Lipsky. 2005. IL-21 induces differentiation of human naive and memory B cells into antibody-secreting plasma cells. J. Immunol. 1757867-7879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gill, G. 2004. SUMO and ubiquitin in the nucleus: different functions, similar mechanisms? Genes Dev. 182046-2059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gyory, I., J. Wu, G. Fejer, E. Seto, and K. L. Wright. 2004. PRDI-BF1 recruits the histone H3 methyltransferase G9a in transcriptional silencing. Nat. Immunol. 5299-308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Heintzman, N. D., R. K. Stuart, G. Hon, Y. Fu, C. W. Ching, R. D. Hawkins, L. O. Barrera, S. Van Calcar, C. Qu, K. A. Ching, W. Wang, Z. Weng, R. D. Green, G. E. Crawford, and B. Ren. 2007. Distinct and predictive chromatin signatures of transcriptional promoters and enhancers in the human genome. Nat. Genet. 39311-318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Holbert, M. A., and R. Marmorstein. 2005. Structure and activity of enzymes that remove histone modifications. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 15673-680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Huang, J., R. Sengupta, A. B. Espejo, M. G. Lee, J. A. Dorsey, M. Richter, S. Opravil, R. Shiekhattar, M. T. Bedford, T. Jenuwein, and S. L. Berger. 2007. p53 is regulated by the lysine demethylase LSD1. Nature 449105-108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kallies, A., J. Hasbold, D. M. Tarlinton, W. Dietrich, L. M. Corcoran, P. D. Hodgkin, and S. L. Nutt. 2004. Plasma cell ontogeny defined by quantitative changes in blimp-1 expression. J. Exp. Med. 200967-977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kallies, A., E. D. Hawkins, G. T. Belz, D. Metcalf, M. Hommel, L. M. Corcoran, P. D. Hodgkin, and S. L. Nutt. 2006. Transcriptional repressor Blimp-1 is essential for T cell homeostasis and self-tolerance. Nat. Immunol. 7466-474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Keller, A. D., and T. Maniatis. 1992. Only two of the five zinc fingers of the eukaryotic transcriptional repressor PRDI-BF1 are required for sequence-specific DNA binding. Mol. Cell. Biol. 121940-1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kouzarides, T. 2007. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell 128693-705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kuo, T. C., and K. L. Calame. 2004. B lymphocyte-induced maturation protein (Blimp)-1, IFN regulatory factor (IRF)-1, and IRF-2 can bind to the same regulatory sites. J. Immunol. 1735556-5563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lachner, M., and T. Jenuwein. 2002. The many faces of histone lysine methylation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 14286-298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lan, F., A. C. Nottke, and Y. Shi. 2008. Mechanisms involved in the regulation of histone lysine demethylases. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 201-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lee, M. G., C. Wynder, D. A. Bochar, M. A. Hakimi, N. Cooch, and R. Shiekhattar. 2006. Functional interplay between histone demethylase and deacetylase enzymes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 266395-6402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Li, B., M. Carey, and J. L. Workman. 2007. The role of chromatin during transcription. Cell 128707-719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lin, F. R., H. K. Kuo, H. Y. Ying, F. H. Yang, and K. I. Lin. 2007. Induction of apoptosis in plasma cells by B lymphocyte-induced maturation protein-1 knockdown. Cancer Res. 6711914-11923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lin, K. I., C. Angelin-Duclos, T. C. Kuo, and K. Calame. 2002. Blimp-1-dependent repression of Pax-5 is required for differentiation of B cells to immunoglobulin M-secreting plasma cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 224771-4780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lin, K. I., Y. Y. Kao, H. K. Kuo, W. B. Yang, A. Chou, H. H. Lin, A. L. Yu, and C. H. Wong. 2006. Reishi polysaccharides induce immunoglobulin production through the TLR4/TLR2-mediated induction of transcription factor Blimp-1. J. Biol. Chem. 28124111-24123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lin, Y., K. Wong, and K. Calame. 1997. Repression of c-myc transcription by Blimp-1, an inducer of terminal B cell differentiation. Science 276596-599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Liu, W. H., H. W. Hsiao, W. I. Tsou, and M. Z. Lai. 2007. Notch inhibits apoptosis by direct interference with XIAP ubiquitination and degradation. EMBO J. 261660-1669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Luger, K., A. W. Mader, R. K. Richmond, D. F. Sargent, and T. J. Richmond. 1997. Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2.8 Å resolution. Nature 389251-260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Magnusdottir, E., S. Kalachikov, K. Mizukoshi, D. Savitsky, A. Ishida-Yamamoto, A. A. Panteleyev, and K. Calame. 2007. Epidermal terminal differentiation depends on B lymphocyte-induced maturation protein-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 10414988-14993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Martin, C., and Y. Zhang. 2005. The diverse functions of histone lysine methylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6838-849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Martins, G. A., L. Cimmino, M. Shapiro-Shelef, M. Szabolcs, A. Herron, E. Magnusdottir, and K. Calame. 