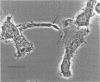
Abstract
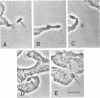
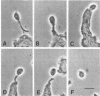
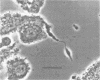
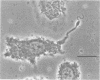
Leishmania donovani is an important intracellular protozoal pathogen of humans, which resides solely within mononuclear phagocytes. Phase-contrast microscopy and cinemicroscopy were used to examine the interaction of L. donovani promastigotes with human phagocytes to characterize and quantitate the sequence of events that results in leishmanial infection.
Full text
PDF

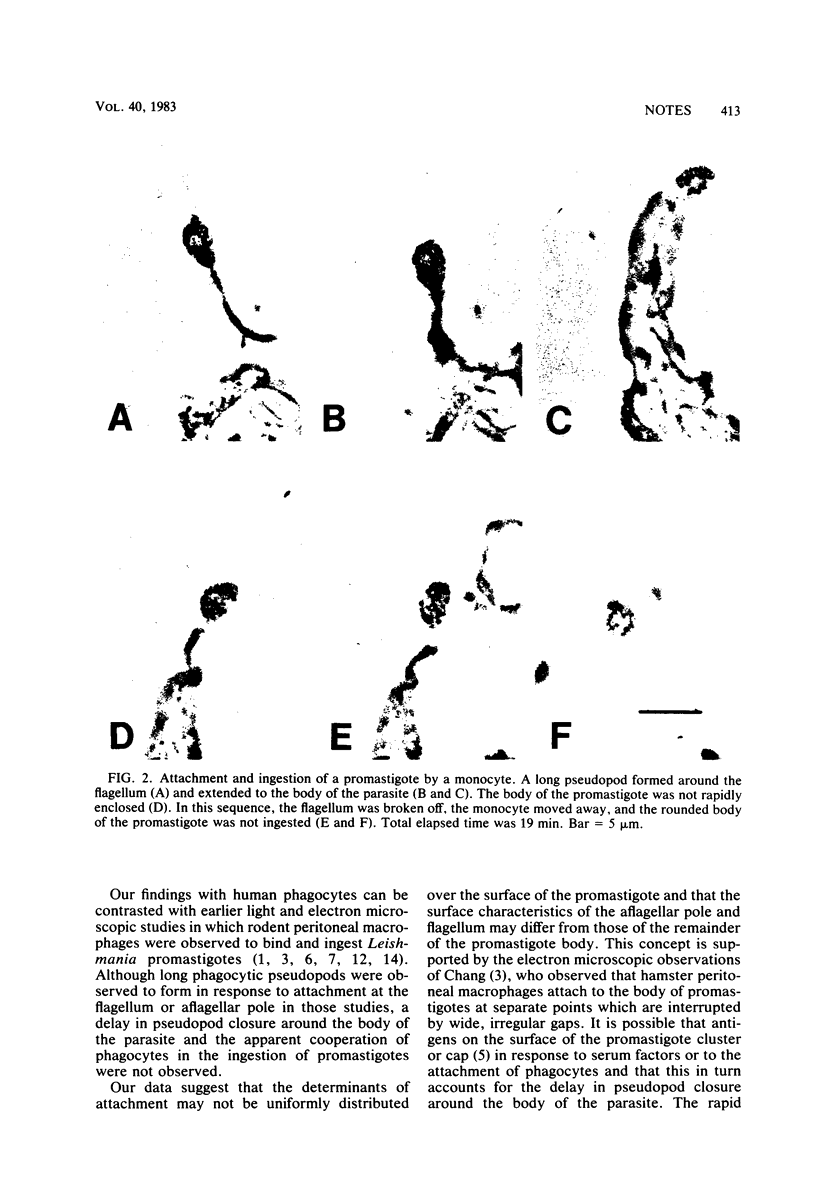
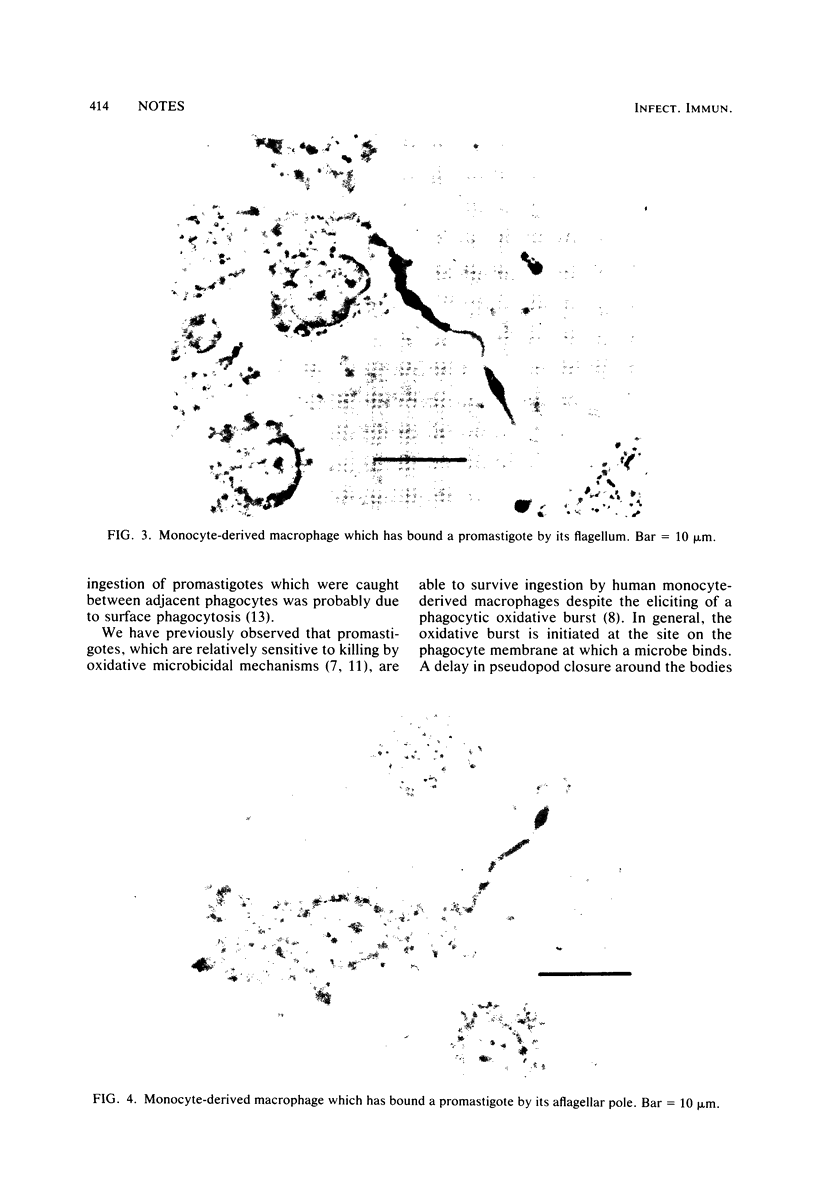
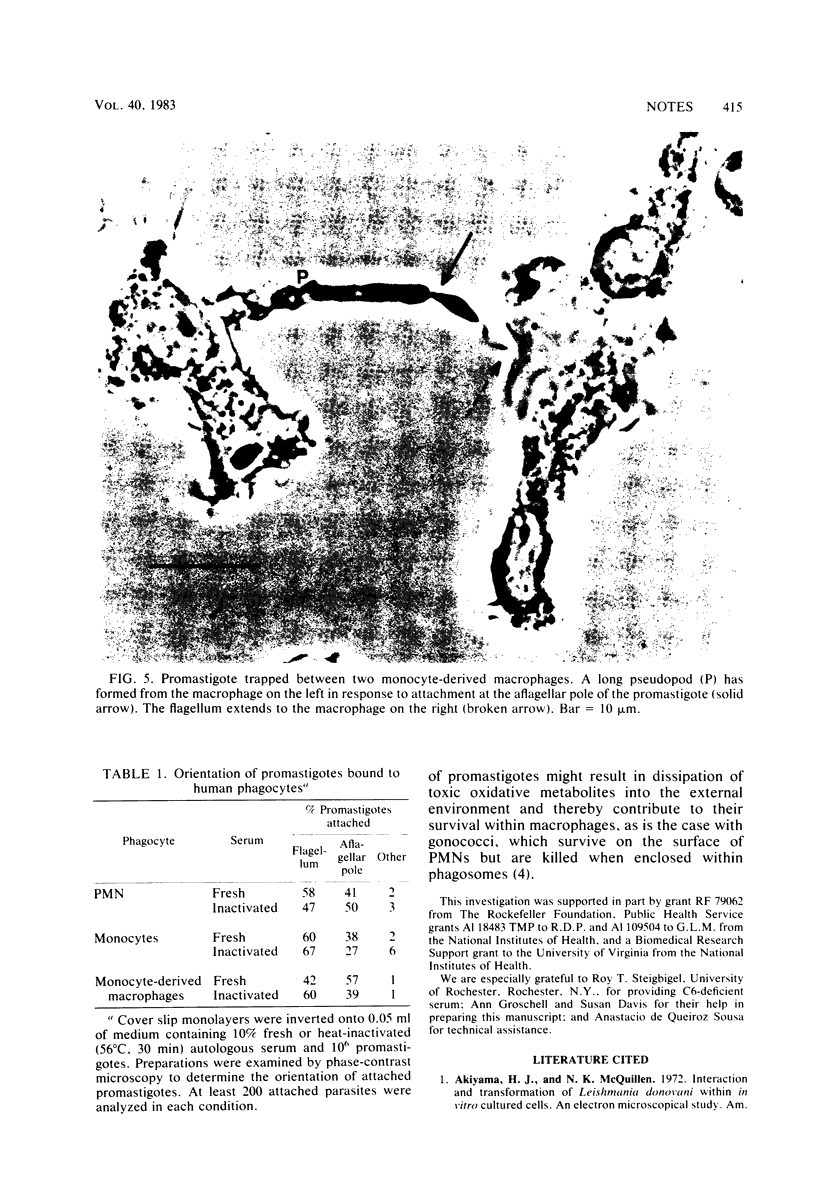

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berens R. L., Brun R., Krassner S. M. A simple monophasic medium for axenic culture of hemoflagellates. J Parasitol. 1976 Jun;62(3):360–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. P. Leishmania donovani: promastigote--macrophage surface interactions in vitro. Exp Parasitol. 1979 Oct;48(2):175–189. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(79)90097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Densen P., Mandell G. L. Gonococcal interactions with polymorphonuclear neutrophils: importance of the phagosome for bactericidal activity. