Abstract
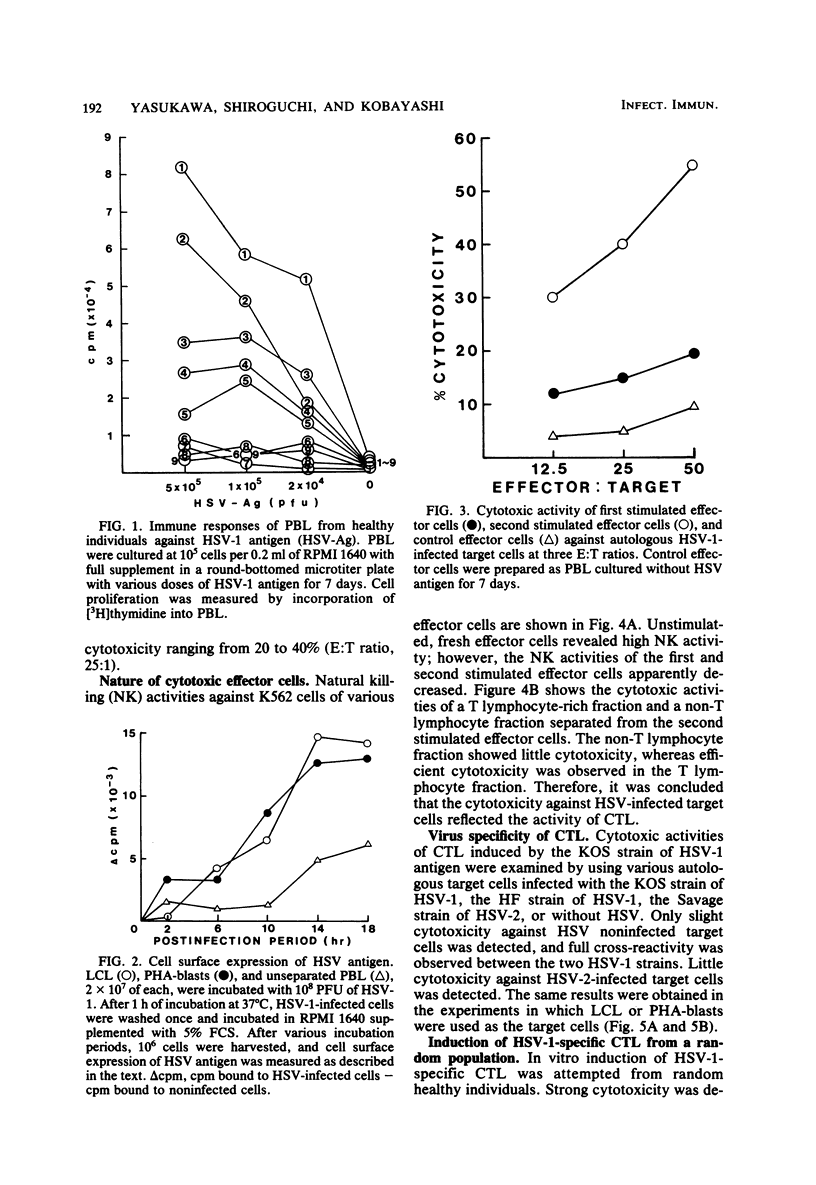
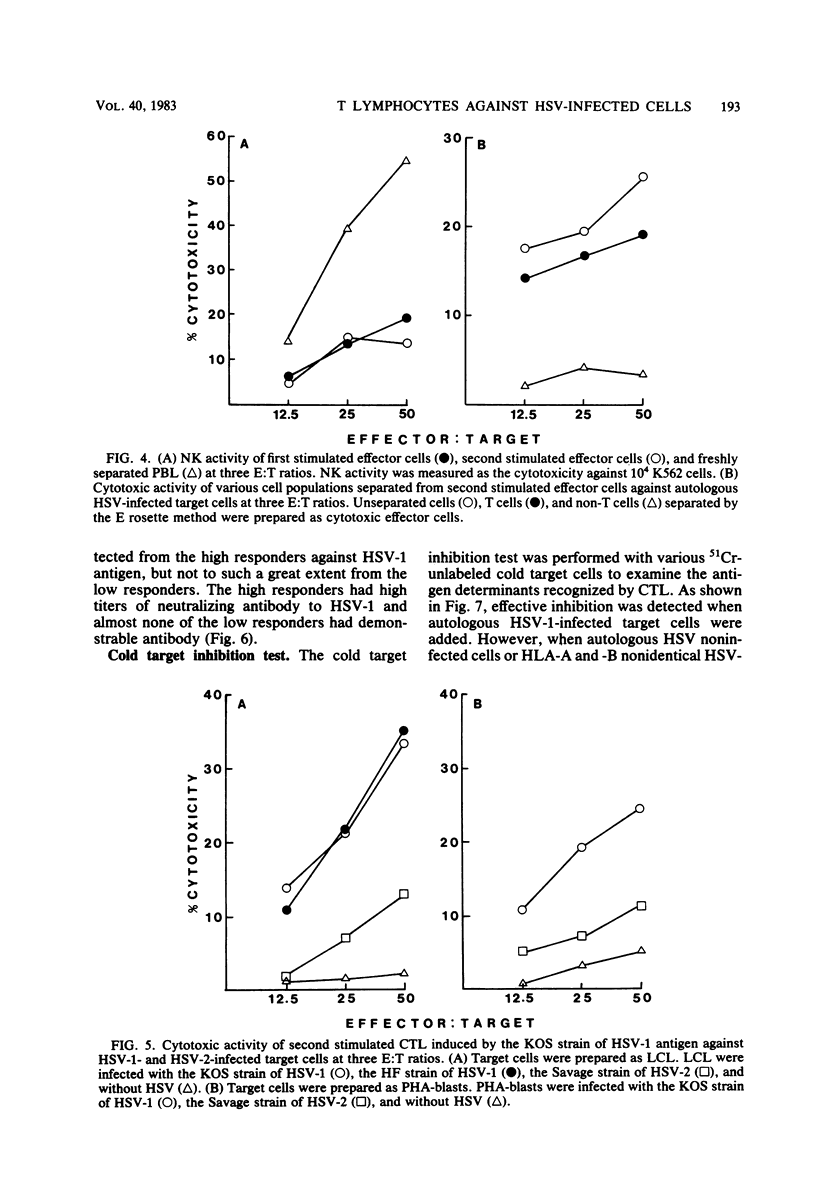
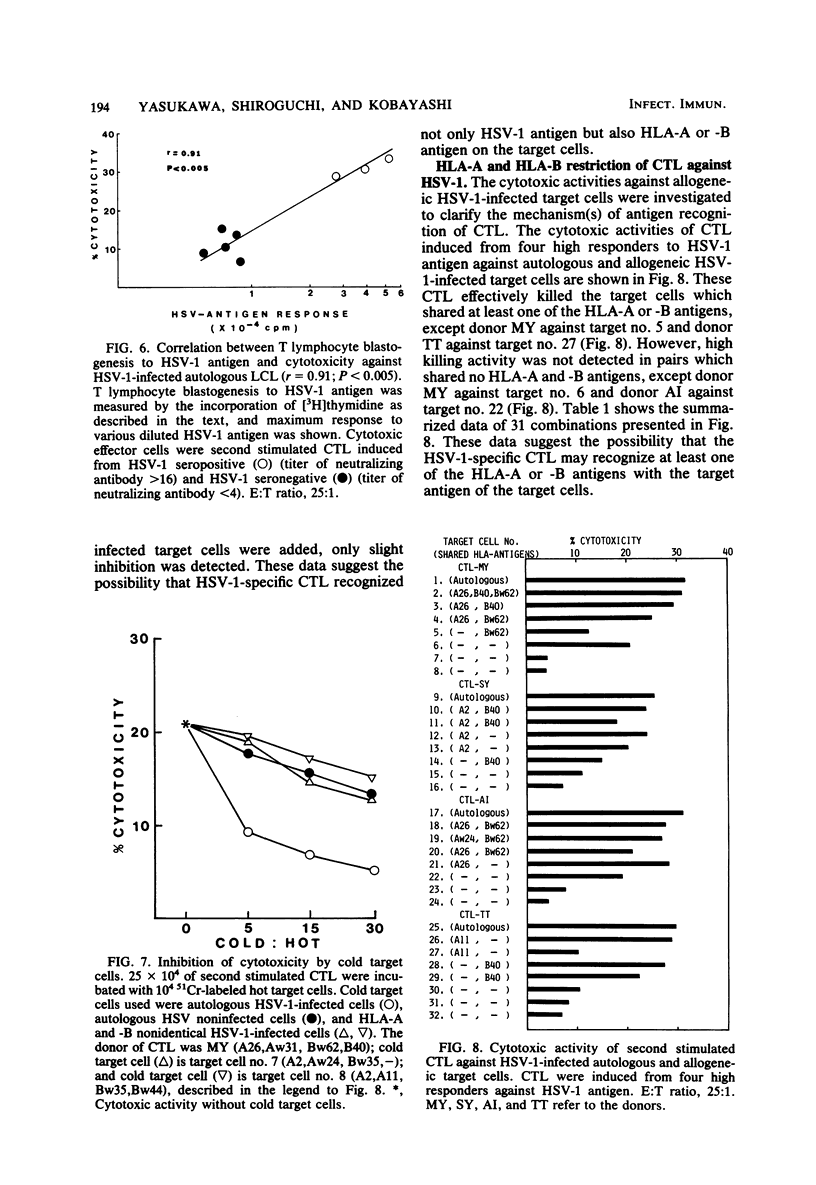
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) against herpes simplex virus (HSV) were induced in vitro from human peripheral blood lymphocytes by stimulation with HSV antigen. CTL generated by HSV type 1 (HSV-1) antigen stimulation killed not only HSV-1-infected target cells but also HSV type 2 (HSV-2)-infected target cells, though at a lower level. This evidence suggests that CTL against HSV recognize the HSV type-specific and type-common determinants on HSV-infected target cells. These CTL were generated from high responders against HSV-1 antigen as measured by antigen-specific T lymphocyte proliferation in vitro, but not to such an efficient degree from low responders. The cytotoxic activities of CTL against the allogeneic HSV-infected target cells were high when at least one of the HLA-A or -B antigens was shared. However, the HLA-A and -B nonidentical target cells were not killed effectively. The data presented here suggest the possibility of HLA restriction of HSV-specific CTL in humans.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergholtz B. O., Thorsby E. Macrophage-dependent response of immune human T lymphocytes to PPD in vitro. Influence of HLA-D histocompatibility. Scand J Immunol. 1977;6(8):779–786. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1977.tb02151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biddison W. E., Krangel M. S., Strominger J. L., Ward F. E., Shearer G. M., Shaw S. Virus-immune cytotoxic T cells recognize structural differences between serologically indistinguishable HLA-A2 molecules. Hum Immunol. 1980 Oct;1(3):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(80)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickmeiss E., Soeberg B., Svejgaard A. Human cell-mediated cytotoxicity against modified target cells is restricted by HLA. Nature. 1977 Dec 8;270(5637):526–528. doi: 10.1038/270526a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. C., Blanden R. V., Zinkernagel R. M. Specificity of virus-immune effector T cells for H-2K or H-2D compatible interactions: implications for H-antigen diversity. Transplant Rev. 1976;29:89–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1976.tb00198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberle R., Russell R. G., Rouse B. T. Cell-mediated immunity to herpes simplex virus: recognition of type-specific and type-common surface antigens by cytotoxic T cell populations. