Abstract
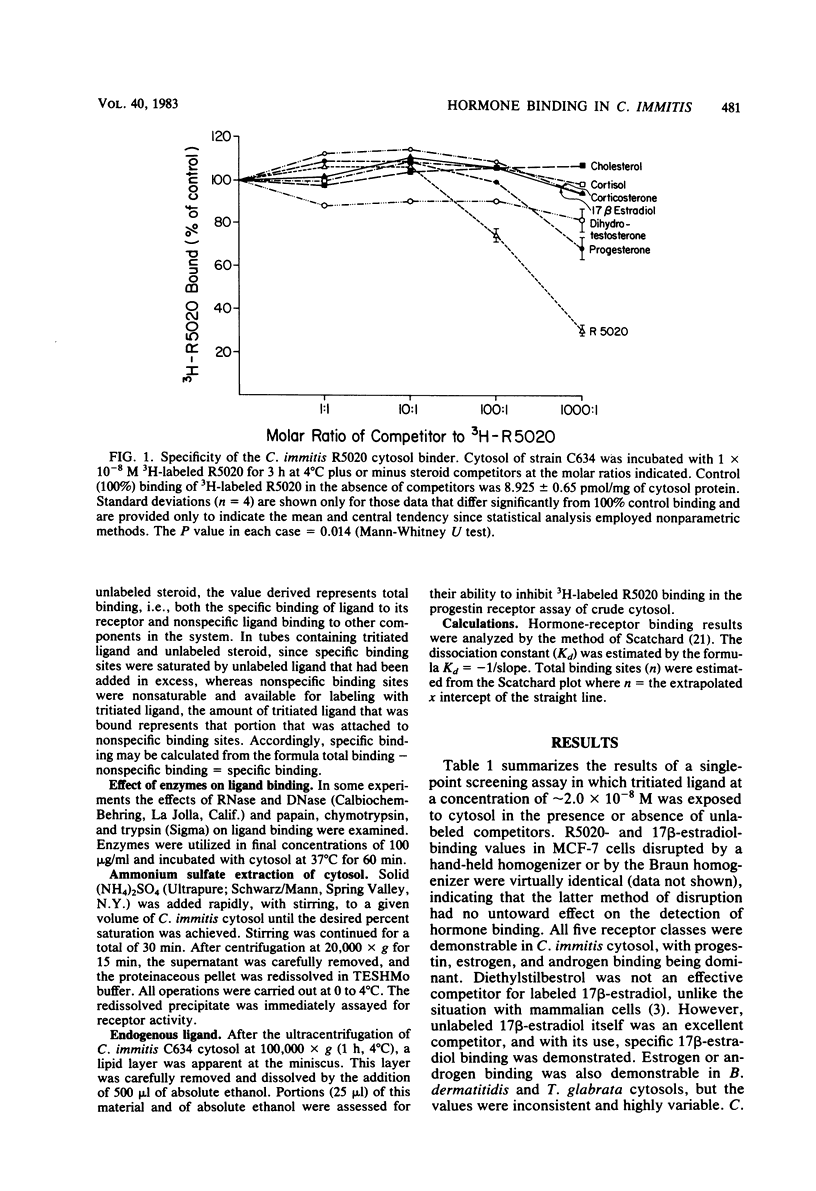
Pregnancy is a major risk factor for coccidioidal dissemination. Because rates of Coccidioides immitis growth and endospore release are stimulated in vitro by levels of unbound progesterone and 17 beta-estradiol that are achievable, in vivo, in the sera of pregnant women (i.e., 10(-9) to 10(-8) M), a specific-hormone-binding system in C. immitis was sought. Fungal cytosols were incubated with tritiated steroids plus or minus radioinert steroids to identify specific binding systems. All five strains of C. immitis tested exhibited specific saturable binding for progestin, estrogen, androgen, and (to a lesser extent) corticosterone and glucocorticoid hormone classes. Only low or inconsistent estrogen or androgen binding was found in Blastomyces dermatitidis and Torulopsis glabrata. Cryptococcus neoformans, Paracoccidioides brasiliensis, and non-albicans Candida species showed no binding. Scatchard analysis of progestin and estrogen binding in C. immitis revealed a high-capacity, low-affinity binding system that was unaffected by RNase and DNase, but 40 to 60% degraded by trypsin or heating. Ammonium sulfate precipitation resolved a high-affinity, low-capacity binding system (Kd = 1.24 X 10(-9) to 3.60 X 10(-8) M; number of binding sites = 0.014 to 0.20 pmol/mg of protein). The Kd of this system is sufficient to compete for unbound hormone in the sera of pregnant women. The high-capacity, low-affinity system may serve as a repository for hormone before its attachment to the specific binder. These studies suggest that the effects of nanomolar concentrations of sex hormones on C. immitis may be mediated by a specific cytosol protein-binding system and that stimulatory events observed in vitro may have relevance for the mechanism of coccidioidal dissemination in pregnancy.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. H., Peck E. J., Jr Female sex steroids: receptors and function. Monogr Endocrinol. 1979;14:I-XII, 1-245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drutz D. J., Catanzaro A. Coccidioidomycosis. Part I. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Mar;117(3):559–585. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.3.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drutz D. J., Huppert M., Sun S. H., McGuire W. L. Human sex hormones stimulate the growth and maturation of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):897–907. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.897-907.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards D. P., McGuire W. L. 17 alpha-Estradiol is a biologically active estrogen in human breast cancer cells in tissue culture. Endocrinology. 1980 Oct;107(4):884–891. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-4-884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman D., Do Y., Burshell A., Stathis P., Loose D. S. An estrogen-binding protein and endogenous ligand in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: possible hormone receptor system. Science. 1982 Oct 15;218(4569):297–298. doi: 10.1126/science.6289434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz K. B., Costlow M. E., McGuire W. L. MCF-7; a human breast cancer cell line with estrogen, androgen, progesterone, and glucocorticoid receptors. Steroids. 