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1161–1171. doi: 10.1172/JCI109235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer D. M. Antibody-induced modulation of Leishmania donovani surface membrane antigens. J Immunol. 1976 Dec;117(6):2081–2091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. H., Peters W. The resistance of intracellular Leishmania parasites to digestion by lysosomal enzymes. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1977 Sep;71(3):295–312. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1977.11687192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W. Susceptibility of Leishmania to oxygen intermediates and killing by normal macrophages. J Exp Med. 1981 May 1;153(5):1302–1315. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.5.1302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. D., Harcus J. L., Symes P. H., Romito R., Donowitz G. R. Failure of the phagocytic oxidative response to protect human monocyte-derived macrophages from infection by Leishmania donovani. J Immunol. 1982 Sep;129(3):1282–1286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. D., Romito R., Symes P. H., Harcus J. L. Interaction of Leishmania donovani promastigotes with human monocyte-derived macrophages: parasite entry, intracellular survival, and multiplication. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1249–1253. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1249-1253.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. D., Steigbigel R. T. Mechanism of lethal effect of human serum upon Leishmania donovani. J Immunol. 1980 Nov;125(5):2195–2201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. D., Steigbigel R. T. Phagocytosis and killing of the protozoan Leishmania donovani by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1438–1443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman A. A., Sethi K. K. Intracellular behaviour of Leishmania enriettii within murine macrophages. Experientia. 1978 May 15;34(5):598–599. doi: 10.1007/BF01936981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenian A., Rowles P., Gingell D. Scanning electron-microscopic study of the uptake of Leishmania parasites by macrophages. J Cell Sci. 1979 Oct;39:187–199. doi: 10.1242/jcs.39.1.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]