Abstract
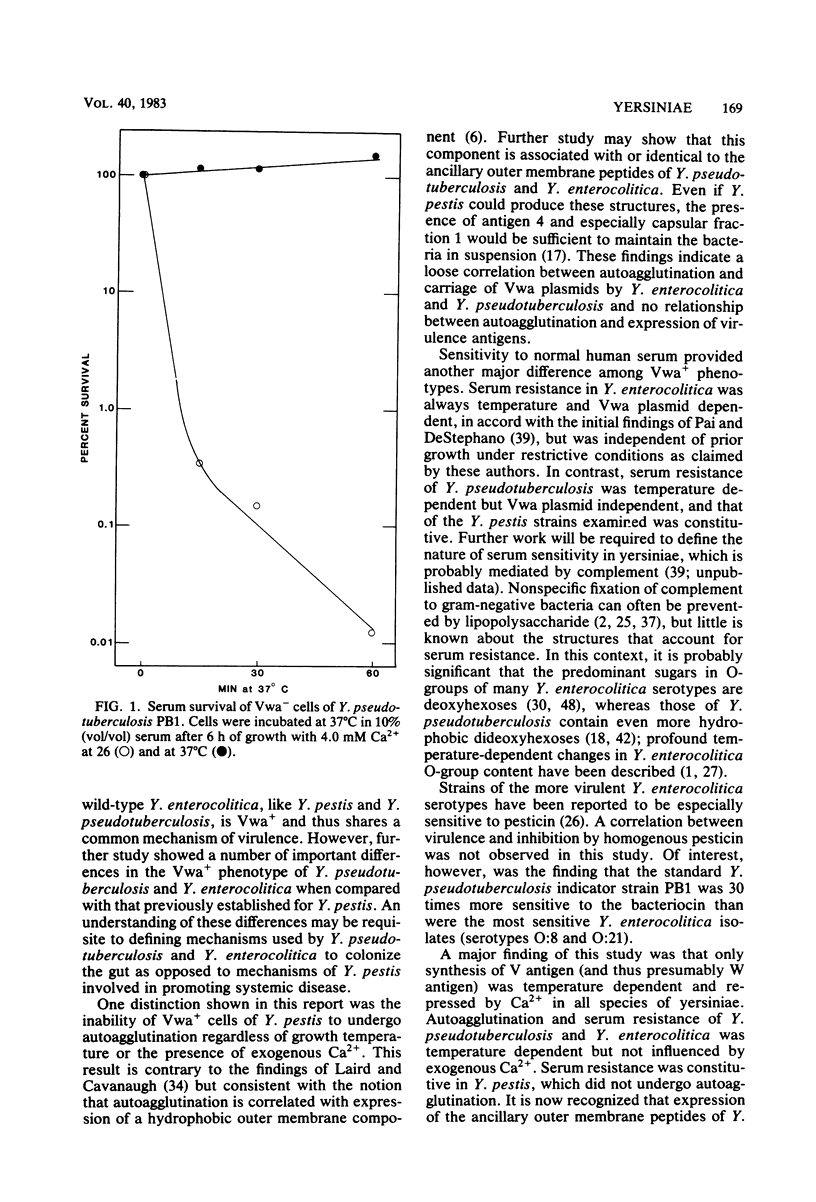
Expression of the Vwa+ phenotype of Yersinia pestis in vitro is known to reflect maximum induction of virulence (or V and W antigens) at 37 degrees C with concomitant restriction of cell division. Both phenomena are potentiated by 20 mM Mg2+ and prevented by cultivation at 26 or 37 degrees C with 2.5 mM Ca2+. We have now compared this classic plasmid-mediated phenotype with those of Vwa+ Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Yersinia enterocolitica which, unlike Y. pestis, produce ancillary outer membrane peptides unrelated to the V and W antigens. All of 10 wild-type strains of Y. enterocolitica (serotypes O:3, O:4,32, O:8, O:9, O:15, and O:21) exhibited a nutritional requirement for Ca2+ at 37 degrees C and produced significant V antigen. Like Y. pseudotuberculosis, autoagglutination of Vwa+ Y. enterocolitica was dependent upon prior growth at 37 degrees C but was not influenced by Ca2+. Autoagglutination of Y. pestis was never observed. Resistance of Y. enterocolitica to 10% human serum was typically dependent upon prior growth at 37 degrees C, either with or without added Ca2+, and carriage of a Vwa plasmid. In contrast, serum resistance of Y. pseudotuberculosis was temperature but not plasmid dependent and that of Y. pestis was constitutive.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acker G., Wartenberg K., Knapp W. Zuckerzusammensetzung des Lipopolysaccharids und Feinstruktur der äusseren Membran (Zellwand) bei Yersinia enterocolitica. Zentralbl Bakteriol A. 1980;247(2):229–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. J., Scott G. K. Comparison of the effects of different lipopolysaccharides on the serum bactericidal reactions of two strains of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):831–832. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.831-832.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BACON G. A., BURROWS T. W. The basis of virulence in Pasteurella pestis: an antigen determining virulence. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Oct;37(5):481–493. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUBAKER R. R., SURGALLA M. J. THE EFFECT OF CA++ AND MG++ ON LYSIS, GROWTH, AND PRODUCTION OF VIRULENCE ANTIGENS BY PASTEURELLA PESTIS. J Infect Dis. 1964 Feb;114:13–25. doi: 10.1093/infdis/114.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W., BACON G. A. The effects of loss of different virulence determinants on the virulence and immunogenicity of strains of Pasteurella pestis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1958 Jun;39(3):278–291. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W., JACKSON S. The pigmentation of Pasteurella pestis on a defined medium containing haemin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Dec;37(6):570–576. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W. VIRULENCE OF PASTEURELLA PESTIS AND IMMUNITY TO PLAGUE. Ergeb Mikrobiol Immunitatsforsch Exp Ther. 1963;37:59–113. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-36742-1_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Gurion R., Shafferman A. Essential virulence determinants of different Yersinia species are carried on a common plasmid. Plasmid. 1981 Mar;5(2):183–187. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker R. R. Growth of Pasteurella pseudotuberculosis in simulated intracellular and extracellular environments. J Infect Dis. 1967 Dec;117(5):403–417. doi: 10.1093/infdis/117.5.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker R. R. Interconversion of Purine Mononucleotides in Pasteurella pestis. Infect Immun. 1970 May;1(5):446–454. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.5.446-454.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker R. R. The genus Yersinia: biochemistry and genetics of virulence. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1972;57:111–158. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65297-4_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Norlander L., Wolf-Watz H. Temperature-inducible outer membrane protein of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Yersinia enterocolitica is associated with the virulence plasmid. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):506–512. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.506-512.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRUMPTON M. J., DAVIES D. A. An antigenic analysis of Pasteurella pestis by diffusion of antigens and antibodies in agar. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1956 Mar 27;144(918):109–134. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1956.0021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. B., Collins F. M. Experimental Yersinia enterocolitica infection in mice: kinetics of growth. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):851–857. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.851-857.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. B., Zahorchak R. J., Brubaker R. R. Plague virulence antigens from Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):638–640. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.638-640.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charnetzky W. T., Brubaker R. R. RNA synthesis in Yersinia pestis during growth restriction in calcium-deficient medium. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):1089–1095. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.1089-1095.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES D. A. Dideoxysugars of Pasteurella pseudotuberculosis-specific polysaccharides, and the occurrence of ascarylose. Nature. 1961 Jul 1;191:43–44. doi: 10.1038/191043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEVIGNAT R. Variétés de l'espèce Pasteurella pestis; nouvelle hypothèse. Bull World Health Organ. 1951;4(2):247–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle M. P., Hugdahl M. B., Chang M. T., Beery J. T. Serological relatedness of mouse-virulent Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):1234–1240. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.1234-1240.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferber D. M., Brubaker R. R. Plasmids in Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):839–841. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.839-841.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferber D. M., Fowler J. M., Brubaker R. R. Mutations to tolerance and resistance to pesticin and colicins in Escherichia coli phi. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):506–511. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.506-511.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Lazere J. R., Casey T. Plasmid associated with pathogenicity and calcium dependency of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):682–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.682-685.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Lazere J. R., Casey T., Wohlhieter J. A. Presence of a virulence-associated plasmid in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):1044–1047. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.1044-1047.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGUCHI K., CARLIN C. E. Studies on the nutrition and physiology of Pasteurella pestis. II. A defined medium for the growth of Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1958 Apr;75(4):409–413. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.4.409-413.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGUCHI K., SMITH J. L. Studies on the nutrition and physiology of Pasteurella pestis. VI. A differential plating medium for the estimation of the mutation rate to avirulence. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:605–608. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.605-608.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison D. N., Laird W., Robinson D. M., Cavanaugh D. C. Commonality of a virulence factor among Yersinia species. J Infect Dis. 1980 Mar;141(3):413–413. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.3.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellmann E., Schenk I. Beeinflusst die Bebrütungstemperatur den Endotoxingehalt von yersinia enterocolitica? Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1982 Apr;251(4):529–536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman J., Lindberg B., Brubaker R. R. Structural studies of the O-specific side-chains of the lipopolysaccharide from Yersinia enterocolitica Ye 128. Carbohydr Res. 1980 Jan 1;78(1):212–214. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)83675-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Brubaker R. R. Characterization of pesticin. Separation of antibacterial activities. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4749–4753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay B. A., Wachsmuth K., Gemski P. New virulence-associated plasmid in Yersinia enterocolitica. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1161–1163. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1161-1163.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWTON W. D., ERDMAN R. L., SURGALLA M. J. BIOSYNTHESIS AND PURIFICATION OF V AND W ANTIGEN IN PASTEURELLA PESTIS. J Immunol. 1963 Aug;91:179–184. doi: 10.21236/ad0299868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird W. J., Cavanaugh D. C. Correlation of autoagglutination and virulence of yersiniae. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):430–432. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.430-432.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Kline L. F. Activation of the classical and properdin pathways of complement by bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS). J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):362–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai C. H., DeStephano L. Serum resistance associated with virulence in Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):605–611. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.605-611.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmids and plasmid-associated determinants of Yersinia enterocolitica pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):775–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.775-782.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson M., Harkness T. K. Intracellular Pasteurella pseudotuberculosis: Multiplication in Cultured Spleen and Kidney Cells. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):631–639. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.631-639.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson K., Lindberg B., Brubaker R. R. Structure of O-specific side chains of lipopolysaccharides from Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. J Bacteriol. 1974 Mar;117(3):1010–1016. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.3.1010-1016.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiemann D. A., Devenish J. A. Relationship of HeLa cell infectivity to biochemical, serological, and virulence characteristics of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):497–506. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.497-506.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Brubaker R. R. Cytoplasmic and membrane proteins of yersiniae cultivated under conditions simulating mammalian intracellular environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1224–1228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Brubaker R. R. Localization in Yersinia pestis of peptides associated with virulence. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):129–135. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.129-135.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tee G. L., Scott G. K. Analysis of outer membrane components of Escherichia coli ML308 225 and of a serum-resistant mutant. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):387–392. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.387-392.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesikari T., Nurmi T., Mäki M., Skurnik M., Sundqvist C., Granfors K., Grönroos P. Plasmids in Yersinia enterocolitica serotypes O:3 and O:9: correlation with epithelial cell adherence in vitro. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):870–876. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.870-876.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wartenberg K., Lysy J., Knapp W. On the sugar content of the lipopolysaccharides of the various strains known as Yersinia enterocolitica. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1975;230(3):361–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wauters G., Le Minor L., Chalon A. M., Lassen J. Supplément au schéma antigénique de "Yersinia enterocolitica". Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1972 May;122(5):951–956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahorchak R. J., Brubaker R. R. Effect of exogenous nucleotides on Ca2+ dependence and V antigen synthesis in Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):953–959. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.953-959.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahorchak R. J., Charnetzky W. T., Little R. V., Brubaker R. R. Consequences of Ca2+ deficiency on macromolecular synthesis and adenylate energy charge in Yersinia pestis. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):792–799. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.792-799.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


