Abstract
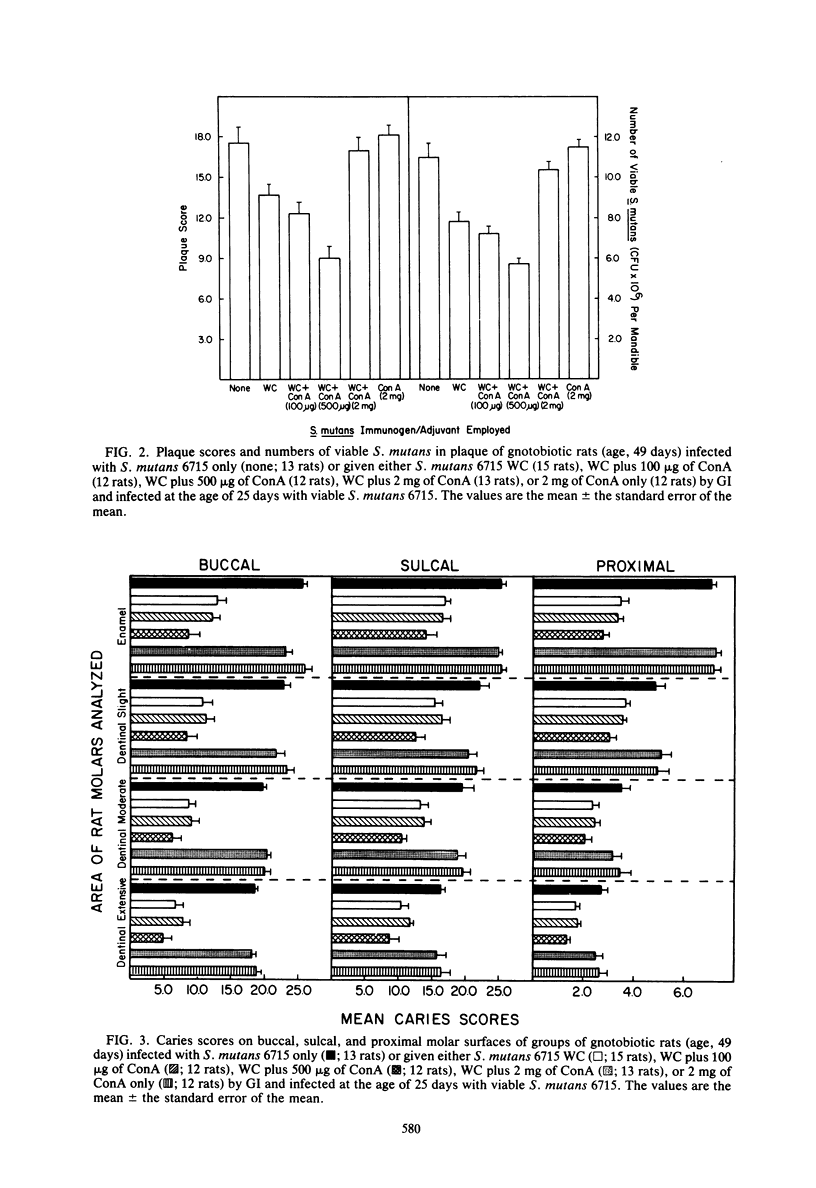
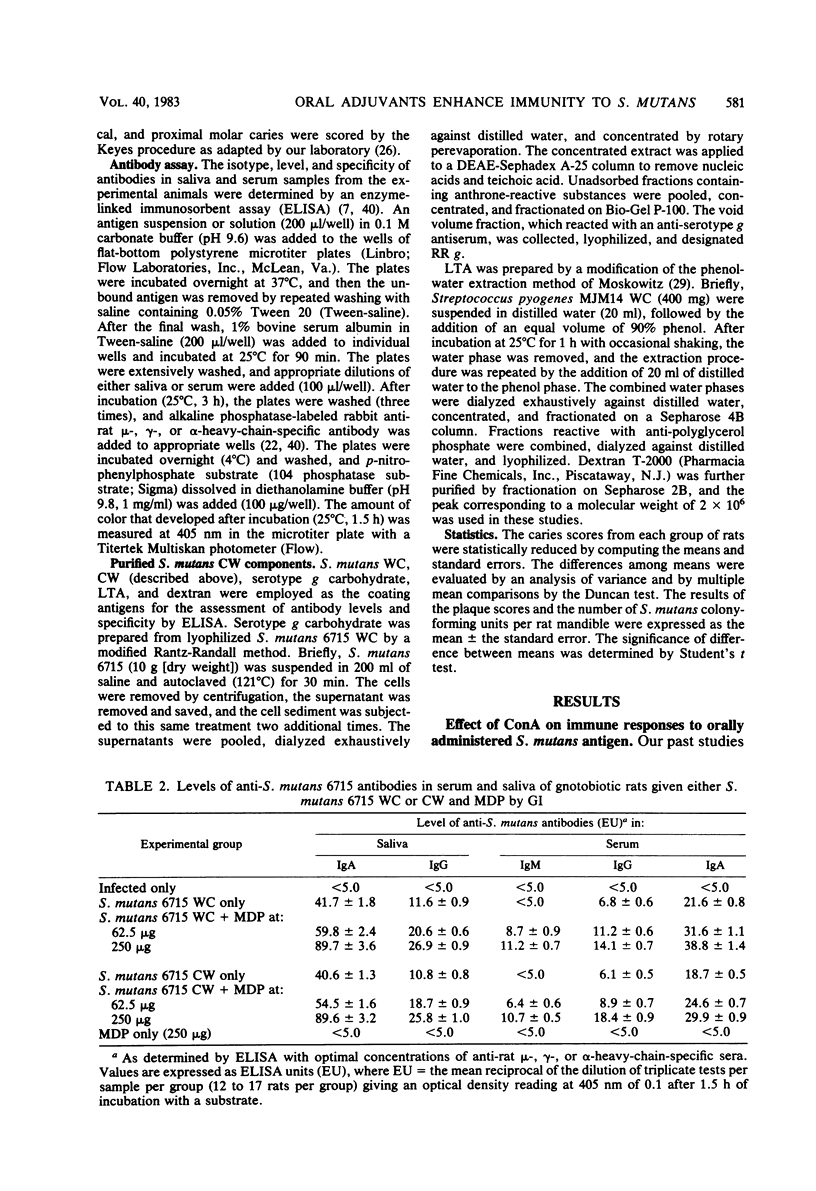
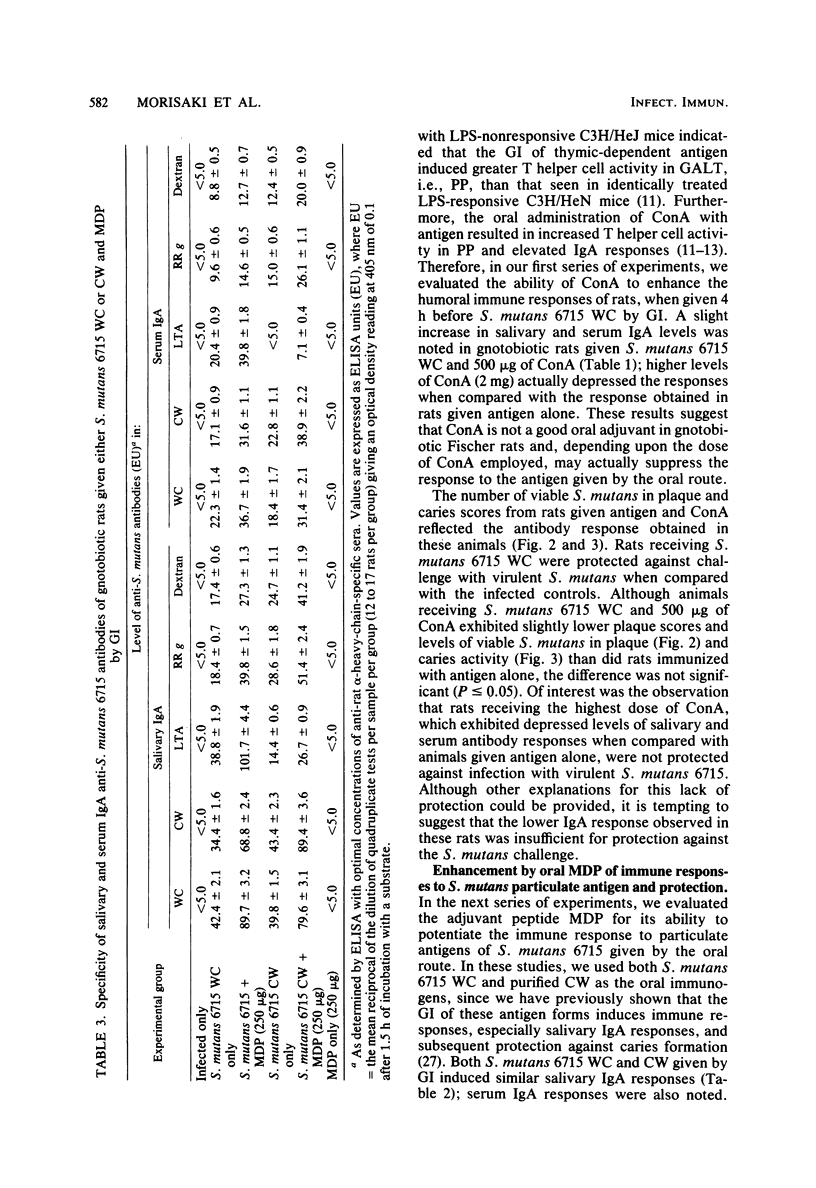
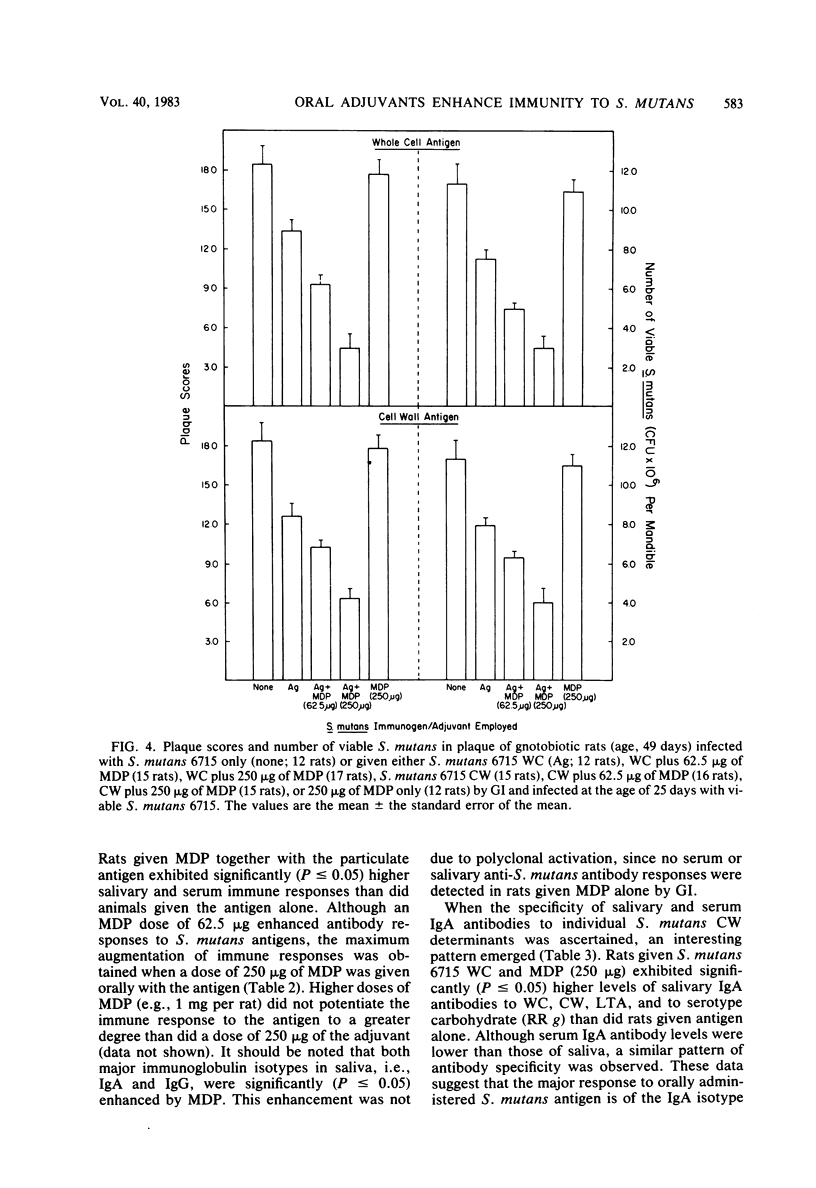
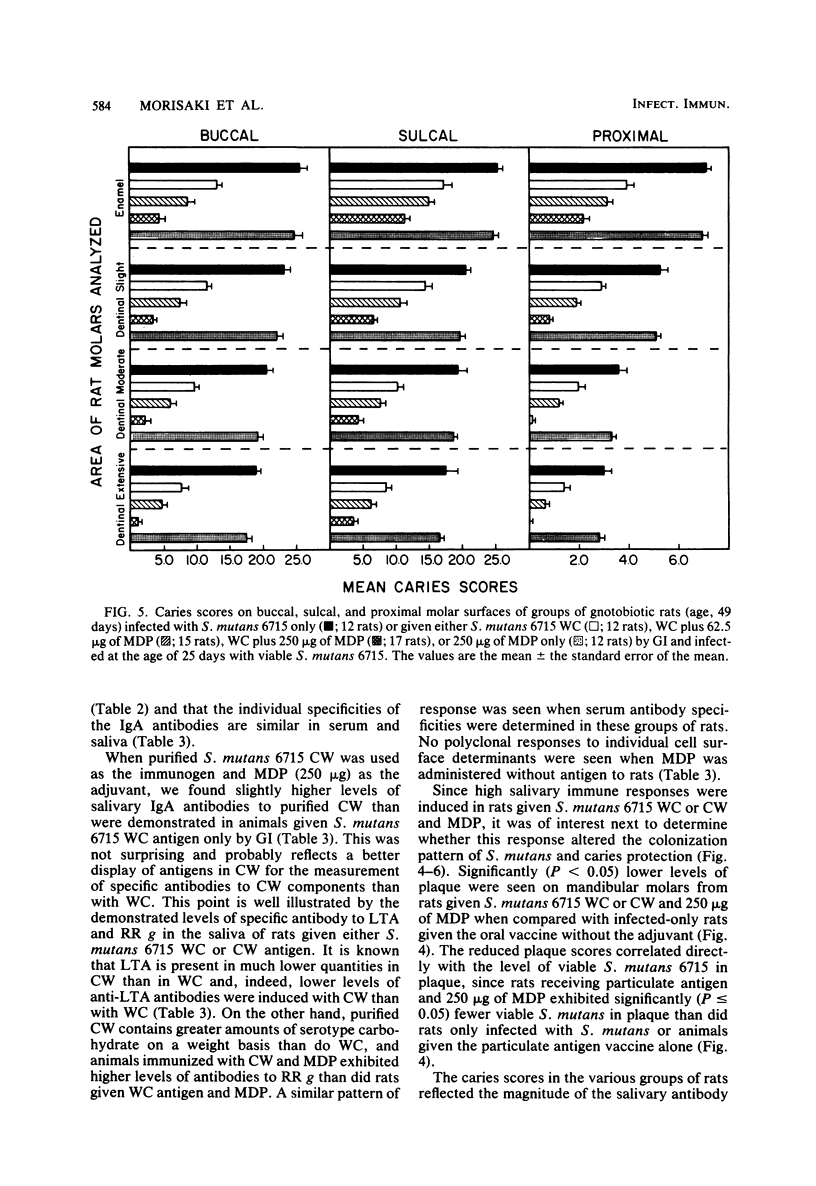
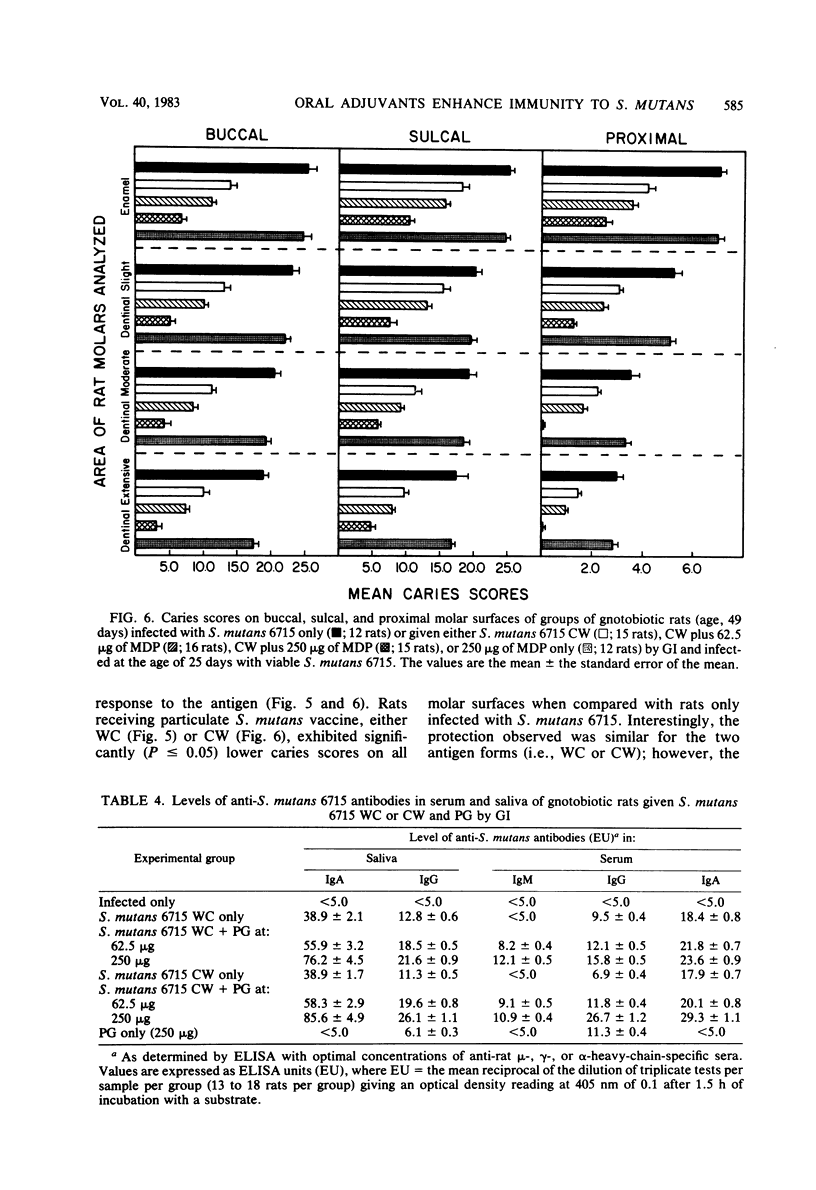
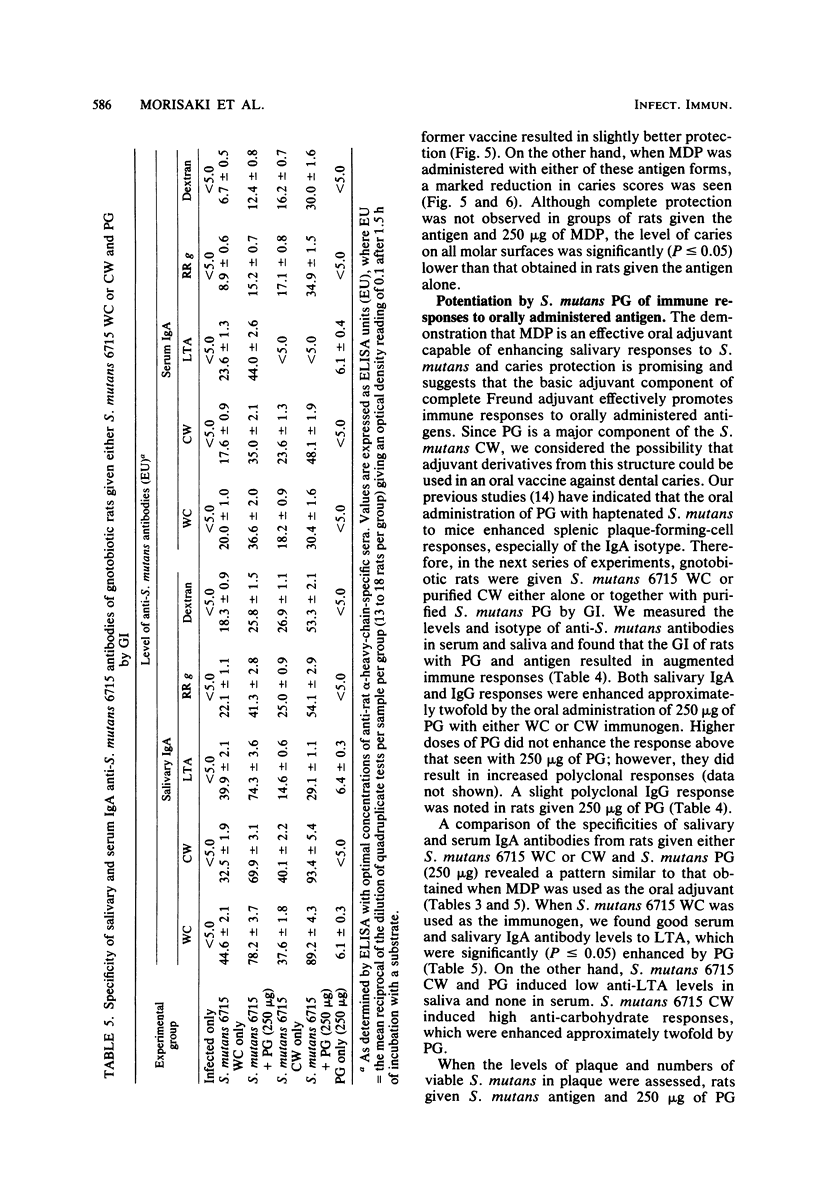
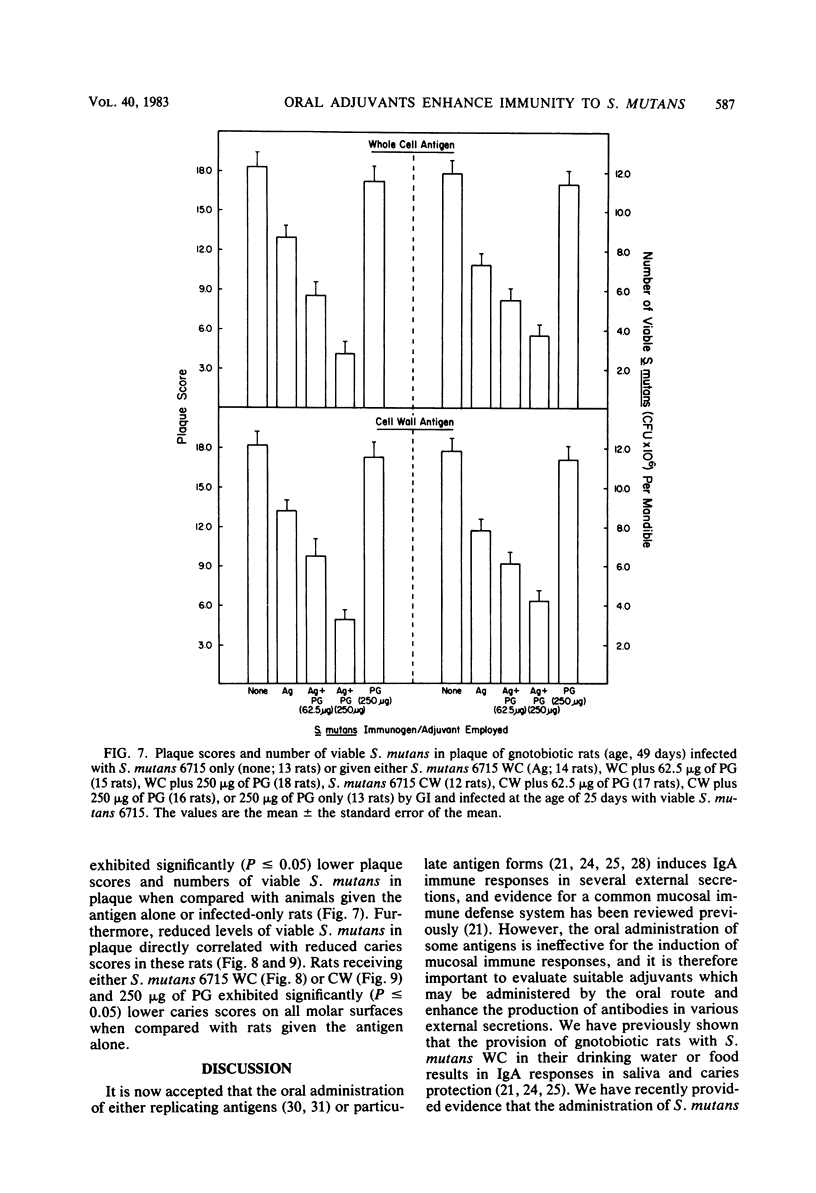
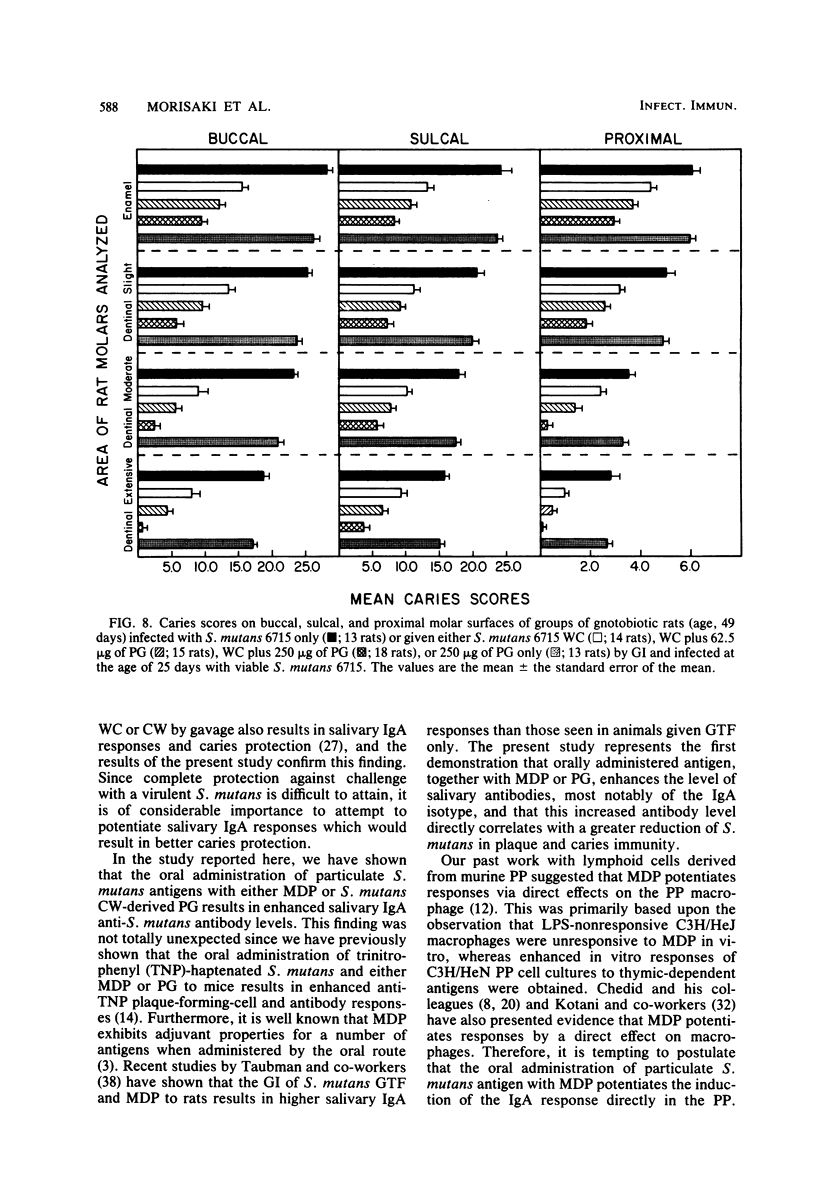
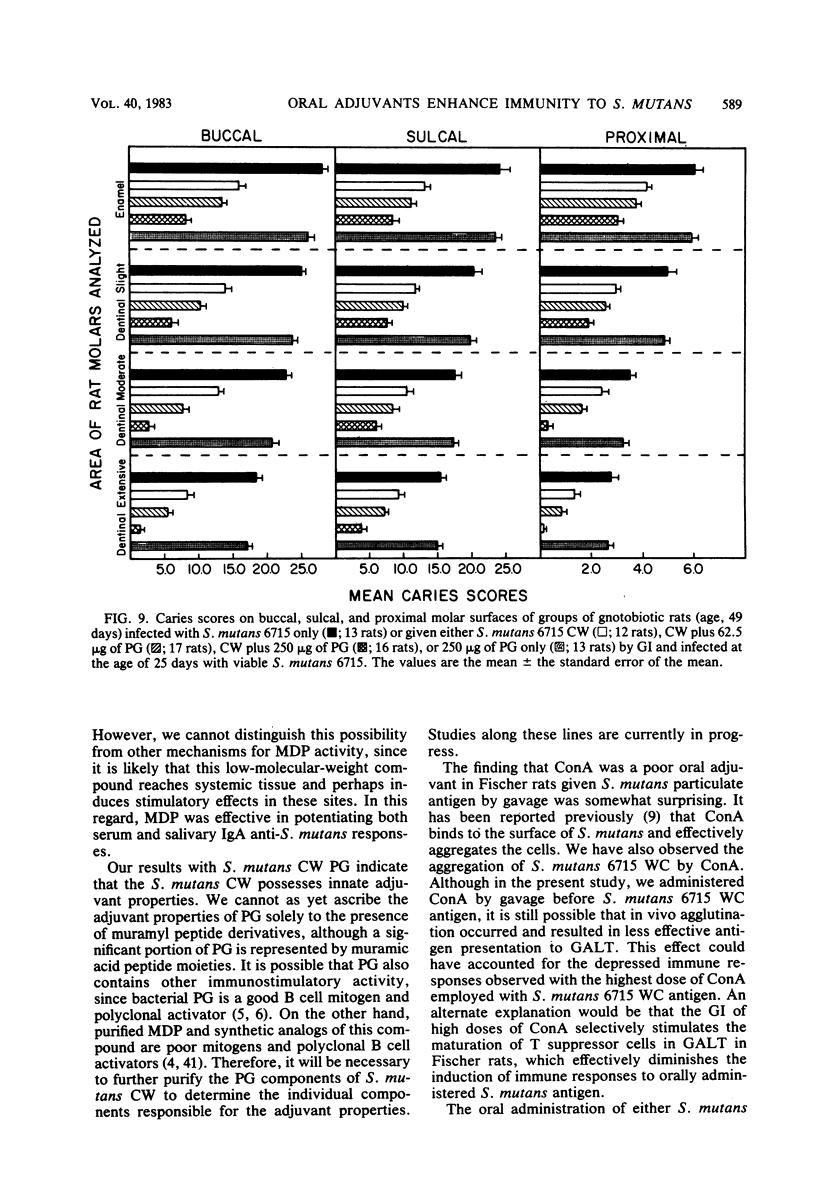
In the present study, we compared the ability of the soluble adjuvants concanavalin A (ConA), muramyl dipeptide (MDP), and peptidoglycan (PG) to enhance immune responses to orally administered particulate antigens of Streptococcus mutans 6715 in gnotobiotic rats. The isotype and levels of antibody in saliva and in serum from experimental rats were determined by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using S. mutans whole cells (WC) as the coating antigen. The specificities of salivary and serum immunoglobulin A (IgA) antibodies to particulate S. mutans antigens, lipoteichoic acid, S. mutans serotype g carbohydrate, and dextran were also determined. When 50 micrograms of ConA was used as the oral adjuvant with S. mutans 6715 WC immunogen, a slight enhancement of immune responses was obtained. A higher dose of ConA suppressed humoral responses to the immunogen. Enhanced immune responses, especially of the IgA isotype, in both serum and saliva were induced in gnotobiotic rats given MDP and either S. mutans 6715 WC or purified cell walls (CW) by gastric intubation. Elevated IgA antibody levels to CW, lipoteichoic acid, and carbohydrate were observed in rats given S. mutans WC and MDP by gastric intubation, whereas oral