Abstract
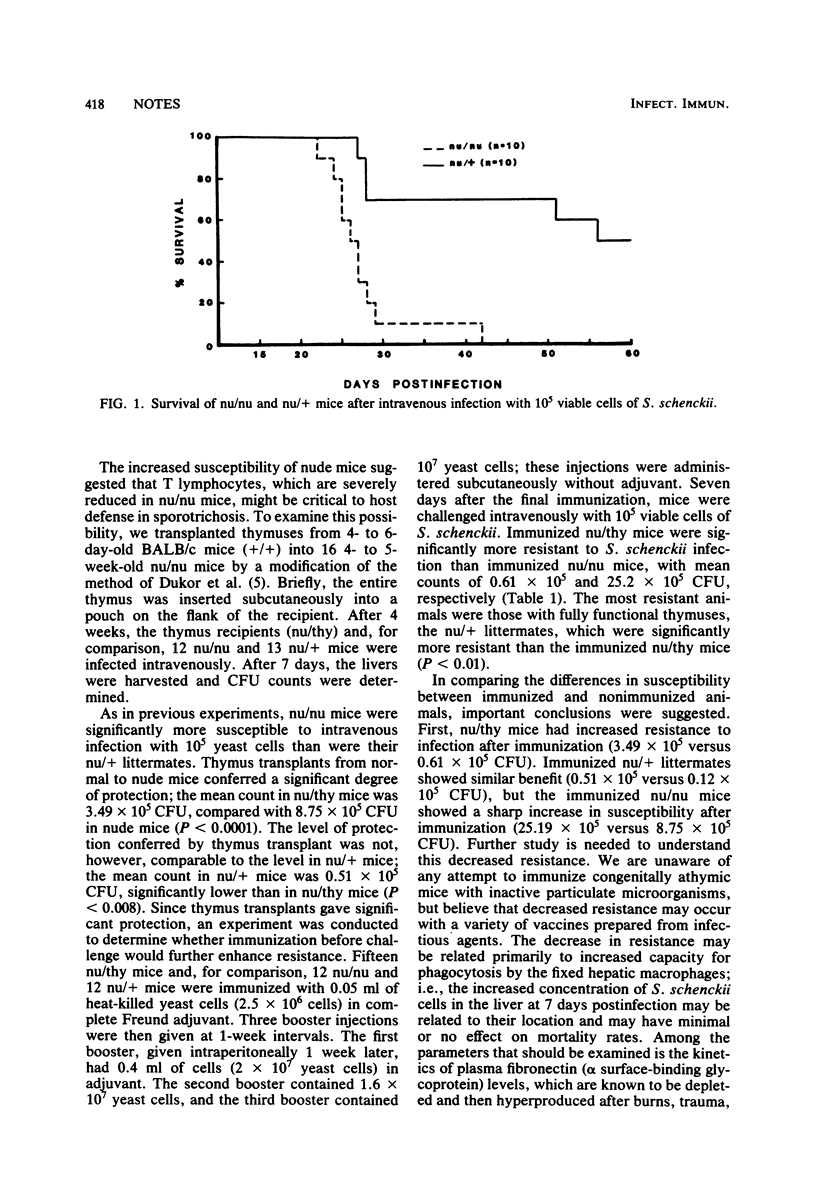
Congenitally athymic (nu/nu) mice were found to be more susceptible to intravenous challenge with Sporothrix schenckii than their phenotypically normal (nu/+) littermates as measured by lethality and the number of viable yeast cells in the liver 7 days postinfection. Thymus reconstitution of nu/nu mice (nu/thy) conferred a significant degree of resistance to sporotrichosis. Immunization greatly enhanced the resistance of nu/thy and nu/+ mice, but unexpectedly increased the susceptibility of nu/nu mice. The susceptibility of nonimmunized nu/nu mice and the finding that thymus transplants augmented resistance to sporotrichosis suggest that T lymphocytes are critical to host defense.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asherson G. L., Zembala M. Contact sensitivity in the mouse. IV. The role of lymphocytes and macrophages in passive transfer and the mechanism of their interaction. J Exp Med. 1970 Jul 1;132(1):1–15. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman L., Pappagianis D., Benjamini E. Significance of T cells in resistance to experimental murine coccidioidomycosis. Infect Immun. 1977 Sep;17(3):580–585. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.3.580-585.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenstock F. A., Saba T. M., Roccario E., Cho E., Kaplan J. E. Opsonic fibronectin after trauma and particle injection determined by a peritoneal macrophage monolayer assay. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1981 Jul;30(1):61–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler J. E. Acute systemic candidiasis in normal and congenitally thymic-deficient (nude) mice. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1976 Feb;19(2):121–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dukor P., Miller J. F., House W., Allman V. Regeneration of thymus grafts. I. Histological and cytological aspects. Transplantation. 1965 Sep;3(5):639–668. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196509000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybill J. R., Drutz D. J. Host defense in cryptococcosis. II. Cryptococcosis in the nude mouse. Cell Immunol. 1978 Oct;40(2):263–274. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90334-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanser M. E., Saba T. M., Scovill W. A. Opsonic glycoprotein (plasma fibronectin) levels after burn injury. Relationship to extent of burn and development of sepsis. Ann Surg. 1980 Dec;192(6):776–782. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198012000-00014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen H. S., Jr Biologic properties of skin test antigens of yeast form Sporotrichum schenckii. J Infect Dis. 1968 Apr;118(2):173–180. doi: 10.1093/infdis/118.2.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saba T. M., Jaffe E. Plasma fibronectin (opsonic glycoprotein): its synthesis by vascular endothelial cells and role in cardiopulmonary integrity after trauma as related to reticuloendothelial function. Am J Med. 1980 Apr;68(4):577–594. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90310-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiraishi A., Nakagaki K., Arai T. Experimental sporotrichosis in congenitally athymic (nude) mice. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1979 Sep;26(3):333–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Graybill J. R., Drutz D. J. Histoplasma capsulatum infection in nude mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):973–977. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.973-977.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