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):795–803. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.795-803.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engleman E. G., McMichael A. J., Batey M. E., McDevitt H. O. A suppressor T cell of the mixed lymphocyte reaction in man specific for the stimulating alloantigen. Evidence that identity at HLA-D between suppressor and responder is required for suppression. J Exp Med. 1978 Jan 1;147(1):137–146. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukukawa T., Hirano T., Sakaguchi N., Teranishi T., Tsuyuguchi I., Nagao N., Naito N., Yoshimura K., Okubo Y., Tohda H. In vitro induction of HLA-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes against autologous Epstein-Barr Virus transformed B lymphoblastoid cell line. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1697–1701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulmy E., Termijtelen A., Bradley B. A., van Rood J. J. Y-antigen killing by T cells of women is restricted by HLA. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):544–545. doi: 10.1038/266544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawman M. J., Courtney R. J., Eberle R., Schaffer P. A., O'Hara M. K., Rouse B. T. Cell-mediated immunity to herpes simplex virus: specificity of cytotoxic T cells. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):451–461. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.451-461.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael A. J., Parham P., Brodsky F. M., Pilch J. R. Influenza virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes recognize HLA-molecules. Blocking by monoclonal anti-HLA antibodies. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2 Pt 2):195s–203s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael A. J., Ting A., Zweerink H. J., Askonas B. A. HLA restriction of cell-mediated lysis of influenza virus-infected human cells. Nature. 1977 Dec 8;270(5637):524–526. doi: 10.1038/270524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael A. HLA restriction of human cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for influenza virus. Poor recognition of virus associated with HLA A2. J Exp Med. 1978 Dec 1;148(6):1458–1467. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.6.1458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori R., Tasaki T., Kimura G., Takeya K. Depression of acquired resistance against herpes simplex virus infection in neonatally thymectomized mice. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1967;21(3):459–462. doi: 10.1007/BF01241745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss D. J., Wallace L. E., Rickinson A. B., Epstein M. A. Cytotoxic T cell recognition of Epstein-Barr virus-infected B cells. I. Specificity and HLA restriction of effector cells reactivated in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Sep;11(9):686–693. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahmias A. J., Roizman B. Infection with herpes-simplex viruses 1 and 2. 3. N Engl J Med. 1973 Oct 11;289(15):781–789. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197310112891505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Dondero D. V., Gallo D., Devlin V., Woodie J. D. Serological analysis of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 with monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):363–367. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.363-367.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfizenmaier K., Jung H., Starzinski-Powitz A., Röllinghoff M., Wagner H. The role of T cells in anti-herpes simplex virus immunity. I. Induction of antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):939–944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfizenmaier K., Starzinski-Powitz A., Röllinghoff M., Falks D., Wagner H. T-cell-mediated cytotoxicity against herpes simplex virus-infected target cells. Nature. 1977 Feb 17;265(5595):630–632. doi: 10.1038/265630a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rager-Zisman B., Allison A. C. Mechanism of immunologic resistance to herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) infection. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):35–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickinson A. B., Wallace L. E., Epstein M. A. HLA-restricted T-cell recognition of Epstein-Barr virus-infected B cells. Nature. 1980 Feb 28;283(5750):865–867. doi: 10.1038/283865a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell A. S., Schlaut J. Association of HLA-A1 antigen and susceptibility to recurrent cold sores. Arch Dermatol. 