1975 Dec;26(6):785–795. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(75)90110-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz K. B., McGuire W. L. Estrogen control of progesterone receptor in human breast cancer. Correlation with nuclear processing of estrogen receptor. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2223–2228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huppert M., Sun S. H., Gross A. J. Evaluation of an experimental animal model for testing antifungal substances. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 May;1(5):367–372. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.5.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzenellenbogen B. S., Katzenellenbogen J. A., Mordecai D. Zearalenones: characterization of the estrogenic potencies and receptor interactions of a series of fungal beta-resorcylic acid lactones. Endocrinology. 1979 Jul;105(1):33–40. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-1-33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz I. M. Numbers of receptor sites from Scatchard graphs: facts and fantasies. Science. 1982 Sep 24;217(4566):1247–1249. doi: 10.1126/science.6287580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE H. B., COBB J. M., SMITH C. E. Immunity to coccidioi-domycosis induced in mice by purified spherule, arthrospore, and mycelial vaccines. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Apr;22:436–449. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1960.tb00711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loose D. S., Feldman D. Characterization of a unique corticosterone-binding protein in Candida albicans. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):4925–4930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loose D. S., Schurman D. J., Feldman D. A corticosteroid binding protein and endogenous ligand in C. albicans indicating a possible steroid-receptor system. Nature. 1981 Oct 8;293(5832):477–479. doi: 10.1038/293477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P. M., Horwitz K. B., Ryan D. S., McGuire W. L. Phytoestrogen interaction with estrogen receptors in human breast cancer cells. Endocrinology. 1978 Nov;103(5):1860–1867. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-5-1860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell B. L., Drutz D. J. Confirmation of corticosterone and progesterone binding activity in Candida albicans. J Infect Dis. 1983 Feb;147(2):359–359. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.2.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soule H. D., Vazguez J., Long A., Albert S., Brennan M. A human cell line from a pleural effusion derived from a breast carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Nov;51(5):1409–1416. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.5.1409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S. H., Huppert M. A cytological study of morphogenesis in Coccidioides immitis. Sabouraudia. 1976 Jul;14(2):185–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