2006. Transcriptional repressor Blimp-1 regulates T cell homeostasis and function. Nat. Immunol. 7457-465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Messika, E. J., P. S. Lu, Y. J. Sung, T. Yao, J. T. Chi, Y. H. Chien, and M. M. Davis. 1998. Differential effect of B lymphocyte-induced maturation protein (Blimp-1) expression on cell fate during B cell development. J. Exp. Med. 188515-525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Metzger, E., M. Wissmann, N. Yin, J. M. Muller, R. Schneider, A. H. Peters, T. Gunther, R. Buettner, and R. Schule. 2005. LSD1 demethylates repressive histone marks to promote androgen-receptor-dependent transcription. Nature 437436-439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ohinata, Y., B. Payer, D. O'Carroll, K. Ancelin, Y. Ono, M. Sano, S. C. Barton, T. Obukhanych, M. Nussenzweig, A. Tarakhovsky, M. Saitou, and M. A. Surani. 2005. Blimp1 is a critical determinant of the germ cell lineage in mice. Nature 436207-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Piskurich, J. F., K. I. Lin, Y. Lin, Y. Wang, J. P. Ting, and K. Calame. 2000. BLIMP-I mediates extinction of major histocompatibility class II transactivator expression in plasma cells. Nat. Immunol. 1526-532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Ren, B., K. J. Chee, T. H. Kim, and T. Maniatis. 1999. PRDI-BF1/Blimp-1 repression is mediated by corepressors of the Groucho family of proteins. Genes Dev. 13125-137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Rudolph, T., M. Yonezawa, S. Lein, K. Heidrich, S. Kubicek, C. Schafer, S. Phalke, M. Walther, A. Schmidt, T. Jenuwein, and G. Reuter. 2007. Heterochromatin formation in Drosophila is initiated through active removal of H3K4 methylation by the LSD1 homolog SU(VAR)3-3. Mol. Cell 26103-115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Saleque, S., J. Kim, H. M. Rooke, and S. H. Orkin. 2007. Epigenetic regulation of hematopoietic differentiation by Gfi-1 and Gfi-1b is mediated by the cofactors CoREST and LSD1. Mol. Cell 27562-572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Sciammas, R., and M. M. Davis. 2004. Modular nature of Blimp-1 in the regulation of gene expression during B cell maturation. J. Immunol. 1725427-5440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Shaffer, A. L., K. I. Lin, T. C. Kuo, X. Yu, E. M. Hurt, A. Rosenwald, J. M. Giltnane, L. Yang, H. Zhao, K. Calame, and L. M. Staudt. 2002. Blimp-1 orchestrates plasma cell differentiation by extinguishing the mature B cell gene expression program. Immunity 1751-62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Shapiro-Shelef, M., K. I. Lin, L. J. McHeyzer-Williams, J. Liao, M. G. McHeyzer-Williams, and K. Calame. 2003. Blimp-1 is required for the formation of immunoglobulin secreting plasma cells and pre-plasma memory B cells. Immunity 19607-620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Shapiro-Shelef, M., K. I. Lin, D. Savitsky, J. Liao, and K. Calame. 2005. Blimp-1 is required for maintenance of long-lived plasma cells in the bone marrow. J. Exp. Med. 51471-1476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Shi, Y., F. Lan, C. Matson, P. Mulligan, J. R. Whetstine, P. A. Cole, and R. A. Casero. 2004. Histone demethylation mediated by the nuclear amine oxidase homolog LSD1. Cell 119941-953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Shi, Y. J., C. Matson, F. Lan, S. Iwase, T. Baba, and Y. Shi. 2005. Regulation of LSD1 histone demethylase activity by its associated factors. Mol. Cell 19857-864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Shilatifard, A. 2006. Chromatin modifications by methylation and ubiquitination: implications in the regulation of gene expression. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 75243-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Sims, R. J., III, K. Nishioka, and D. Reinberg. 2003. Histone lysine methylation: a signature for chromatin function. Trends Genet. 19629-639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Stavropoulos, P., G. Blobel, and A. Hoelz. 2006. Crystal structure and mechanism of human lysine-specific demethylase-1. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 13626-632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Sui, G., and Y. Shi. 2005. Gene silencing by a DNA vector-based RNAi technology. Methods Mol. Biol. 309205-218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Tsai, W. W., T. T. Nguyen, Y. Shi, and M. C. Barton. 2008. p53-targeted LSD1 functions in repression of chromatin structure and transcription in vivo. Mol. Cell. Biol. 285139-5146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wang, J., K. Scully, X. Zhu, L. Cai, J. Zhang, G. G. Prefontaine, A. Krones, K. A. Ohgi, P. Zhu, I. Garcia-Bassets, F. Liu, H. Taylor, J. Lozach, F. L. Jayes, K. S. Korach, C. K. Glass, X. D. Fu, and M. G. Rosenfeld. 2007. Opposing LSD1 complexes function in developmental gene activation and repression programmes. Nature 446882-887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Yu, J., C. Angelin-Duclos, J. Greenwood, J. Liao, and K. Calame. 2000. Transcriptional repression by blimp-1 (PRDI-BF1) involves recruitment of histone deacetylase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 202592-2603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Zhang, Y., and D. Reinberg. 2001. Transcription regulation by histone methylation: interplay between different covalent modifications of the core histone tails. Genes Dev. 152343-2360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]