1977 Dec;113(12):1721–1722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasazuki T., Kaneoka H., Nishimura Y., Kaneoka R., Hayama M., Ohkuni H. An HLA-linked immune suppression gene in man. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2 Pt 2):297s–313s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasazuki T., Kohno Y., Iwamoto I., Tanimura M., Naito S. Association between an HLA haplotype and low responsiveness to tetanus toxoid in man. Nature. 1978 Mar 23;272(5651):359–361. doi: 10.1038/272359b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethi K. K., Stroehmann I., Brandis H. Human T-cell cultures from virus-sensitized donors can mediate virus-specific and HLA-restricted cell lysis. Nature. 1980 Aug 14;286(5774):718–720. doi: 10.1038/286718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethi K. K., Wolff M. H. The nature of host-cell herpes-simplex virus interactions(s) that renders cells susceptible to virus-specific cytotoxic T cells. Immunobiology. 1980 Dec;157(4-5):365–378. doi: 10.1016/s0171-2985(80)80006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw S., Biddison W. E. HLA-linked genetic control of the specicity of human cytotoxic T-cell responses to influenza virus. J Exp Med. 1979 Mar 1;149(3):565–575. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.3.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonoda S., Schlamowitz M. Studies of 125I trace labeling of immunoglobulin G by chloramine-T. Immunochemistry. 1970 Nov;7(11):885–898. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90051-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Sugamura K., Hinuma Y. Heterogeneity of allogeneic restriction of human cytotoxic T cell clones specific for Epstein Barr virus. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1241–1245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace L. E., Moss D. J., Rickinson A. B., McMichael A. J., Epstein M. A. Cytotoxic T cell recognition of Epstein-Barr virus-infected B cells. II. Blocking studies with monoclonal antibodies to HLA determinants. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Sep;11(9):694–699. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner M. S., Bianco C., Nussenzweig V. Enhanced binding of neuraminidase-treated sheep erythrocytes to human T lymphocytes. Blood. 1973 Dec;42(6):939–946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