immunization with S. mutans CW and MDP resulted in higher antibody levels to CW and carbohydrate and lower levels to lipoteichoic acid when compared with the antibody levels in rats given antigen alone. Rats orally immunized with either S. mutans WC or CW and MDP and challenged with virulent S. mutans 6715 exhibited significantly (P less than or equal to 0.05) lower plaque scores, numbers of viable S. mutans in plaque, and caries scores than did rats immunized with antigen alone or in infected-only controls. In another series of experiments, a PG fraction derived from S. mutans 6715 CW was assessed for adjuvant properties. The oral administration of PG and either S. mutans WC or CW induced good salivary and serum IgA antibody responses. The specificity of the antibodies was similar to that obtained in rats given antigen and MDP. Rats receiving either S. mutans WC or CW and PG and challenged with virulent S. mutans 6715 had lower plaque scores, fewer numbers of viable S. mutans in plaque, and lower caries activity than did infected rats receiving S. mutans WC or CW immunogen alone. These results provide evidence that soluble adjuvants derived from the gram-positive bacterial CW, e.g., MDP and PG, are effective oral adjuvants and augment IgA immune responses to particulate S. mutans antigens which are protective against the mucosally associated disease, dental caries.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cebra J. J., Gearhart P. J., Kamat R., Robertson S. M., Tseng J. Origin and differentiation of lymphocytes involved in the secretory IgA responses. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 1):201–215. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challacombe S. J., Russell M. W., Hawkes J. E., Bergmeier L. A., Lehner T. Passage of immunoglobulins from plasma to the oral cavity in rhesus monkeys. Immunology. 1978 Dec;35(6):923–931. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chedid L., Audibert F., Lefrancier P., Choay J., Lederer E. Modulation of the immune response by a synthetic adjuvant and analogs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2472–2475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damais C., Bona C., Chedid L., Fleck J., Nauciel C., Martin J. P. Mitogenic effect of bacterial peptidoglycans possessing adjuvant activity. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):268–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziarski R. Preferential induction of autoantibody secretion in polyclonal activation by peptidoglycan and lipopolysaccharide. I. In vitro studies. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1018–1025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fevrier M., Birrien J. L., Leclerc C., Chedid L., Liacopoulos P. The macrophage, target cell of the synthetic adjuvant muramyl dipeptide. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Aug;8(8):558–562. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Gill K., Slade H. D. Binding of lectins to Streptococcus mutans cells and type-specific polysaccharides, and effect on adherence. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):708–716. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.708-716.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Narita T., Kotani S., Kato K. Studies on cell walls of group A Streptococcus pyogenes, type 12. II. Pyrogenic and related biological activities of the higher molecular weight fraction of an enzymatic digest of the cell walls. Biken J. 1971 Sep;14(3):217–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyono H., Babb J. L., Michalek S. M., McGhee J. R. Cellular basis for elevated IgA responses in C3H/HeJ mice. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):732–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyono H., McGhee J. R., Kearney J. F., Michalek S. M. Enhancement of in vitro immune responses of murine Peyer's patch cultures by concanavalin A, muramyl dipeptide and lipopolysaccharide. Scand J Immunol. 1982 Apr;15(4):329–339. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1982.tb00656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyono H., McGhee J. R., Wannemuehler M. J., Frangakis M. V., Spalding D. M., Michalek S. M., Koopman W. J. In vivo immune response to a T-cell-dependent antigen by cultures of disassociated murine Peyer's patch. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):596–600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyono H., Michalek S. M., Mosteller L. M., Torii M., Hamada S., McGhee J. R. Enhancement of murine immune responses to orally administered haptenated Streptococcus mutans. Scand J Immunol. 1982 Dec;16(6):455–463. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1982.tb00746.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T., Russell M. W., Caldwell J. Immunisation with a purified protein from Streptococcus mutans against dental caries in rhesus monkeys. Lancet. 1980 May 10;1(8176):995–996. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91437-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T., Russell M. W., Caldwell J., Smith R. Immunization with purified protein antigens from Streptococcus mutans against dental caries in rhesus monkeys. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):407–415. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.407-415.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J., Rowan J., Straffon L. H., Loos P. J. Association of Streptococcus mutants with human dental decay. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1252–1260. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1252-1260.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J., Straffon L. H. Longitudinal investigation of the role of Streptococcus mutans in human fissure decay. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):498–507. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.498-507.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löwy I., Bona C., Chedid L. Target cells for the activity of a synthetic adjuvant: muramyl dipeptide. Cell Immunol. 1977 Mar 1;29(1):195–199. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90288-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. R., Michalek S. M. Immunobiology of dental caries: microbial aspects and local immunity. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:595–638. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.003115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee, Michalek S. M., Webb J., Navia J. M., Rahman A. F., Legler D. W. Effective immunity to dental caries: protection of gnotobiotic rats by local immunization with Streptococcus mutans. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):300–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalek S. M., McGhee J. R., Babb J. L. Effective immunity to dental caries: dose-dependent studies of secretory immunity by oral administration of Streptococcus mutans to rats. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):217–224. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.217-224.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalek S. M., McGhee J. R., Mestecky J., Arnold R. R., Bozzo L. Ingestion of Streptococcus mutans induces secretory immunoglobulin A and caries immunity. Science. 1976 Jun 18;192(4245):1238–1240. doi: 10.1126/science.1273589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalek S. M., McGhee J. R., Shiota T., Devenyns D. Virulence of Streptococcus mutans: cariogenicity of S. mutans in adult gnotobiotic rats. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):466–471. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.466-471.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalek S. M., Morisaki I., Harmon C. C., Hamada S., McGhee J. R. Effective immunity to dental caries: gastric intubation of Streptococcus mutans whole cells or cell walls induces protective immunity in gnotobiotic rats. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):645–654. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.645-654.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery P. C., Rosner B. R., Cohn J. The secretory antibody response. Anti-DNP antibodies induced by dinitrophenylated type 3 pneumococcus. Immunol Commun. 1974;3(2):143–156. doi: 10.3109/08820137409055752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz M. Separation and properties of a red cell sensitizing substance from streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2200–2204. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2200-2204.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogra P. L., Karzon D. T. Distribution of poliovirus antibody in serum, nasopharynx and alimentary tract following segmental immunization of lower alimentary tract with poliovaccine. J Immunol. 1969 Jun;102(6):1423–1430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabst M. J., Cummings N. P., Shiba T., Kusumoto S., Kotani S. Lipophilic derivative of muramyl dipeptide is more active than muramyl dipeptide in priming macrophages to release superoxide anion. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):617–622. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.617-622.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux M. E., McWilliams M., Phillips-Quagliata J. M., Weisz-Carrington P., Lamm M. E. Origin of IgA-secreting plasma cells in the mammary gland. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1311–1322. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. W., Bergmeier L. A., Zanders E. D., Lehner T. Protein antigens of Streptococcus mutans: purification and properties of a double antigen and its protease-resistant component. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):486–493. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.486-493.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. J., Taubman M. A., Ebersole J. L. Effect of oral administration of glucosyltransferase antigens on experimental dental caries. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):82–89. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.82-89.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. J., Taubman M. A., Ebersole J. L. Effects of local immunization with glucosyltransferase fractions from Streptococcus mutans on dental caries in hamsters caused by homologous and heterologous serotypes of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):843–851. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.843-851.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. J., Taubman M. A., Ebersole J. L. Local and systemic antibody response to oral administration of glucosyltransferase antigen complex. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):441–450. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.441-450.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taubman M. A., Smith D. J. Effects of local immunization with glucosyltransferase fractions from Streptococcus mutans on dental caries in rats and hamsters. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):710–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J., Whitlock C. Effect of a synthetic adjuvant on the induction of primary immune responses in T cell-depleted spleen cultures. J Immunol. 1978 Jul;121(1):383–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisz-Carrington P., Roux M. E., McWilliams M., PHILLIPS-Quagliata J. M., Lamm M. E. Organ and isotype distribution of plasma cells producing specific antibody after oral immunization: evidence for a generalized secretory immune system. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1705–1708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


